IB Geography - Paper 2 Core IB HL 2024
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Global energy balance
when there is a balance between the energy received by the earth and energy radiated back into space (input = output)
Natural greenhouse effect
a natural process where shortwave radiation reaches the earth's surface and outgoing long wave radiation is trapped by greenhouse gases in the lower atmosphere leading to a warming of the earth's temps
Enhanced greenhouse effect
a disturbance in the earth energy balance due to the increasing amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere as a result of human activities resulting in an increase in long wave radiation trapped in the lower atmosphere resulting in global warming.
Feedback loop
a process by which a system responds to a change by either amplifying the change or reducing the change
Global dimming
when particles are emitted into the atmospher, causing a barrier which blocks incoming shortwave radiation, causing less radiation to reach and be absorbed by earth so the earth cools
Examples of GHGs
Water vapour, CO2, Methane, Nitrous oxide
Civil society
A civil society is comprised of groups or organizations working in the interest of the citizens but operating outside of the government and for-profit sectors
Mitigation
actions that reduce the emissions that contribute to climate change
Adaptation
actions that minimize or prevent the negative impacts of climate change
Examples of mitigation techniques
using clean energy
cap-and-trade
geo-engineering
ocean fertilization
building design
Examples of adaptation techniques
carbon capture at source
public transport
manufacturing
agriculture
Spatial variation in net radiation
Angle of incidence of insulation (seasons)
Higher levels of surface albedo
Insulation has to pass through more of the Earth's atmosphere (latitude)
2 Natural causes of changes to the global energy balance
Volcanic eruptions - volcanoes release huge amounts of ash and sulfur dioxide which when combined with water vapour reflects a lot of insulation back into space changing the energy balance
Changes to solar output - changes occur due to natural solar cycles, one such cycle includes changes in the procession of the earth around the sun. Its orbit changes over time becoming more olyptical impacting the amount and location of incoming insulation
What does the term "natural increase" mean?
the growth rate of a population; the difference between birthrate and death rate. Birth - death rate = natural increase in the population. (Sometimes net migration is added in.)
MIC
Middle Income Country
GDP
Gross Domestic Product- the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy
GNI per capita
Gross national income divided by the number of people in the population.
Life expectancy
The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions E.G Japan's life expectancy is 87 years old.
IMR
(infant mortality rate) The annual number of deaths of infants under one year of age, compared with total live births. Its is expressed as the annual number of deaths among infants among infants per 1000 births rather than a percentage. This is important because it tell how developed a country is, if they have a high IMR they are a LEDC and if it is low they are a MEDC.
CMR
(child mortality rate. )The number of deaths of children before the age of 5 per 1,000 of the population per year
Poverty
Living on $1.90 a day. Inability to meet basic needs for food, clothing, and shelter.
Literacy Rate
The percentage % of a country's people who can read and write.
HDI
Human Development Index. Three indexes are measured. Health (Life expectancy), Education (Literacy Rate) and Income (GNI per capita).
Sustainability
Meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
A universal set of 17 goals including targets and indicators that UN
member states are expected to use to frame their agendas and political policies over the next 15
years.
BRICS countries are:
Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa
Migration
A movement from one country or region to another
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years e.g Nigeria has 7 on average.
population distribution
how population is spread out in an area/country/globally.
sparsely populated
an area that has few people living in it. The population is low and spread out.
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people e.g Tokyo has 36 million
population density
The number of people living per km2
Birth rate
The number of births per 1,000 of the population per year
Death rate (mortality rate)
The number of deaths per 1,000 of the population
population growth
The rate of increase in population over a period of time.
Example of a MEDC country
New Zealand
Example of an middle income country
Brazil
Example of an LIC/LEDC country
Bangladesh
Reasons for high birth rates
-no contraception
-religious groups
-high IMR(wants to increase chance of survival)
-bad health care
- Abortion illegal
- Poor sex education
Reasons for low birth rates
-availability of contraception
-good health care
-late marriages
-stress full lives
-anti-natalist policy
-increased cost of raising children
Reasons for high death rates
1. war - loose lives in war
2. Inadequate health care
3. smoking/ alcohol - MEDC people becoming attached
4. obesity- causes heart disease and lung, more in MEDC due to fast food, fatty food high in salt and sugar
5. Ageing populations
6. Disease and famine
Reasons for low death rates
-good healthcare
-good diet and exercise
-low IMR
-clean water
-no diseases
-Higher number of doctors per 1,000 population
- Advancements in technology x-ray/ fitbit
population momentum
The propensity for a growing population to continue growing even though fertility/birth rate is declining because of their young age distribution and due to a longer life expectancy and migration
LEDCs mean:
Less Economic Developing Country / Poorer/low income countries e.g Mali in Africa
MEDCs mean:
More Economic Developed Country / Wealthy/Well developed country e.g Singapore
If birth rates are high and death rates are low, what happens to the population?
The population grows
If the birth rates are high and the death rates are also high, what happens to the population growth?
Stays stable - no growth
If the birth rates are low and the death rates are low, what happens to the population growth?
The population declines
Today's Total world Population is:
7.8 billion
The world's population is expected to reach_____________ by 2100?
11 billion
Which country has the highest total population?
China 1.4 billion
sustainable development
Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. Includes the three pillars of sustainability (social, economic and environmental).
consumption
The level of use of society makes of the resources available to it. Economic development and changing lifestyles and aspirations usually result in accelerated consumption of resources e.g the growing middle class.
Water security
the ability to access sufficient quantities of clean water to maintain adequate standards of food and goods production, proper sanitation, and sustainable health care.
food security
Physical, social, and economic access at all times to safe and nutritious food sufficient to meet dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
Energy security
having access to enough reliable and affordable energy sources to meet one's needs at an affordable price.
natural resources
Materials or substances such as minerals, forests, water, and fertile land that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain
extreme poverty
Living on less than $1.90 a day. When a person's income is too low for basic human needs to be met, resulting in hunger and homelessness.
New Global Middle Class (NGMC)
People with discretionary income. They can spend this on consumer goods, holidays, cars, travel. One classification is people earning more than US$10,000 annually. Asia has the largest portion of the global middle class. Around 2.8 billion.
SDGs
UN Sustainable Development Goals
relative poverty
When a person's income is too low to maintain the average standard of living in a particular society. Very wealthy people within nations can lead to more people being in relative poverty.
ecological footprint
A crude measurement of the area of land or water required to provide a person (or society) with the energy, food and resources needed to live and to absorb waste. Measured in GHA.
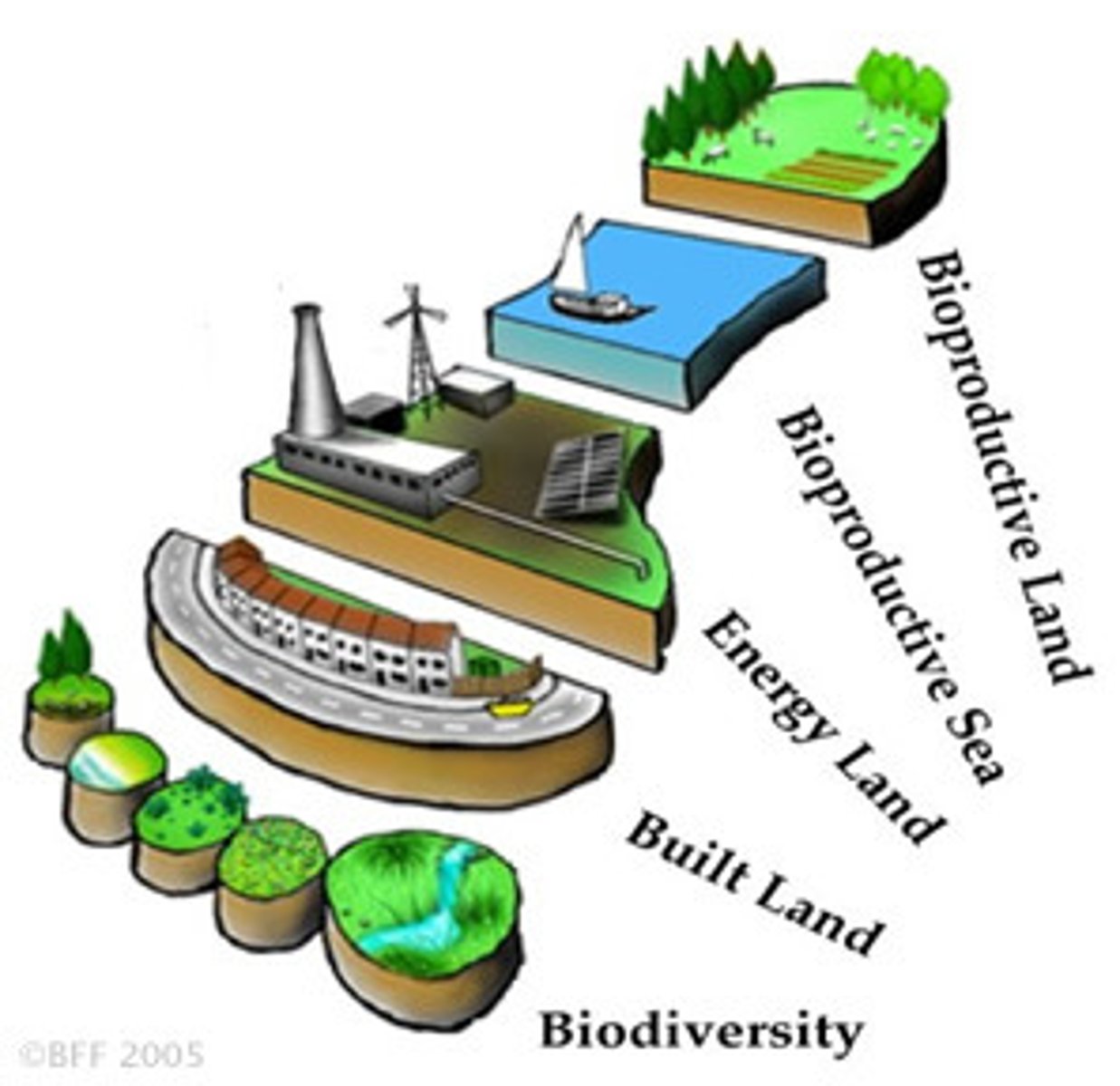
Physical carrying capacity
The maximum number of people an area of land can support with current levels of people/technology.
absolute poverty
the point at which a household's income falls below the necessary level to purchase food to physically sustain its members
Renewable Resources
Any natural resource that can replenish itself in a relatively short period of time, usually no longer than the length of a human life.e.g forestry as re growth can re occur. Renewable energy sources include geothermal, hydroelectric, solar, wind.
Hydrocarbons / Non-renewable resources
Fossil fuels - A resource which is finite / cannot be reused or replaced easily e.g oil, coal natural gas, iron,copper)
Embedded Water (Virtual Water)
A measure of the amount of water used in the production and transport to market food and commodities. (virtual water) May also include the use of local water resources and the use of water resources in distant places.
Newly emerging economies (NEEs)
Countries that have begun to experience higher rates of economic development, usually with higher levels of industrialisation. They differ from LICs in that they no longer rely primarily on agriculture, have made gains in infrastructure and industrial growth, and are experiencing increasing incomes and high levels of investment, eg Vietnam, South Korea, Turkey and Thailand.
Carrying Capacity Overshoot
Is a state in which there are too many people for the environment to sustain (with food, drinkable water, breathable air, etc.). In more scientific terms, there is overshoot when the ecological footprint of a human population in a geographical area exceeds that place's carrying capacity, damaging the environment faster than it can be repaired by nature
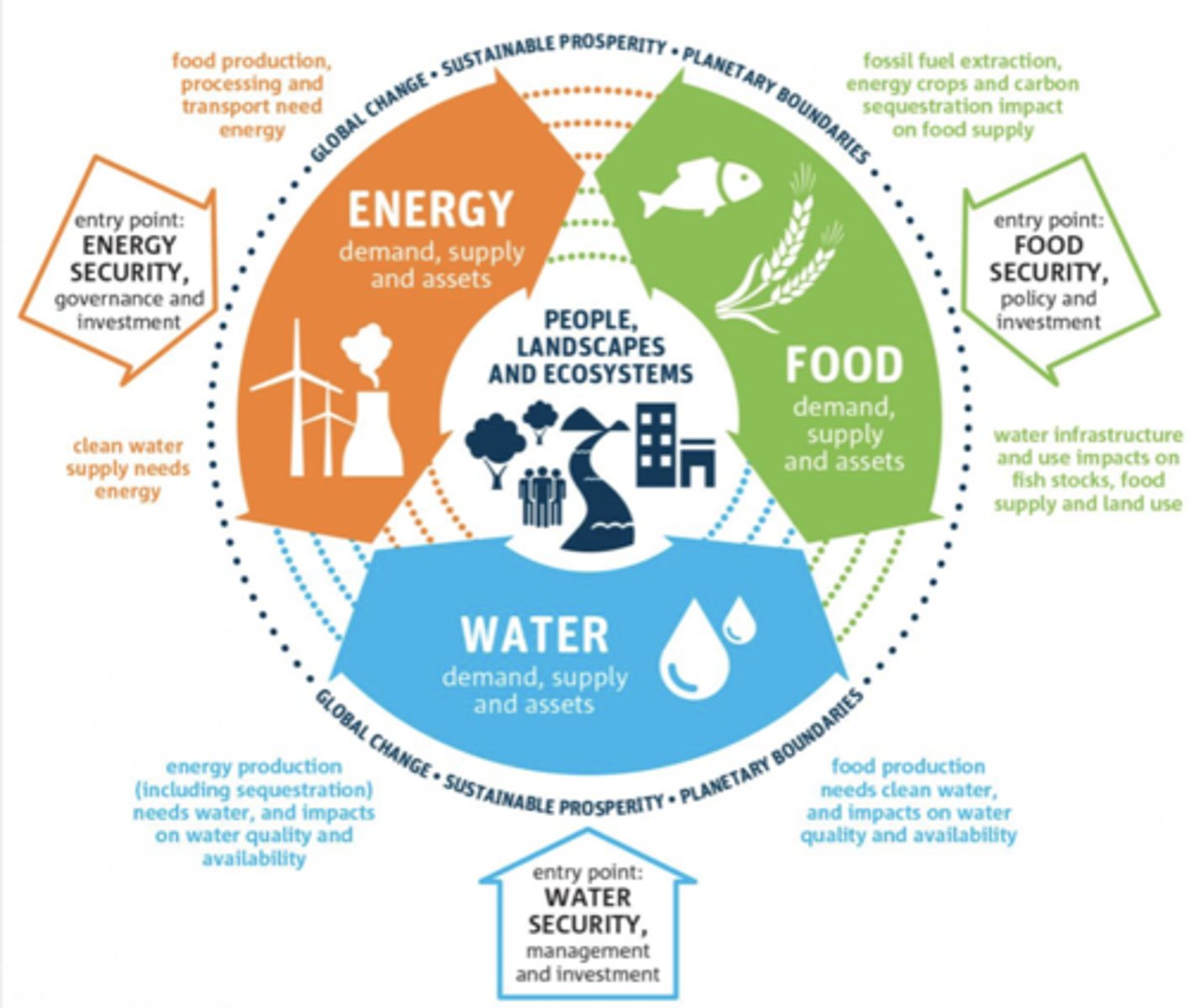
Water, Food, Energy Nexus
The water, energy and food sectors are interlinked. They have complex and dynamic interrelationships. Understanding of these interrelationships is essential if natural resources are to be used and managed more sustainably.
safe water
Water that is safe to drink or to use for cooking, bathing without health risk problems such as water borne diseases e.g cholera and typhoid
Energy Pathways
Flows of energy that link producer regions with consumer regions e.g power lines, pipelines e.g Dakota pipeline USA.
Economic water scarcity
Where water is available locally but not accessible for humans to use due to institutional or financial capital reasons / lack of technology or infrastructure to extract water.
Physical water scarcity
Where water resource development is approaching or has exceeded unsustainable levels. The annual water supply falls below 1,000 cumecs per person. Annual rainfall is normally less than 250mm.
food availability
the state of people having enough access to food that can be reached by those that need it including food aid and imports.
Globalisation definition
the process by which businesses and telecommunications or other organizations e.g TNCs develop international influence or start operating on an international scale.
How does the growth in the middle class impact on land use?
- More land needed, cutting down of forests/expansion onto marginal land
- More land is needed for transport infrastructure
- Land acquisition in developing countries by -transnational companies for food and minerals, takes land from indigenous populations.
- Land use for housing developments - Middle income groups have more money and aspirations and want to live in their own houses / no longer need to live with their parents and this increases the demand for housing which is built on land previously covered by trees
carbon footprint
measure of the impact human activities have on the environment in terms of the amount of greenhouse gases produced, measured in units of carbon dioxide

water footprint
A rough measure of the volume of water that we use directly and indirectly to keep a person or group alive and to support their lifestyles.
Biocapacity
a measure of the area and quality of land and water available to supply a population with resources
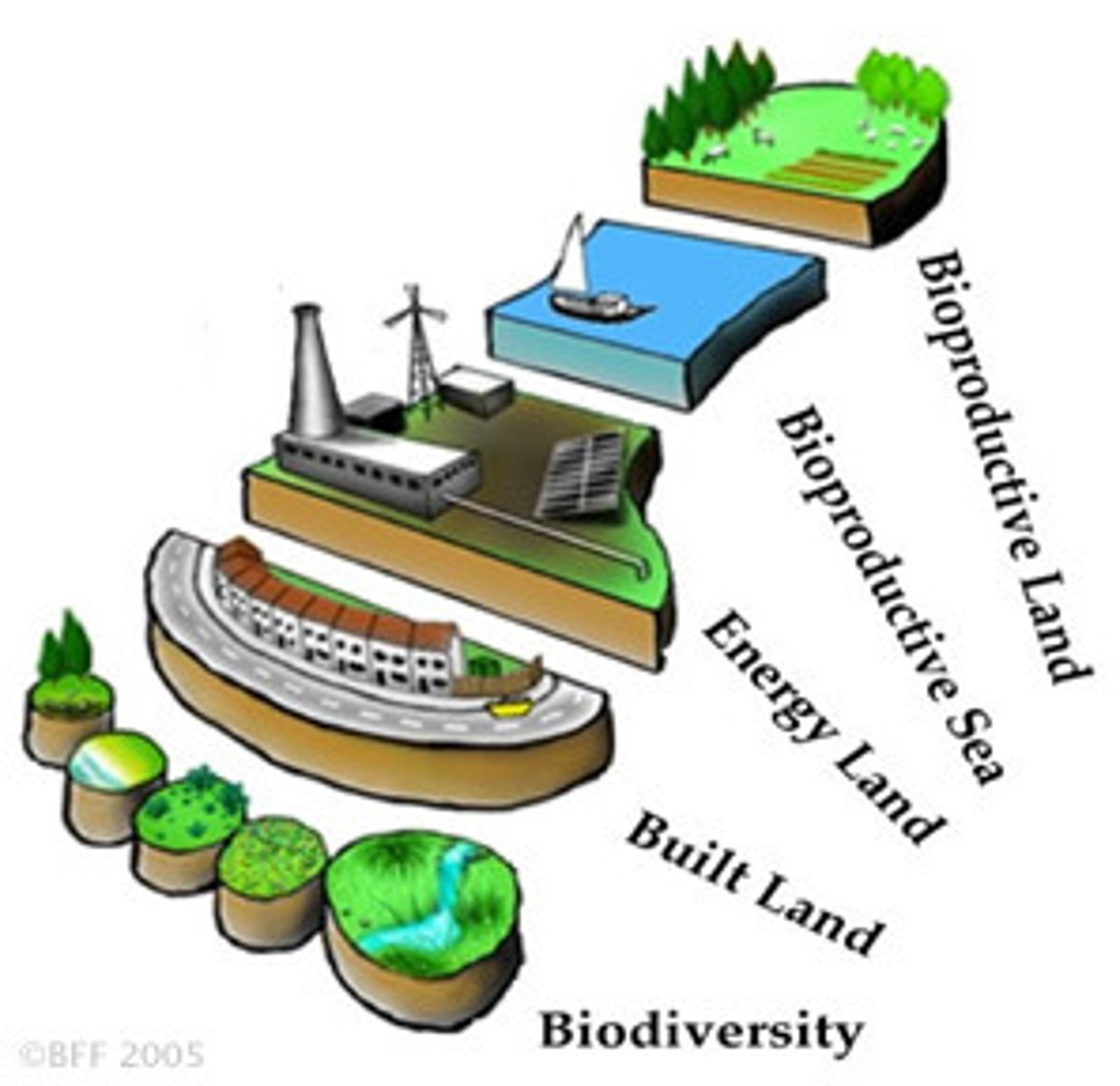
The planets biocapacity (ability to produce) is
1.9 ha. per person
Nuclear power
Energy from splitting Uranium atoms.

Protectionism
the theory or practice of shielding a country's domestic industries from foreign competition by taxing imports.
Why are global diets changing?
- With improved education comes greater health awareness - more understanding on the importance of a balanced diet.
- Globalisation and advancements in technology have increased advertising, especially by multinational food firms / TNCs such as Starbucks, McDonalds
- Environmental awareness - The growth of veganism/vegetarian - importance of having a flexi diet - do you need meat for every meal?? January has become Veganuary
- Growth in the global middle class - able to afford more meat
Globalisation has allowed for an increase in imports of global food produce - people have more access to buy cheaper meet, rice, vegetables etc
Rapid urbanization has lead to a shift to energy-dense diets {fast food meals - quick energy meals}
nutrition transition
A change in a diet from stable carbohydrates and more towards meat, fish and dairy products. This shift in diet typically happens when income rises e.g fro US$2 a day to US$10 a day. The growth in the global middle class e.g in China has seen the greatest nutrition transition
A country with WFE Insecurity
India
A Country with WFE Security
Canada
e-waste
Electronic Waste - Discarded electronic equipment such as computers, cell phones, television sets, etc.

Grey Water
waste water generated from processes such as washing dishes, bathing and laundry - This water is reusable
resource consumption
The process of using natural resources such as water, food and energy, materials, or finished products to satisfy human wants or needs.