chapter 5 the integumentary system
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
epidermis
the superficial region of the skin, avascular, contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, dendritic cells, and tactile (merkel) cells
dermis
mostly connective tissue, vascular
keratinocytes
produce keratin (what makes skin waterproof), connected tightly by desmosomes, which is why skin comes off in layers
melanocytes
produce melanin which is packed into melanosomes. we all have the same amt of these, just diff amts of melanin produced, melanosomes are transferred to keratinocytes to protect nucleus from uv
dendritic cells
macrophages in deep epidermis
merkel cells
aka tactile cells, sensory neurons
stratum basale
first layer of skin
firmly attached to dermis
single cell layer
aka stratum germinativum
2nd layer of skin
stratum spinosum
several cell layers thick
weblike system of intermediate prekeratin filaments
keratinocytex appear spikey so called prickle cells
stratum granulosum
3rd layer of skin
thin layer of flattened cells
cells above this layer die (too far from blood supply dermal capillaries)
cells accumulate lamellar granules, a water-resistant glycolipids to slow water loss
statum lucidum
only in thick skin (palms of hands and soles of feet)
4th layer
translucentr keratinocytes so called the clear layer
very strong so adds protection
stratum corneum
outer layer of skin
papillary dermis
superficial layer of areolar connective
allows phagocytes to patrol for microorganisms
dermal papillae
fingerlike projections into epidermis (stratum basale)
projections contain capillary loops, free nerve endings, and touch receptors (meissners corpuscles)
dermal ridges
give rise ro epidermal ridges (ie fingerprints)
friction ridges
sweat pores in fingerprints leave the unique fingerprint pattern
reticular dermis
~80% of dermal thickness
lots of dense fibrous connective tissue
lots of elastic fibers to provide stretch recoil properties
collagen fibers provide strength
ECM contains pockets of adipose cells
cutaneous plexus
network of blood vessels between reticular layer and hypodermis (fat below the skin)
cleavage (tension) lines
caused by collagen fibers running parallel to skin surface
externally invisible
incisions parallel heal better, so surgeons follow the lines
wrinkles follow these lines
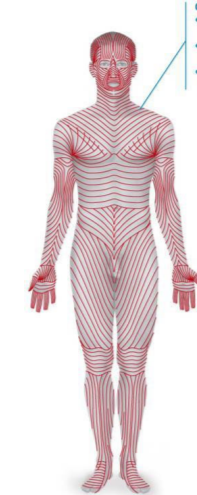
flexure lines
dermal folds at or near joints
dermis is closely attached to deeper structures
skins inability to slide causes deep creases
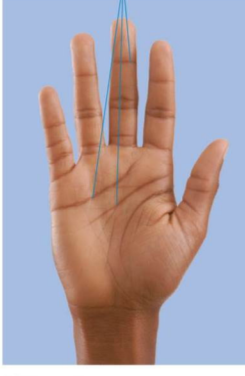
striae
aka stretch marks
lines of cleavage have stretched causing dermal tears
silvery white scars
skin colour
affected by
melanin
made from tyrosine
carotene
accumulates in stratum corneum and hypodermis
hemoglobin
cyanosis
blue tint to skin, low oxgenation of hemoglobin
pallor
blanching or pale colour
anemia, low BP
erythema
redness
fever, hypertension (high BP), inflammation, allergy
jaundice
yellow cast
issue w biliruben, liver disorders
ecchymoses
or hematomas, bruises
clotted blood beneath skin
hair functions
protect from heat loss
sheild skin from sunlight
hair on head cushions to gaurd physical trauma
warn of insects of skin
more sensory nerve edings near the base of a hair follicle, so we feel it if a bug brushes the hair
hair
flexible strands of dead keratinized cells, keratin is harder, shaft (keratinization is complete) and root(keratinization is still happening)
medulla
central core of hair strand
this part must be coloured so we use bleach to reach it
cortex
middle part of a hair strand, several layers of flattened cells surroundingf the medulla
cuticle of hair
outermost layer of hair, overlapping layers of single cells
red hair
contains an extra pigment, pheomelanin
peripheral connective tissue sheath
derived from dermis
aka fibrous sheath
glassy membrane
thickened basal lamina
epithelial root sheath
derived from epidermis
hair matrix
inner part of bulb thats actively dividing
arrector pili
small band of smooth muscle attached to follicle
hair papilla
dermal tissue containing a knot of capillaries that supplies nutrients to growing hair
vellus hair
pale fine body hair of children and women
terminal hair
coarse long hair
head, eyebrows, pubes, armpit, facial hair
hirsutism
excess facial hair in women due to pcos (polycystic ovary syndrome)
alopecia
hair thinning
male pattern baldness
follicular response to DHT (dihydrotestosterone)
nail bed
epidermis underneath keratinized nail plate
nail matrix
thickened part of bed responsible for nail growth
eponychium
aka cuticle, important keeps pathogens out
hyponychium
area under free edge of nail that accumulates dirt
lunule
thickened nail matrix, half moon at bottom of nail, appears white diff colour can indicate disease
koilonchya
spoon nail, concave nail can indicate iron deficiency
sudoriferous glands
exocrine sweat glands
eccrine and apocrine sweat glands
eccrine (merocrine) sweat glands
thermoregulation by releasing sweat, controlled by sympathetic nervous system
apocrine sweat glands
genital and armpit sweat, have BO, begin functioning at puberty
other modified apocrine glands
mammary glands, ceruminous glands (lining of ear canal secretes cerumen which is earwax)
sebaceous (oil) glands
most develop from hair follicles and secrete into hair follicles, secrete sebum (oily holocrine secretion)
seborrhea
aka cradle cap, overactive sebaceous glands in infants
chemical barrier
cells secrete defensin, and sebum which lower skin pH defending against bacterial multiplication
melanin provides chemical barrier against uv radiation
insensible perspiration
normal resting body temprature produces unnoticeable sweat
sensible perspiration
increase in noticble sweat to cool body
basal cell carcinoma
Does not metastasize, least malignant and most common
stratum basale cells invade dermis and hypodermis
kinda poking in, goes into papillary layer
commonly appears in high sun areas (ex nose)
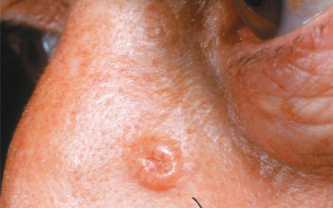
squamous cell carcinoma
second most common type
keratinocytes of stratum spinosum (second layer of skin)
scaly reddened papule on (commonly) scalp, ears, lower lip, and hands
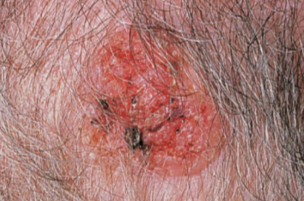
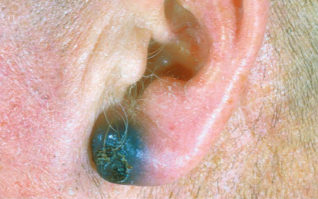
melanoma
cancer of melanocytes, most dangerous due to being highly metastatic (and resistant to chemotherapy)
ABCD RULE
A: asymmetry (the two sides of pigmentation dont match)
B: border irregularity
C: colour (several)
D: diameter (larger than 6 mm)
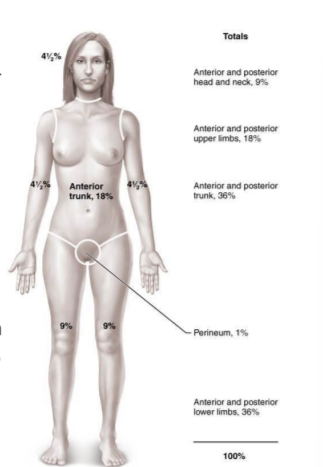
rule of nines
to evalute burns, boy is broken down into 11 sections, with each section representing 9%
estimate volume of fluid loss and hm fluid to give
critical burns
> 25% of the body has second degree burns
>10% has third degree
Face hands or feet have third degree burns
burn treatment
Debridement (removal of the burned skin)
antibiotics
temporary covering (artificial skin)
skin grafts