Intermediate Radiographic Procedures Midterm Practice Questions
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Which of the following structures should be seen in profile on an AP shoulder projection with internal rotation?
A. Acromion
B. Lesser tubercle
C. Coracoid process
D. Greater tubercle
B. Lesser tubercle
What kVp range is typically used for imaging the clavicle?
A. 75-85
B. 65-75
C. 55-65
D. 90-100
A. 75-85
Which IR orientation is most appropriate for a hypersthenic patient undergoing a chest radiograph?
A. Portrait
B. Diagonal
C. Landscape
D. Vertical
C. Landscape
Where is the CR directed for an AP axial clavicle?
A. Mid scapula
B. 2 inches inferior to the coracoid
C. Midshaft of the clavicle
D. Coracoid process
C. Midshaft of the clavicle
What is the proper patient breathing instruction for an AP projection of the clavicle?
A. Take in a deep breath and hold it
B. Expose on expiration
C. Rapid breathing
D. Orthostatic technique
B. Expose on expiration
Which of the following projections is used to demonstrate AC joint separation?
A. AP clavicle
B. AP AC joints
C. PA oblique scapular Y
D. AP AC joints with weights
D. AP AC joints with weights
The lateral scapula for the acromion and coracoid process requires the arm to be:
A. Flexed and placed behind the back
B. Across the chest
C. Abducted 90°
D. Relaxed at the side
A. Flexed and placed behind the back
Which structure articulates with the acromial end of the clavicle?
A. Manubrium
B. Glenoid cavity
C. Sternum
D. Acromion
D. Acromion
Why are AC joints imaged with and without weights?
A. To evaluate fracture displacement
B. To compare muscle tone
C. To detect joint space widening and separation
D. To test range of motion
C. To detect joint space widening and separation
What is the correct tube angle for a AP axial clavicle projection?
A. 15-30° cephalic
B. 15-30° caudal
C. 5-10° cephalic
D. 0° caudal
A. 15-30° cephalic
The lateral chest projection is performed with the patient's:
A. Right side against the bucky
B. Left side against the bucky
C. Back against the IR
D. Face toward the tube
B. Left side against the bucky
In which projection is the scapula best visualized free from lung superimposition?
A. Lateral scapula
B. AP shoulder internal rotation
C. AP scapula with orthostatic breathing
D. Scapular Y view
C. AP scapula with orthostatic breathing
What is the arm position for a lateral scapula projection to visualize the body of the scapula?
A. Arm across the chest, hand on opposite shoulder
B. Arm behind the back
C. Arm abducted 90 degrees
D. Arm straight down at the side
A. Arm across the chest, hand on opposite shoulder
Which of the following techniques is used to blur lung markings during an AP scapula projection?
A. Short exposure time
B. Orthostatic breathing
C. Holding breath after full inspiration
D. High kVp
B. Orthostatic breathing
Which of the following demonstrates an open glenohumeral joint space best?
A. PA oblique scapular Y
B. AP shoulder internal rotation
C. Axillary shoulder view
D. AP oblique shoulder
D. AP oblique shoulder
Where is the CR directed for an upright AP erect abdomen?
A. Iliac crest
B. 2 inches above the iliac crest
C. Level of ASIS
D. Pubic symphysis
B. 2 inches above the iliac crest
What is the correct arm position for the lateral projection of the humerus?
A. Extended and externally rotated
B. Flexed 90°, hand on hip
C. Across the chest
D. Behind the back
B. Flexed 90°, hand on hip
Which of the following best demonstrates the entire clavicle with minimal rib superimposition?
A. PA clavicle
B. AP clavicle
C. AP axial clavicle
D. PA axial clavicle
C. AP axial clavicle
Which of the following is considered part of the shoulder girdle?
A. Scapula
B. Sternum
C. Distal humerus
D. Radius
A. Scapula
Which projection is most appropriate for evaluating a potential pneumothorax?
A. AP shoulder
B. PA chest
C. AP abdomen
D. AP scapula
B. PA chest
Why is the left lateral projection of the chest preferred over the right lateral?
A. To minimize magnification of the lungs
B. To reduce patient dose
C. To place the heart closer to the IR
D. To demonstrate fluid levels
C. To place the heart closer to the IR
Which shoulder projection is best to assess proximal humerus dislocation?
A. AP internal rotation shoulder
B. Transthoracic lateral proximal humerus
C. Axillary projection
D. AP oblique scapular Y shoulder
D. AP oblique scapular Y shoulder
Which method is interchangeably with transthoracic Lateral shoulder (or proximal humerus)?
A. Lawrence Method
B. Neer Method
C. Grashey Method
D. Gayler Method
A. Lawrence Method
Which method is interchangeable with AP oblique shoulder?
A. Lawrence Method
B. Neer Method
C. Grashey Method
D. Gayler Method
C. Grashey Method
Which of the following projections is most sensitive to demonstrating air-fluid levels in the chest when a patient is unable to sit or stand up?
A. Lateral decubitus
B. AP supine chest
C. AP shoulder
D. AP scapula
A. Lateral decubitus
For an AP abdomen (KUB), the CR is directed to:
A. The level of the ASIS
B. The midpoint between the symphysis and the xiphoid
C. 2 inches above the iliac crest
D. The level of the iliac crest
D. The level of the iliac crest
Which projection uses a 15-30° cephalic angle directed to the midshaft of the clavicle?
A. AP scapula
B. PA clavicle
C. AP axial clavicle
D. AP shoulder internal rotation
C. AP axial clavicle
What should be included in a AP supine KUB projections?
A. Proximal Femur
B. Pubis Symphysis
C. Proximal Humerus
D. Only diaphragm
B. Pubis Symphysis
Which of the following requires an orthostatic (breathing) technique?
A. Lateral humerus
B. PA chest
C. AP scapula
D. AP axial clavicle
C. AP scapula
Which method is used for imaging the AC joints?
A. Pearson
B. Lawrence
C. Grashey
D. Neer
A. Pearson
What breathing instruction should be given for the AP axial clavicle projection?
A. Hold breath after expiration
B. Hold breath after full inspiration
C. Normal breathing
D. Orthostatic breathing technique
B. Hold breath after full inspiration
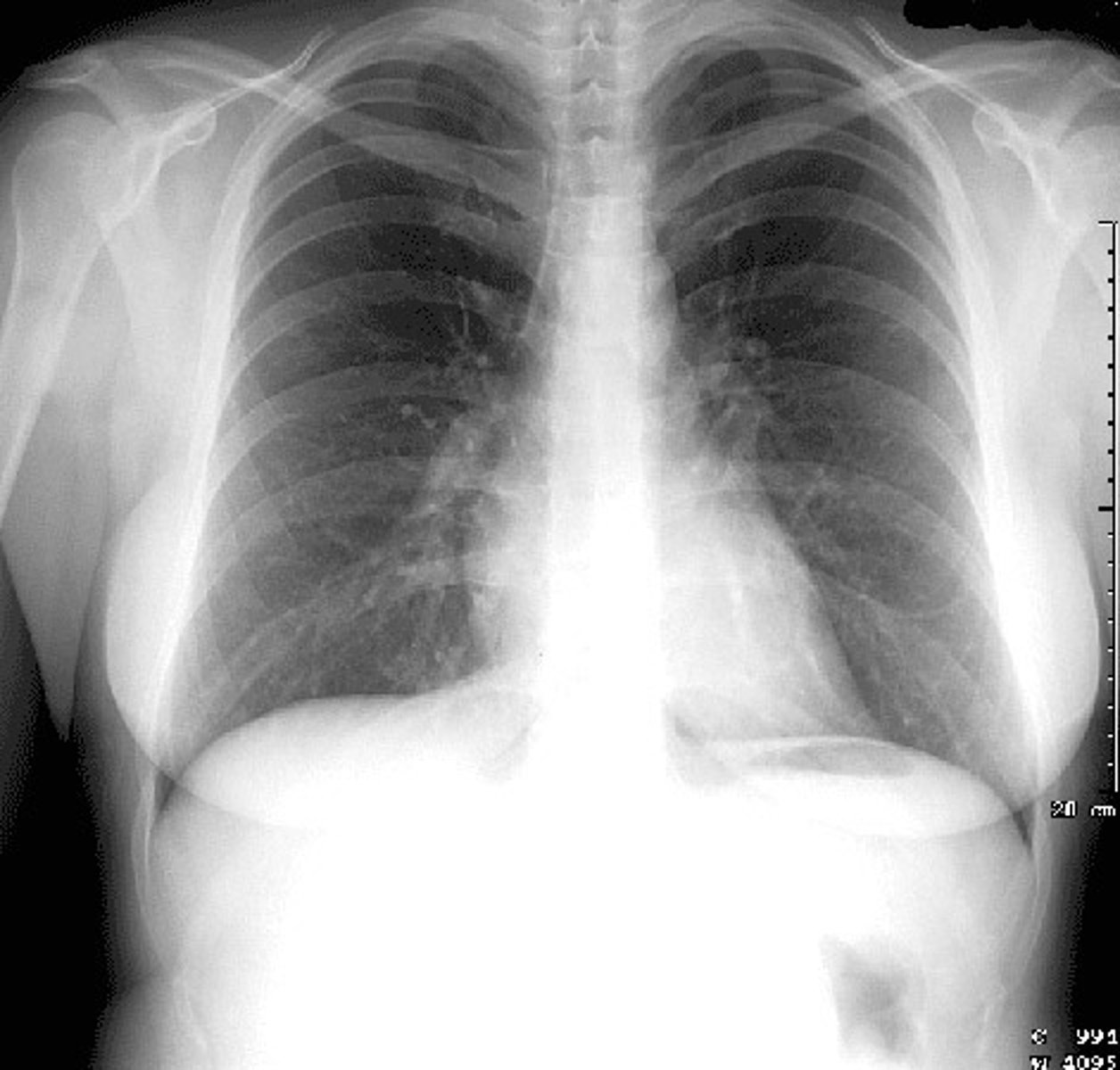
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
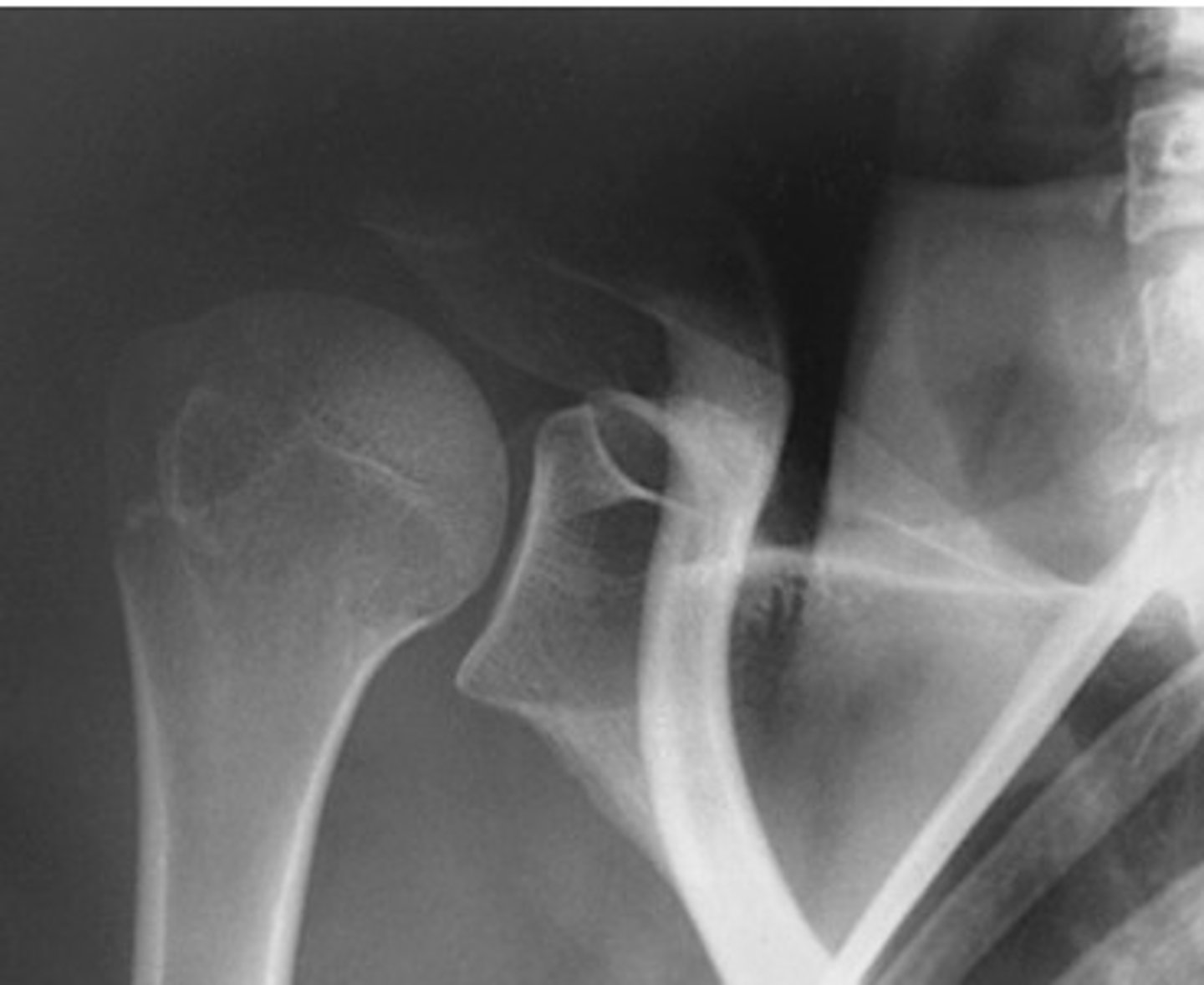
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
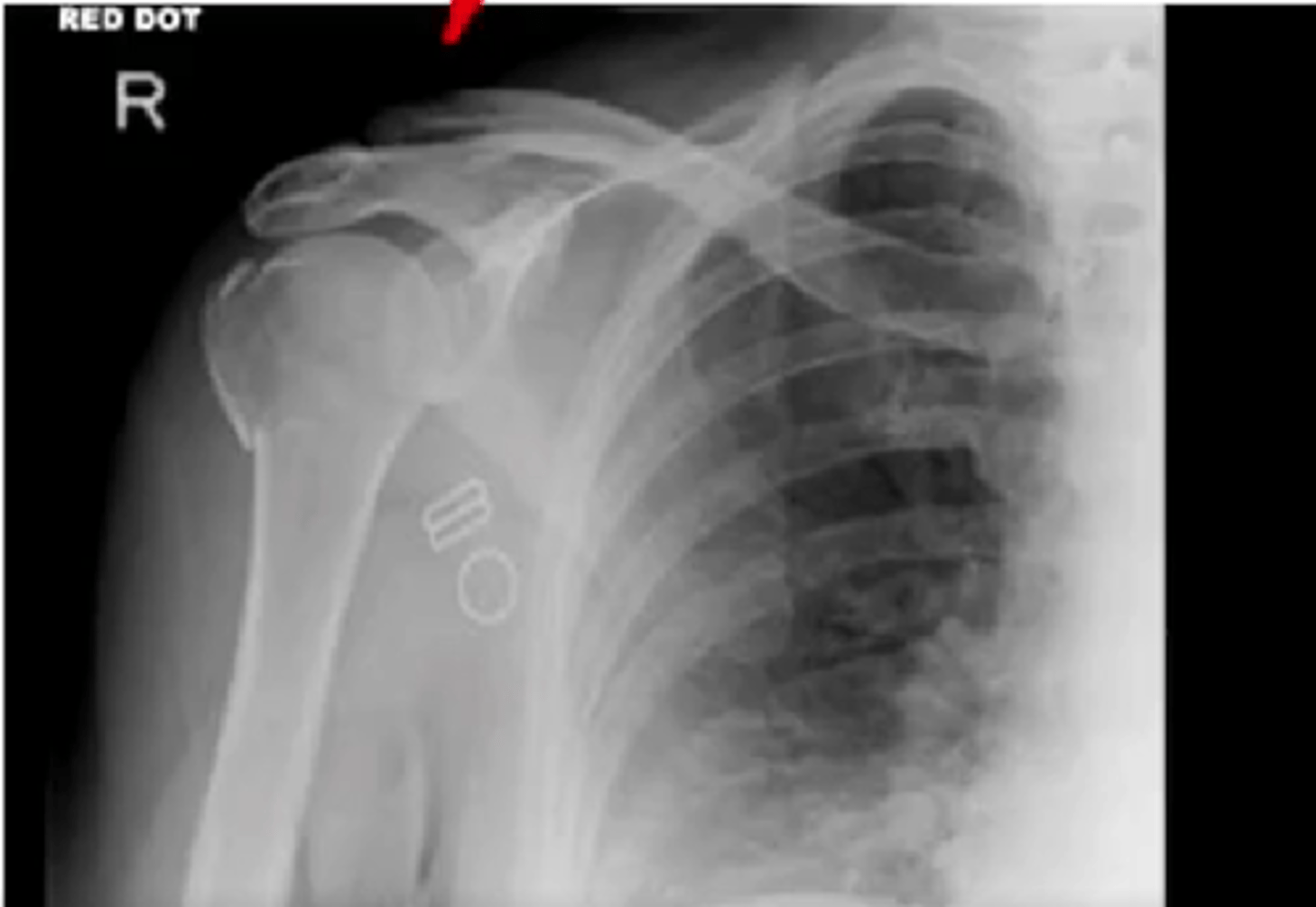
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
A patient arrives at the ER with a fractured humerus on the right arm. Which projections should the doctor order?
A. Right Lateral Humerus and AP Humerus with external rotation
B. Right Transthoracic Lateral Humerus and AP Humerus with neutral rotation
C. Left Transthoracic Lateral Humerus and AP Humerus with neutral rotation
D. Left Transthoracic Lateral Humerus and AP Humerus with internal rotation
B. Right Transthoracic Lateral and AP Humerus with neutral rotation
In a properly positioned PA chest x-ray, how many posterior ribs should be visible above the diaphragm?
A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 10
D. 10
The stomach is located in which abdominal quadrant?
A. RUQ
B. RLQ
C. LUQ
D. LLQ
C. LUQ
During your history taking of a patient, you ask the patient to show you the location of their pain and the patient points around where their liver is located. Which quadrant are they pointing at?
A. RUQ
B. RLQ
C. LUQ
D. LLQ
A. RUQ
When performing an upright abdomen, the top of the IR should be placed at what anatomical landmark to ensure the diaphragm is included?
A. Iliac crest
B. ASIS
C. Symphysis pubis
D. Axilla
D. Axilla
Which of the following is a correct evaluation criteria for an AP scapula?
A. Lateral border should be free from superimposition with ribs and lungs
B. Lateral border must be superimposed on ribs
C. Entire scapula including coracoid must be superimposed
D. Only the inferior angle should be visible
A. Lateral border should be free from superimposition with ribs and lungs
Which of the following is incorrect about PA Chest erect?
A. Allows the diaphragm to move down farther
B. Demonstrates air-fluid levels within the chest cavity
C. Prevents engorgement of pulmonary vessels
D. Demonstrates air-fluid levels with in the superior portion of the stomach
D. Demonstrates air-fluid levels with in the superior portion of the stomach
What is the correct CR angulation for an AP axial projection of the toes?
A. 5° cephalic
B. 10-15° cephalic
C. 10-15° caudal
D. Perpendicular
B. 10-15° cephalic
Which projection is best for visualizing a possible Jones fracture?
A. AP axial foot
B. AP oblique foot
C. Lateral calcaneus
D. Axial calcaneus
B. AP oblique foot
Where does the CR enter for an AP axial projection of the foot?
A. Base of the 5th metatarsal
B. Medial malleolus
C. 3rd metatarsophalangeal joint
D. Base of the 3rd metatarsal
D. Base of the 3rd metatarsal
In which projection are the third through fifth metatarsals best demonstrated without superimposition?
A. AP oblique foot
B. Lateral foot
C. AP foot
D. AP axial toes
A. AP oblique foot
What is the correct CR entry point for an Plantardorsal axial projection of the calcaneus?
A. 3rd MTP joint
B. Base of 1st metatarsal
C. Medial malleolus
D. Base of the 3rd metatarsal
D. Base of the 3rd metatarsal
Where should the CR enter for a lateral projection of the calcaneus?
A. Base of 3rd metatarsal
B. 1 inch inferior to medial malleolus
C. Subtalar joint
D. Plantar surface
B. 1 inch inferior to medial malleolus
What kVp range is generally used for imaging the toes and foot?
A. 40-50 kVp
B. 50-70 kVp
C. 65-85 kVp
D. 70-90 kVp
B. 50-70 kVp
A true lateral of the foot requires:
A. Plantar surface perpendicular to IR
B. Dorsiflexion and medial rotation
C. Lateral malleolus anterior to medial
D. No dorsiflexion
A. Plantar surface perpendicular to IR
Which projection of the toes demonstrates the IP and MTP joints most clearly?
A. AP
B. AP oblique
C. Lateral
D. AP axial
D. AP axial
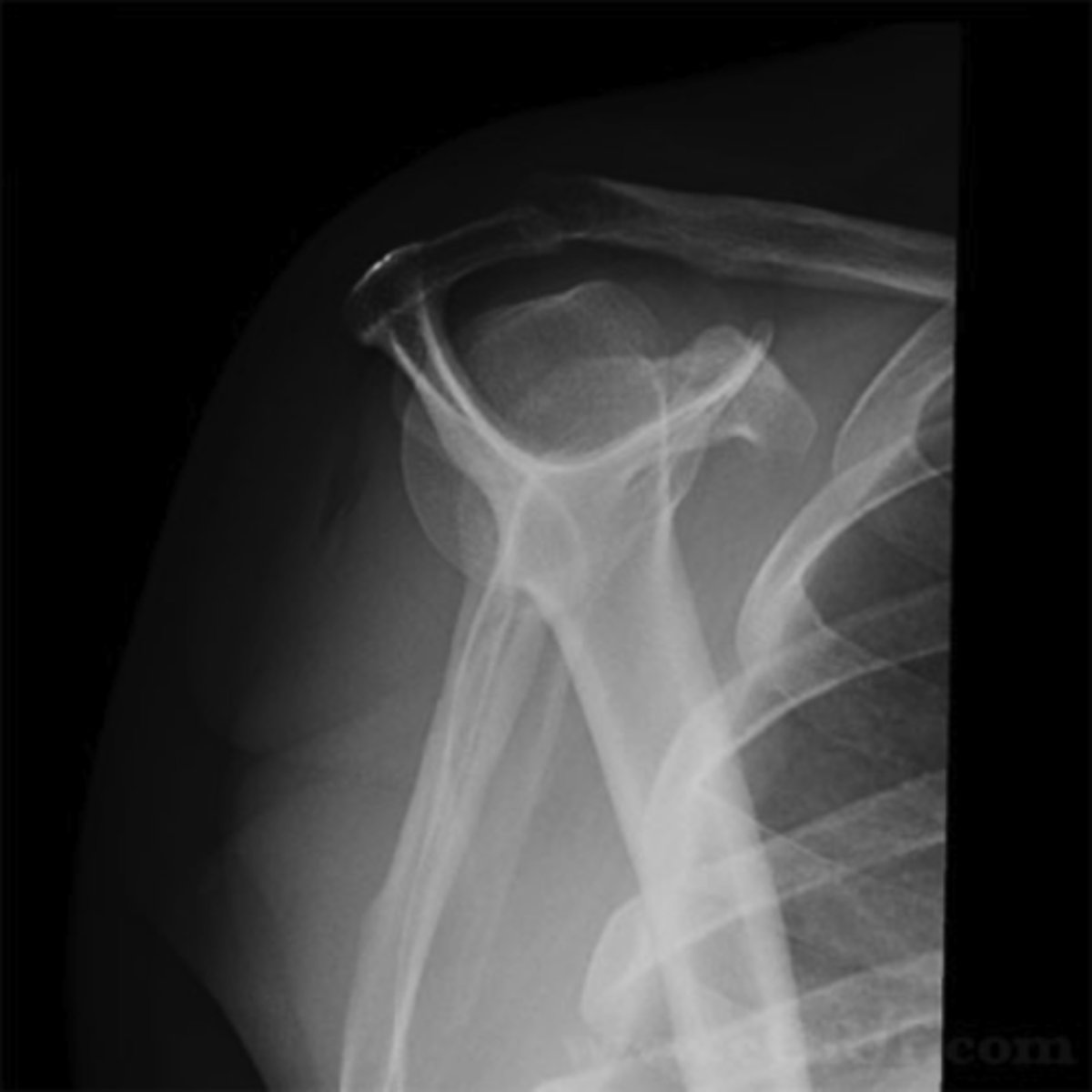
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
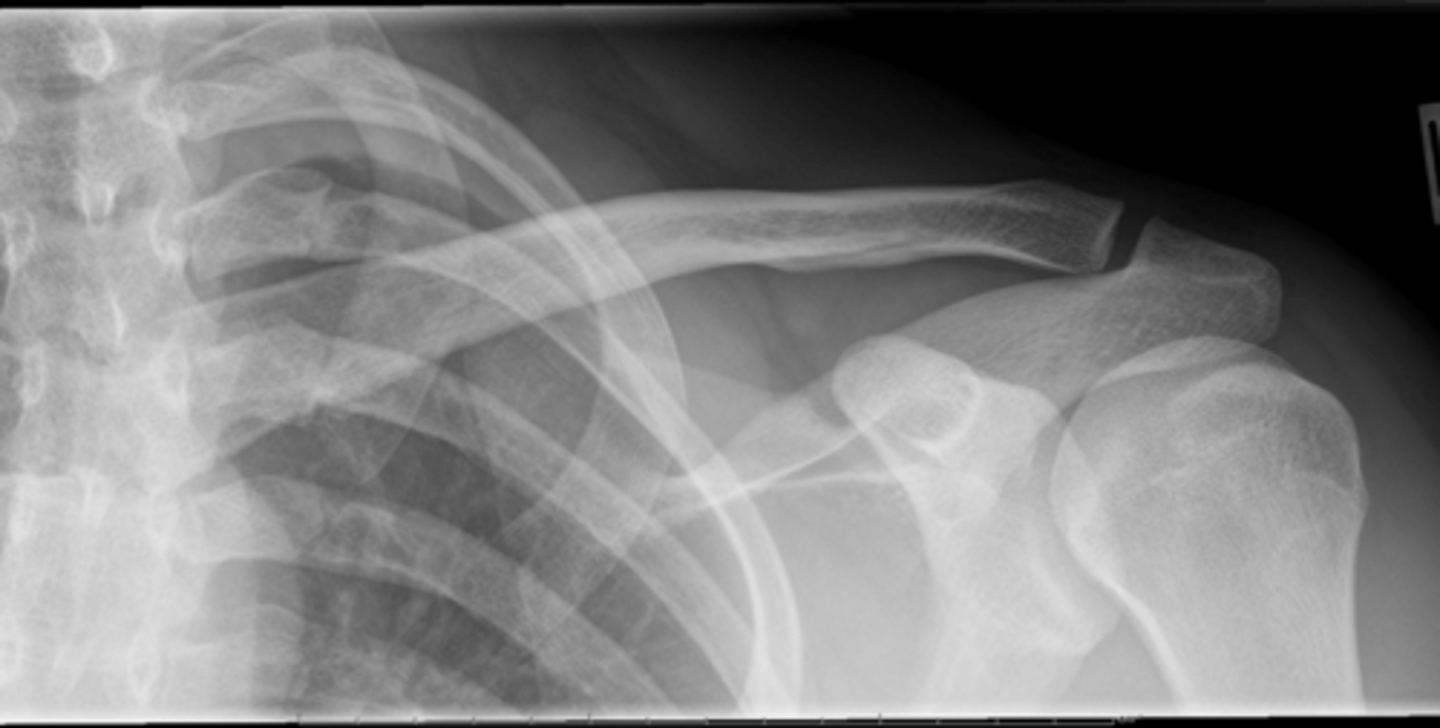
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
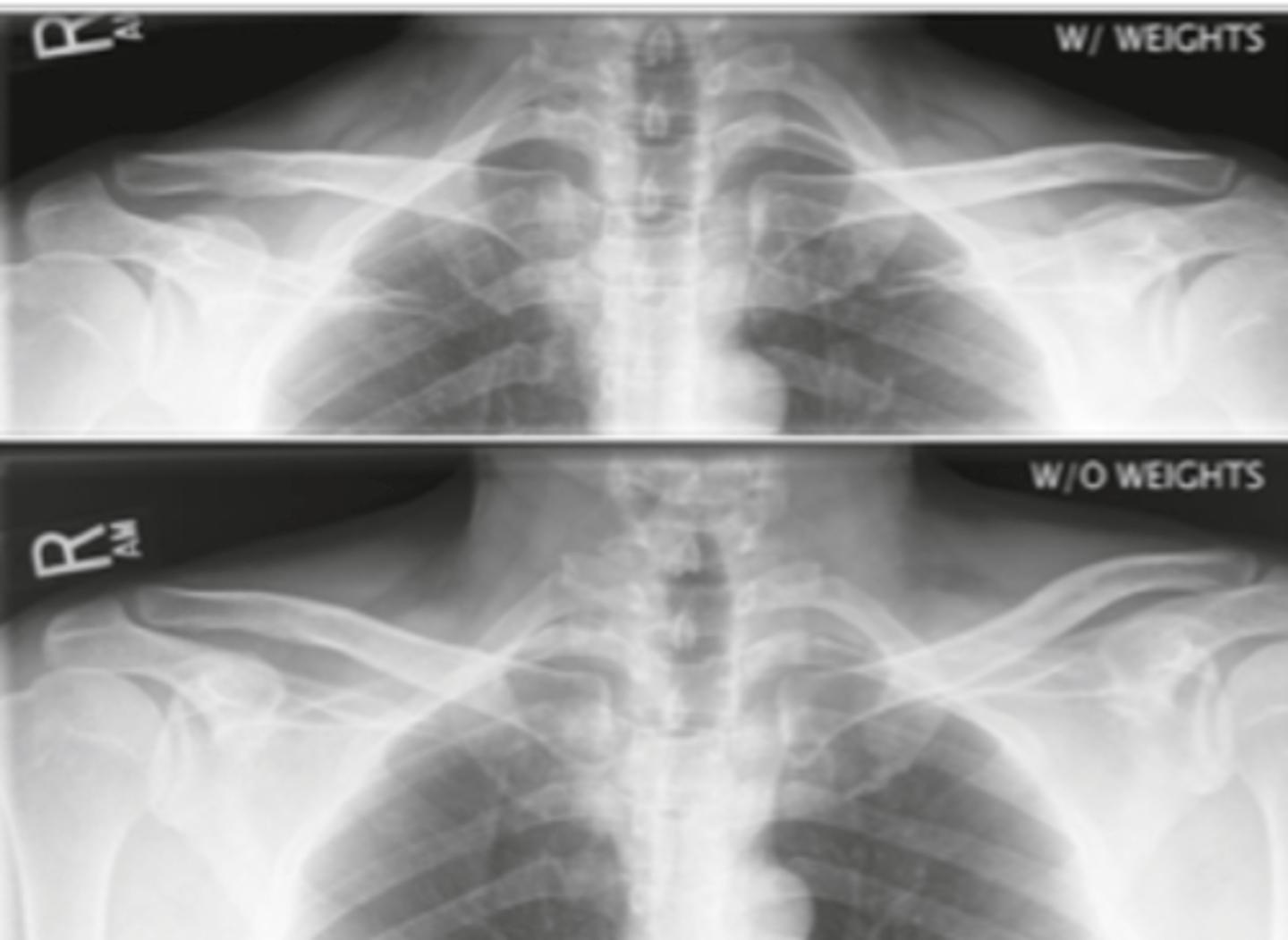
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
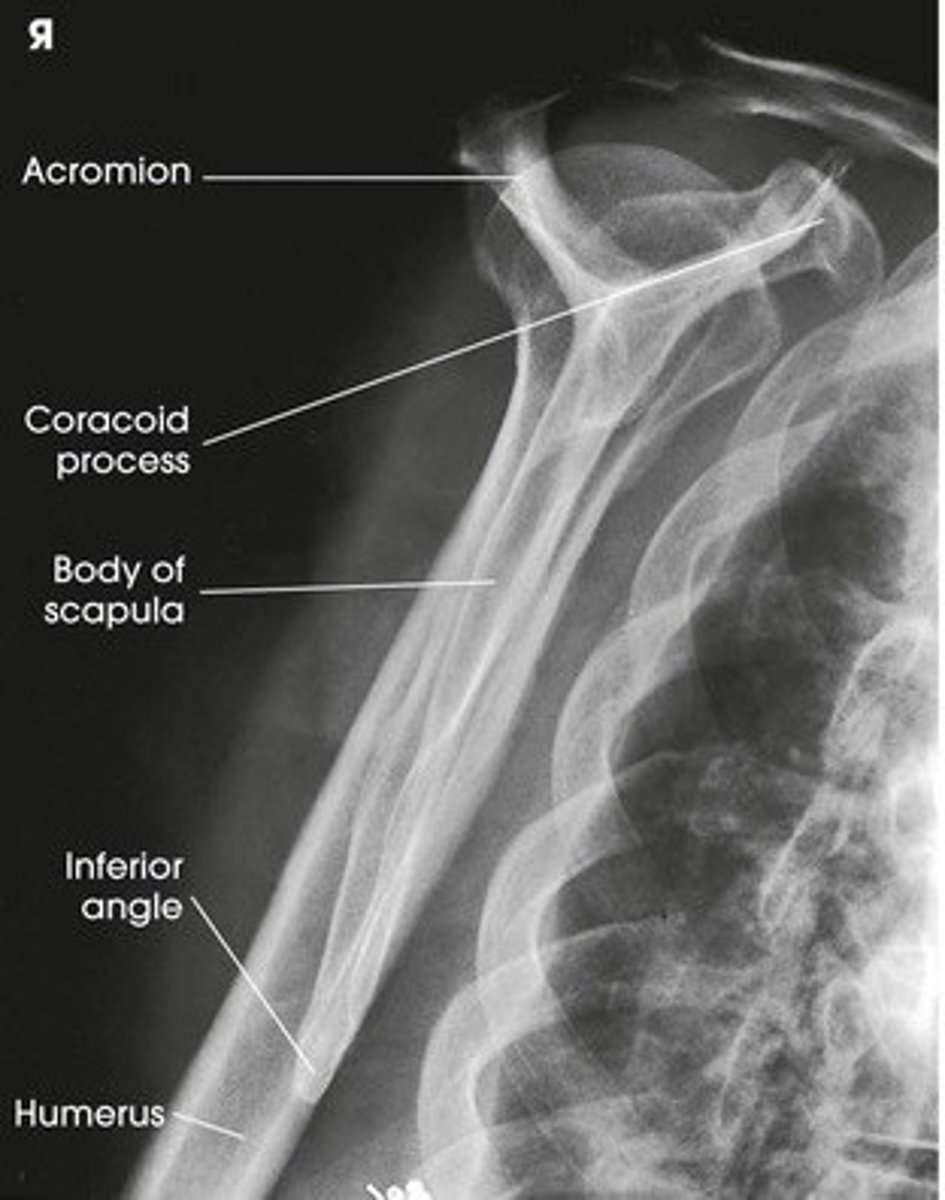
Evaluate the Image
1. What projection is shown in the image?
2. What are the clinical indications for this projection?
3. Is this an optimal image?
4. Name all of the anatomy.
5. Does this image meet all criteria?
6. Where is the CR placed?
7. If applicable, what method is interchangeable with this projection?
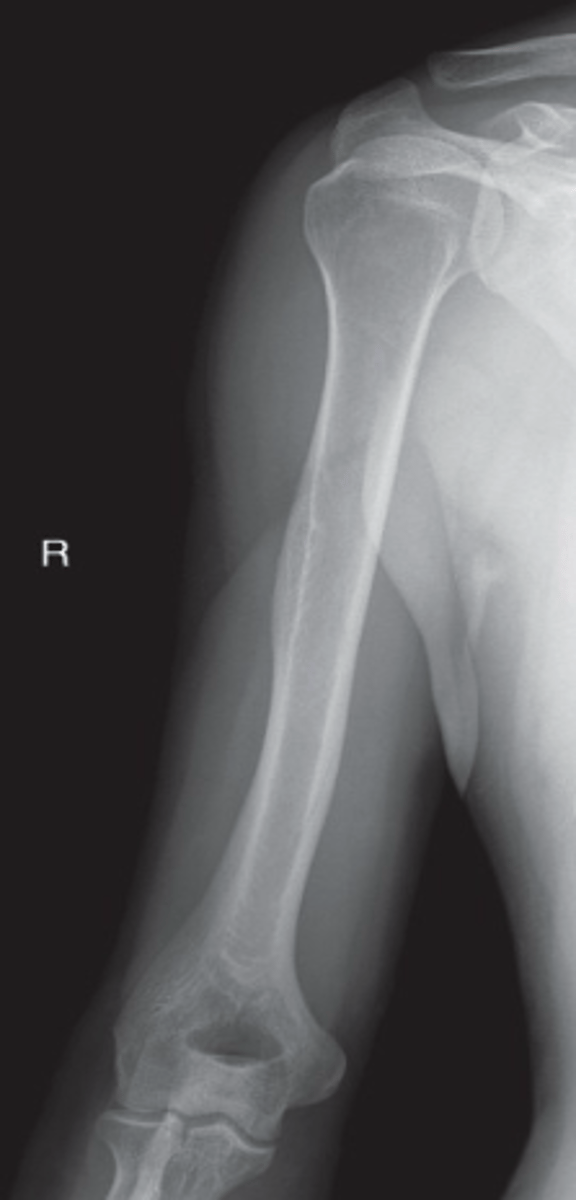
For a properly exposed AP abdomen (KUB), which of the following structures should be visible?
A. Diaphragm
B. Costophrenic angles
C. Psoas muscles and lower liver border
D. Only the lumbar spine
C. Psoas muscles and lower liver border
The AP oblique projection (Grashey method) of the shoulder requires how much rotation and in which direction?
A. 35-45° toward affected side
B. 15-20° toward affected side
C. 15-20° away from affected side
D. 45-60° away from affected side
A. 35-45° toward affected side
Where is the central ray directed for a lateral scapula projection?
A. Glenoid cavity
B. 2 inches inferior to the acromion
C. Level of coracoid process
D. Mid vertebral border of the scapula
D. Mid vertebral border of the scapula
Which of the following structures should be seen in profile on an AP shoulder projection with external rotation?
A. Acromion
B. Lesser tubercle
C. Coracoid process
D. Greater tubercle
D. Greater tubercle
Why is it important to wait 5-10 minutes before performing an erect abdomen?
A. To separate air-fluid levels
B. To let the diaphragm settle
C. To allow time for breathing instructions
D. To allow barium to coat the stomach
A. To separate air-fluid levels
Which exposure factor is most appropriate for imaging the chest using a PA projection?
A. 55-65 kVp with short exposure
B. 110-125 kVp with high mA and short exposure
C. 100-115 kVp with high mA and short exposure
D. 90-100 kVp with long exposure
B. 110-125 kVp with high mA and short exposure
What structure is best demonstrated in profile on a medial oblique foot?
A. Navicular
B. 1st metatarsal
C. Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal
D. Anterior talus
C. Tuberosity of 5th metatarsal
Which condition is defined as an avulsion fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal?
A. Smith's fracture
B. Jones fracture
C. Colles fracture
D. Bennett's fracture
B. Jones fracture
Which of the following is the correct tube angle and direction for a plantodorsal axial projection of the calcaneus?
A. 30° caudad
B. 15° cephalic
C. 40° caudad
D. 40° cephalic
D. 40° cephalic
The CR for a lateral projection of digit number one on the foot should be directed to the:
A. IP joint
B. PIP joint
C. 3rd MTP joint
D. Base of 5th metatarsal
A. IP joint
What positioning error would cause the metatarsals to overlap on an AP oblique foot?
A. Excessive dorsiflexion
B. Rotation less than 30°
C. Over-rotation beyond 45°
D. Not angling the CR
C. Over-rotation beyond 45°
Which of the following body habitus require the IR to be landscape for an abdomen or chest?
A. Hyperstenic
B. Sthenic
C. Hyposthenic
D. Asthenic
E. Both A and B
E. Both A and B (sthenic can be either landscape or portrait)
Which of the anatomical structures is not visible in a AP abdomen erect radiograph?
A. Pubis symphysis
B. Diaphragm
C. Kidneys
D. Ascending Colon
A. Pubis symphysis
Hyersthenic patients (bariatric) require a minimum of _________ images for an AP supine abdomen.
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
B. 2
What is the desired time that a patient must be erect before taking an AP erect abdomen radiograph?
A. 5 minutes
B. 5 - 10 minutes
C. 8 - 10 minutes
D. 10 - 20 minutes
D. 10 - 20 minutes
What is the minimum time that a patient must be erect before taking an AP erect abdomen radiograph?
A. 5 minutes
B. 5 - 10 minutes
C. 8 - 10 minutes
D. 10 - 20 minutes
A. 5 minutes
What is a common abdomen series?
A. AP supine Abdomen
B. PA erect Chest, AP supine Abdomen, and AP erect Abdomen
C. AP erect Abdomen, and AP supine KUB
D. AP erect Abdomen, AP supine KUB, and Lateral Abdomen
C. AP erect Abdomen, and AP supine Abdomen
Which of the following projections is part of the acute abdomen series?
A. AP erect Abdomen
B. PA erect Chest
C. AP supine KUB
D. Both A and B
E. A, B, and C
E. A, B, and C
The acute abdomen series demonstrates which of the following?
A. Abdomen contents
B. Separation of joints
C. Air-Fluid levels
D. Both A and C
E. A, B, and C
D. Both A and C
A routine 3-view hand series includes which of the following projections?
A. PA, AP oblique, and lateral
B. PA, PA oblique, and fan lateral
C. PA, lateral, and tangential
D. AP, PA oblique, and lateral
B. PA, PA oblique, and fan lateral
Which condition is best evaluated using the PA axial projection with ulnar deviation of the wrist?
A. Boxer's fracture
B. Colles' fracture
C. Lunate dislocation
D. Scaphoid fracture
D. Scaphoid fracture
Which positioning error is present if the distal radius and ulna are not superimposed on a lateral forearm?
A. Wrist is in true lateral
B. Over-rotation
C. Improper elbow flexion
D. Under-rotation
D. Under-rotation
Which view best visualizes the lateral and medial malleoli in profile and open ankle mortise?
A. AP ankle
B. AP oblique ankle 45°
C. AP mortise ankle 15-20°
D. Lateral ankle
C. AP mortise ankle 15-20°
Which structure should be superimposed in a properly positioned lateral forearm?
A. Distal radius and ulna
B. Ulna and humerus
C. Radial head and coronoid process
D. Radius and ulna proximally only
A. Distal radius and ulna
The correct centering point for an AP projection of the forearm is:
A. Mid-elbow joint
B. Radial tuberosity
C. Midpoint between the wrist and elbow
D. Ulnar styloid
C. Midpoint between the wrist and elbow
Which of the following is incorrect about the changes between a routine CXR versus an adaptation CXR?
A. Exposure factors don't change when not using a grid
B. Patient's breathing can be altered and can't inspire two full inspiration
C. The number of ribs seen above the diaphragm can be limited (8-9 ribs is acceptable)
D. Adaptation to patient's ability and condition
A. Exposure factors don't change when not using a grid
Where is the CR placed when position for an AP chest?
A. Mid-Chest, mid-sagittal line
B. At the jugular notch, mid-coronal line
C. 3-4" below the jugular notch, mid-sagittal line
D. At the level of the xiphoid process, mid-coronal line
C. 3-4" below the jugular notch, mid-sagittal line
Which of the following is not correct when performing a lateral CXR in a wheel chair?
A. Move patient's wheel chair as close to the IR as possible
B. Patient's left side towards the IR
C. Lock wheelchair
D. Armrest should be attached to the wheelchair for patient comfort
D. Armrest should be attached to the wheelchair for patient comfort
Which of the following is correct regarding the positioning marker being placed?
A. Right Lateral Decubitus CXR: Left positioning marker should be placed top left corner of the IR
B. Left Lateral Decubitus Abdomen: Left positioning marker should be placed at the top right hand corner
C. Right Lateral Decubitus: Right position marker should be placed at the top left corner
D. Left Lateral Decubitus Abdomen: Right positioning marker should be placed at the center of the IR
A. Right Lateral Decubitus CXR: Left positioning marker should be placed at the top left corner of the IR
For an AP abdomen (KUB), which of the following clinical indications is most common?
A. Pneumonia
B. Bowel obstruction
C. Rib fracture
D. Thoracic spine pain
B. Bowel obstruction
A left lateral chest x-ray reveals posterior rib separation. What does this suggest?
A. Patient rotation
B. Underexposure
C. Good alignment
D. Improper CR angle
A. Patient rotation
What is the correct IR size and orientation for a routine lateral scapula projection?
A. 14 × 17 portrait
B. 10 × 12 portrait
C. 10 × 12 landscape
D. 14 × 17 landscape
B. 10 × 12 portrait
The CR for the transthoracic lateral projection of the proximal humerus should be directed:
A. Mid-shoulder joint
B. Midpoint of thoracic spine
C. Glenoid cavity
D. Surgical neck of affected humerus
D. Surgical neck of affected humerus
Which of the following structures is not part of the shoulder girdle?
A. Scapula
B. Humerus
C. Clavicle
D. All of the above is part of the shoulder girdle
B. Humerus
Which of the following anatomical structures is not part of the scapula?
A. Coronoid process
B. Coracoid process
C. Supraspinous fossa
D. Lateral Border
A. Coronoid process
For an AP axial projection, what would the CR angulation be for an asthenic (thinner) patient?
A. 15° Cephalic
B. 20° Caudal
C. 25° Cephalic
D. 30° Cephalic
D. 30° Cephalic
For an AP axial projection, what would the CR angulation be for a hypersthenic (broad) patient?
A. 15° Cephalic
B. 20° Caudal
C. 25° Cephalic
D. 30° Cephalic
A. 15° Cephalic
What breathing instruction would you use for an AP axial projection of the clavicle?
A. Orthostatic
B. After second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
What breathing instruction would you use for a PA chest projection?
A. Orthostatic
B. Suspend after second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
B. After second full inspiration
What breathing instruction would you use for an AP erect abdomen projection?
A. Orthostatic
B. After second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
What breathing instruction would you use for an AP scapula projection?
A. Orthostatic
B. After second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
A. Orthostatic
What breathing instruction would you use for an AP shoulder projection?
A. Orthostatic
B. After second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
What breathing instruction would you use for an Transthoracic Lateral projection of the proximal humerus?
A. Orthostatic
B. After second full inspiration
C. Suspend after expiration
D. Suspend after inspiration
A. Orthostatic
Which of the following is not a trauma projection of the shoulder?
A. AP internal
B. PA oblique - Scapular Y
C. Transthoracic lateral
D. AP neutral
A. AP internal
True/False: The clavicle is classified as a short bone.
False (considered a long bone)