Endocrinology of Male Puberty
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is normal male puberty?
Normal male puberty is defined as the period where secondary sexual characteristics develop as well as the ability to sexually reproduce
Comprised of two components:
1) Gonadarche
2) Adrenarche
What is Gonadarche in men?
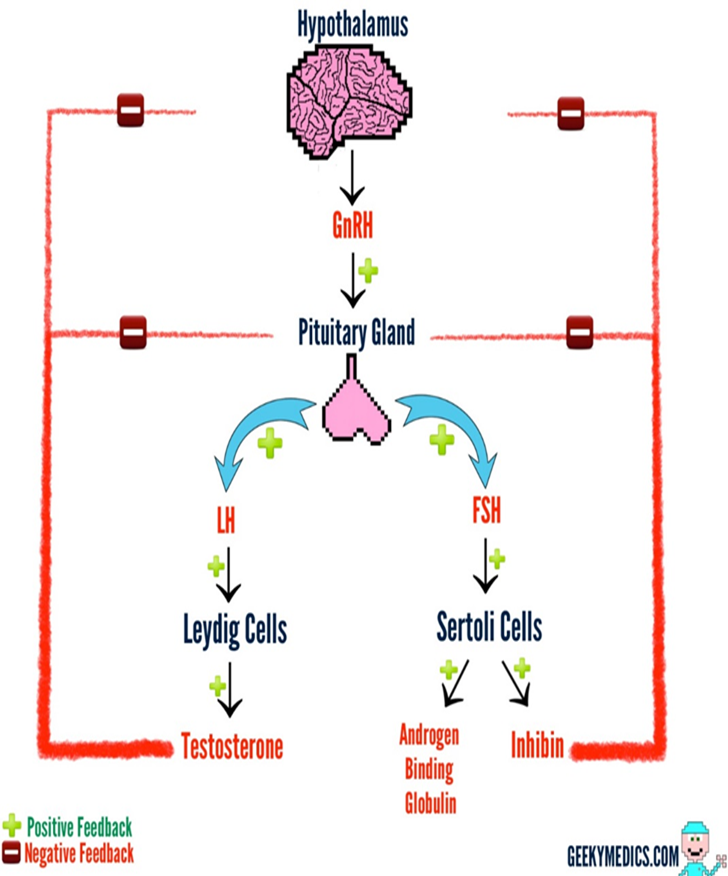
Gonadarche is the maturation of the Hypothalamic-pituitary testicular axis that starts off puberty
Follows an organized sequence of events that results in increased testosterone
1) Hypothalamus increases secretion of GnRH leading to increased production of LH and FSH at the anterior pituitary
→ LH stimulates the Leydig cells to secrete testosterone
→ FSH increases Sertoli cell production of androgen binding protein and inhibin
2) Testosterone is required for maturation of the male genitalia
→ also promotes secondary sex characteristics
→ growth spurt and epiphyseal closure
What is Adrenarche in men?

Adrenarche is regrowth of the zona reticularis leading to increased secretion of adrenal androgens at ages 6-8
1) This is a gradual maturation process that begins in early childhood independent of gonadarche
→ caused by the local conversion of DHEA to testosterone
2) Results in body odor from the apocrine glands and acne in the sebaceous glands of the skin
→ also leads to the development of pubic and axillary hair
What is Tanner Staging in men?
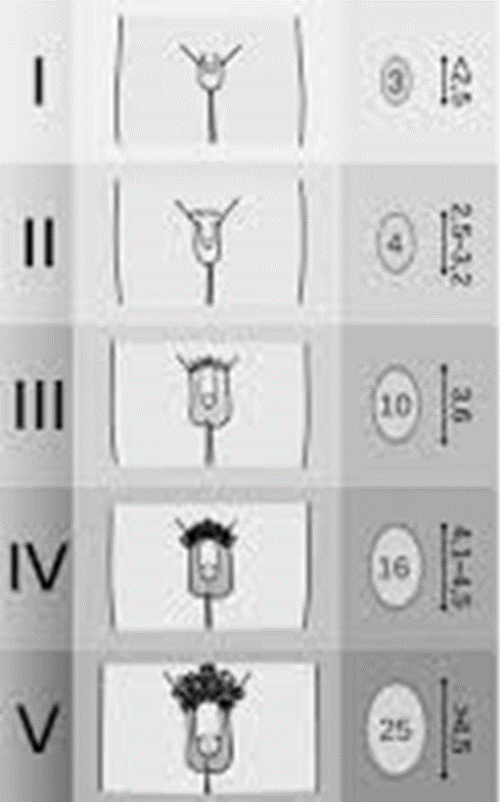

Tanner Staging in men involves the growth of the testes and pubic hair
→ often testicular growth occurs first, with pubic hair growth occurring after
→ growth spurts will often occur in later tanner stages
1) Pubic Hair Growth Stages
→ 1: no hair
→ 2: sparse hair growth
→ 3: dark, coarser hair appears
→ 4: adult hair appears, but is not on the thighs
→ 5: adult hair spreads onto the thighs
2) Testes/Penis/Scrotum Growth Stages
→ 1: testes are <4 cc in volume and less than 2.5 cm in length
→ 2: scrotum and testes start to grow
→ 3: the scrotum keeps growing with the penis starting to grow
→ 4: penis grows even more in length and width
→ 5: adult penis
What is Precocious Puberty in men?

Precocious Puberty is early puberty and is characterized by testicular growth or pubic hair before the age of 9
→ can be either Generalized or Isolated
Generalized: premature onset of the entire axis of puberty either due to activation of the HPT axis or independent testosterone secretion
1) Central/True (gonadotropin dependent) - premature activation of the pituitary gland
→ leads to abnormal LH and FSH with testicular growth. Adrenarche will often occur after testicular growth
2) Peripheral (gonadotropin independent) - premature or independent secretion of testosterone
Isolated: Patients will either have gonadarche or adrenarche isolated on its own from one another
1) premature gonadarche
2) premature adrenarche
→ seen more common in obese children or in African Americans
What is GnRH Stimulation Testing and what are the interpretation of the results in men?
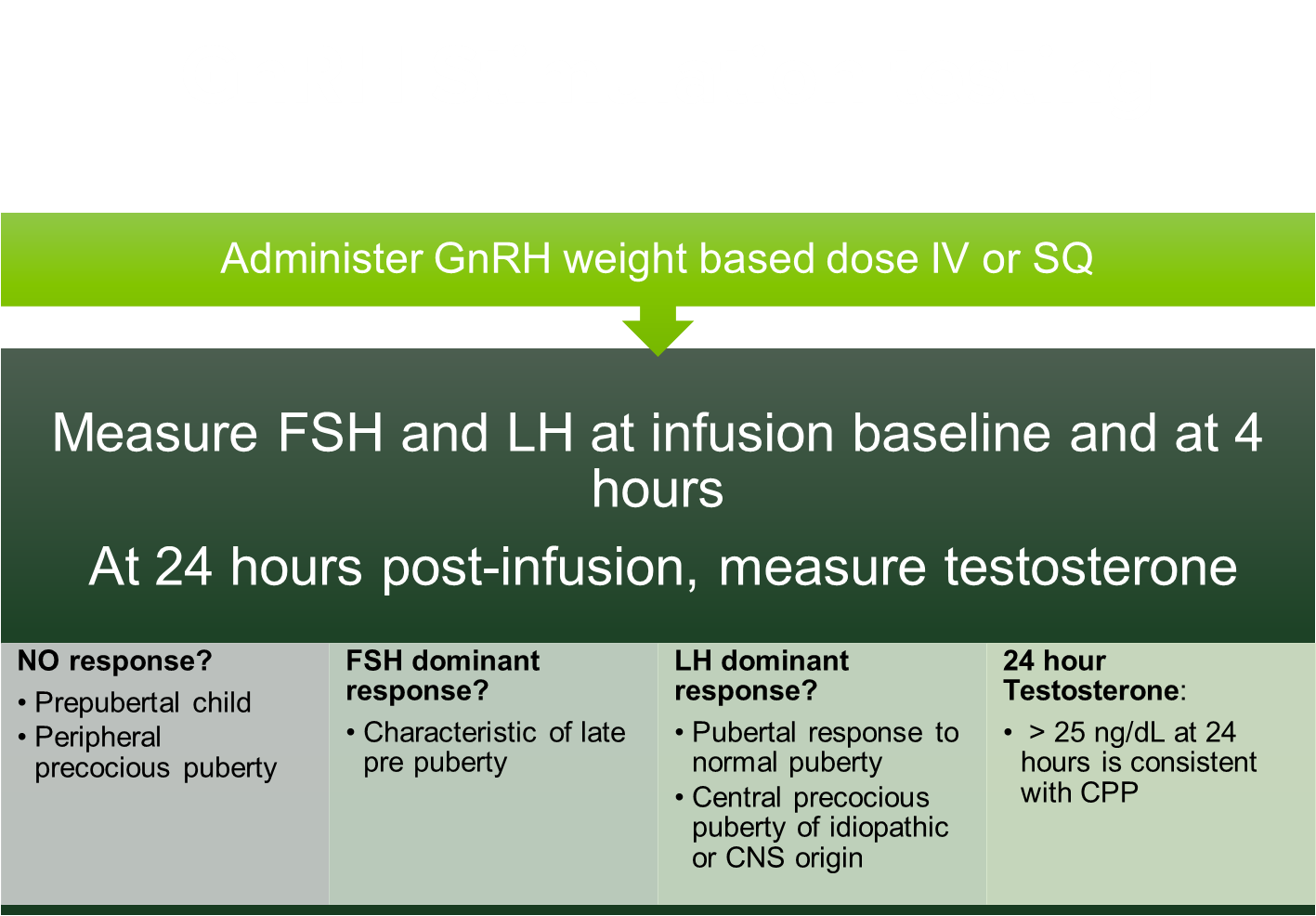
GnRH Stimulation Testing is a method of determining the cause and type of precocious puberty
→ patients are given GnRH and have their FSH and LH levels measured 4 hours after
1) No Response
→ means that the patient is either prepubertal or have peripheral precocious puberty
2) FSH Dominant Response
→ characteristic of late-pre puberty
3) LH Dominant Response
→ either normal puberty or central precocious puberty
4) 24 Hour Testosterone > 25 ng/dL
→ central precocious puberty
What are the characteristics of true precocious puberty?
True or Central Precocious Puberty is characterized by abnormal LH/FSH levels with the presence of testicular growth
1) Patients often have elevated testosterone levels as well as evidence of adrenal androgen activity or testicular growth before 9 years old
→ often have testicular growth BEFORE adrenarche occurs
→ advanced bone age or increase in growth velocity
2) Caused by early maturation of the HPG axis and is most often idiopathic
→ idiopathic causes are less common in men than women
→ may be seen with CNS tumors so you need to MRI the brain
What are the diagnostics of peripheral precocious puberty?
Peripheral Precocious Puberty is caused by excess exposure of sex steroid hormones that come independently from the HPG axis
1) Patients will often have low or normal FSH and LH levels with no increase hormones following GnRH stimulation testing
2) Often seen in patients with testicular or adrenal tumors
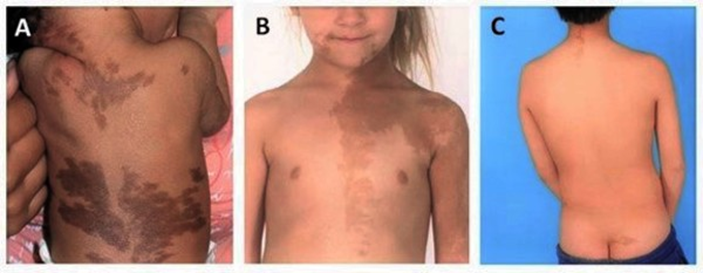
→ can also be seen in patients with McCune Albright Syndrome which will also present with hyperpigmented marks on the skin
3) can also be seen in familial-male limited precocious puberty which is chronic activation of the LH receptor
When and how do you treat precocious puberty?
Precocious Puberty is treated if the patient has abnormal causes of precocious puberty such as intracranial diseases or tumors
→ goals are often to lessen precocious development, and arrest their puberty until closer to normal age
→ also to maximize their adult height
1) Gonadotropin Dependent (Central/True)
→ Injectable GnRH agonists like leuprolide or histrelin
2) Gonadotropin Independent (Peripheral)
→ based on whatever the underlying cause is
What is Delayed Puberty in Men?
Delayed Puberty is the failure of development of secondary sexual characteristics by age 14.
Subdivided into two types
1) Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism is failure of the hypothalamus-pituitary axis to activate
→ Idiopathic
→ systemic
→ poor nutrition
→ genetic defects
→ CNS disorders
→ endocrinopathy
2) Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadism is failure of the end organ (testicle)
→ often caused by primary testicular failure which are commonly autoimmune or environmental in etiology
→ can also have some form of end-organ resistance to androgens which are commonly inherited
What is Kleinfelter Syndrome?
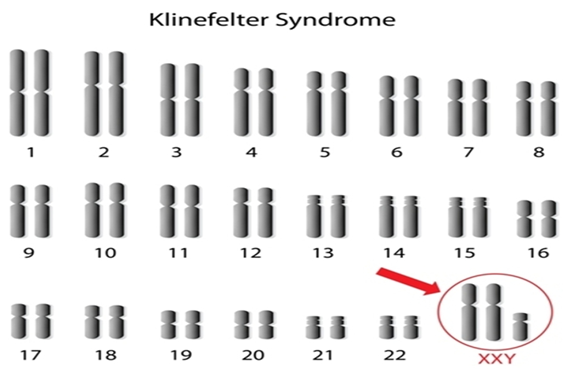
Kleinfelter Syndrome is a disorder of sex chromosome aneuploidy resulting in a patient having XXY or an additional X chromosome due to meiotic nondisjunction
1) Patients will have tall stature and have gynecomastia (enlarged breasts)
→ smaller testicles or gonadal failure
→ often infertile
→ may have normal intelligence but will have higher social anxiety
How is delayed puberty treated in male patients?
Often you just watch and wait
→ if they are older than 14, you can give them testosterone for 3 months to jumpstart puberty