Gene Transfer, Regulation, and Expression in Microbiology and Biotechnology
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
300 Terms
What is vertical gene transfer?
The transfer of genes directly to all progenies during reproduction.
What is horizontal gene transfer?
The transfer of genes between cells of the same generation.
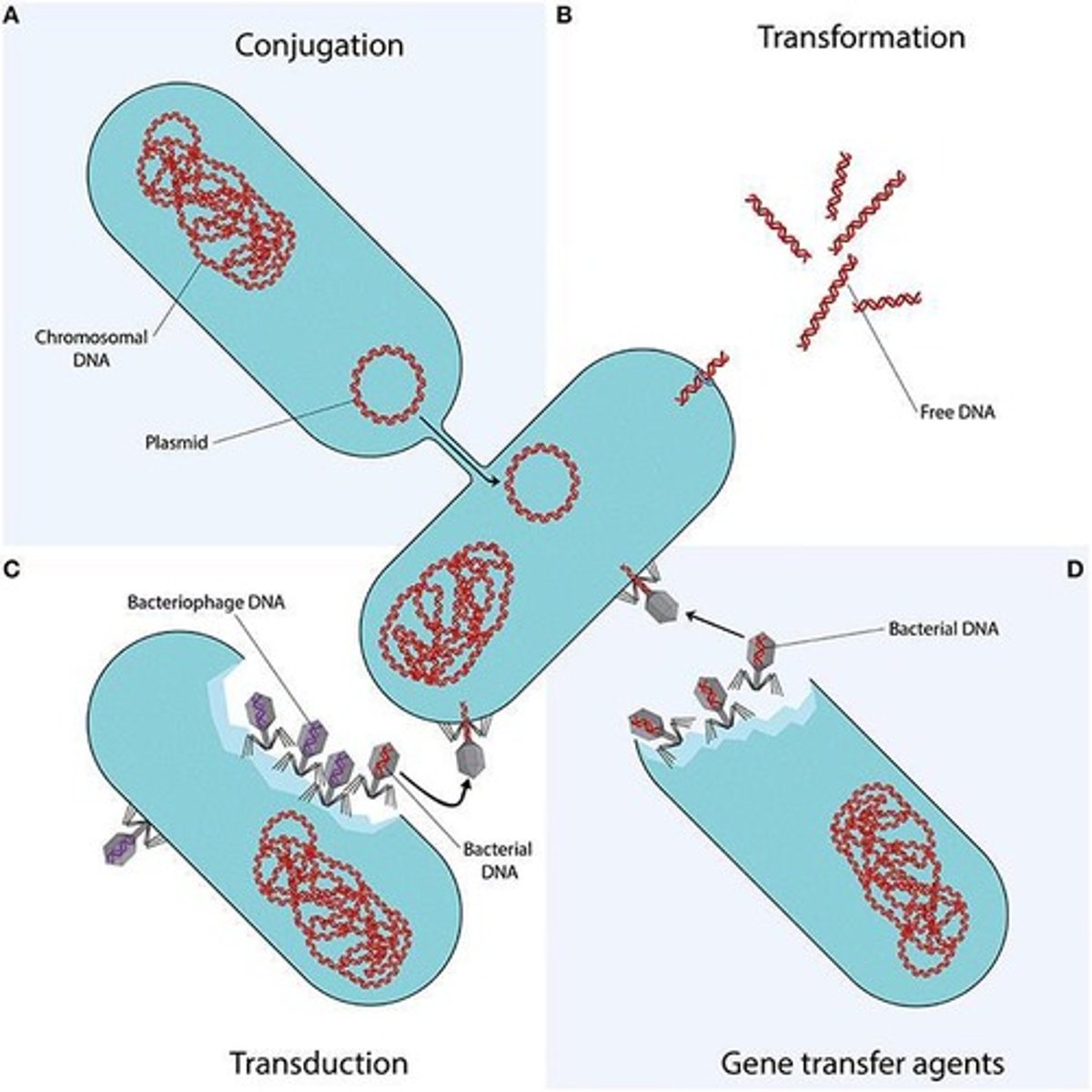
Name the three mechanisms of horizontal gene transfer.
Transformation, Conjugation, Transduction.
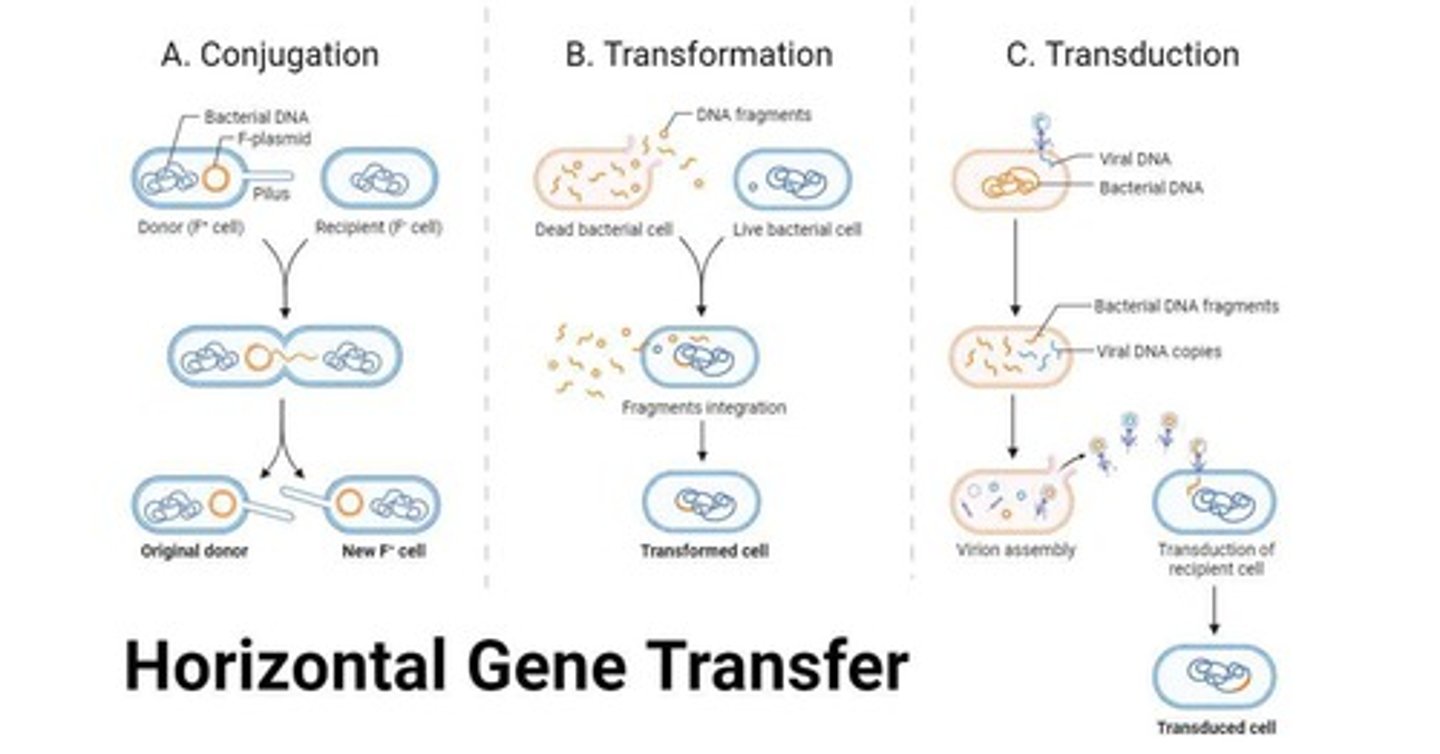
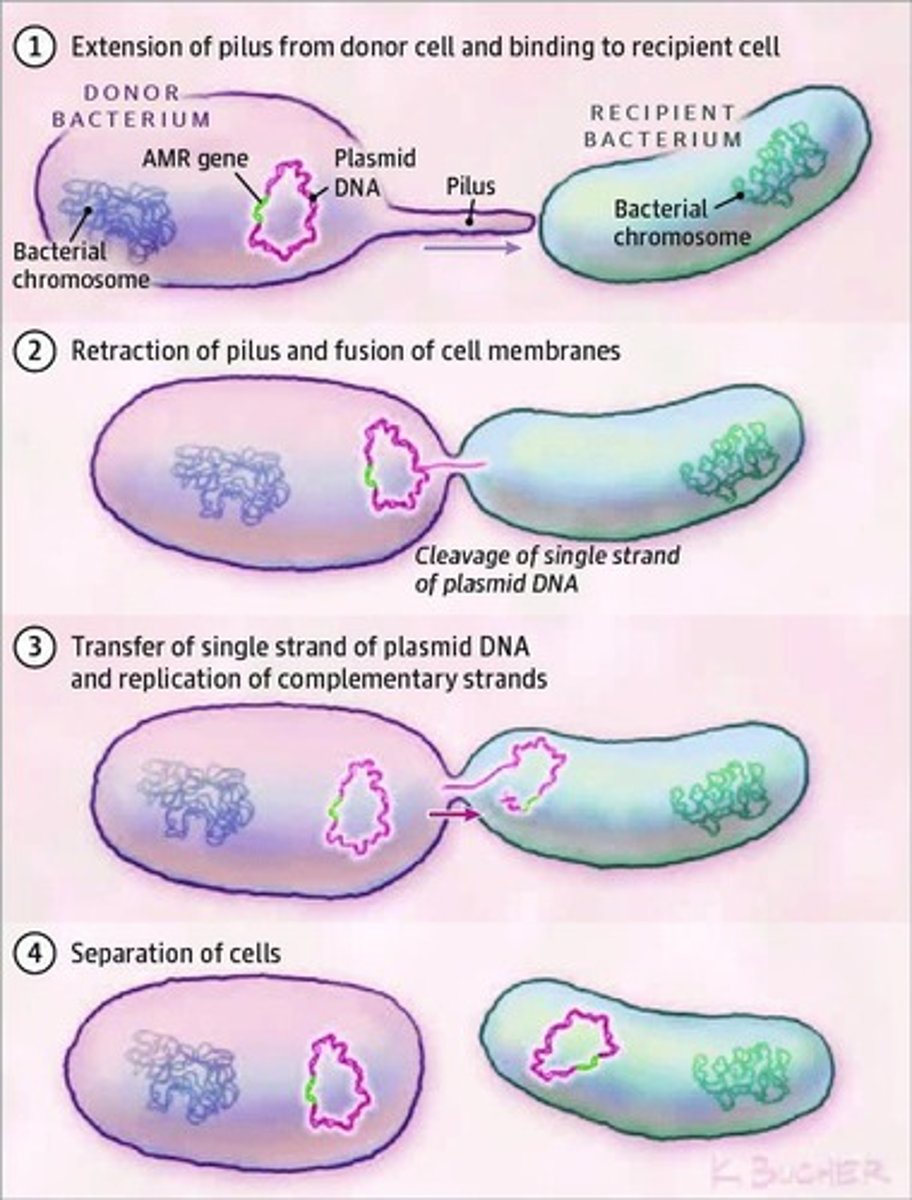
What is the process of conjugation?
A process requiring cell-to-cell contact via pili or adhesins, through which DNA is transferred from the donor cell to the recipient cell.
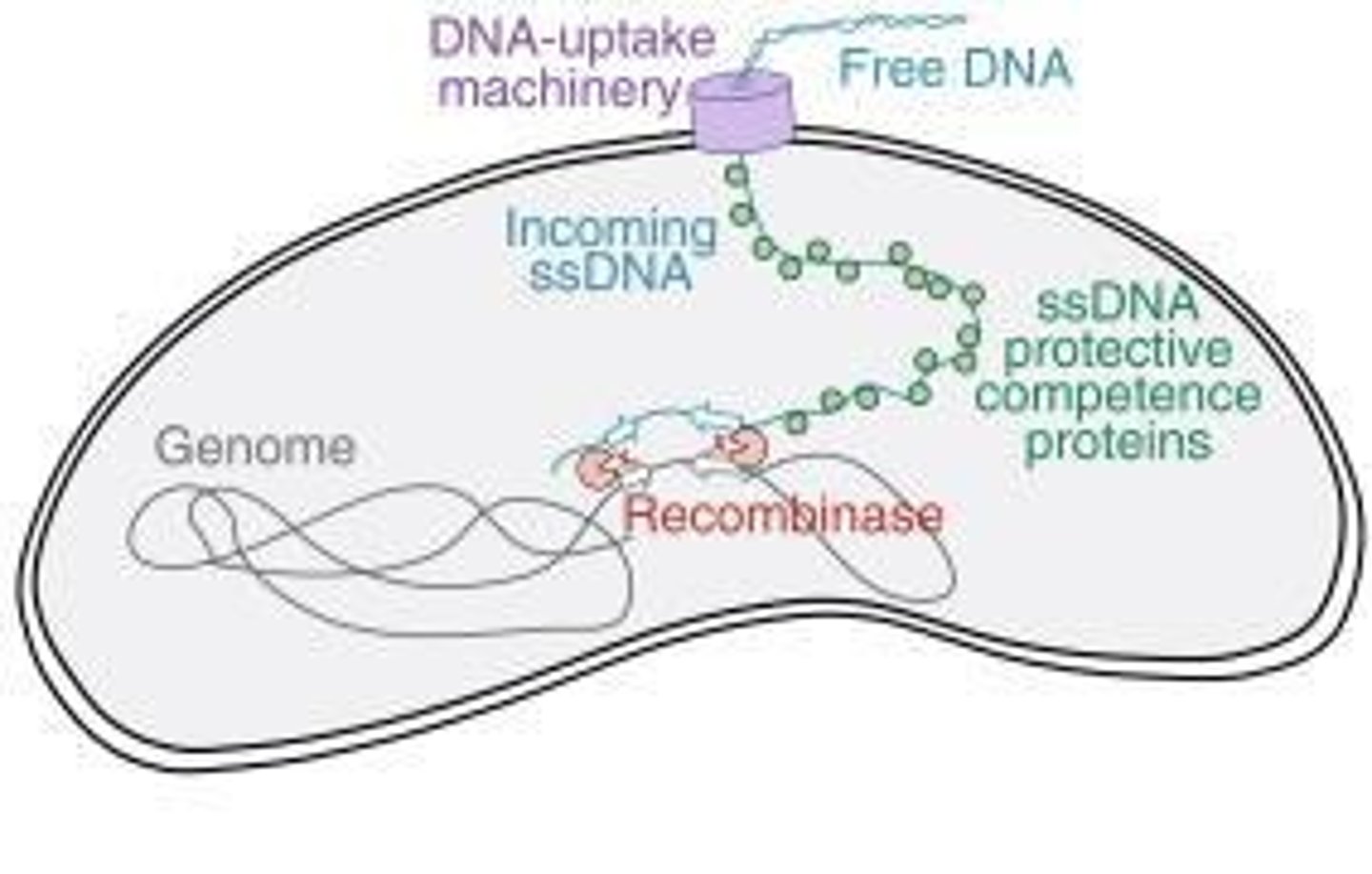
Define transformation in the context of gene transfer.
The uptake, integration, and functional expression of naked fragments of extracellular DNA.
What occurs during generalized transduction?
Bacterial DNA may be accidentally loaded into the phage head and transferred to a recipient cell.
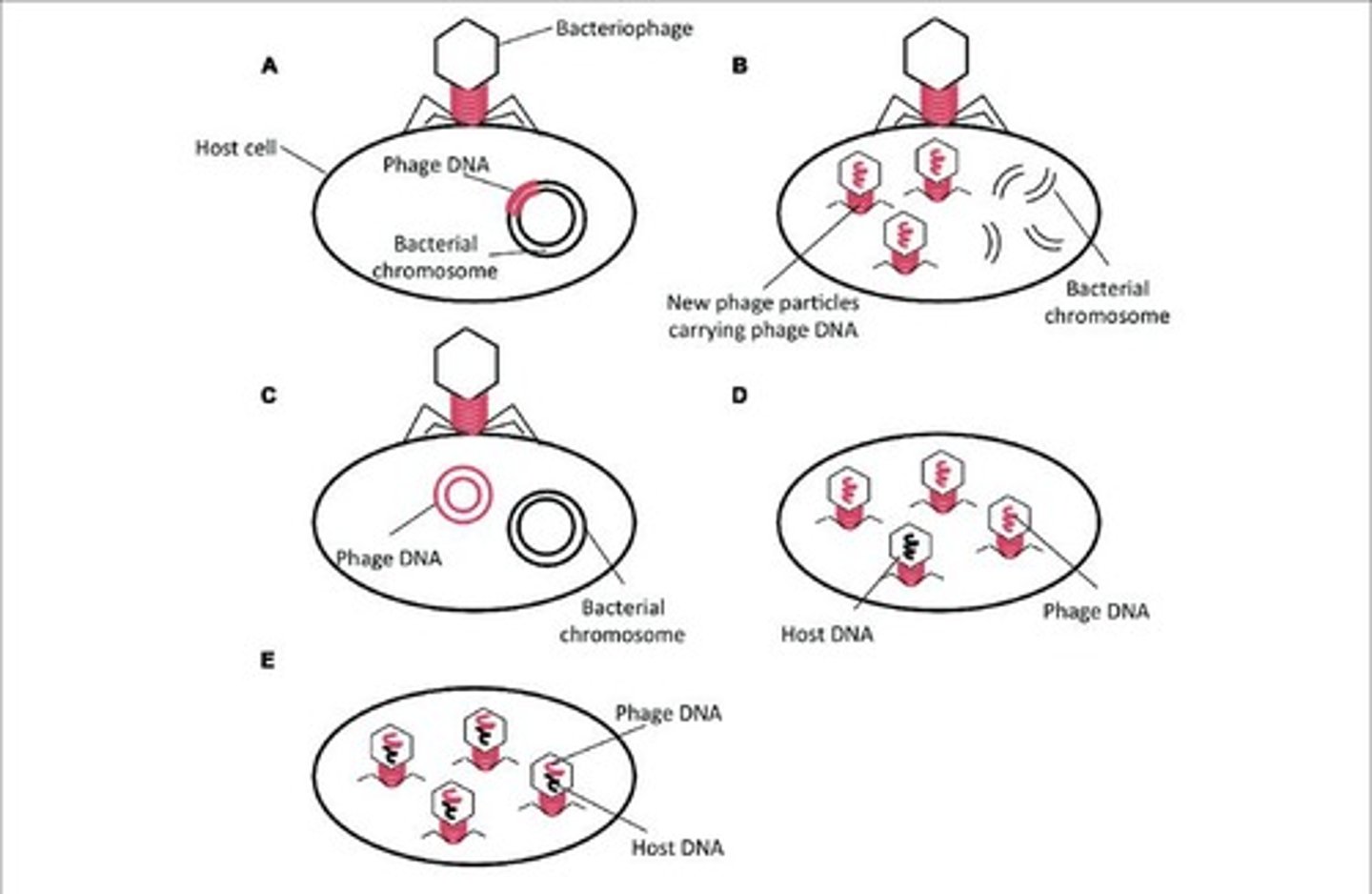
What is specialized transduction?
Genomic DNA neighboring the prophage DNA is co-excised and loaded into a new phage.
What are gene transfer agents (GTAs)?
Bacteriophage-like particles that carry random pieces of the producing cell's genome.
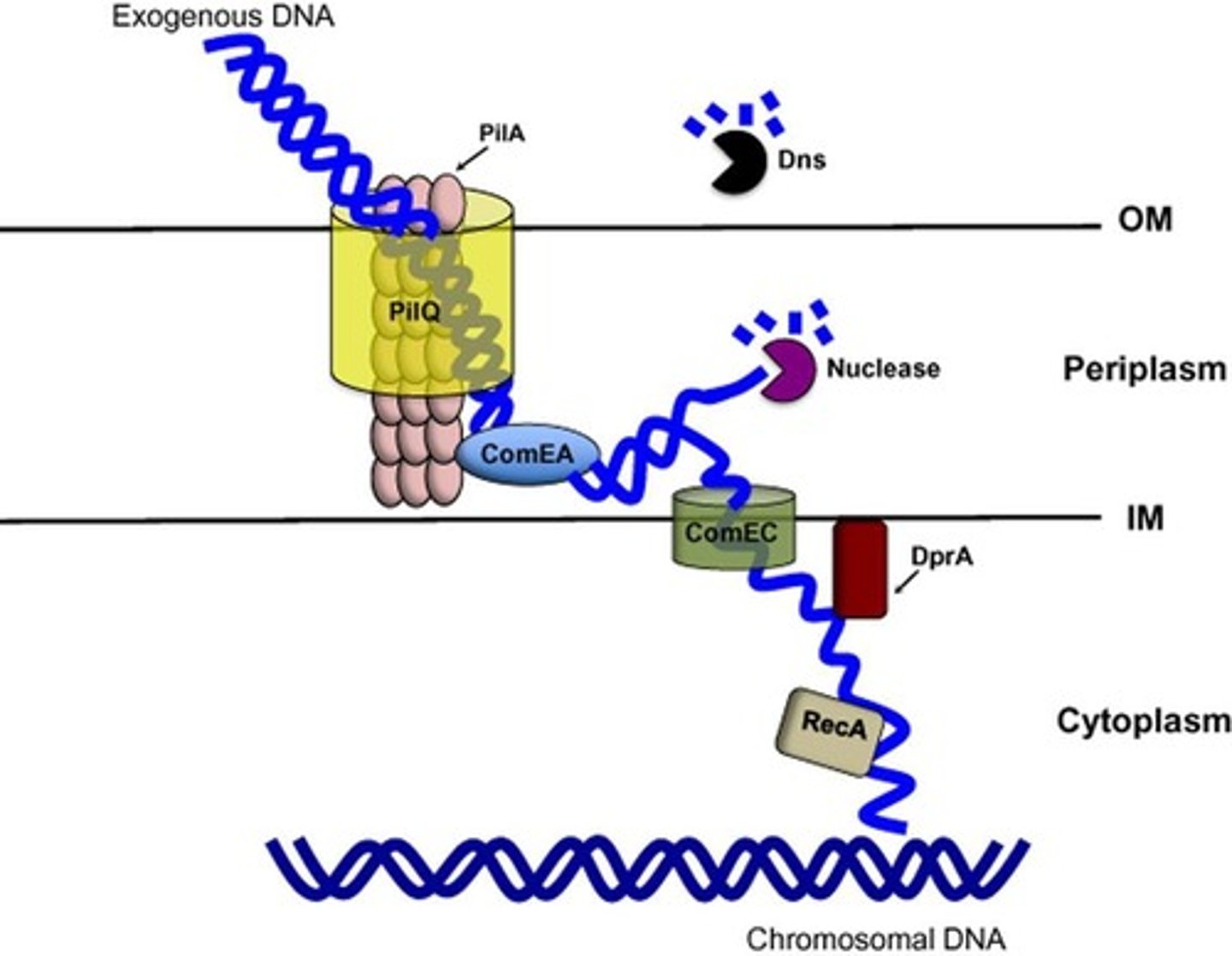
What is the competence state in transformation?
The ability of a bacterium to take up DNA from the medium, which can be natural or artificial.
What triggers the appearance of natural competence in bacteria?
A nutritional shift-down and usually coincides with a decrease in the rate or blockage of DNA synthesis.
How does natural competence differ from artificial competence?
Natural competence is genetically encoded and highly regulated, while artificial competence is induced by chemical and physical methods.
What is the role of the transformation pilus (Tfp) in transformation?
It captures exogenous double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) for uptake.
What happens to the DNA after it binds to the receptor ComEA?
One strand of the DNA enters the cytoplasm through ComEC, while the complement strand is degraded.
What is the function of the DNA protecting protein DprA?
It shields the internalized single-stranded DNA from nuclease attack.
What is the role of the recombinase RecA in transformation?
It promotes a homology search along chromosomal DNA and facilitates strand exchange.
What is the significance of natural transformation in bacteria?
It enables bacteria to acquire new genetic traits and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
How many species of bacteria are known to be naturally transformable?
Approximately 80 species.
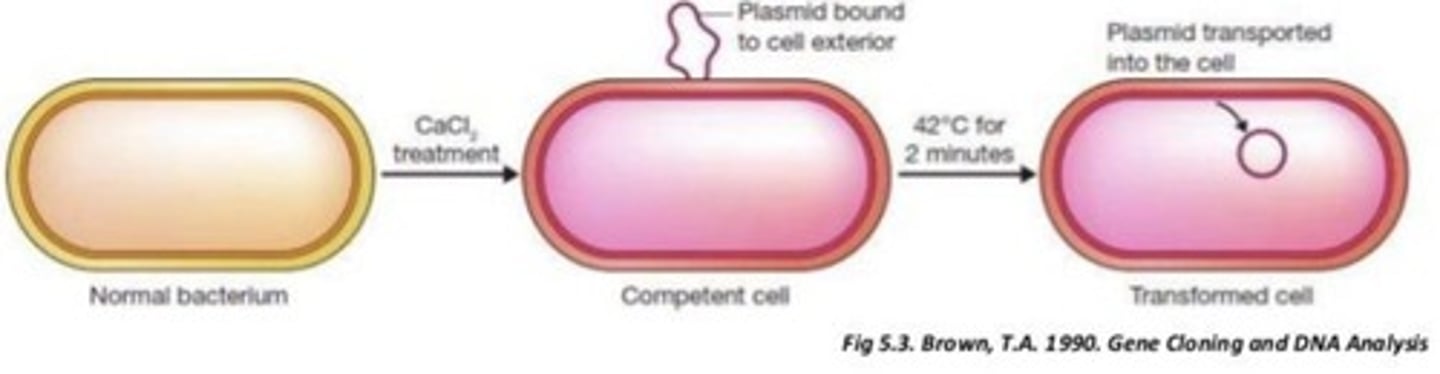
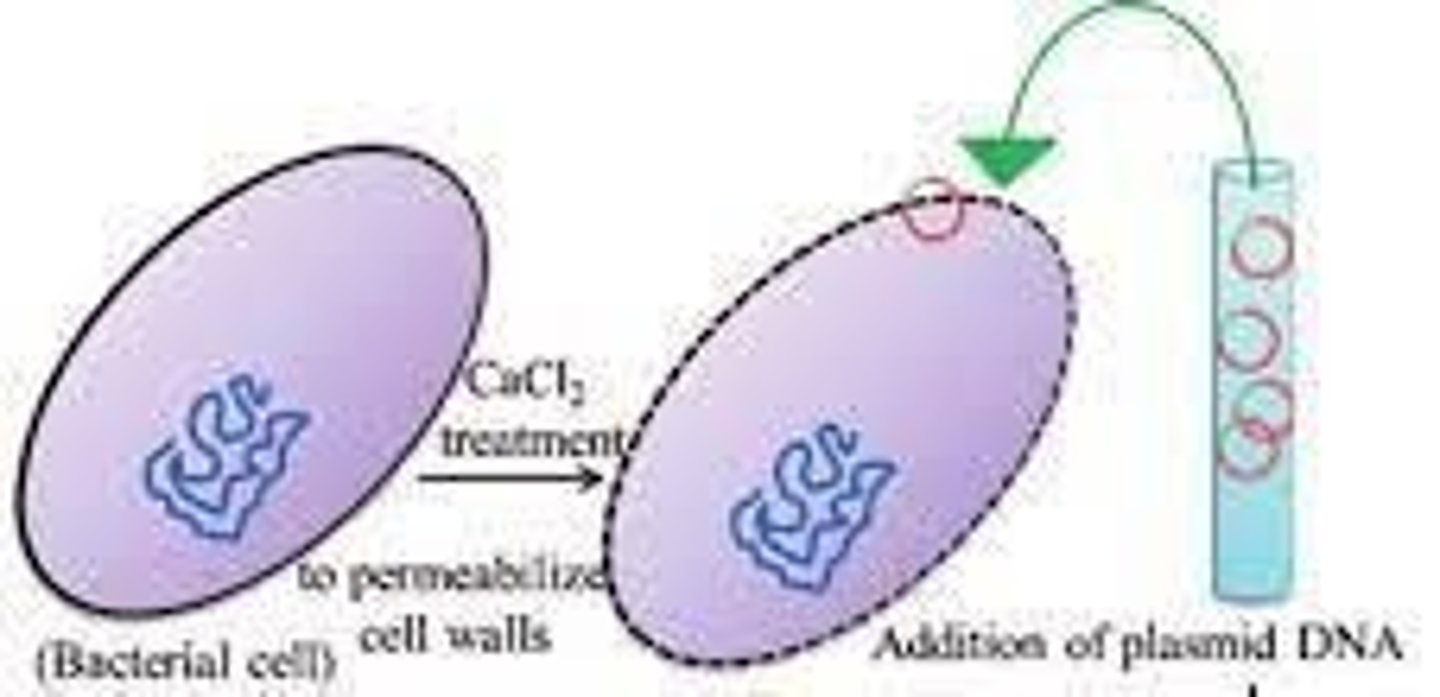
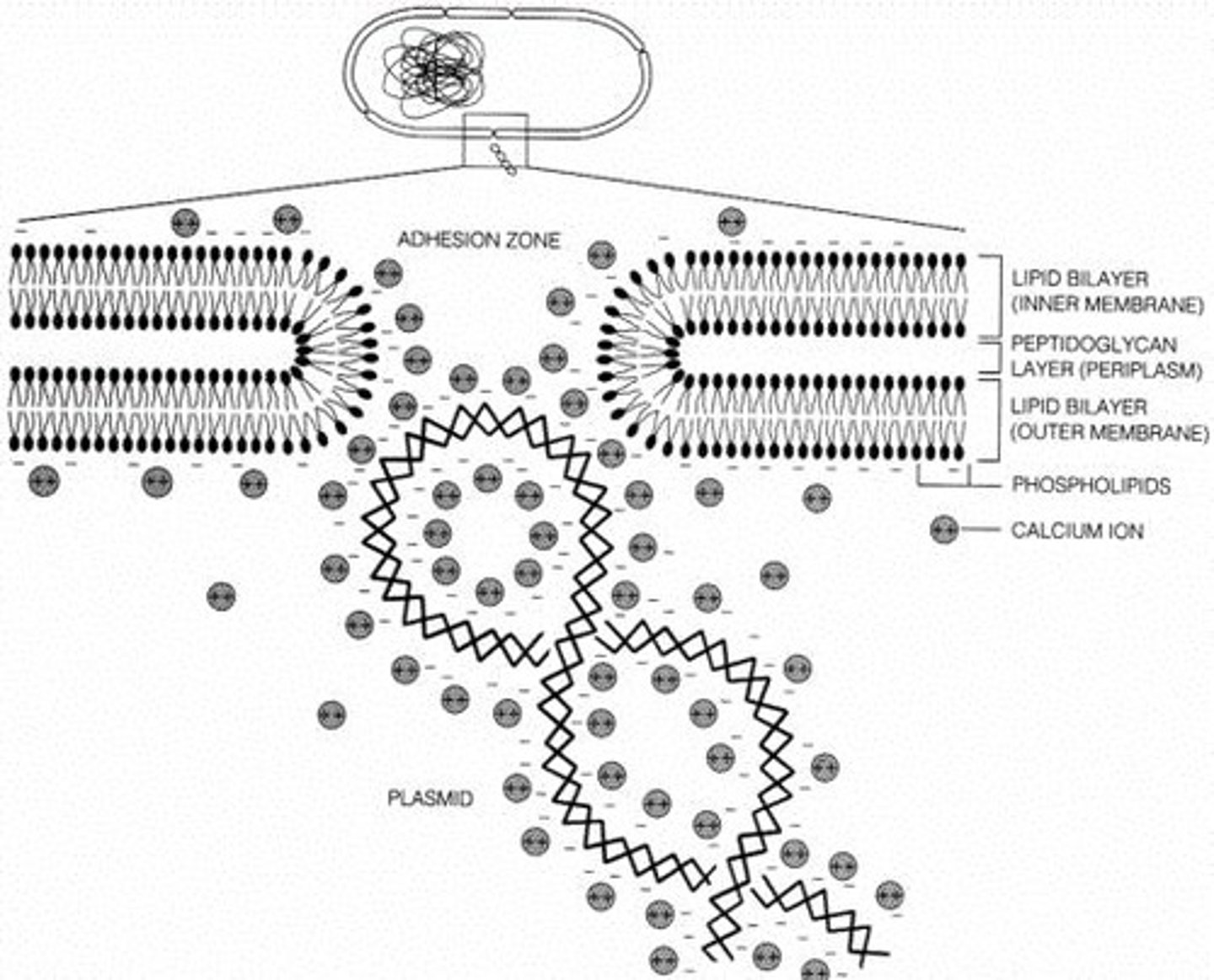
What is the mechanism by which calcium chloride induces artificial competence?
It neutralizes negative charges on the phospholipid layer and DNA, allowing DNA binding to the cell surface.
What is the purpose of heat shock treatment in artificial competence?
It creates a temperature gradient that facilitates the entry of DNA into the cells.
What is the suggested mechanism of how CaCl2 works in transformation?
Ca2+ ions bind to the phosphate groups in DNA and the inner core of lipopolysaccharides in the cell membrane, neutralizing them.
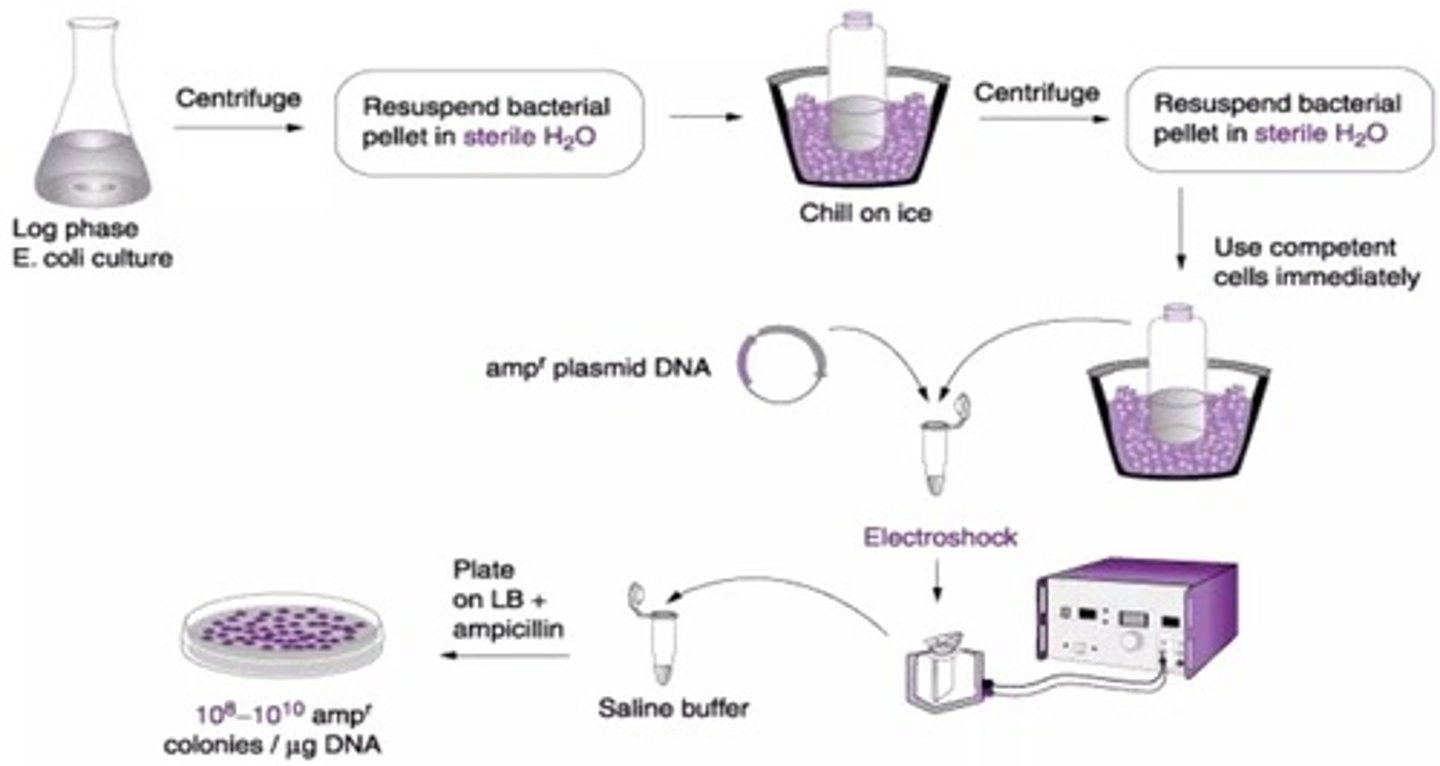
What is the general procedure for calcium chloride transformation?
Cells are placed on CaCl2 solution, grown to log phase, kept on ice, subjected to electro shock, placed on buffer for recovery, and then plated on media.
What is the purpose of heat shock in DNA transformation?
Heat shock allows the uptake of DNA into the host by creating pores in the cell membrane.
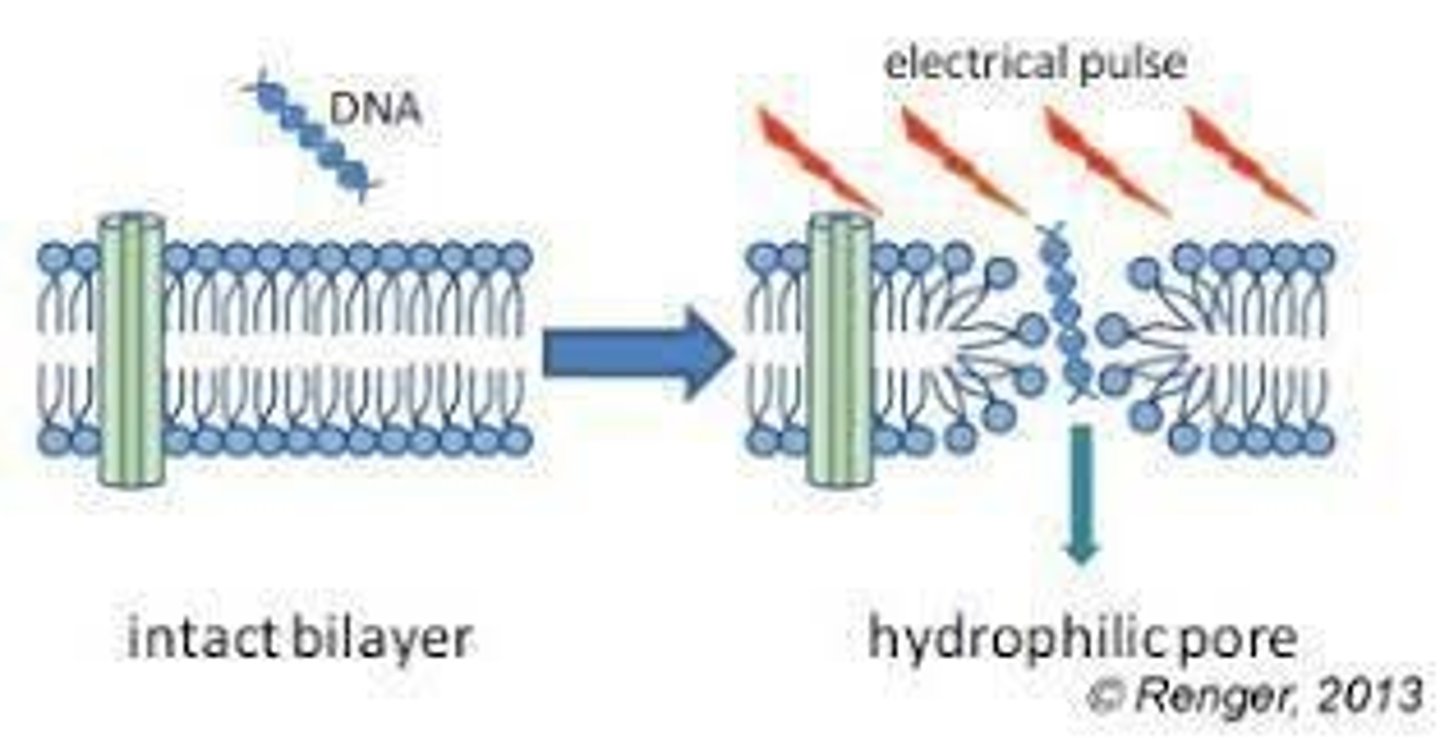
What is electroporation?
Electroporation is the use of high-voltage electric shocks to introduce DNA into cells by enhancing membrane permeability.
What types of cells can be effectively electroporated?
All types of cells, including animal cells, microorganisms, and bacteria.
What is the role of the electric pulse in electroporation?
The electric pulse enhances the formation of pores in the cell membrane, increasing permeability for ions and molecules.
What is the Ti plasmid?
The Ti plasmid is a tumor-inducing plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens that can transfer DNA into plant cells.
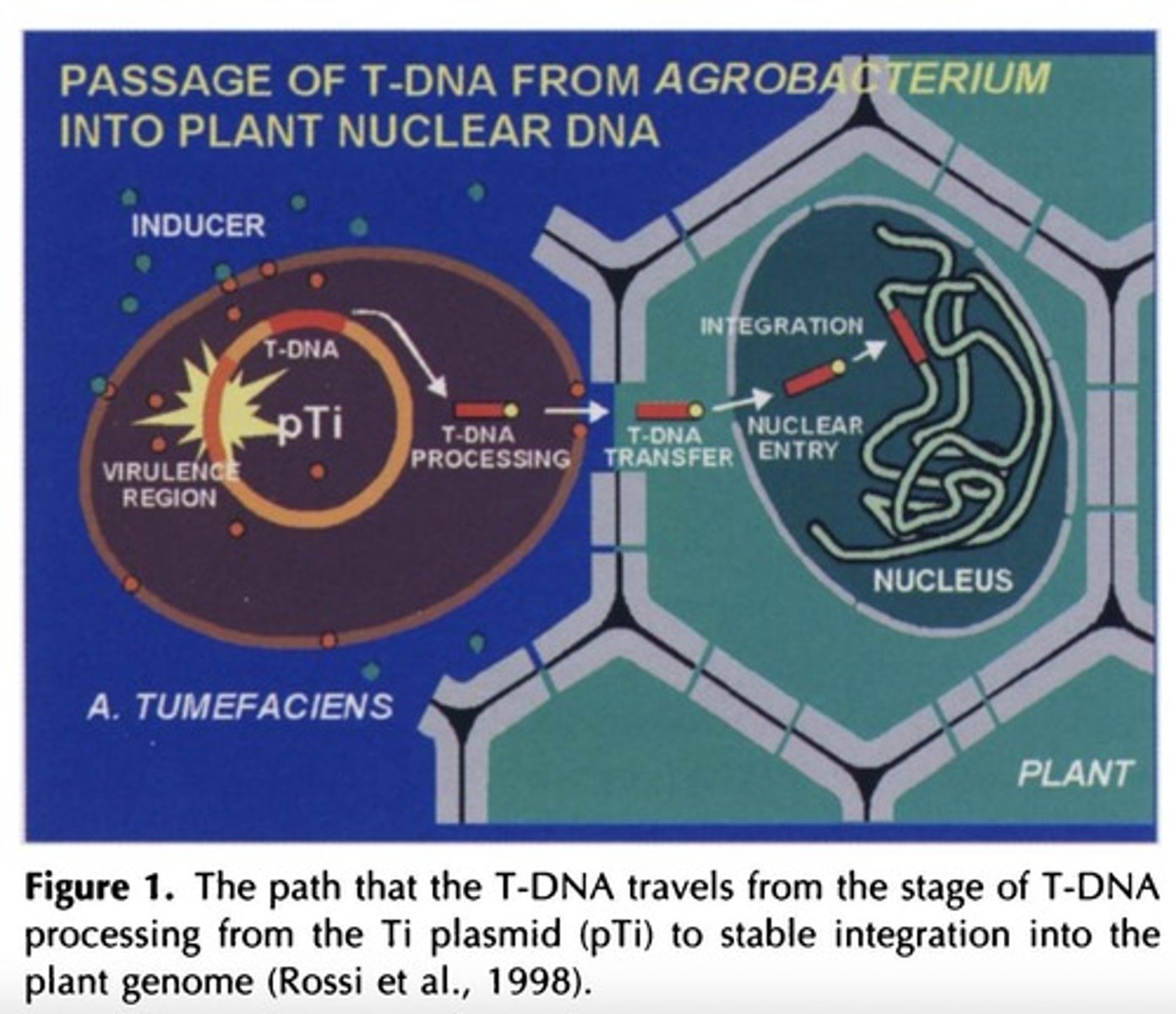
What are the three genetic components required for plant cell transformation using Ti plasmid?
1. T-DNA (mobile DNA element), 2. Virulence area (vir) with vir genes, 3. Border sequences (25 bp) in the Agrobacterium chromosome.
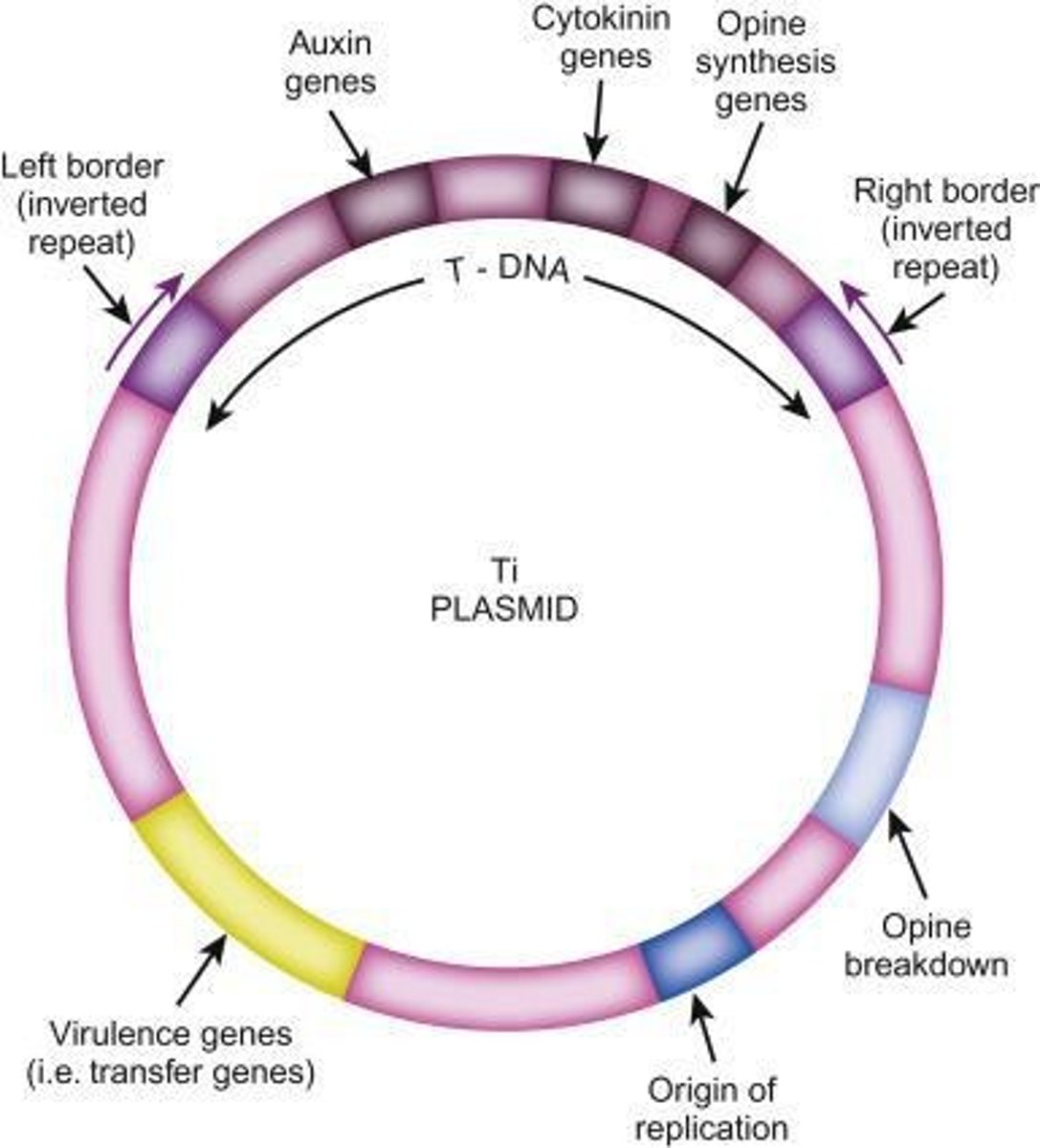
What does T-DNA stand for?
Transfer DNA.
What is transformation efficiency?
Transformation efficiency (TE) measures how successfully foreign DNA is introduced into competent cells, calculated as the number of transformants per microgram of DNA.
How is transformation efficiency calculated?
TE = Number of transformants / µg of DNA used, with units in CFU/µg DNA.
What is the significance of the virulence area in the Ti plasmid?
It contains vir genes that facilitate the transfer of T-DNA into plant cells.
What is the function of auxin and cytokinin genes in T-DNA?
They induce plant cells to grow.
What is the limitation of the Ti plasmid?
It is relatively large and typically only works in plants that can be infected by Agrobacterium tumefaciens; it cannot be used for monocot plants.
What happens to the T-DNA during Agrobacterium-mediated transformation?
The T-DNA is integrated into the plant nuclear genome.
What is the role of opine synthesis genes in T-DNA?
They provide a carbon source for Agrobacterium.
What occurs during the electro shock phase of transformation?
An electric current passes through membrane-porated cells, leading to biochemical reactions that facilitate DNA uptake.
What is a common application of electroporation in biotechnology?
It is used for gene transformation and reprogramming of genomes with foreign DNA.
What is the purpose of plating on media after transformation?
To recover and select for transformed cells.
What is the significance of maintaining cells in log phase before transformation?
Cells in log phase are at optimum health and functioning at their fullest potential.
What does the term 'competent cells' refer to?
Cells that are capable of taking up foreign DNA during transformation.
What is the impact of the electric pulse on cell membranes during electroporation?
It causes structural changes that increase membrane permeability.
What is the role of border sequences in T-DNA mobility?
They determine the mobility of T-DNA and are essential for its integration into the plant genome.
What is the outcome of successful Agrobacterium-mediated transformation?
The creation of a new plant that expresses traits from the introduced foreign DNA.
What is the primary use of calcium chloride in transformation procedures?
To prepare cells for DNA uptake by making them competent.
What is the relationship between the vir genes and T-DNA transfer?
Vir genes facilitate the transfer of T-DNA into the plant cell but do not enter the plant cell themselves.
What happens to the Ti plasmid during the transformation process?
It is modified to include foreign DNA before being reinserted into Agrobacterium for transformation.
Why is electroporation considered easier than alternate techniques?
It requires fewer steps and yields high frequencies of stable transformation and transient gene expression.
What is the formula to calculate transformation efficiency (TE)?
TE = Colonies on plate / µg of DNA plated
How do you calculate the amount of DNA plated?
µg DNA plated = µg DNA in reaction × (volume plated / total recovery volume)
If 10 ng of DNA is used and 100 µL is plated from a 1 mL recovery, how much DNA is plated?
0.001 µg
What is the transformation efficiency if 200 colonies are counted from 0.001 µg of DNA?
TE = 200 / 0.001 µg = 2 × 10^5 CFU/µg DNA
What is the expected transformation efficiency range for chemically competent cells?
10^3-10^6 CFU/µg
What factors affect transformation efficiency?
Purity and concentration of DNA, competency of cells, heat-shock/electroporation conditions, recovery time, and plating accuracy.
What is bacterial conjugation?
A process requiring cell-to-cell contact for DNA transfer from a donor to a recipient cell.
What structures mediate bacterial conjugation?
Cell surface pili or adhesins.
What is the role of the F plasmid in bacterial conjugation?
It allows the donor bacterium to produce a pilus for contact with the recipient.
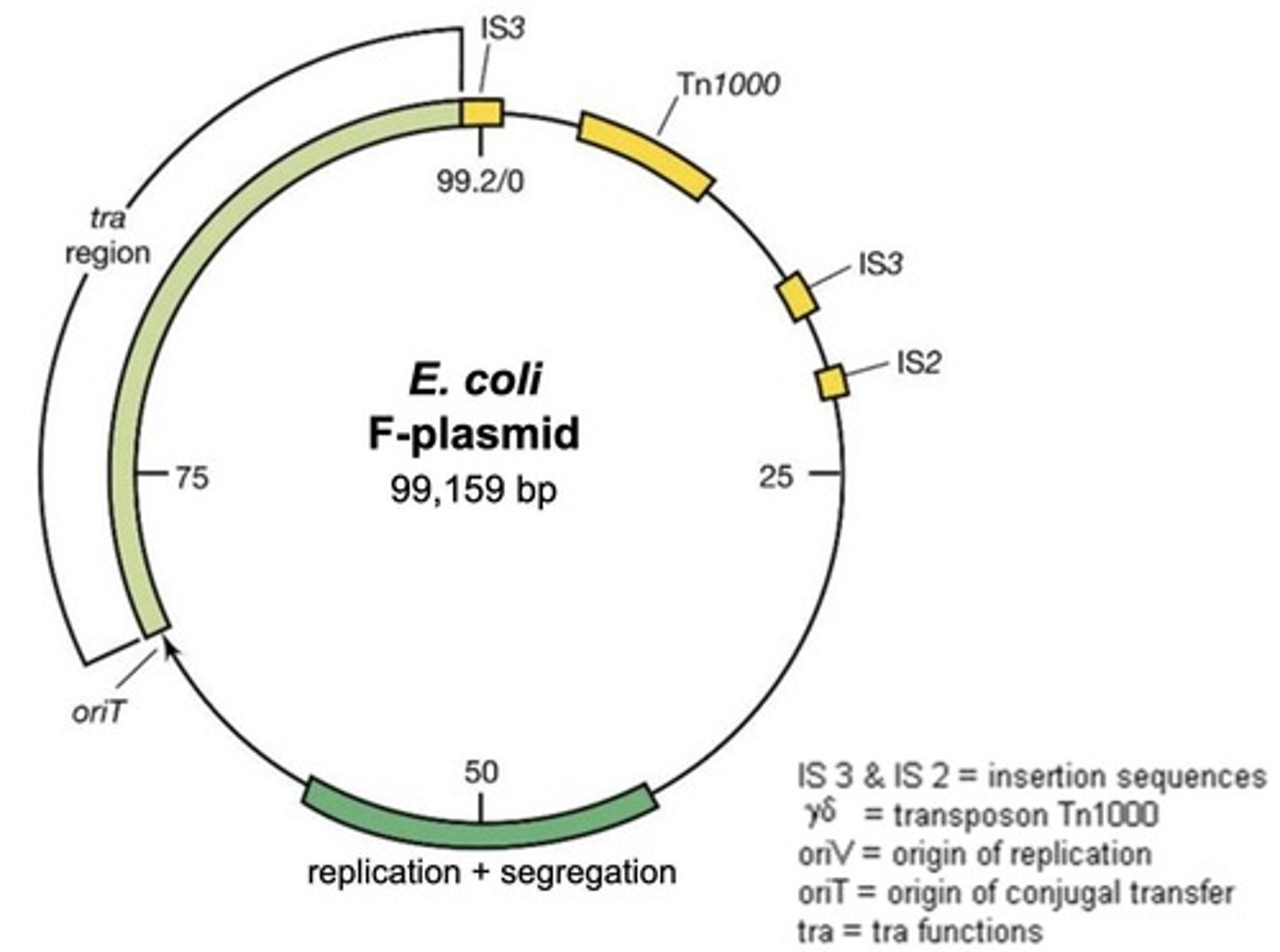
What does F+ and F- indicate in bacterial conjugation?
F+ indicates a donor with an F plasmid; F- indicates a recipient without an F plasmid.
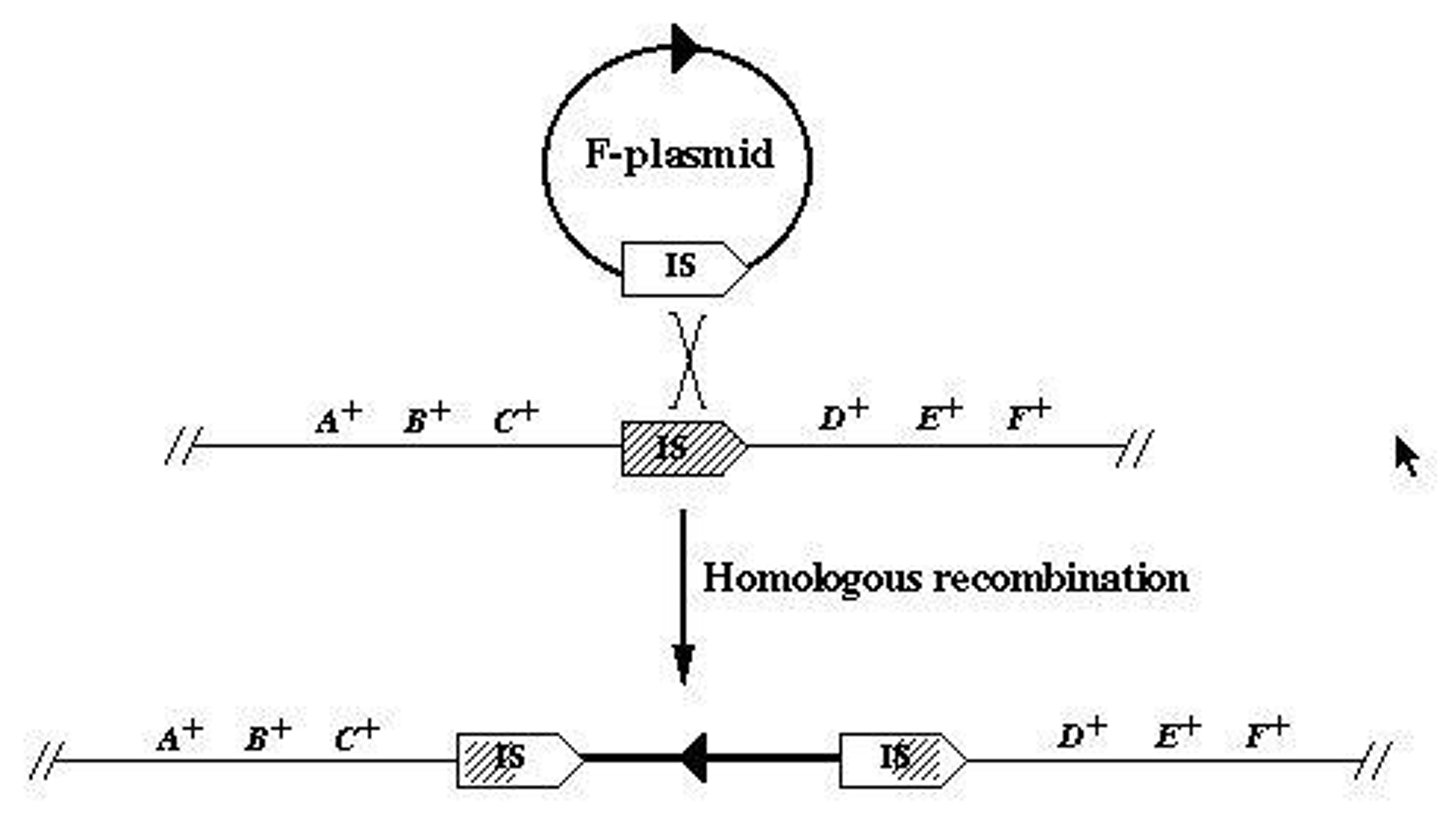
What is an Hfr strain?
A strain where the F plasmid is integrated into the bacterial genome, allowing frequent transfer of chromosomal DNA.
What is an F' plasmid?
An F plasmid that carries some chromosomal DNA along with the F factor.
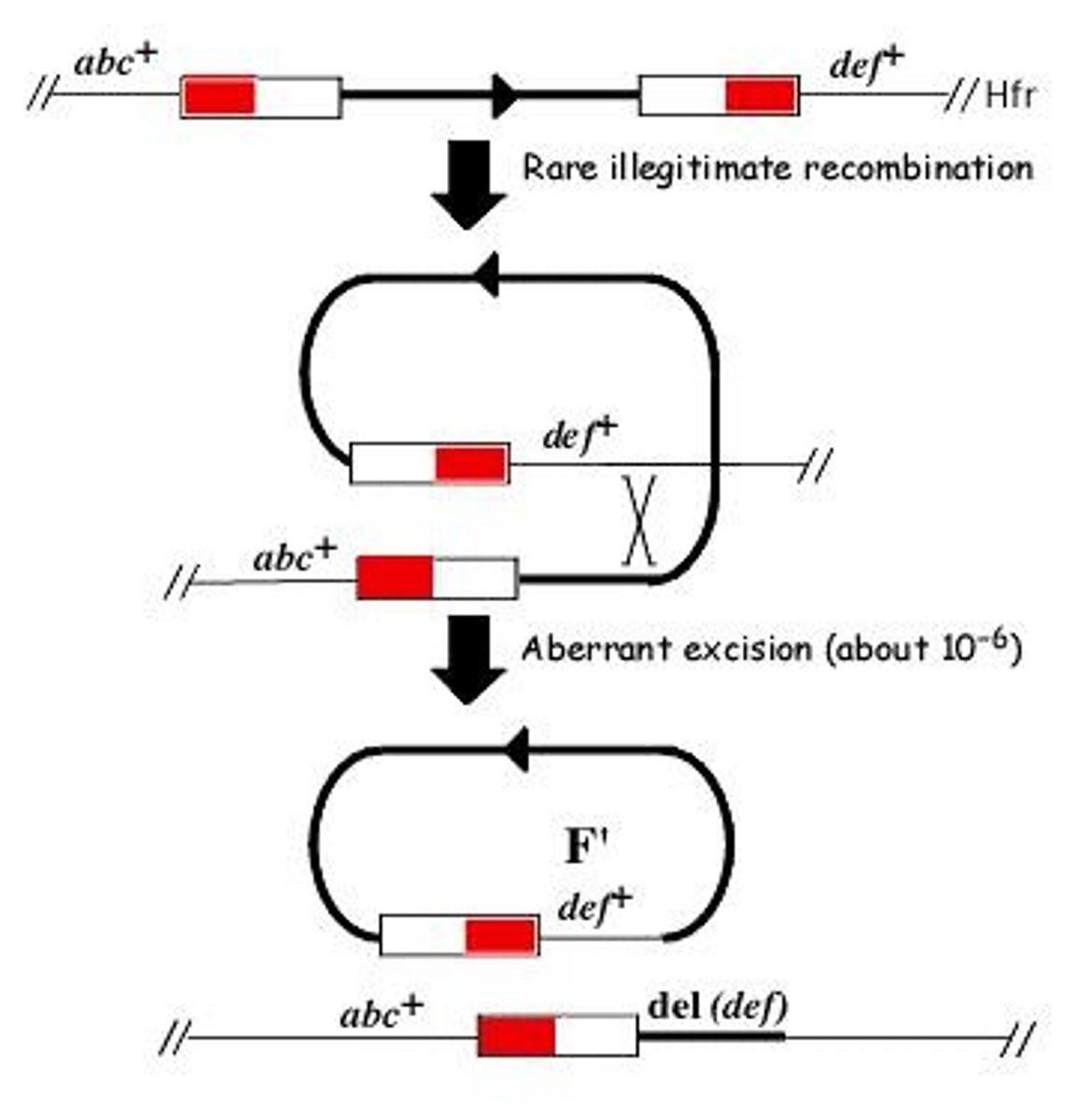
How does an F' plasmid form?
Through illegitimate recombination during the excision of the F plasmid from an Hfr strain.
What is the significance of OriT in the F plasmid?
It is the origin of transfer where conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA is initiated.
What is the function of the tra-region in the F plasmid?
It allows the transfer of genes from one cell to another.
What are insertion sequences (IS) in the context of plasmids?
Mobile DNA elements that can transpose and cause genome rearrangements.
What happens during the formation of Hfr strains?
Homologous recombination occurs between an IS element on the F-plasmid and the same element on the host chromosome.
What is the expected transformation efficiency range for electrocompetent cells?
10^9-10^10 CFU/µg
How is the effective amount of DNA calculated if there is a 50% loss during mixing?
Effective DNA = total DNA × (1 - loss percentage)
What is the transformation efficiency if 75 colonies appear from 0.01125 µg of DNA?
TE ≈ 6666.67 CFU/µg
What is the importance of recovery time in transformation efficiency?
Cells need time to express antibiotic resistance before plating.
What is the role of antibiotic concentration in plating accuracy?
Errors can distort colony counts or kill unwanted cells.
What is the difference between F+ and Hfr strains?
F+ has an F plasmid independent of the genome; Hfr has the F plasmid integrated into the genome.
What is a merodiploid?
A partial diploid created when an F' plasmid carries chromosomal genes.
What is the significance of the tra-region in the F plasmid?
It encodes the genes necessary for the transfer of the plasmid during conjugation.
What is the consequence of improper heat-shock or electroporation conditions?
It can kill cells or reduce DNA uptake.
What is the role of the F-plasmid in bacterial conjugation?
The F-plasmid facilitates the transfer of chromosomal genes from an Hfr donor to a recipient.
What happens if the mating time is limited to 30 minutes?
Distal genes cannot be transferred via the Hfr.
What are F-primes?
F-primes are plasmids that can transfer chromosomal genes to a recipient in a short time.
What is required for the transfer of chromosomal markers into a recA-recipient?
Homologous recombination is necessary for the transfer.
How do F-primes behave in a recA recipient?
F-primes circularize after transfer and replicate independently, allowing donor markers to be maintained.
What is the function of the F-encoded sex pilus?
It establishes contact between donor and recipient cells and retracts to bring them closer.
What is the process of DNA mobilization during conjugation?
Plasmid DNA is nicked at a specific site, and a single strand is transferred to the recipient cell.
What are cis-regulatory sequences?
They control gene expression by recruiting transcription factors to specific DNA sequences.
What are the two main types of transduction?
Generalized transduction and specialized transduction.
What is generalized transduction?
It is the transfer of random bacterial DNA by lytic phages.
Who discovered transduction?
Joshua Lederberg in 1952.
What is the difference between lytic and lysogenic cycles?
In the lytic cycle, the virus destroys the host cell; in the lysogenic cycle, the virus integrates into the host DNA.
What is a prophage?
A bacteriophage genome integrated into the bacterial chromosome or existing as an extrachromosomal plasmid.
What occurs during the attachment phase of the lytic cycle?
Phage proteins bind to specific receptors on the bacterial cell surface.
What happens during the entry phase of the lytic cycle?
The phage injects its double-stranded DNA genome into the bacterium's cytoplasm.
What is the outcome of the lytic cycle?
The host cell bursts, releasing new phage particles.
What is the frequency of generalized transduction?
It is a rare event, with only a small percentage of phage particles carrying donor DNA.
What is the significance of pac sites in generalized transduction?
Pac sites help phages recognize their own DNA for packaging during transduction.
What is the role of the mating pair formation (Mpf) system?
It functions as a secretion machinery for intercellular DNA transfer during bacterial conjugation.
What is the result of faulty excision in specialized transduction?
It leads to the transfer of specific genes near the prophage site.
What is the role of bacteriophages in transduction?
Bacteriophages carry and introduce genetic material from donor to recipient cells.
What is the difference in the range of genes transferred in generalized vs specialized transduction?
Generalized transduction can transfer any gene, while specialized transduction transfers a narrow, specific range.
What is the process of replacement DNA strand synthesis during conjugation?
It occurs concurrently in both the donor (leading strand) and recipient (lagging strand) cells.
What is the significance of counterselection during mating?
It prevents the presence of donor cells during the transfer process.
What is the outcome for both donor and recipient after mating?
Both contain the conjugal plasmid after the mating pair separates.
How does generalized transduction occur?
Phage DNA enters E. coli, replicates, and some bacterial DNA enters the phage capsid, which then infects recipient bacteria.
What is the role of prophage in specialized transduction?
It incorporates viral DNA into bacterial DNA and can later transfer bacterial genes during viral replication.