GI Imaging MIDI Mod 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Air fluid levels due to small bowel obstruction (SBO)

Intramural air because of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
ABCDEs of reading abdominal radiograph
- Air in correct places
- Bones
- Calcifications
- Dilations
- Extraluminal free air/extra stuff
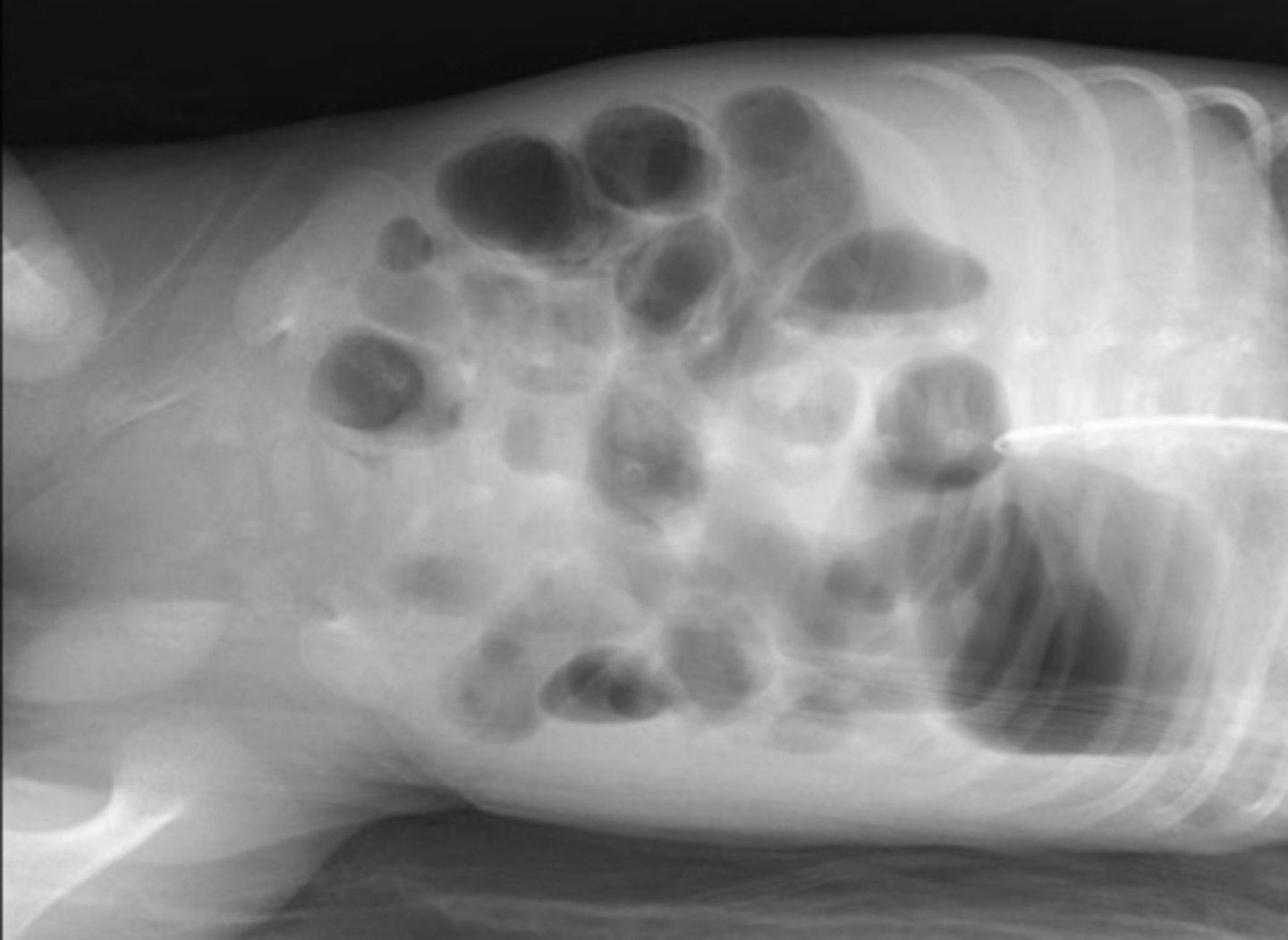
dilated loops of bowel
bowel filled with air or fluid beyond their normal size
in the small bowel, air is usually present in ___-____ loops on non-dilated small bowel. Normal diameter is <____cm
2-3, 2.5
in large bowel, there's almost always air in rectum/sigmoid colon. normal diameter is <____cm
6
3-6-9 rule for normal bowel diameter
- small bowel <3cm
- large bowel <6cm
- cecum <9cm
is a small or large bowel obstruction MC?
small bowel
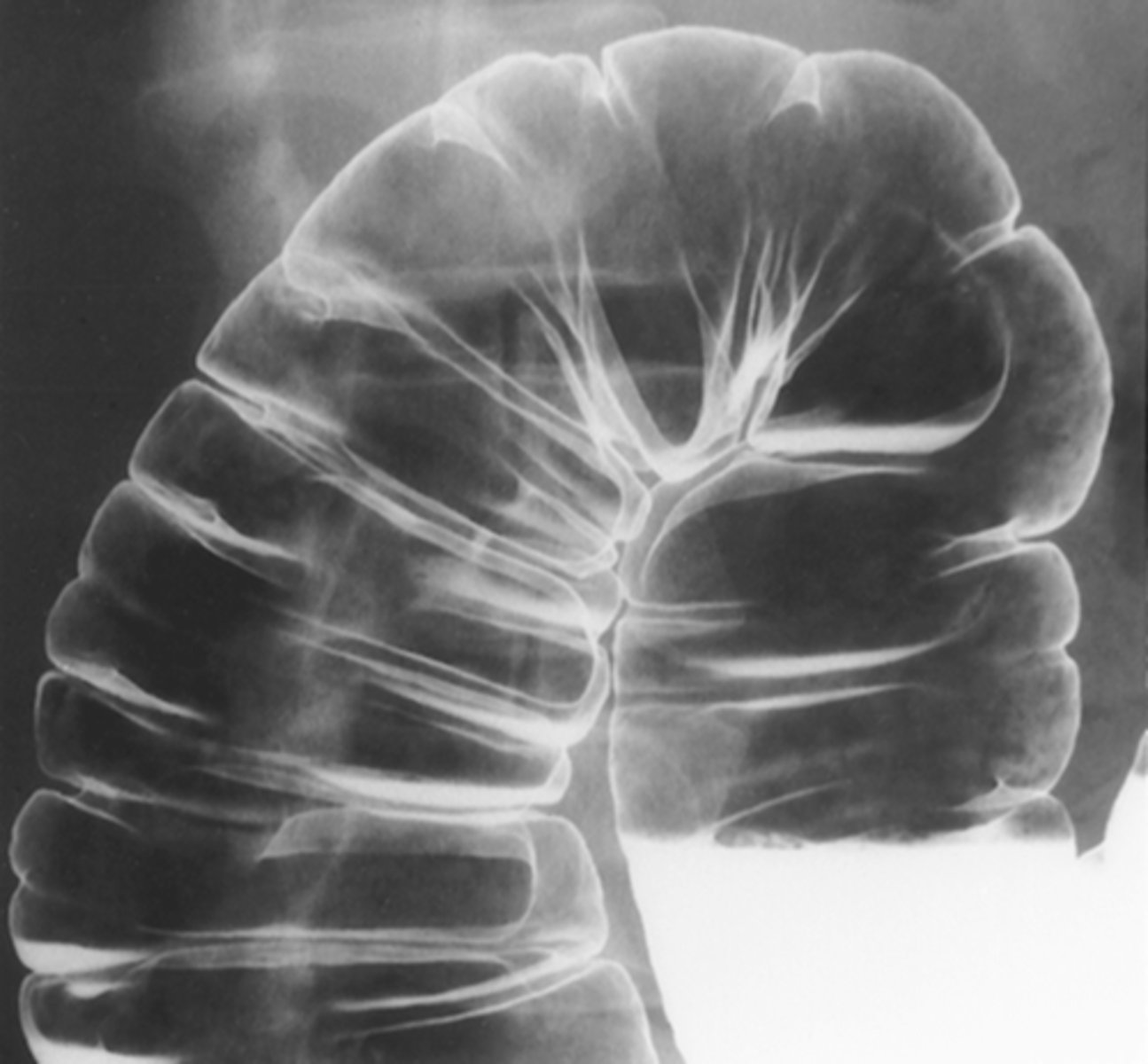
valvulae connivente
thin, circumferential folds that extend across entire lumen of small bowel. Increased number in jejunum, appears like a stack of coins
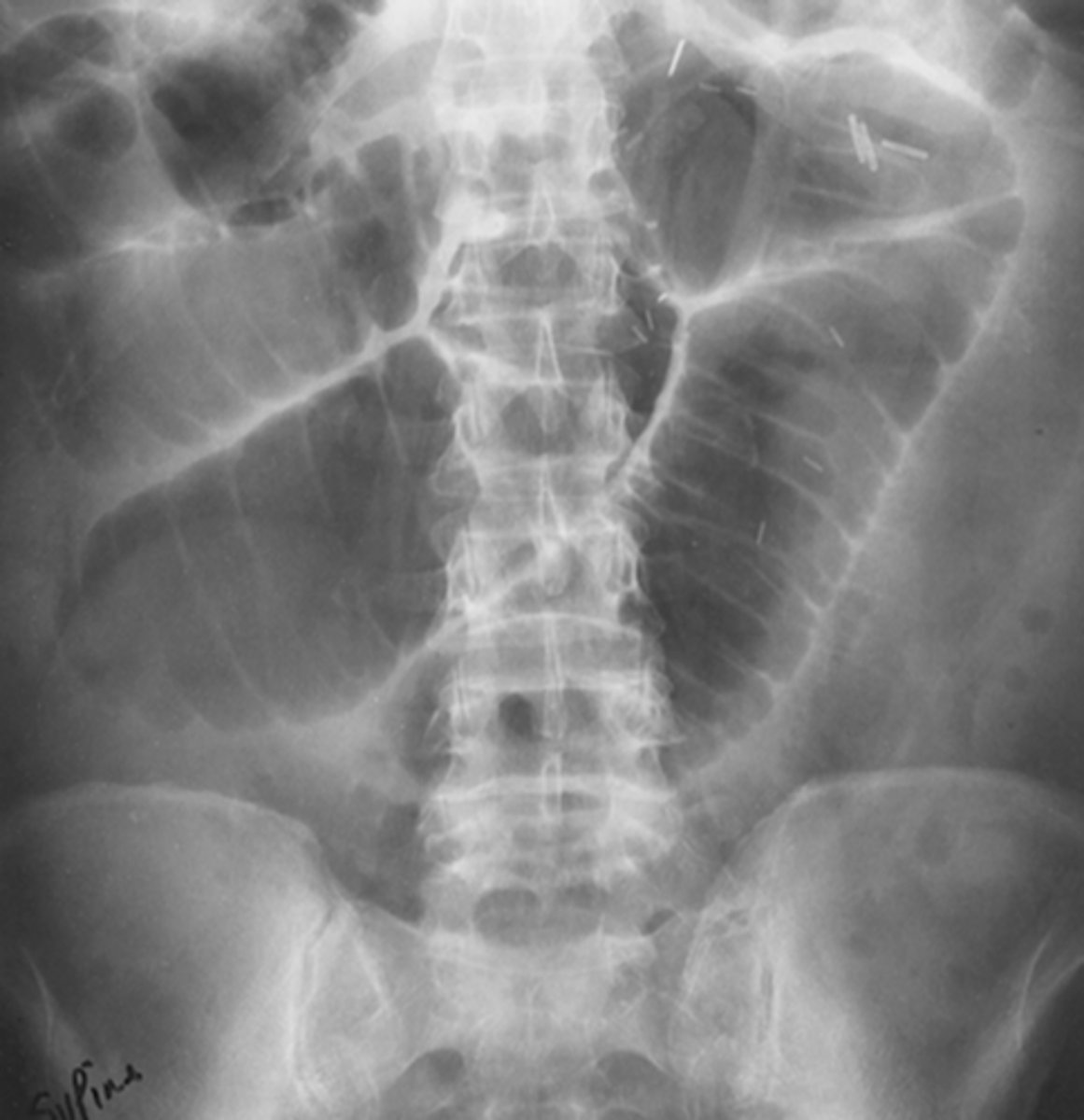
haustral folds
thick, transverse, non-circumferential folds in large bowel with baggy appearance
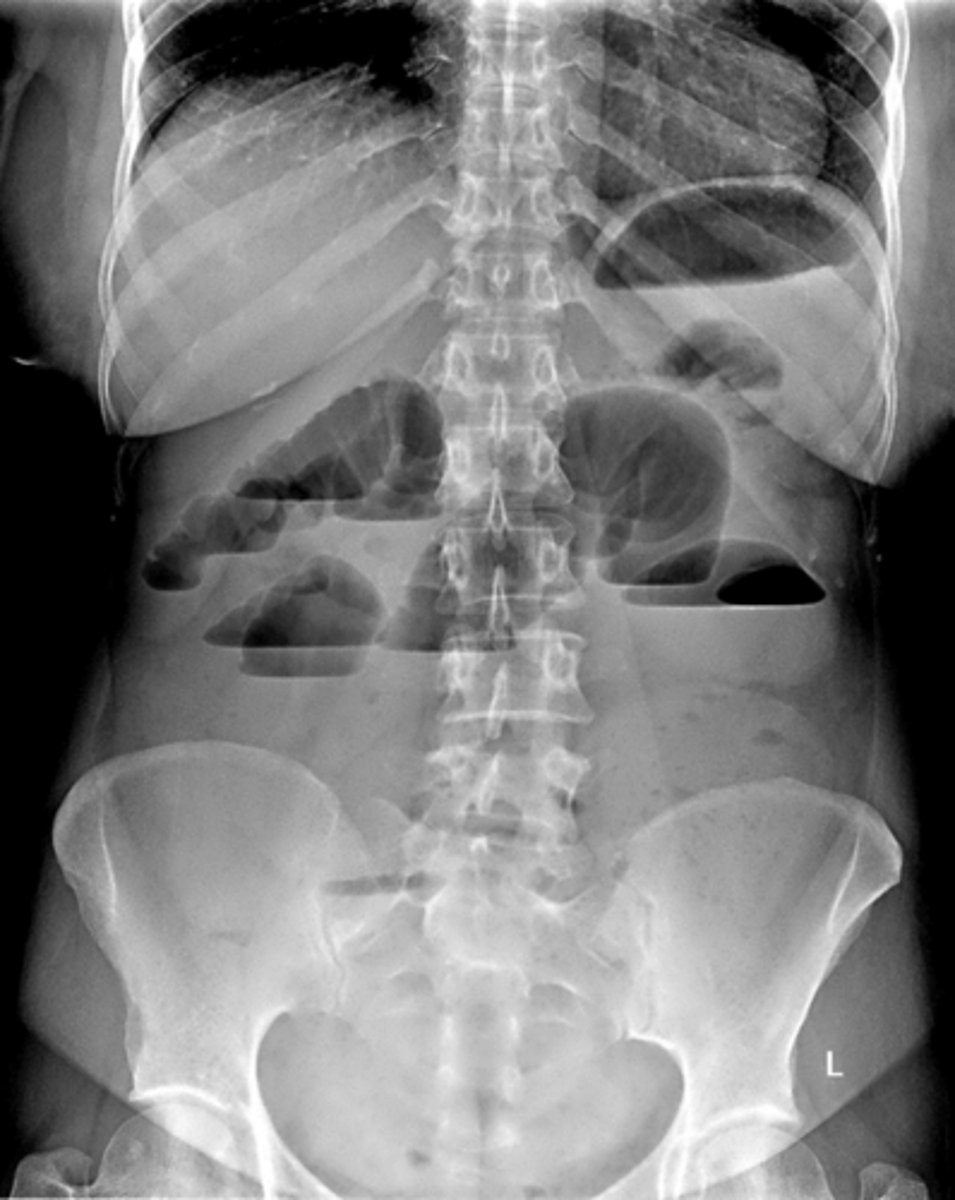
____ bowel has 2-3 air/fluid levels present normally in upright/lateral decubitus view. _____ bowel has no or a few air/fluid levels present on upright XR
small, large
air fluid levels
caused by intestinal obstruction, prevents flow of fluids and gas, appears like a turtle shell
bowel dilation
caused by mechanical obstruction or impaired bowel motility, looks like a slinky
loops ____ to obstruction become dilated with air and fluid. Loops ____ to obstruction become decompressed as their contents are evacuated
proximal, distal
most dilated loop of GI obstruction
- ones with largest resting diameter (cecum)
- loops just proximal to obstruction
MC cause of colon obstruction?
masses (colon CA)
Potential etiologies of colon obstruction
- masses (colon CA)
- diverticular disease (narrowing or stricture)
- volvulus
- intraabdominal adhesions
types of bowel obstruction
- mechanical: physical blockage of colon (colon CA, diverticular dx, volvulus)
- non-mechanical/functional: due to lack of normal m contractions (paralytic ileus, intestinal pseudo-obstruction, narcotic-induced ileus)
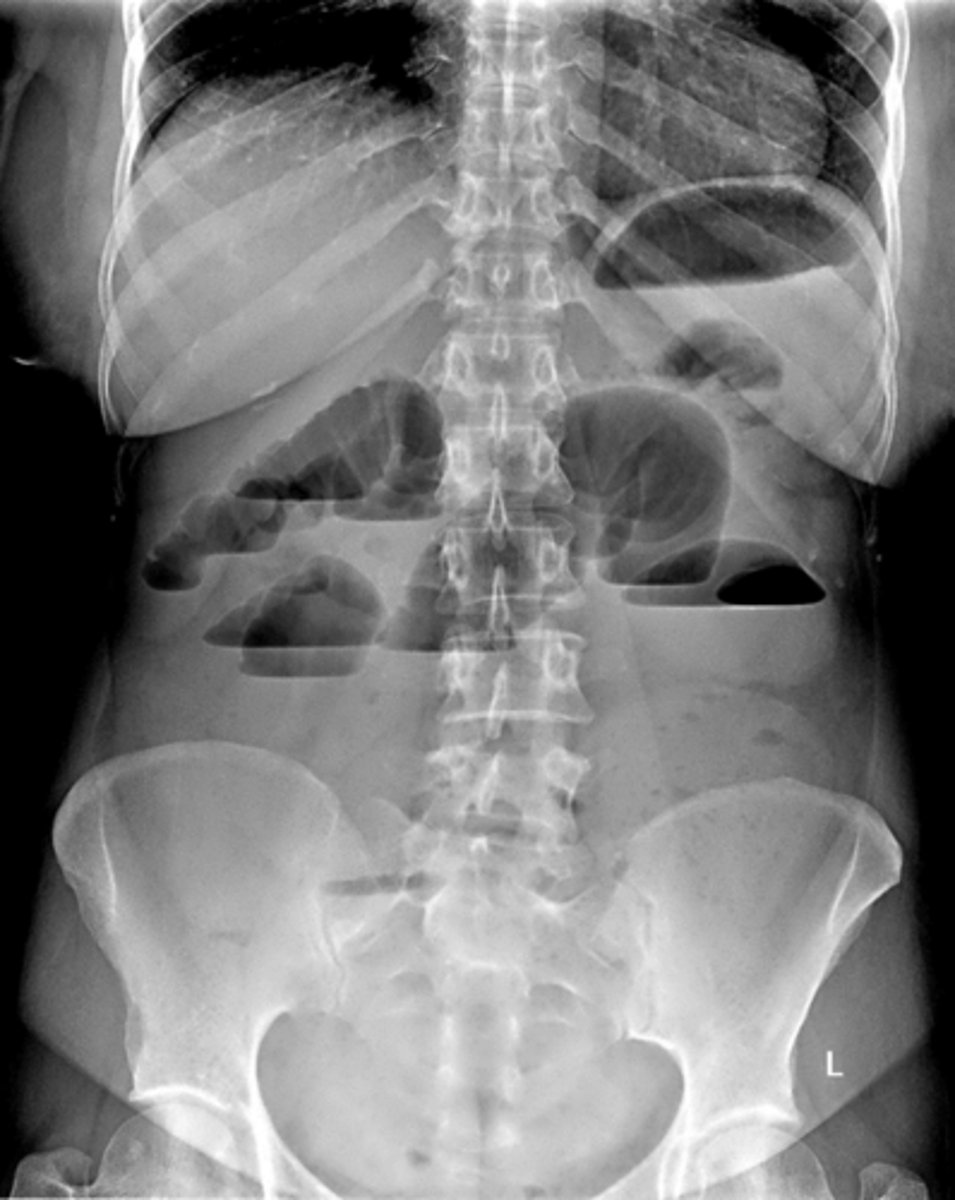
dilated loops of bowel air fluid levels
dilated loops of bowel
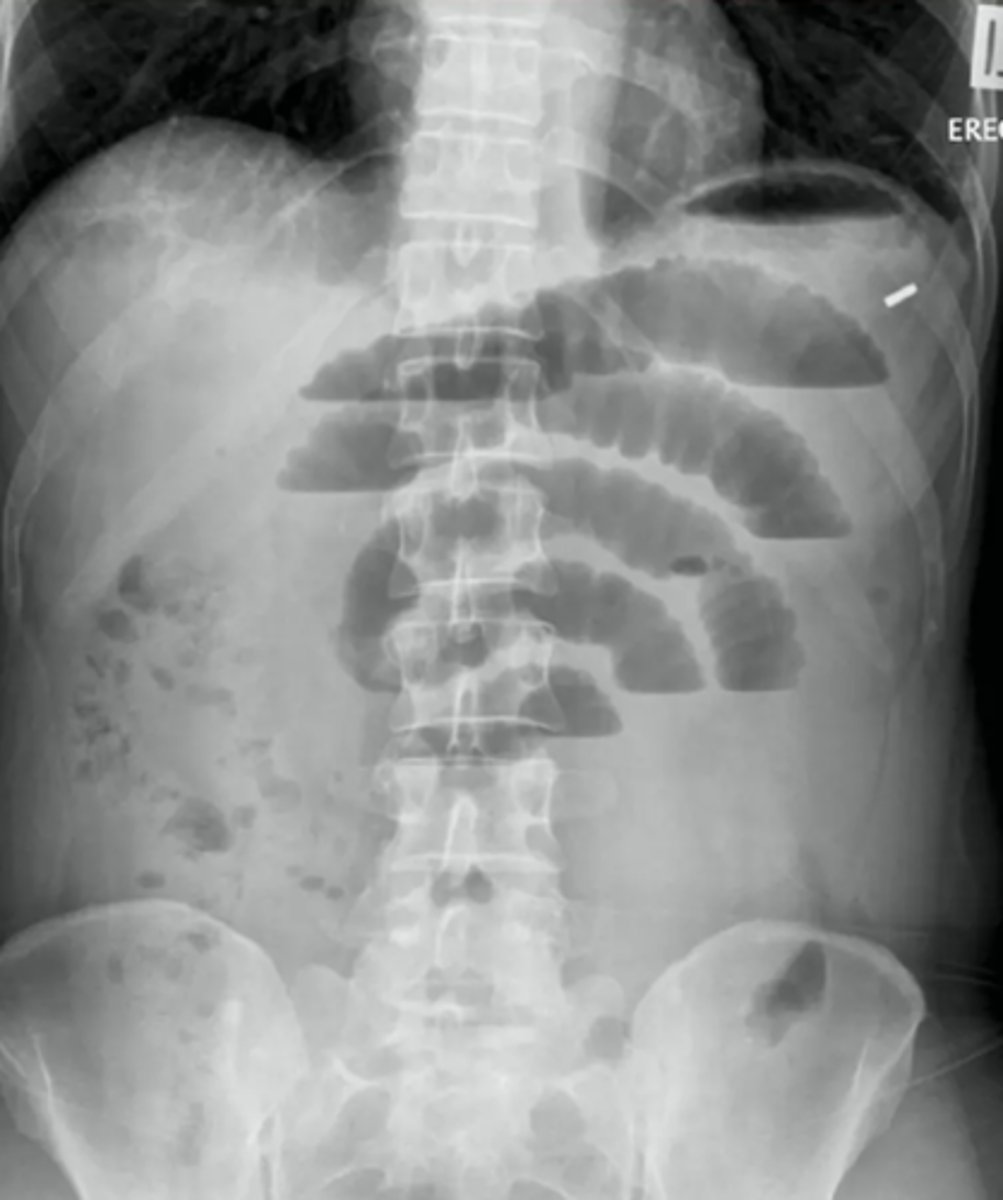
small bowel obstruction usually starts in the ______
LUQ
causes of SBO
post-operative adhesions, malignancy, hernias, gallstone ileus, intussusception, IBD
string of pearls sign- diagnostic of mechanical obstruction
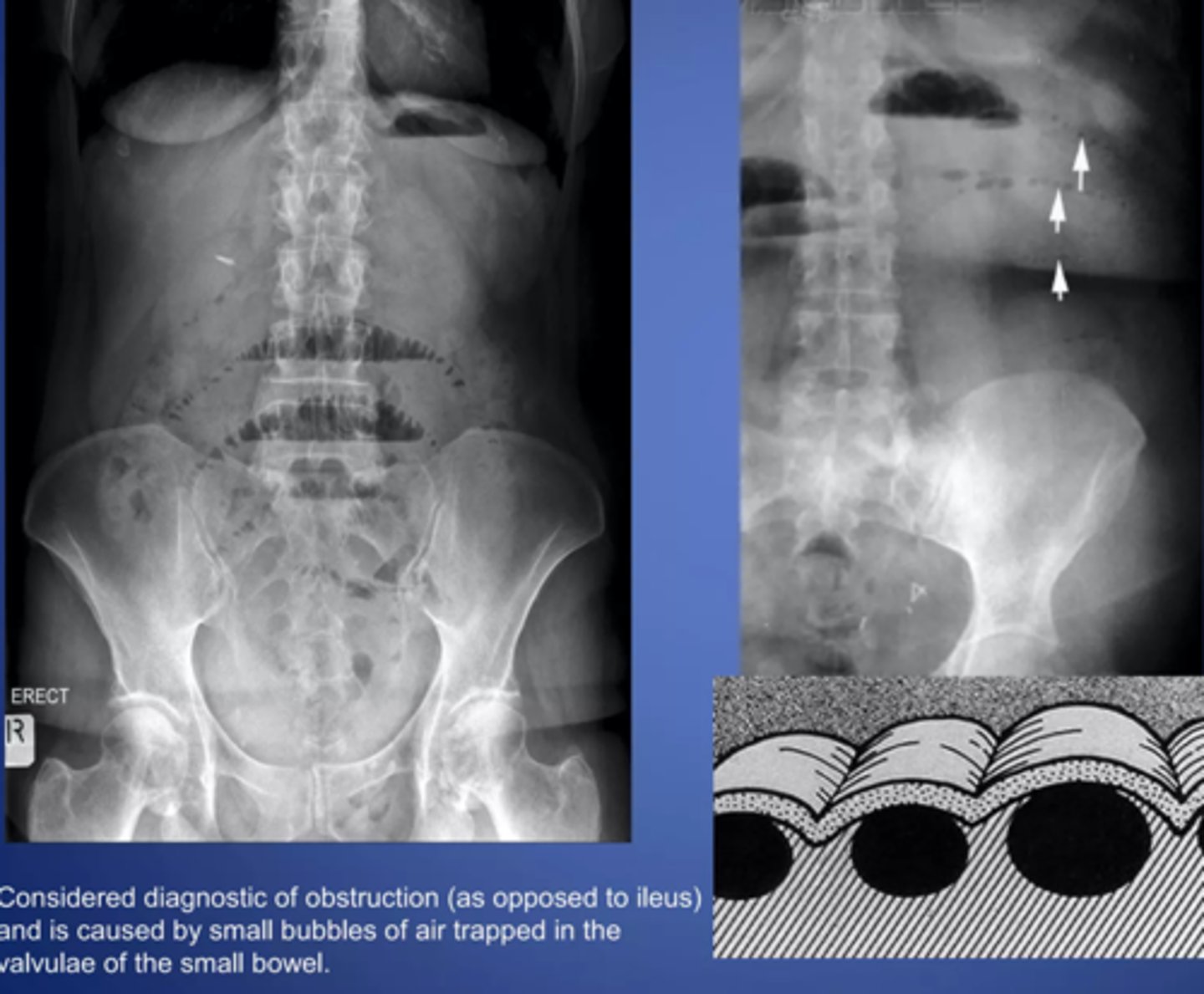
stretch sign- small pockets of gas trapped bn valvulae conniventes within fluid filled bowel
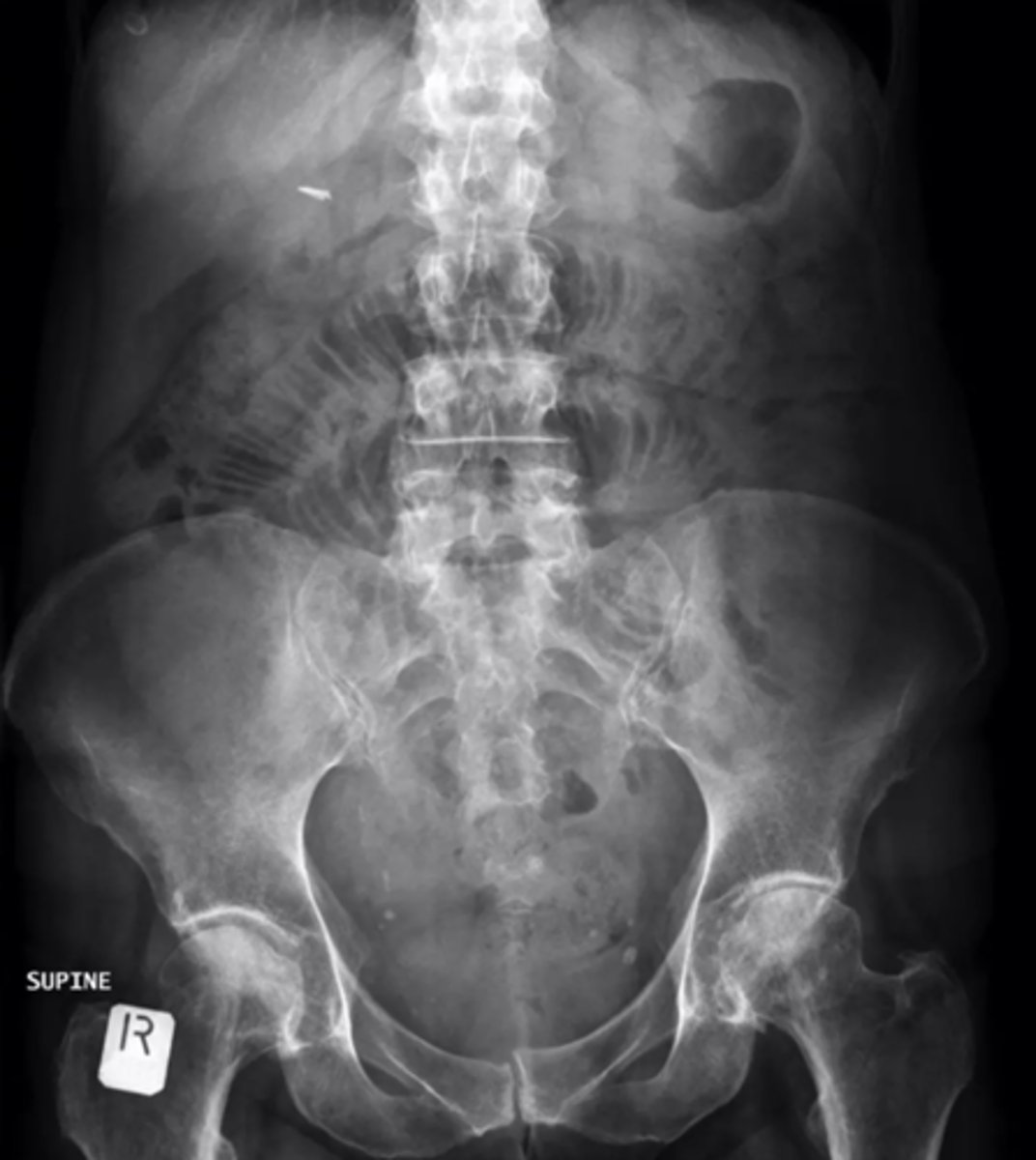
Large bowel obstruction
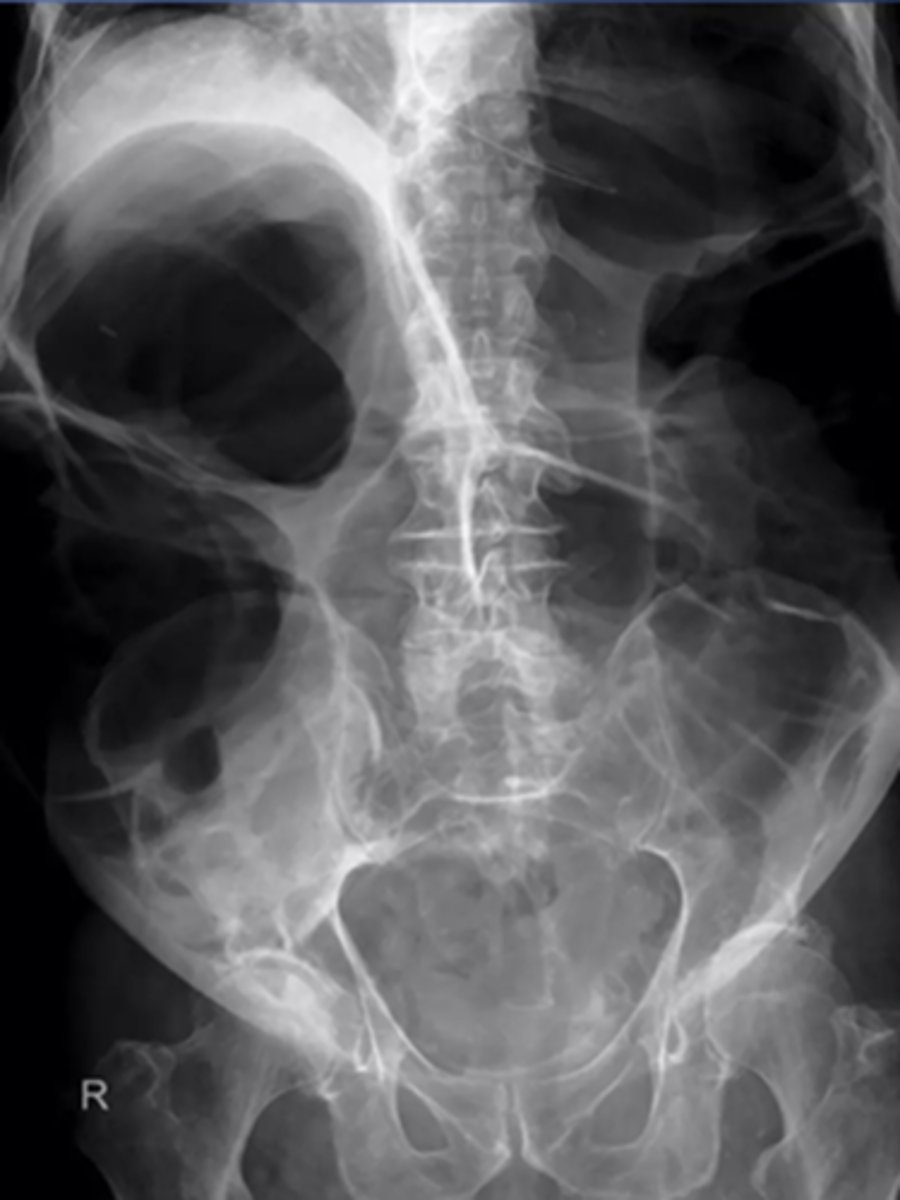
MC areas of LBO
cecum, hepatic/splenic flexures, sigmoid colon, upper portion of the rectum
T or F: signs and sxs of LBOs develop more slowly than SBOs
T
_____ valve determines the radiographic appearance of LBOs
ileocecal
competent ileocecal valve (closed loop)
gas and feces can't reflux into small bowel, pressure builds up only in colon
incompetent ileocecal valve (open loop)
gas and fluid reflux backward into small bowel
MC cause of LBO?
tumor
is perforation of a hollow viscus structure a medical emergency
yes
extraluminal air will rise to the highest part of the abdomen which is under the
diaphragm
crescentic lucency (extraluminal air)
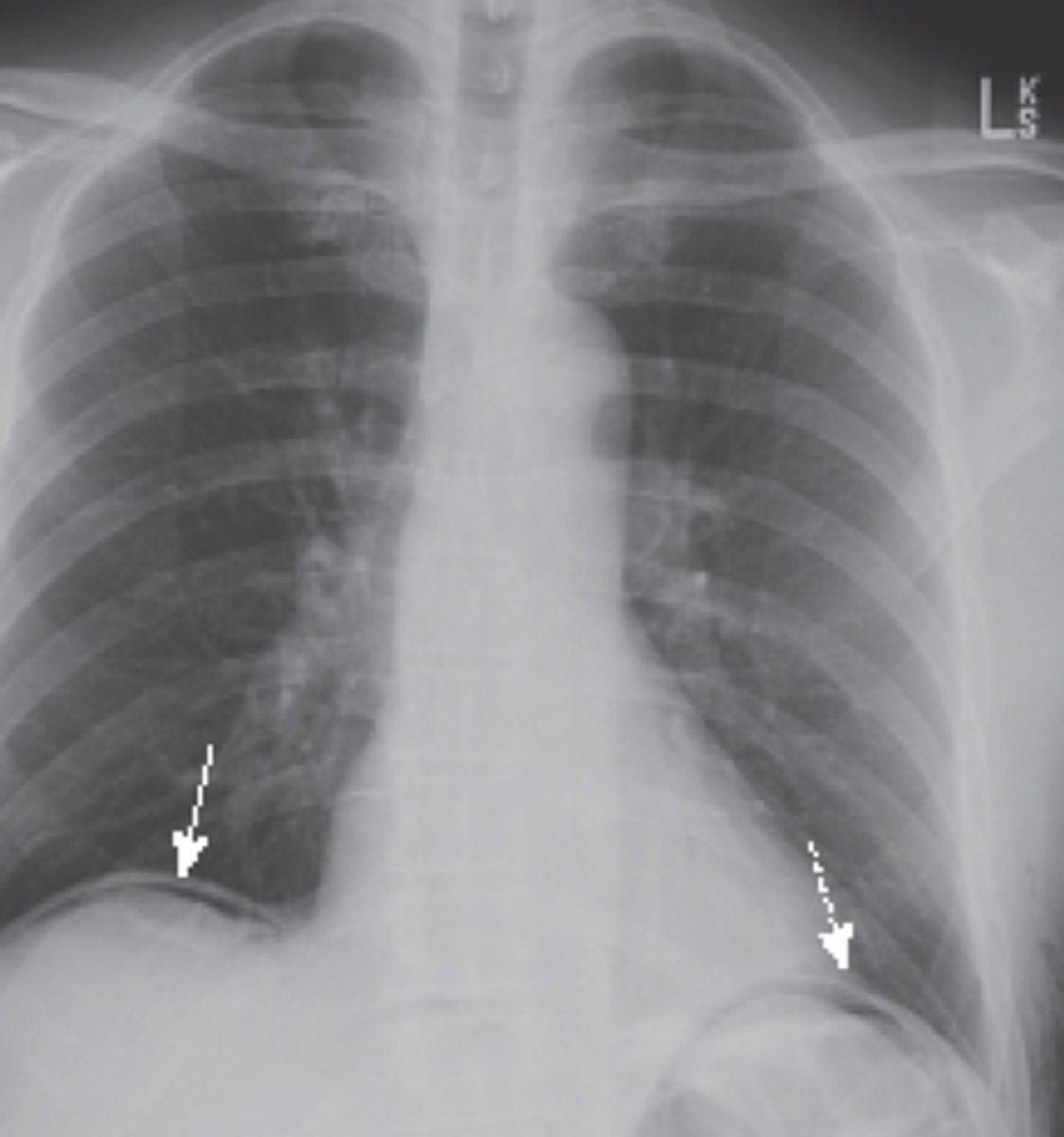
types of extraluminal air
pneumoperitoneum, retroperitoneal free air, air in bowel wall, air in biliary system
pneumoperitoneum
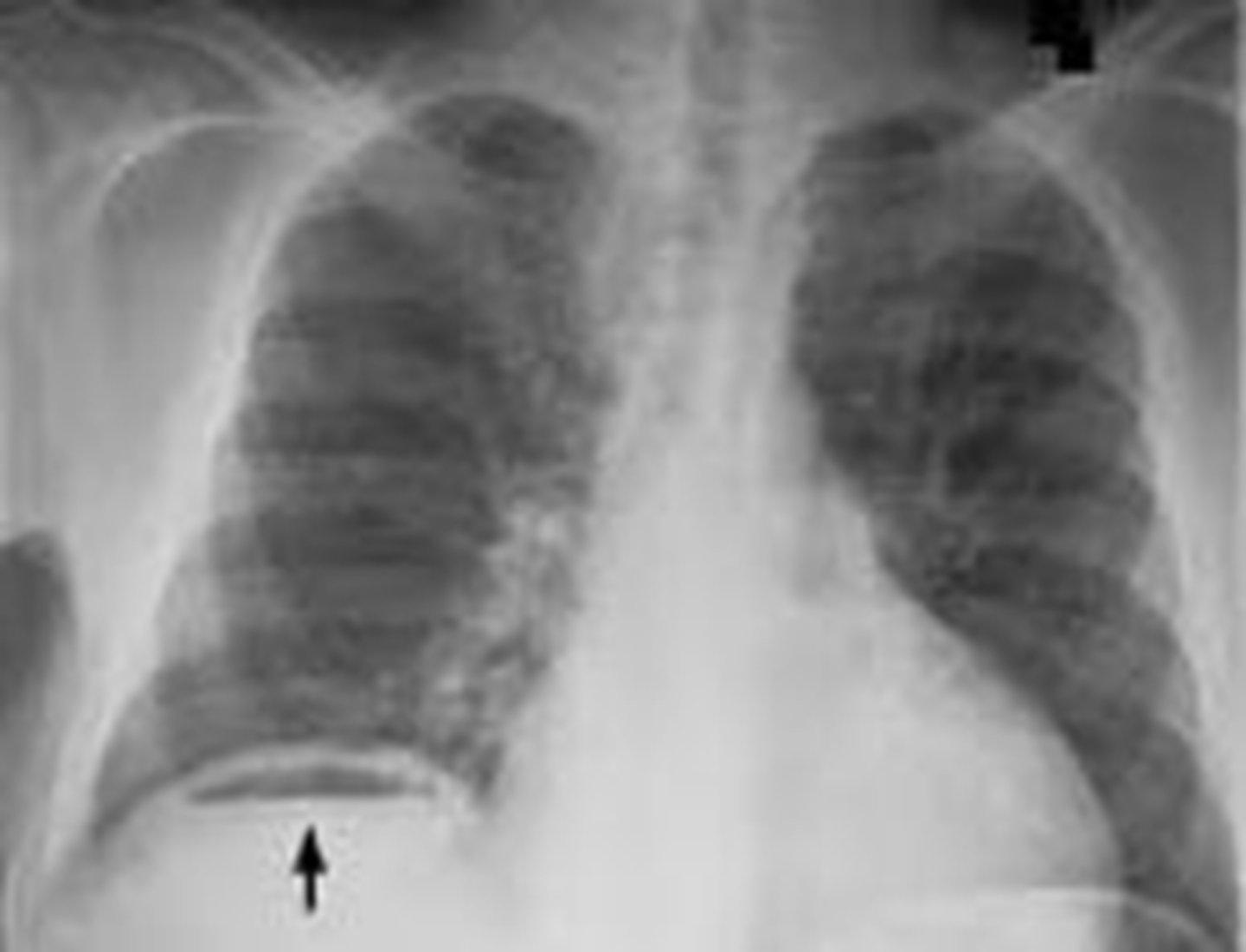
retroperitoneal free air
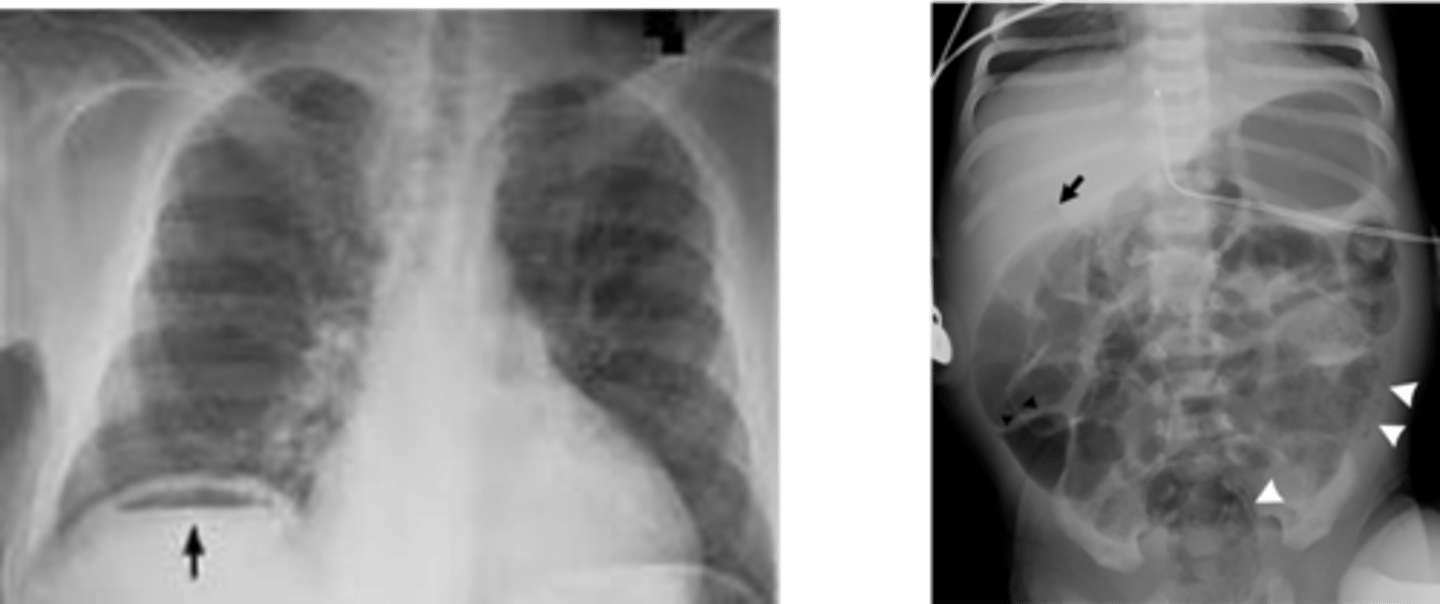
air in bowel wall
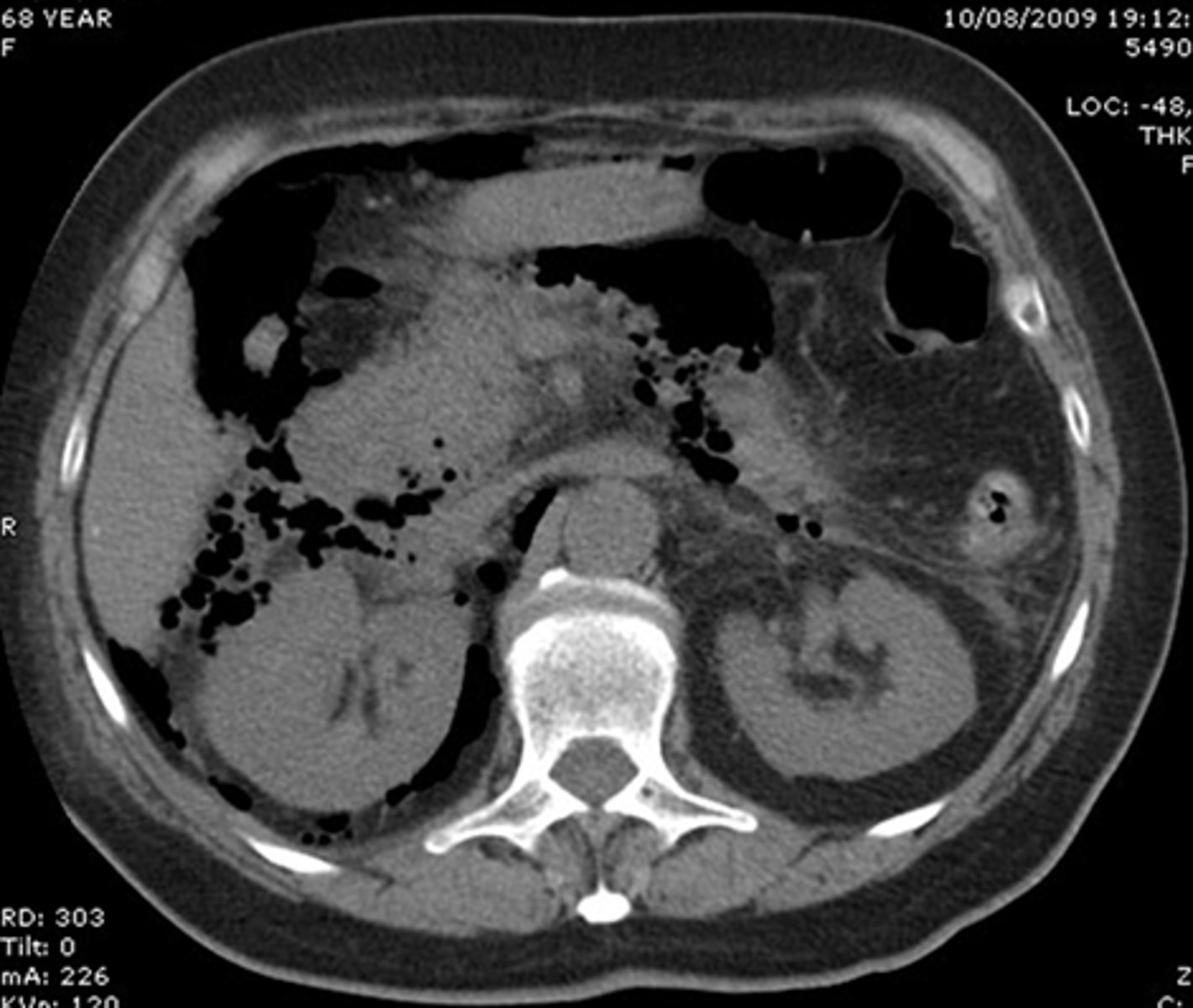
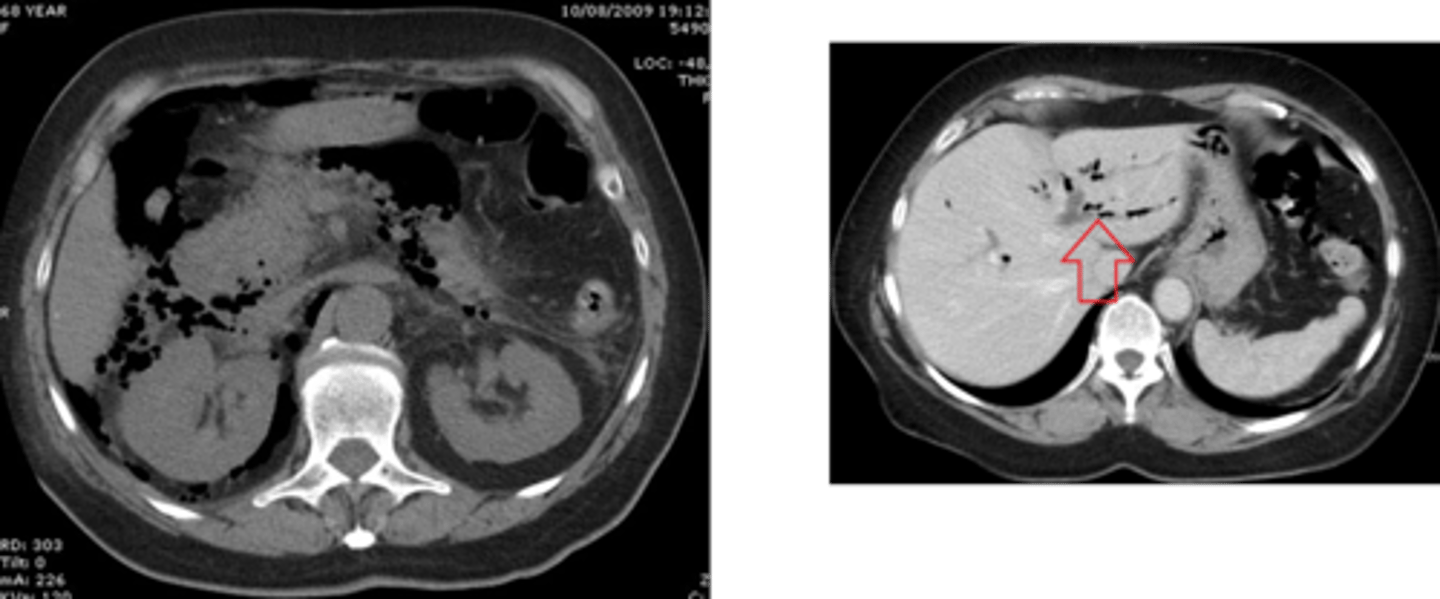
air in biliary system
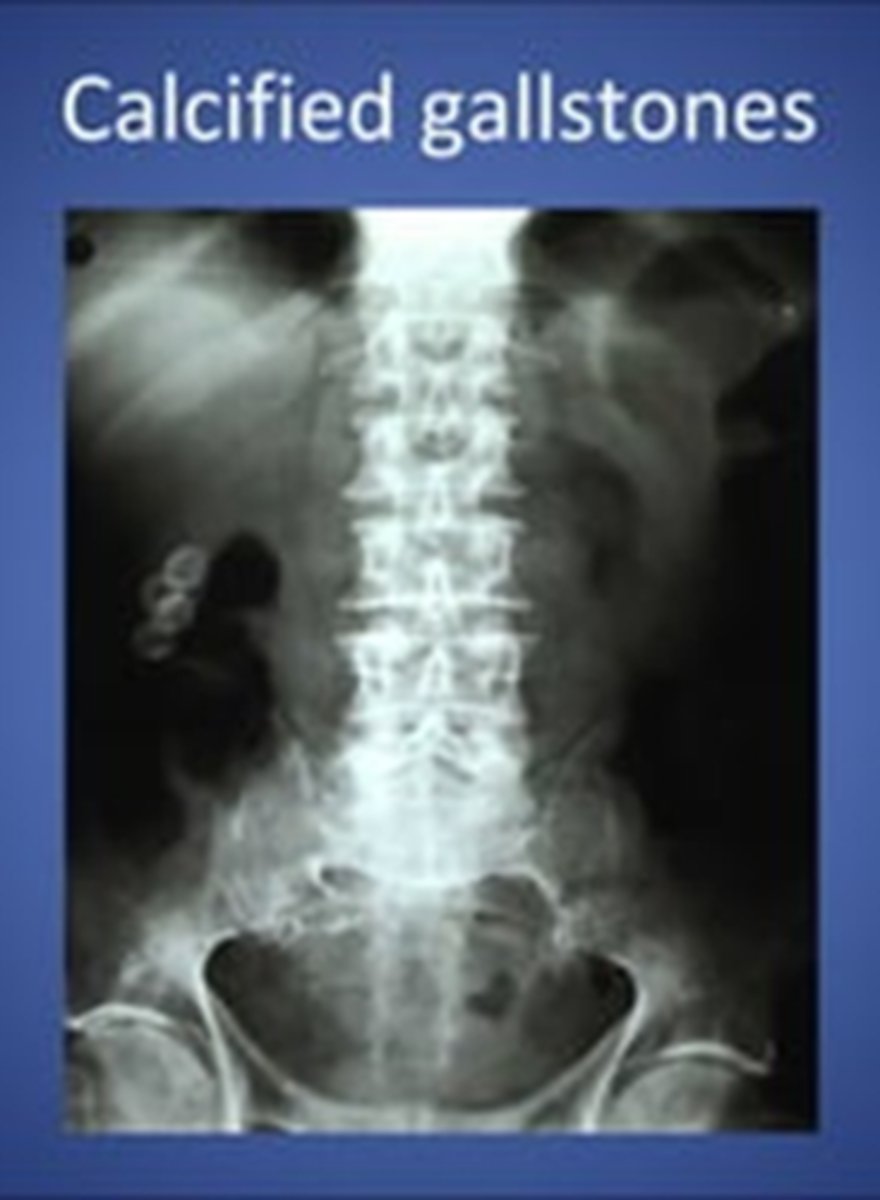
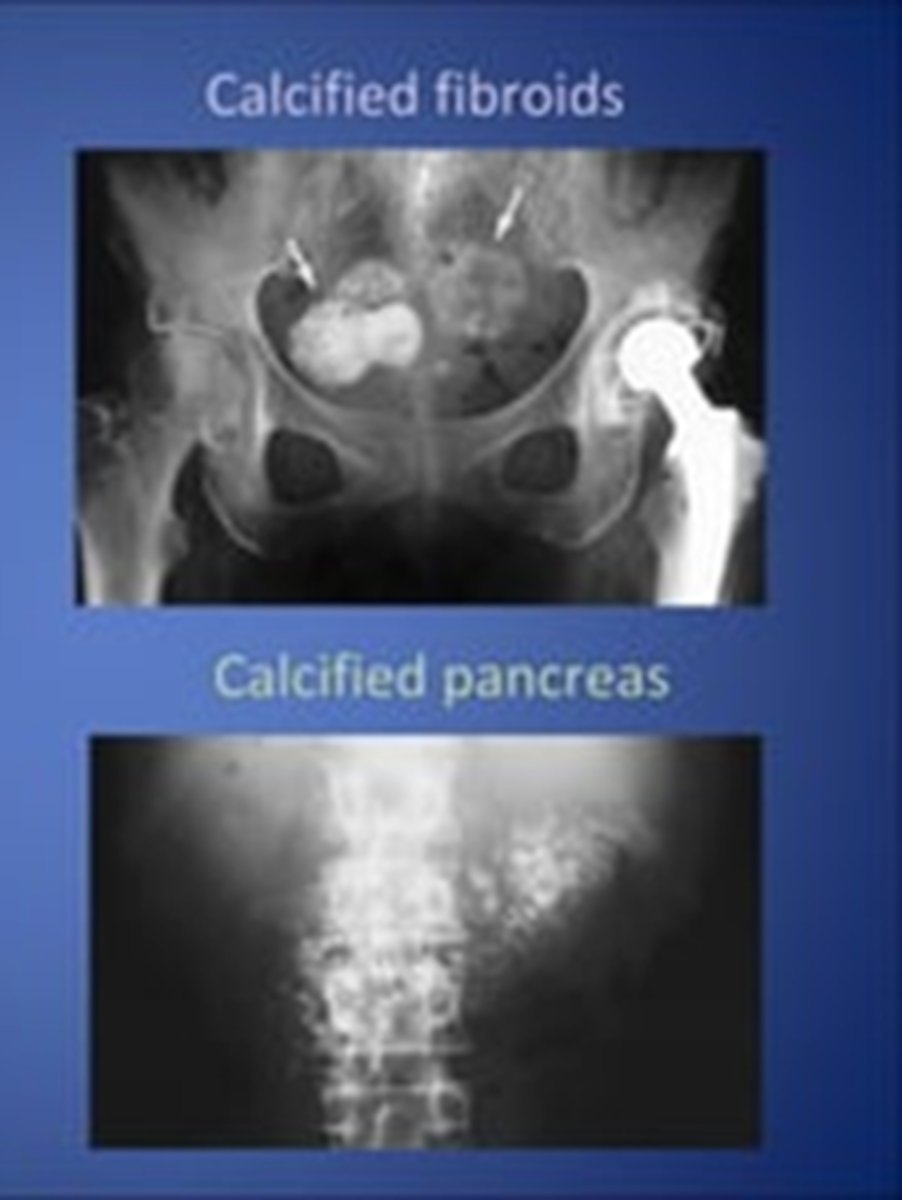
etiology of most calcifications can be determined by evaluatin
anatomic location, pattern of calcification
Lamellar "laminated" pattern
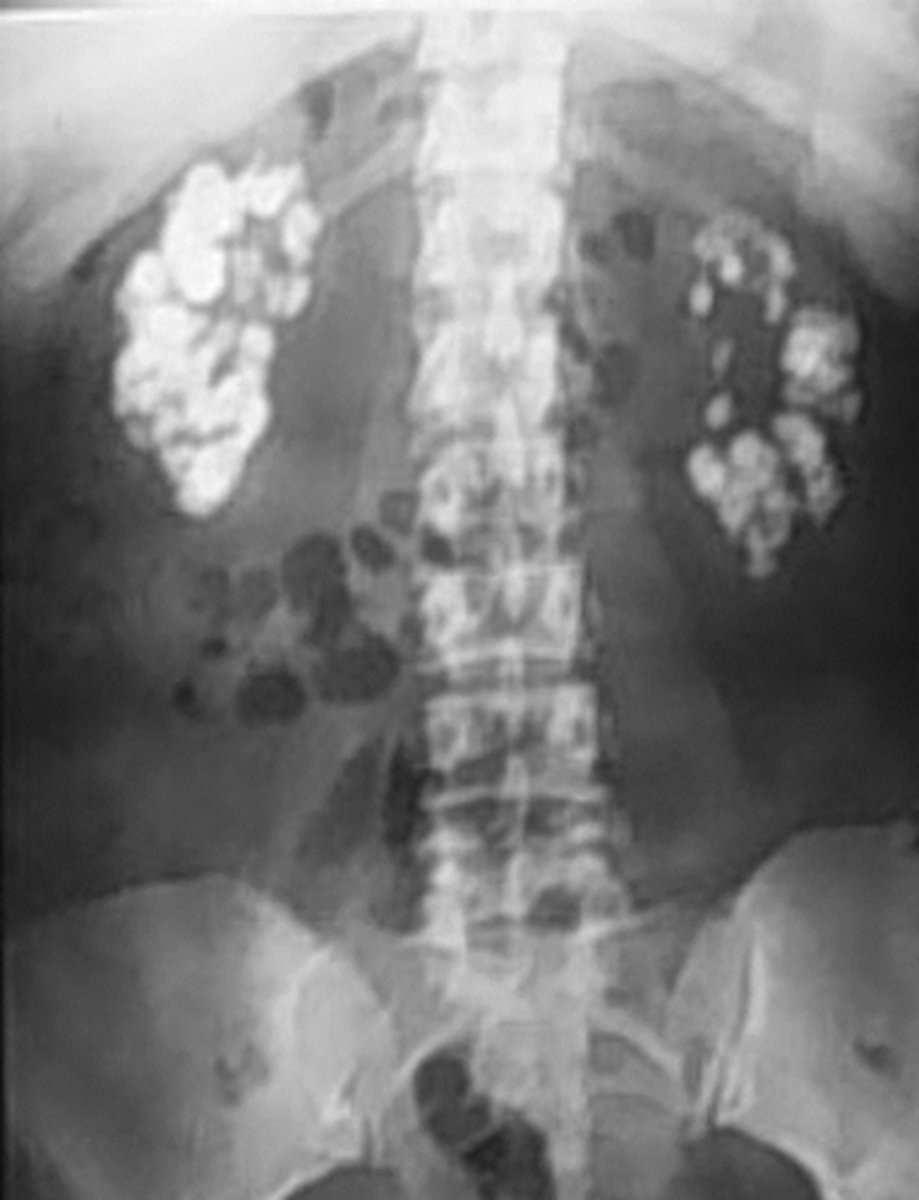
lamellar "laminated" pattern
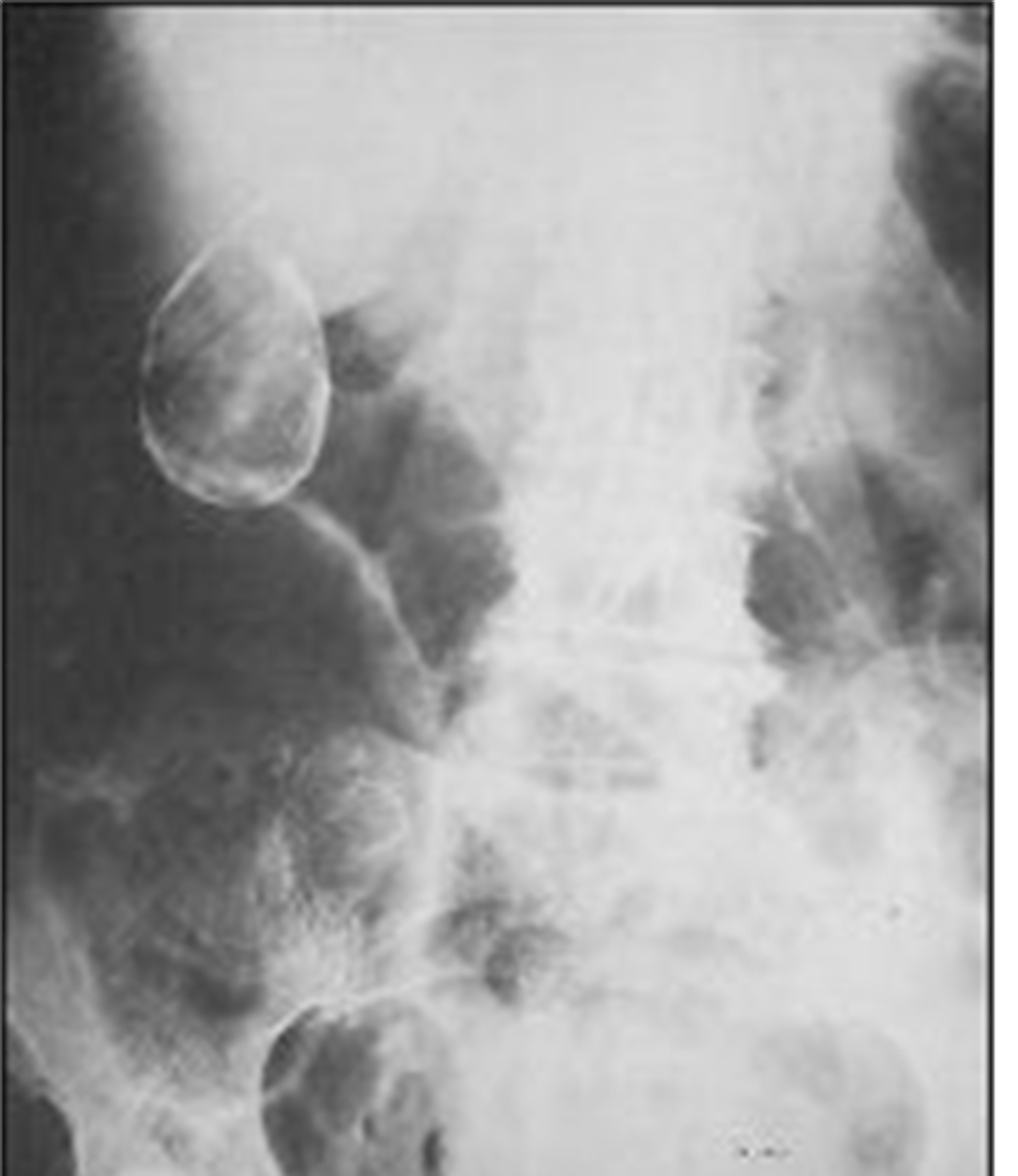
amorphous "popcorn" calculi
porcelain gallbladder
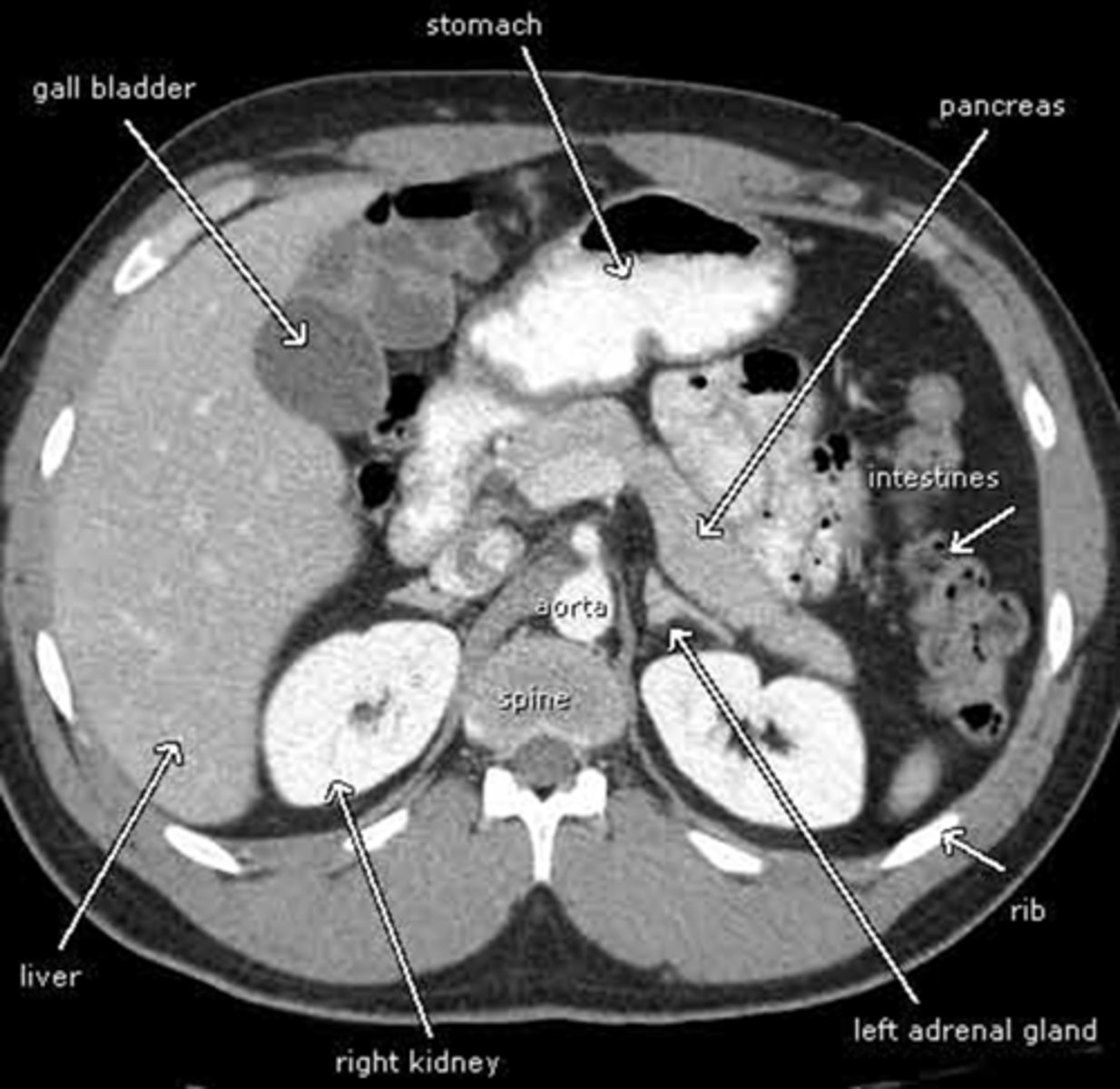
abdominal CT
contrast used with bowel perforations
gastrografin
double contrast study
barium/gastrografin + air/gas
corkscrew esophagus- sign of diffuse esophageal spasm
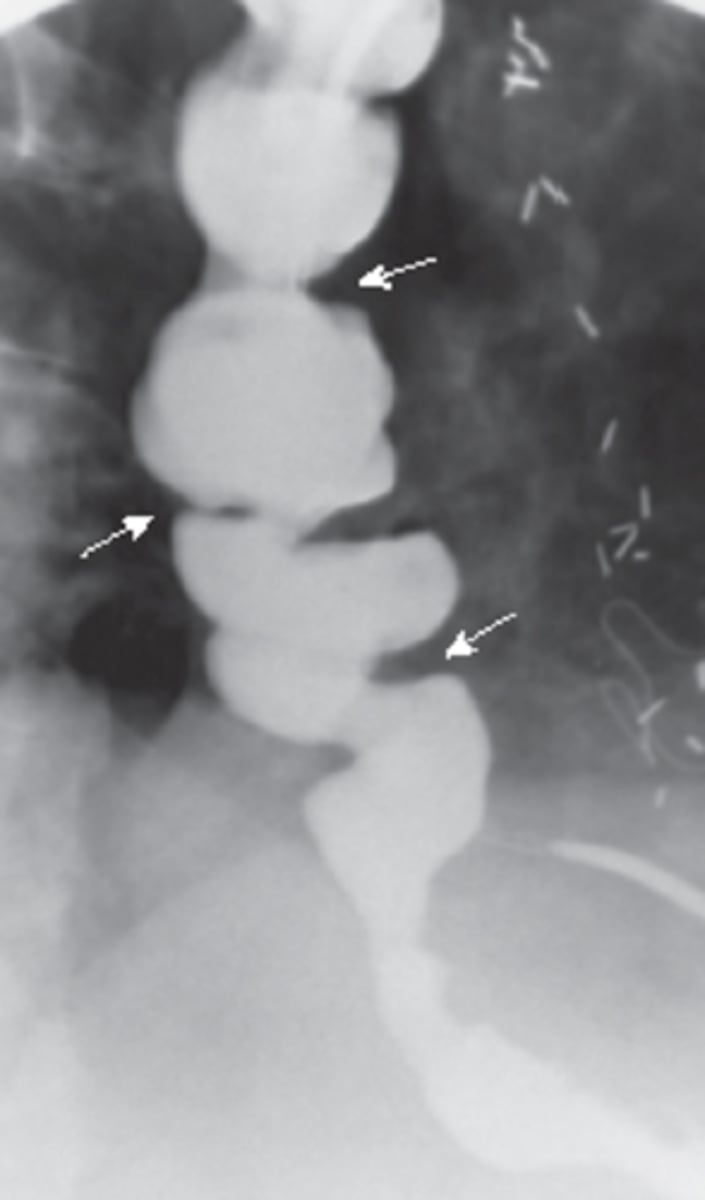
Zenker's diverticulum
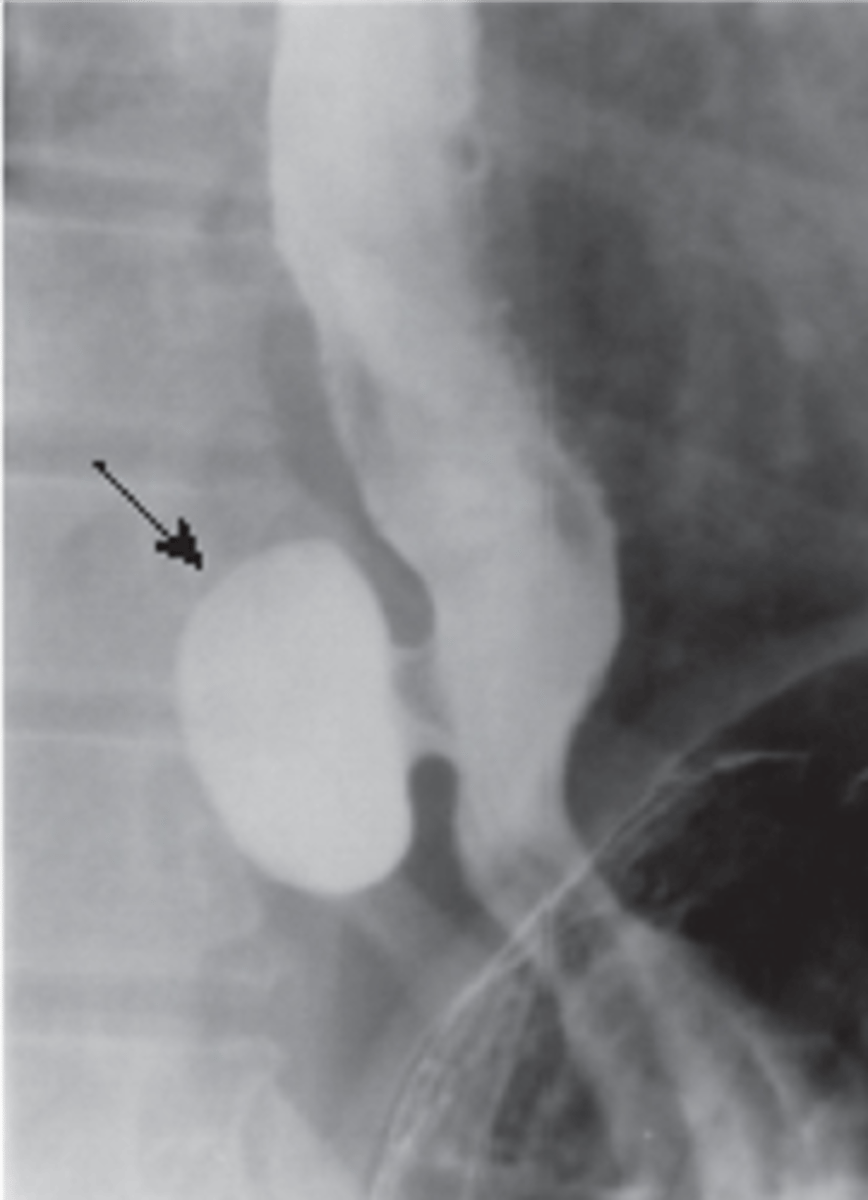
Esophageal narrowing
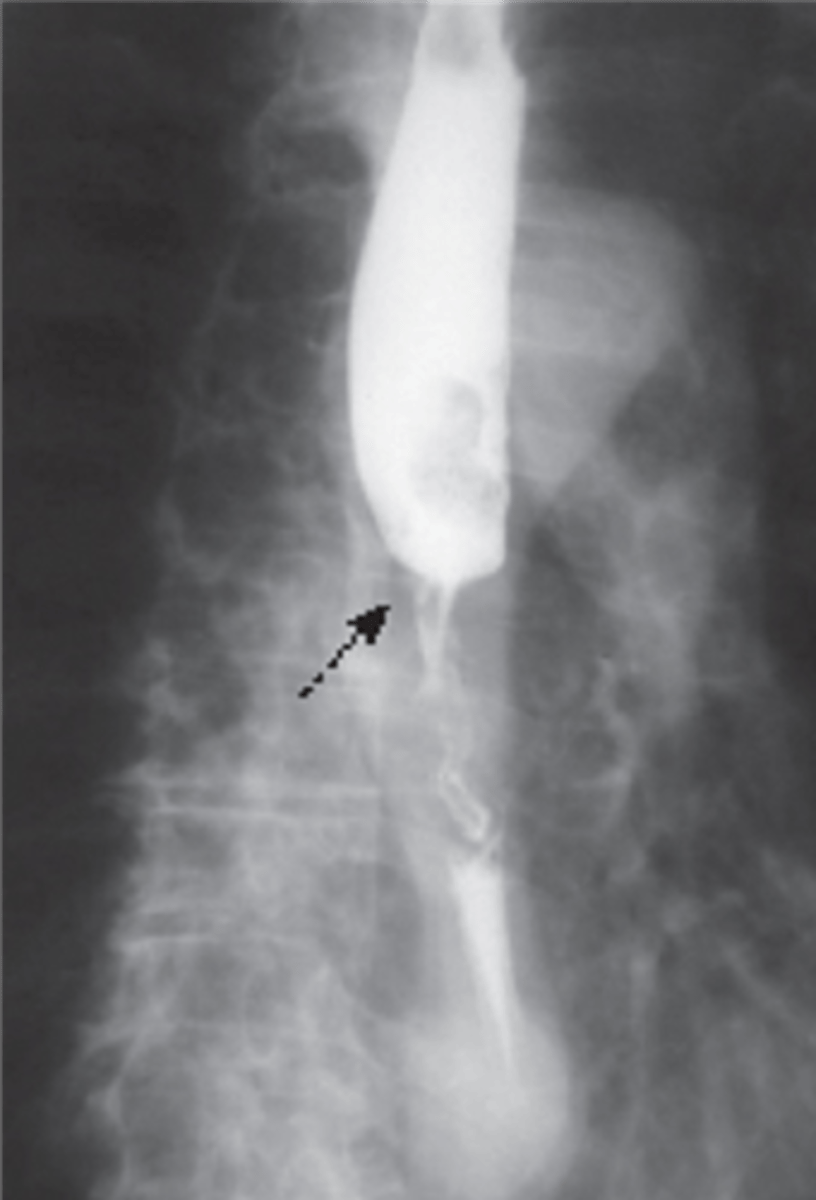
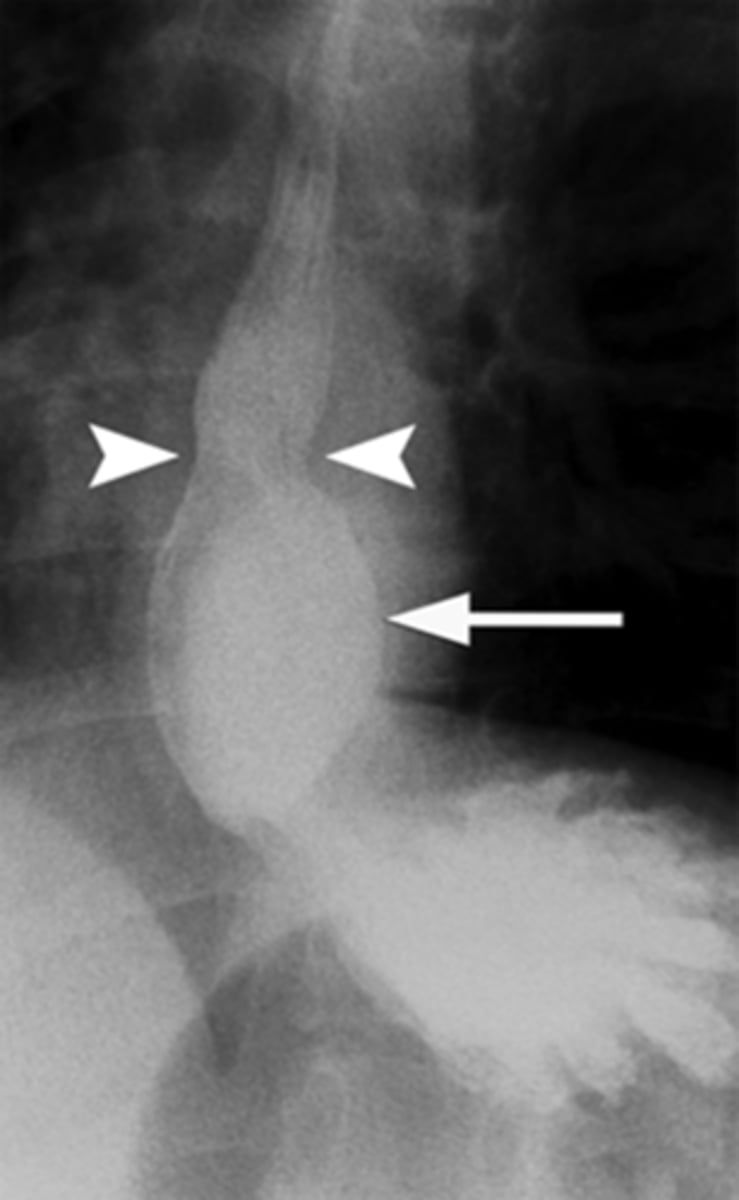
Hiatal hernia
manometric studies (manometry)
measures pressure at lower esophageal sphincter. Low pressure= GERD, high pressure= achalasia/DES
endoscopic evaluation allows for what 3 procedures
visualization, insufflation/aspiration, instrumentation
_____ endoscopy provides color video by way of a radiofrequency transmitter w/ several thousand images transmitted to a belt, worn by pt, over an 8 hour time period
capsule
Ulcerative colitis
apple core lesion- colon CA
diverticulosis
anoscopy
the visual examination of the anal canal and lower rectum
sigmoidoscopy
visual examination of the lower part of the colon (sigmoid)
proctoscopy
examination of the rectum and anus with a proctoscope
All patients >_____ years old should be screened for colon CA with colonoscopy
45
contraindications for colonoscopy
- anticoag or coagulopathic disease process
- suspected perforation
- toxic megacolon
- recent colon anastomosis
- recent acute diverticulitis
study of choice for abnormalities of biliary system
gallbladder US
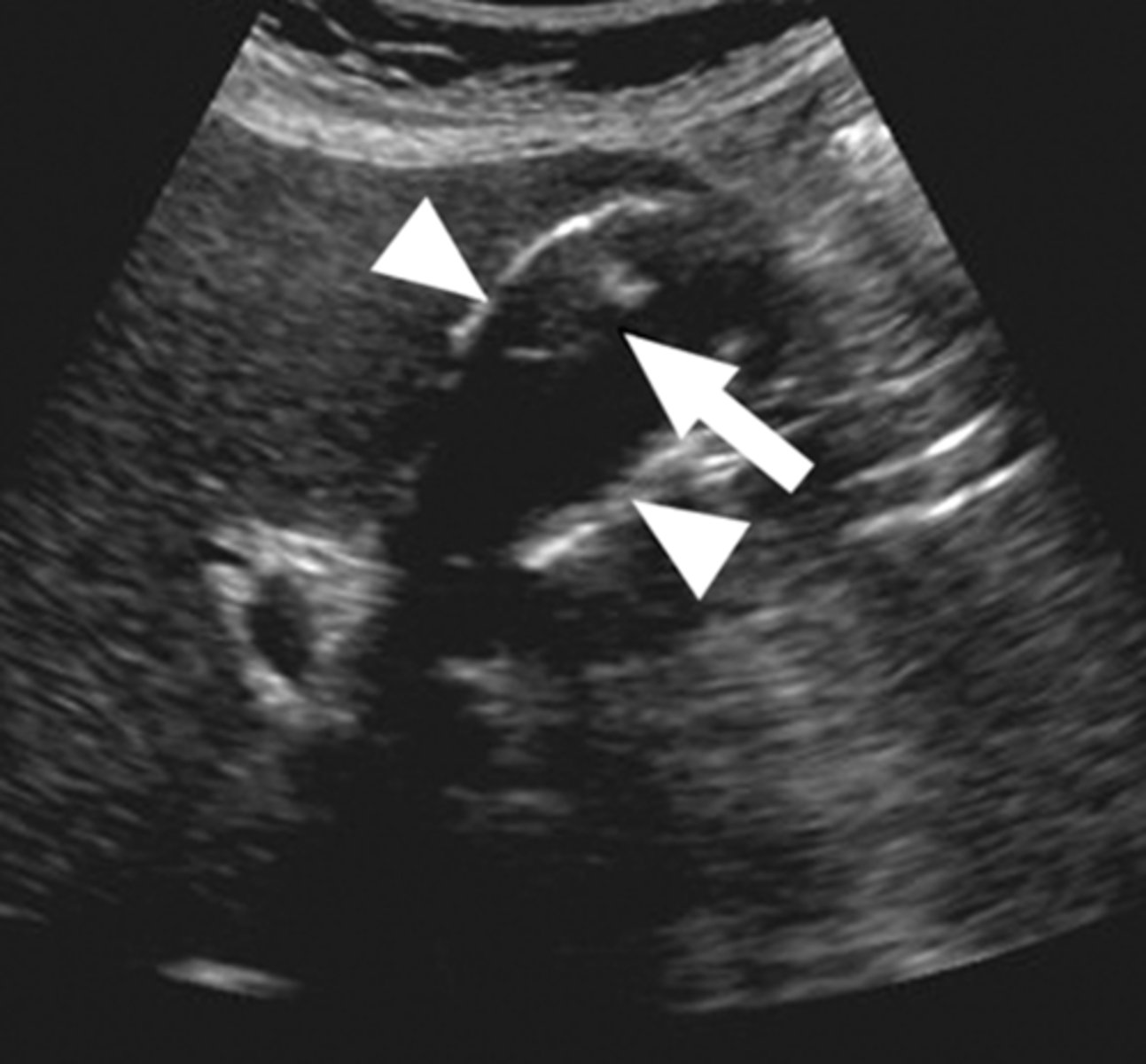
gallstones
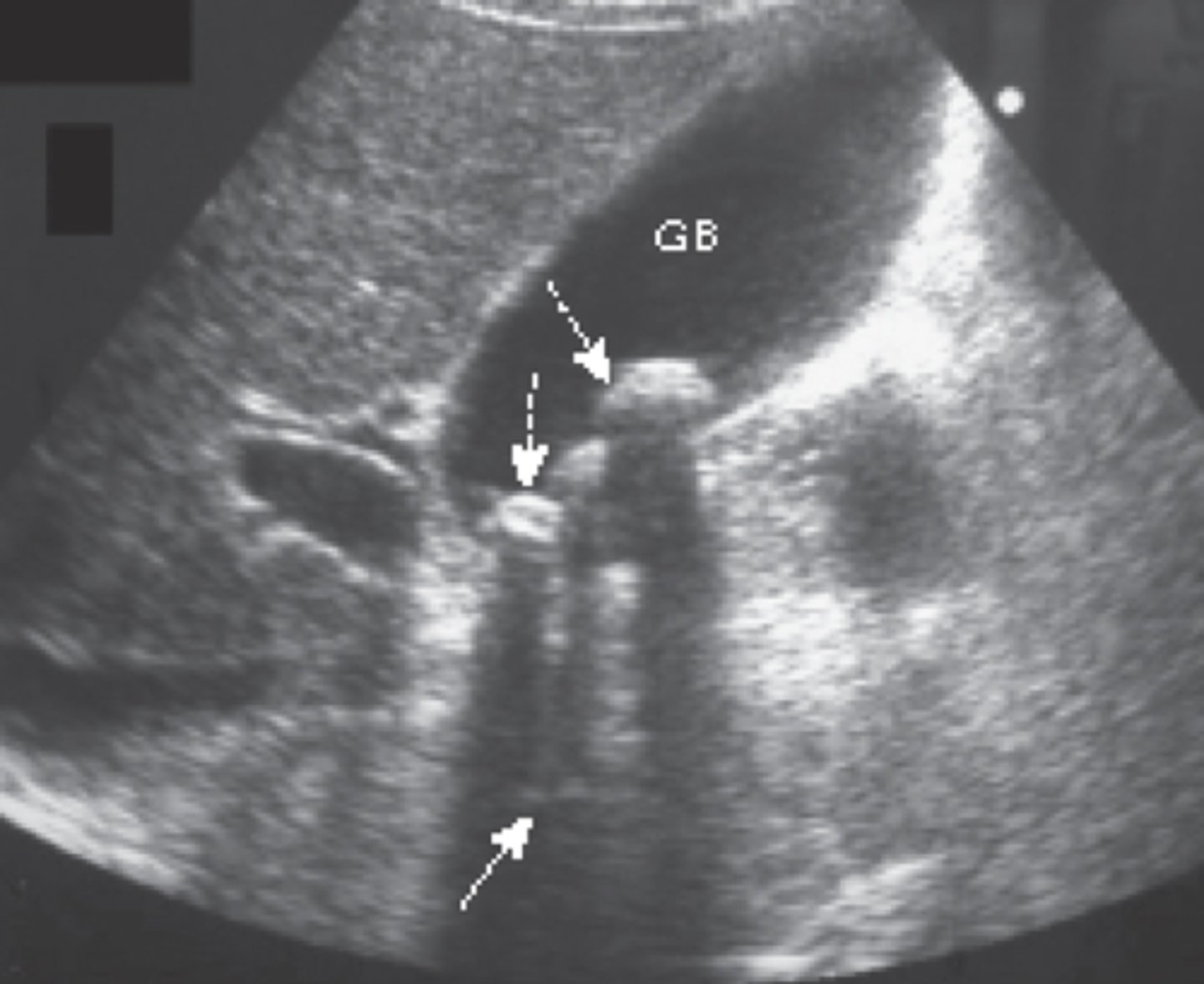
findings of acute cholecystitis
presence of gallstone (neck), thickening of gallbladder wall, fluid around gallbladder, positive murphy's sign
acute cholecystitis
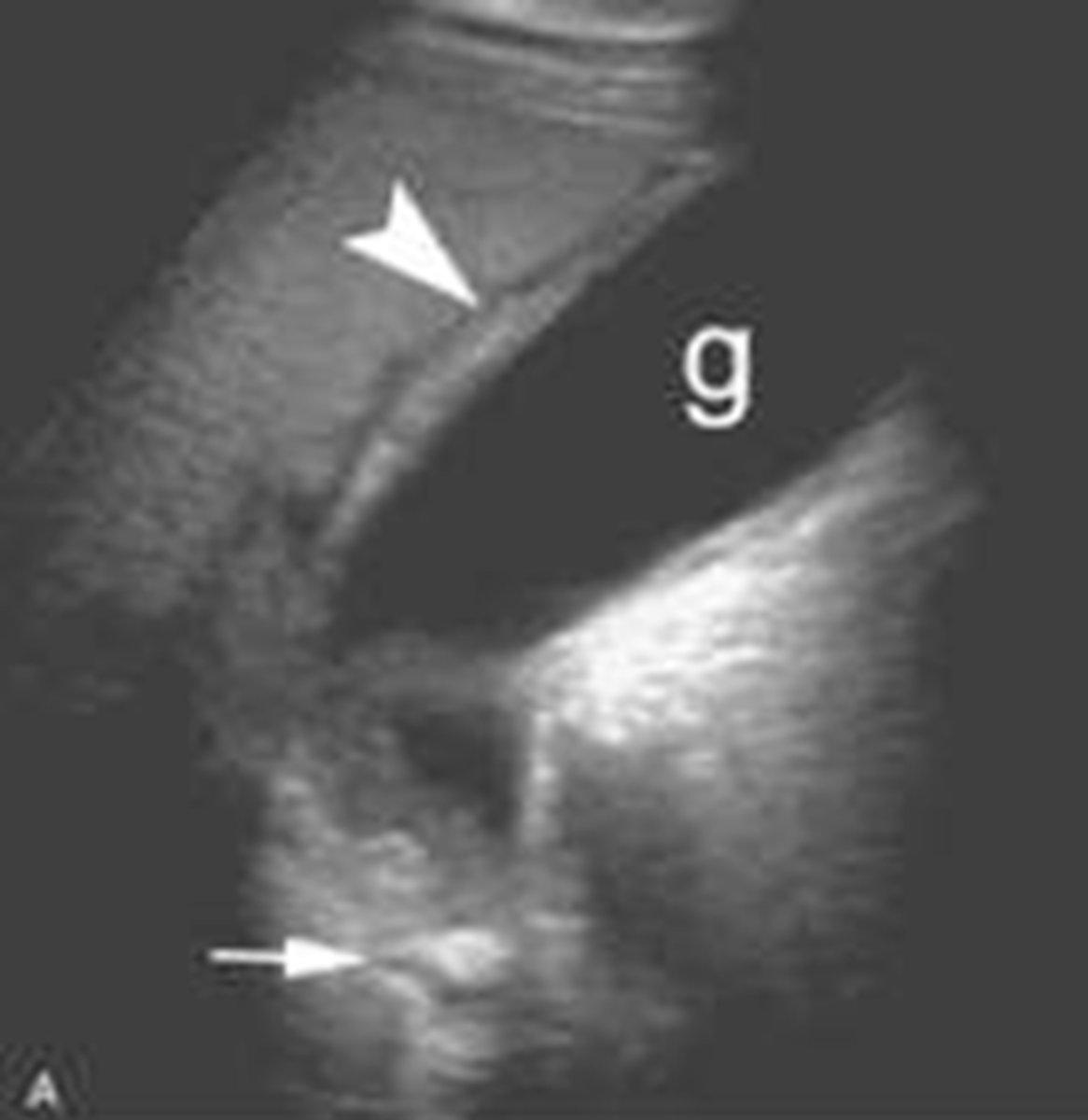
hyperechoic shadowing of gallbladder walls (porcelain gallbladder)
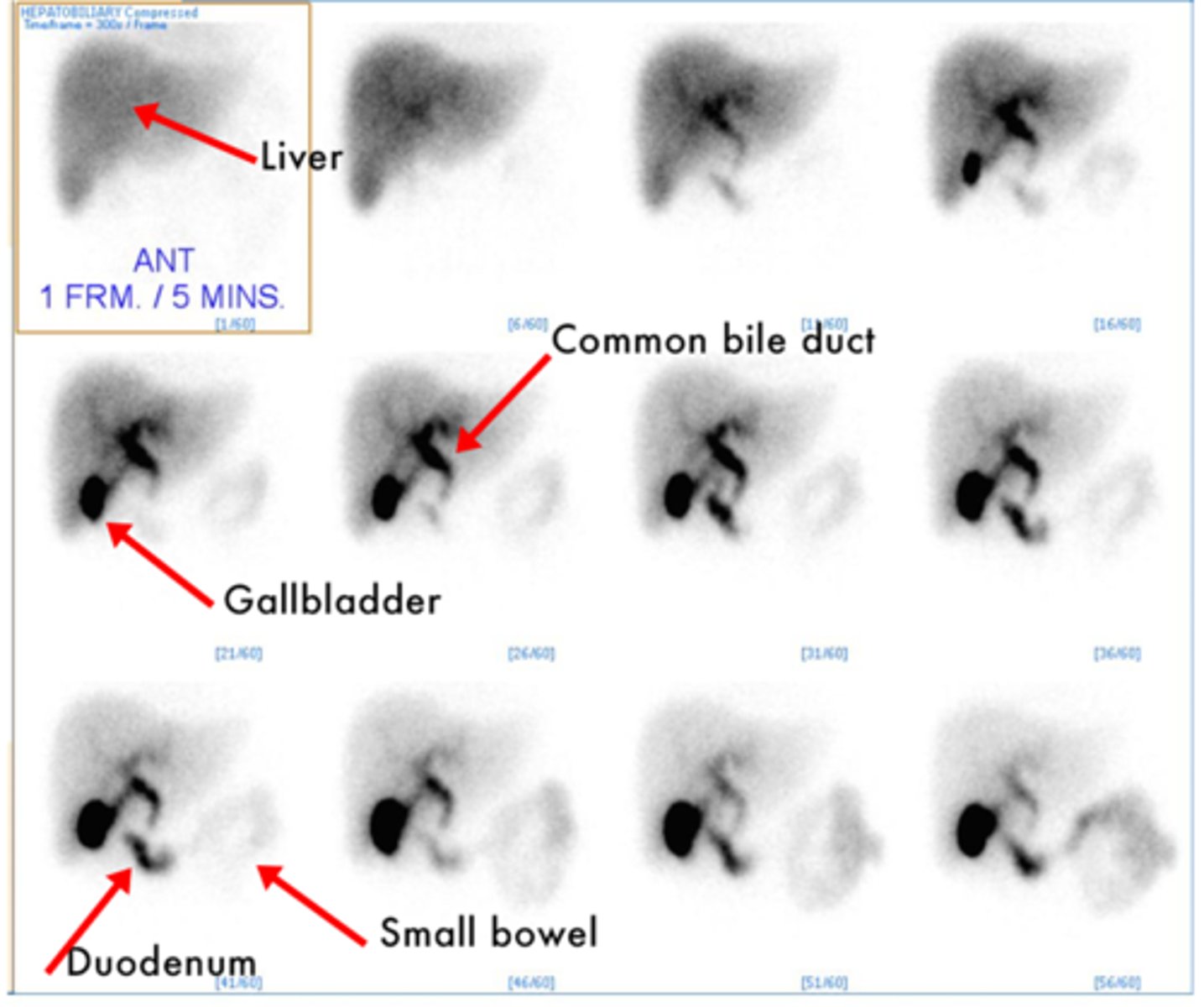
Normal HIDA scan
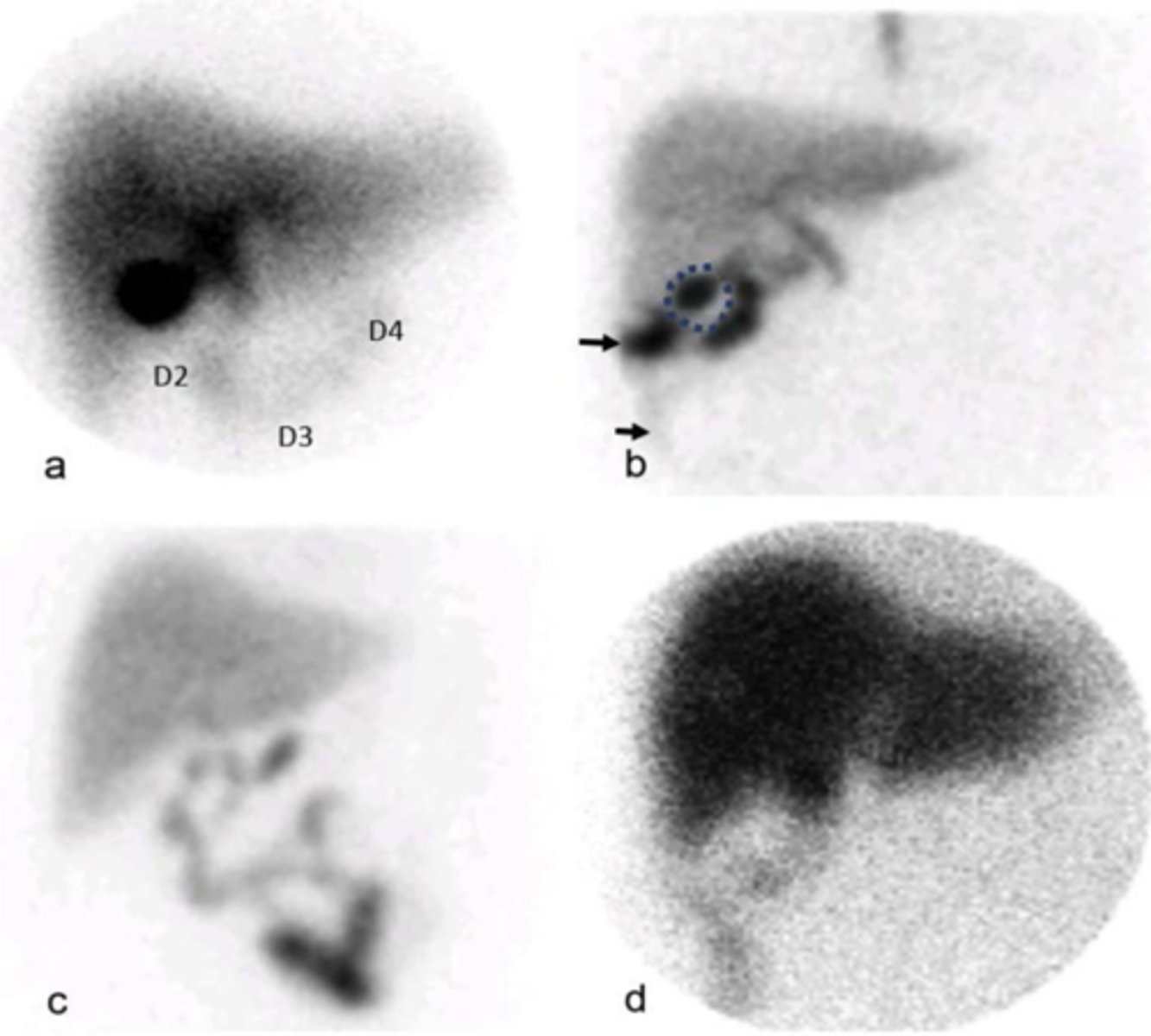
postsurgical biliary leak (HIDA scan)
allows visualization of bile and/or pancreatic duct
ERCP
noninvasive method to image biliary tree without requiring the injection of contrast or dye
MRCP
T2 fluid filled structures appear _______ on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
bright white
MRCP
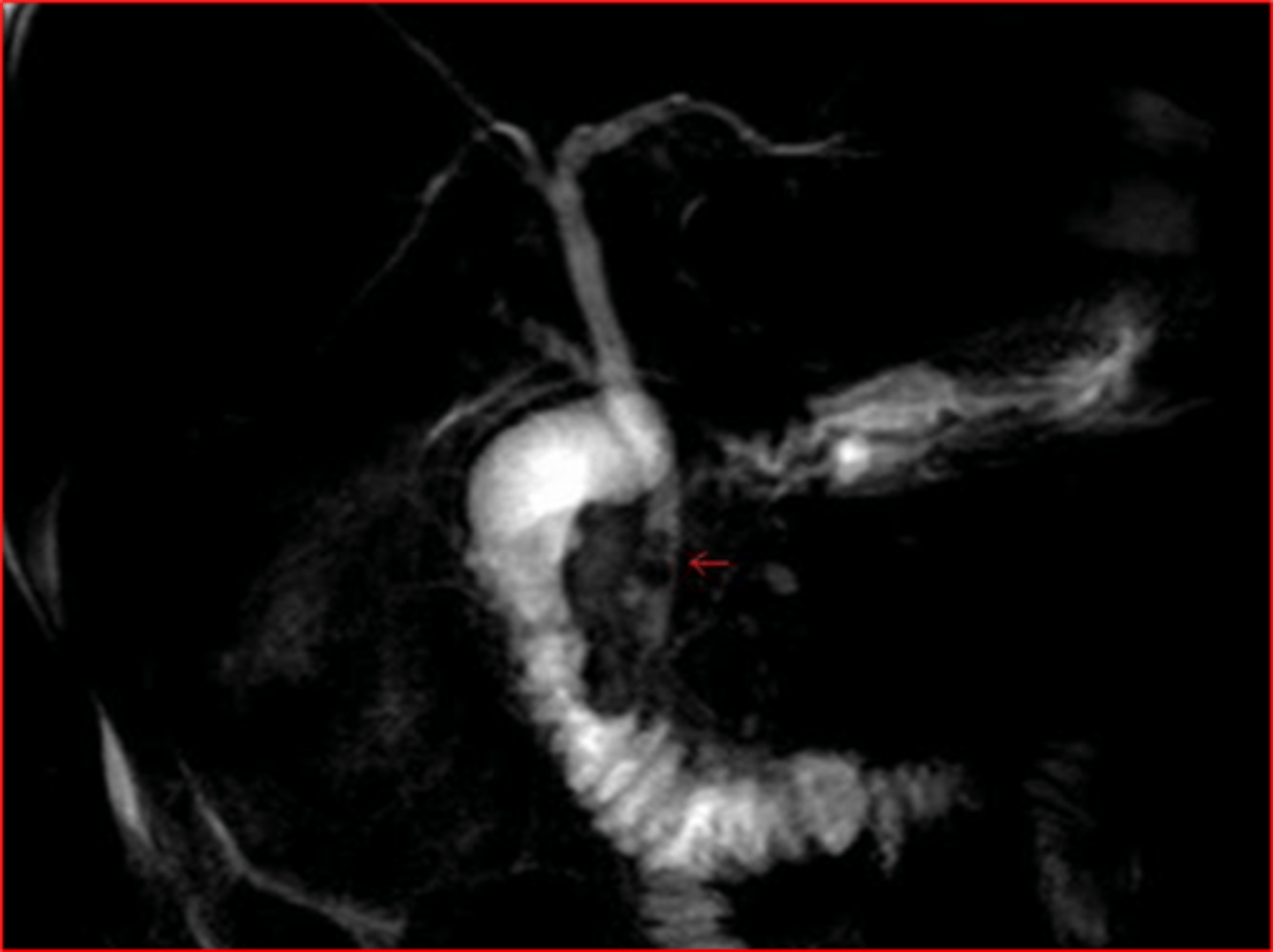
radiographic visualization of bile ducts using XR and contrast, evaluates presence of obstruction or damage of bile ducts
cholangiogram
cholangiogram
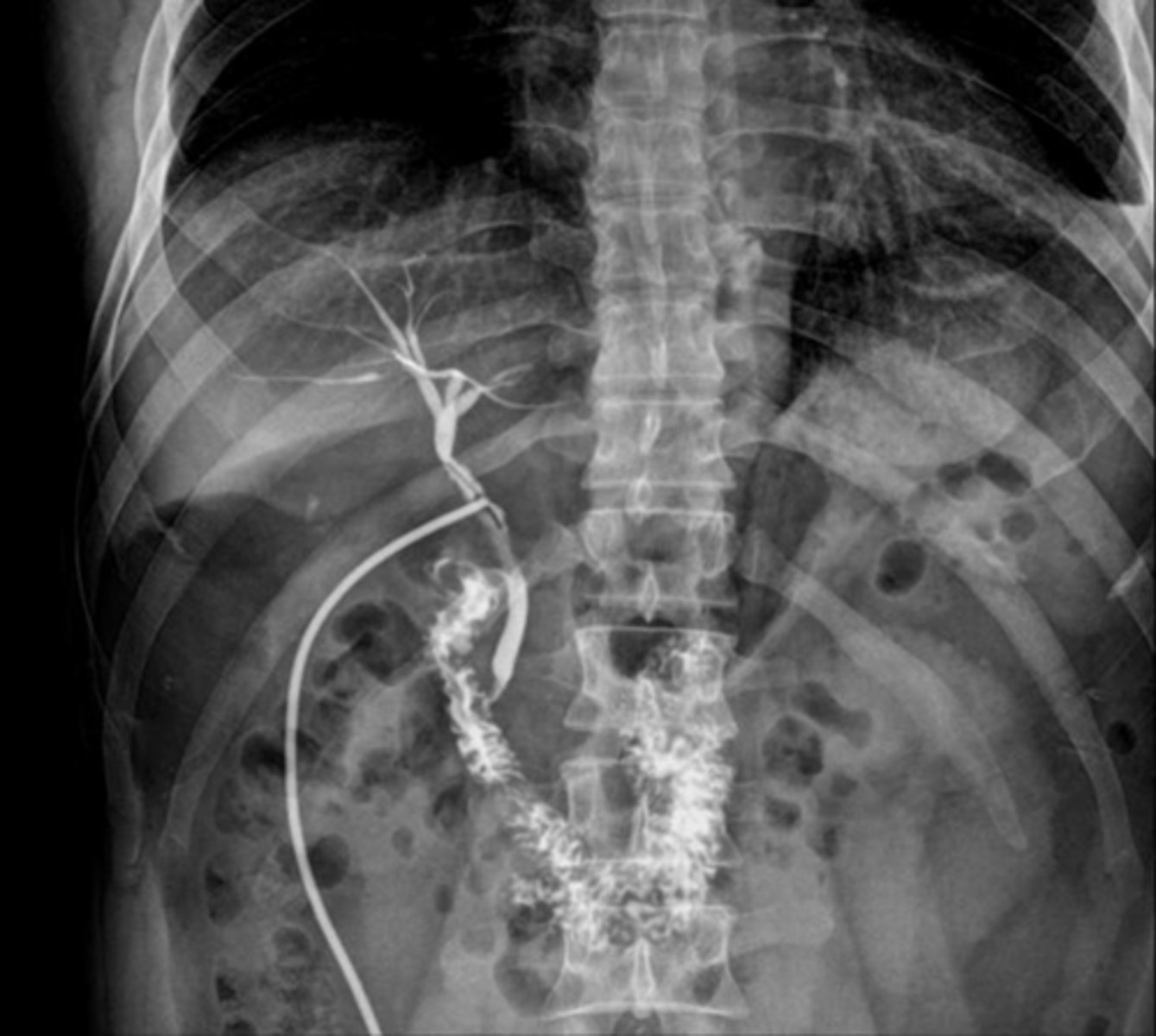
3 different types of cholangiograms
- intraoperative cholangiogram
- postoperative cholangiogram
- percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography