Lecture 11 - Ch 27 - Angiosperms Pt 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What are angiosperms?
Angiosperms are plants that have flowers and fruits, with seeds enclosed in a modified leaf called a carpel.
What develops from the ovary after fertilization in angiosperms?
The ovary develops into a true fruit.
What is the trend in the evolution of vascular plants regarding the sporophyte and gametophyte generations?
The sporophyte generation becomes larger while the gametophyte generation becomes smaller and more dependent on the sporophyte.
What specialized structures do most angiosperms have in their xylem?
Most angiosperms have specialized water-transporting vessel elements and fiber cells for support.
What are some synapomorphies of angiosperms?
Germination of pollen on a stigma, double fertilization, endosperm, and phloem with companion cells.
What is an inflorescence?
An inflorescence is a grouping of flowers, which can be single or in characteristic types like umbels or spikes.
What are the main parts of a flower?
The main parts of a flower include stamens, carpels, petals (corolla), and sepals (calyx).
What distinguishes perfect flowers from imperfect flowers?
Perfect flowers have both mega- and microsporangia, while imperfect flowers have either one or the other.
What does it mean for a plant to be dioecious?
Dioecious plants have male and female flowers on different plants.
How have flowers evolved in terms of floral organ number and symmetry?
Flowers have evolved to have a reduced number of floral organs, changes in symmetry from radial to bilateral, and fusion of parts.
What role do petals and sepals play in flowers?
Petals attract pollinators, while sepals protect the immature flower in bud.
What is double fertilization in angiosperms?
Double fertilization involves one sperm combining with the egg to form a diploid zygote and another sperm combining with two haploid nuclei to form the triploid endosperm.
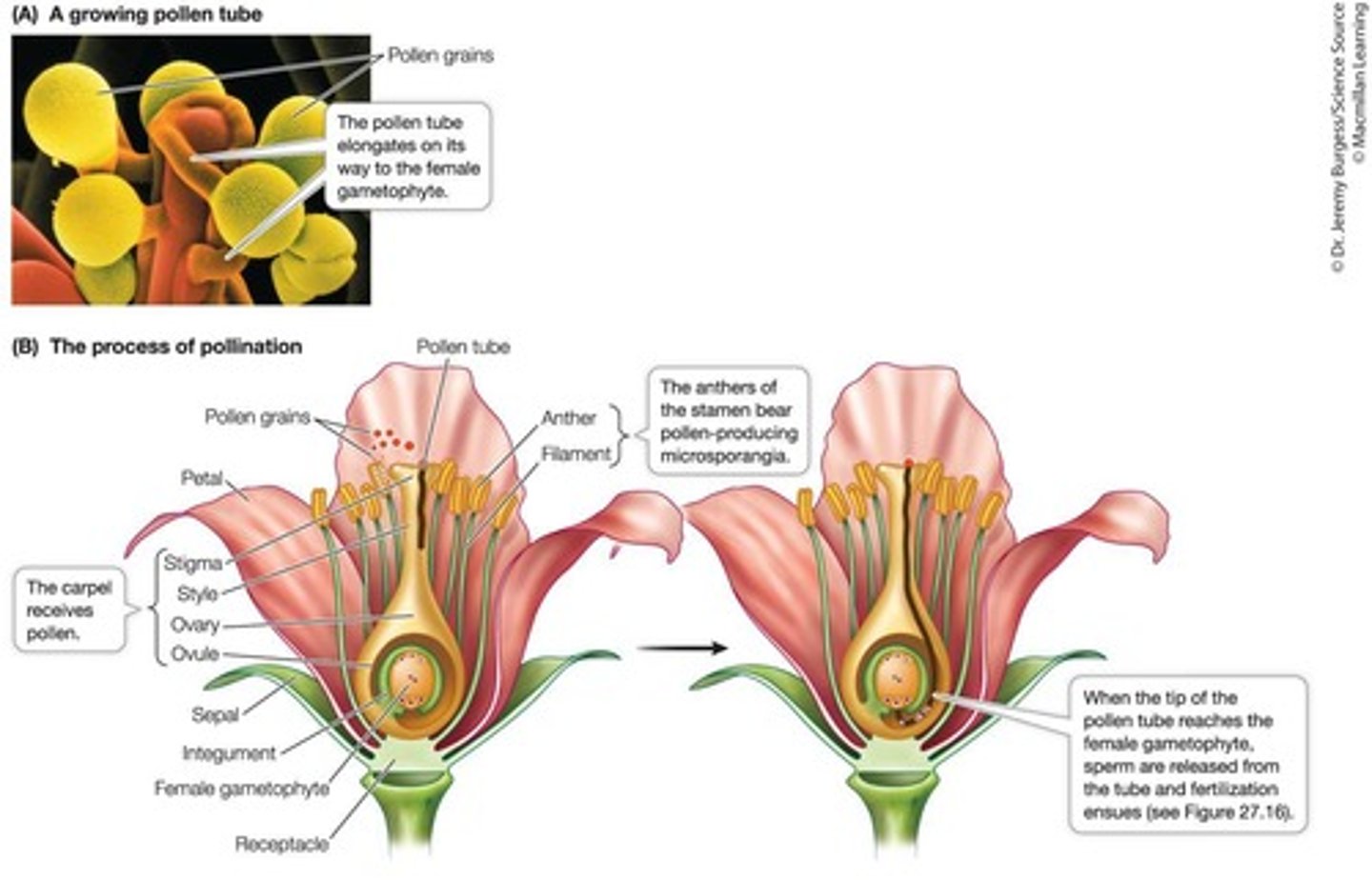
What is the function of endosperm in angiosperms?
Endosperm serves as nutritive tissue for the embryo during early development.
What adaptations do fruits have for seed dispersal?
Fruits may attach to animals, be eaten, or be adapted for dispersal by wind or water.
What are simple fruits and aggregate fruits?
Simple fruits develop from one carpel (e.g., plum), while aggregate fruits develop from several carpels (e.g., raspberry).
How do many flowers entice pollinators?
Many flowers entice pollinators with nectar and pollen as food rewards.
What is the significance of coevolution between plants and their pollinators?
Plants and their pollinators have coevolved, leading to specific relationships, such as one moth species pollinating one yucca species.
What characteristics do bird-pollinated flowers often have?
Bird-pollinated flowers are often red and odorless.
What adaptations do bee-pollinated flowers have?
Bee-pollinated flowers often have conspicuous markings or nectar guides visible only to bees.
What is the role of natural selection in flower structure?
Natural selection has favored longer styles and filaments to increase the likelihood of pollination.
What mechanisms have evolved to prevent self-pollination in perfect flowers?
Many mechanisms, such as requiring different pollinators, have evolved to circumvent self-pollination.
What are simple fruits?
Fruits that develop from one carpel, such as plums.
What are aggregate fruits?
Fruits that develop from several carpels, such as raspberries.
What are multiple fruits?
Fruits that form from a cluster of flowers, such as pineapples and figs.
What are accessory fruits?
Fruits that develop from parts other than carpels, such as apples and strawberries.
Which species is the sister group to all other angiosperms?
Amborella.
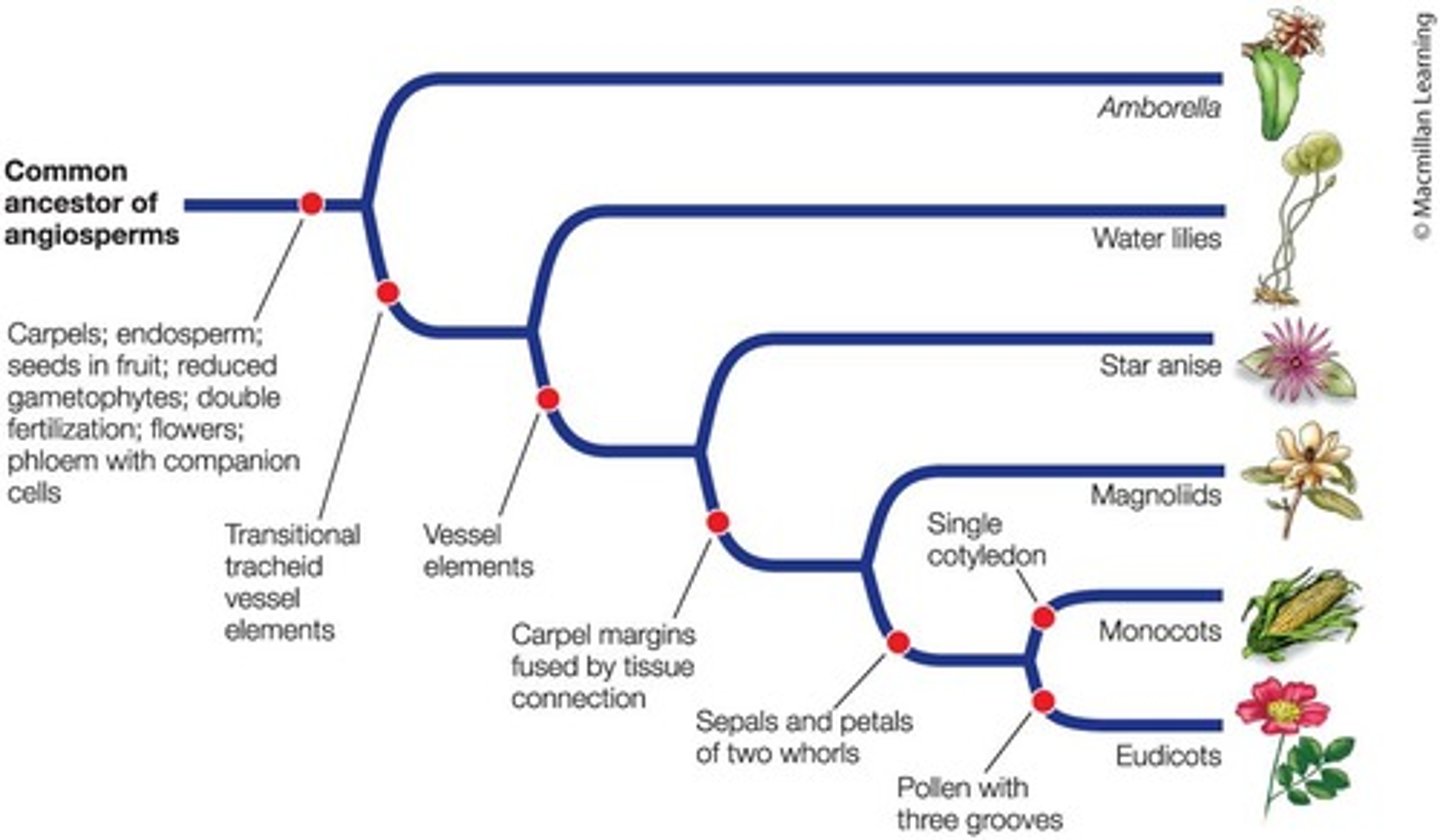
What are the two major clades of angiosperms?
Monocots and Eudicots.
What is a defining feature of monocots?
They have one cotyledon and include grasses, lilies, and palms.
What is a defining feature of eudicots?
They have two cotyledons and include most seed plants like herbs, vines, and trees.
What is the unique feature of angiosperms related to double fertilization?
The nutritive triploid endosperm.
What type of pollination is indicated by flowers with striking patterns visible in UV photography?
Pollination by bees.
How are maple tree seeds primarily dispersed?
By wind.
What role do plants play in ecosystem services?
They produce O2, remove CO2, contribute to soil formation, prevent erosion, and moderate local climate.
What is the significance of the Pacific yew in medicine?
Its bark showed antitumor activity, leading to the isolation of taxol for cancer treatment.
How did ethnobotanists discover medicinal plants?
By studying the uses of plants by different cultures.
What is quinine used to treat?
Malaria.
What is the primary food source for half the world's population?
Rice (Oryza sativa).

Which plant product is used to relieve coughing?
Menthol from Japanese mint.
What is the medical application of atropine derived from belladonna?
To dilate pupils for eye examination.
Which plant-derived substance is used as a muscle relaxant during surgery?
Tubocurarine from the curare plant.
What is the role of plants as primary producers?
They trap energy and carbon through photosynthesis, supporting the food chain.
Which plant is known for providing most daily calories in a native Asian diet?
Oryza sativa (rice).
What is the ecological service that plants do not provide?
Returning nutrients to the soil through photosynthesis.
What is the significance of seed dormancy?
It allows seeds to survive unfavorable conditions until they can germinate.
What is the impact of growing new high-yield crop strains?
It reduces diversity and increases the risk of pests and diseases.