Video Notes: Constant Velocity and Graphs
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from velocity, displacement, distance, time, and how to read Position-Time and Velocity-Time graphs.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Displacement
The straight-line change in position from start to end, including direction; equals Δx and is measured in meters (m).
Distance
The total length of the path traveled, regardless of direction; not the same as displacement.
Velocity
The speed of an object in a given direction; a vector quantity with units of m/s and a sign indicating direction.
Speed
How fast an object is moving; the magnitude of velocity; a scalar value.
Time
The duration over which motion occurs; measured in seconds (s).
Positive Velocity
Velocity greater than zero; indicates movement in the positive direction (e.g., right).
Negative Velocity
Velocity less than zero; indicates movement in the negative direction (e.g., left).
Rest
Zero velocity; the object is not moving.
Position-Time Graph
Plot of position x versus time t; slope represents velocity; positive slope means moving right, negative means left, zero means rest.
Velocity-Time Graph
Plot of velocity v versus time t; area under the curve gives displacement; above axis is positive velocity, below axis is negative.
Slope on p-t
The rate of change of position with time on a Position-Time graph; equals velocity.
Constant Velocity
A motion where velocity does not change over time; displacement increases linearly with time.
Distance-Time Graph (D-t)
Graph of distance traveled versus time; distance increases with movement and never decreases.
Axis Check
Always verify the axes on a graph before interpreting slope or sign.
Displacement Formula
Δx = v × Δt for constant velocity; equivalently v = Δx/Δt.
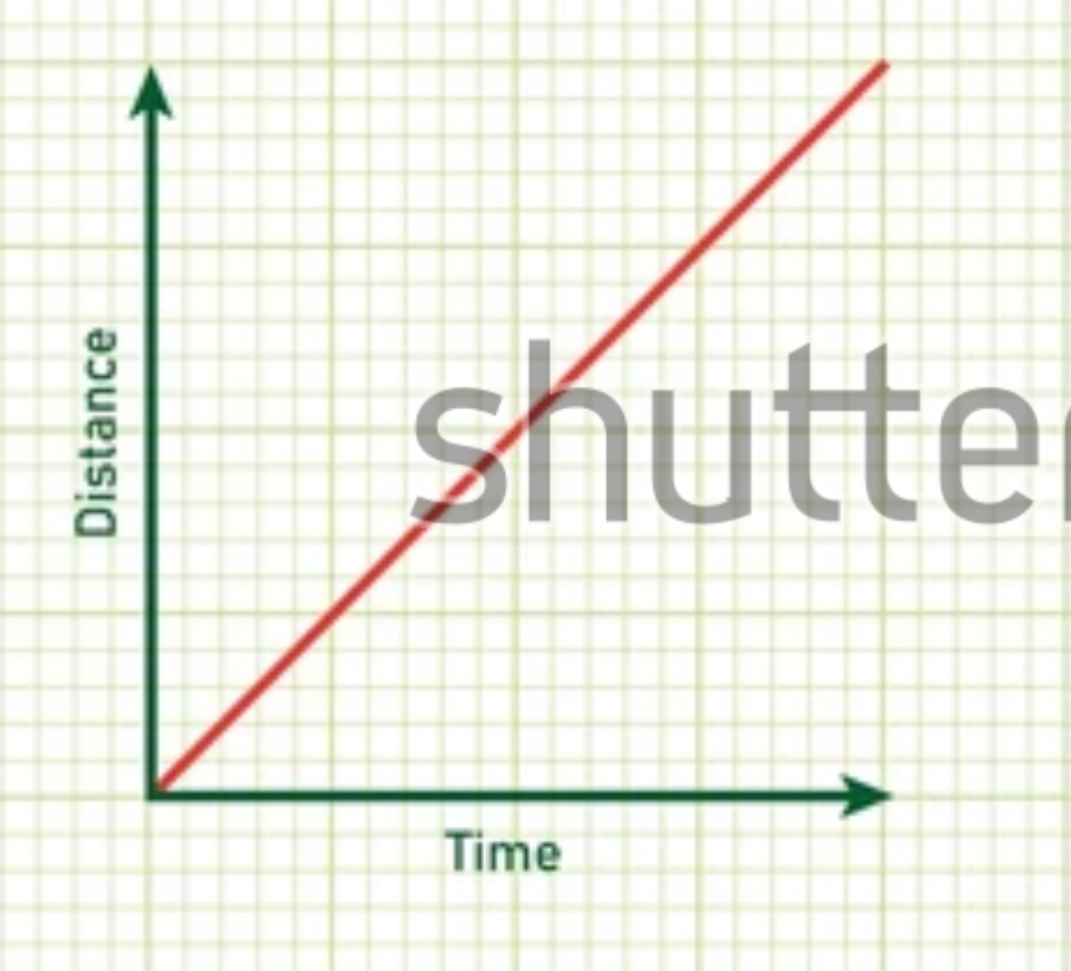
Describe the motion
Object stopped moving
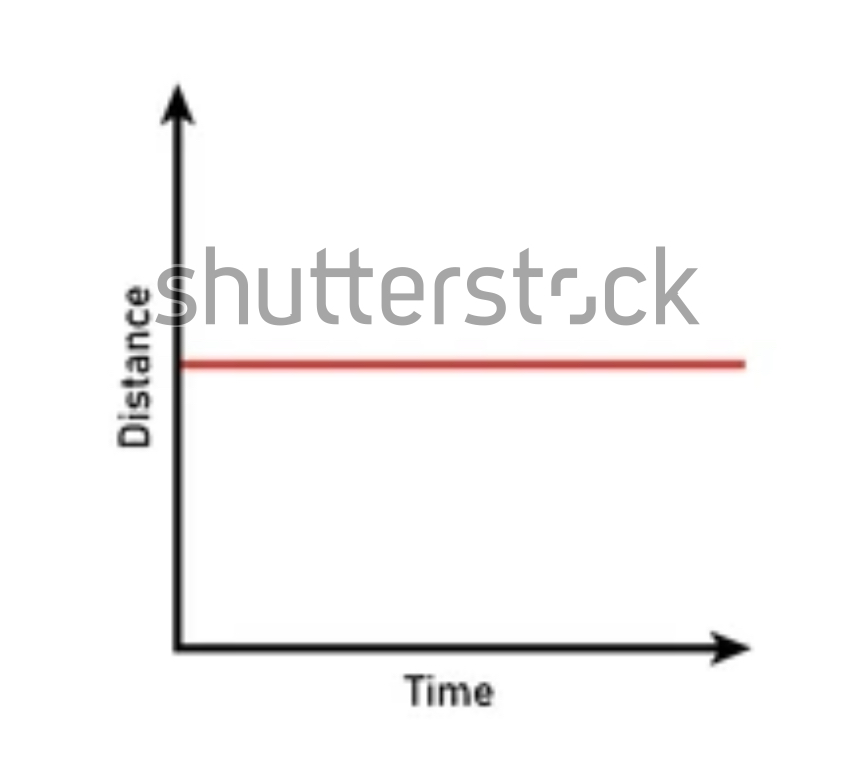
Describe the motion
Distance increasing
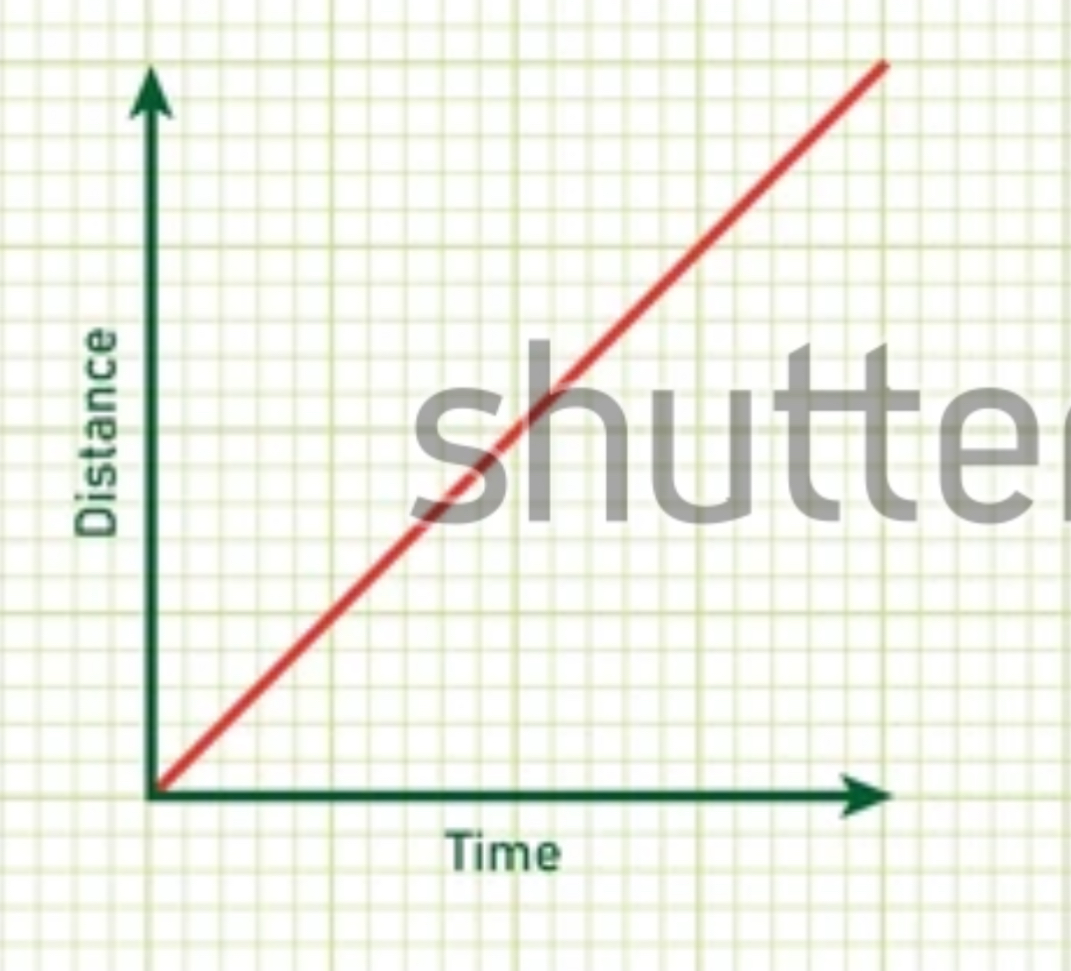
Describe direction
Moving right
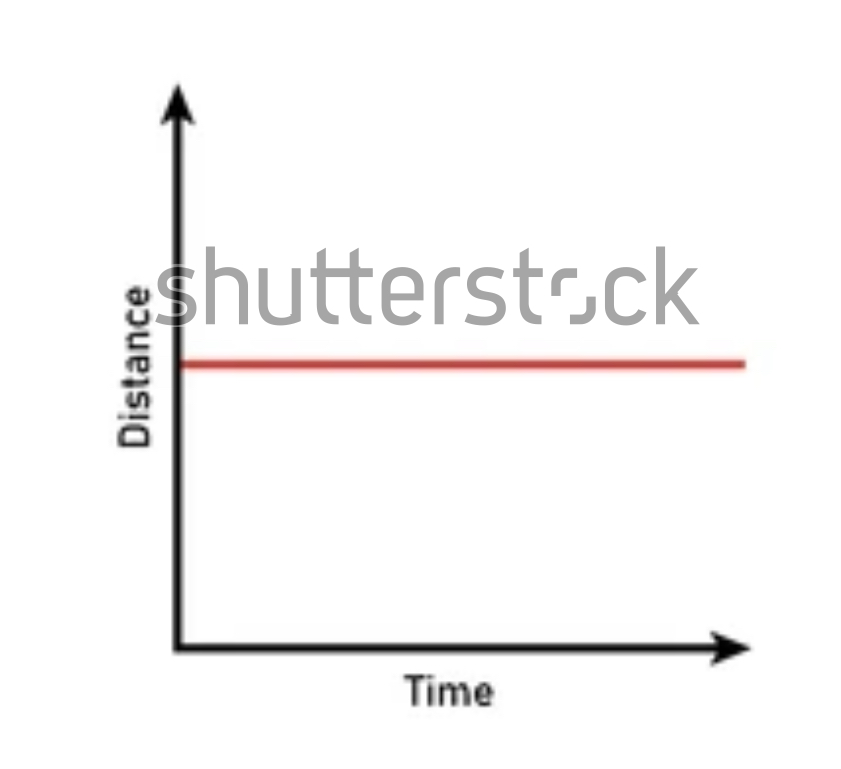
Describe direction
None (stopped moving)