organisation
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
explain how taking anabolic steroids could improve their performance in sport
athlete is faster
more muscle contractions
explain 2 effects of anaerobic respiration on the person’s body
muscle fatigue caused by lactic acid
heavy breathing to provide oxygen needed to break down lactic acid
increased heart rate to provide oxygen needed to break down lactic acid
fewer muscle contractions because less energy released
explain the effect of a partly locked coronary artery
reduced blood flow to heart
less o2 to heart
less glucose to heart
less aerobic respiration
more anaerobic respiration
less energy
less muscle contraction
less blood around the body
less co2 removed from body
therefore breathlessness and tiredness
anaerobic respiration causes production of lactic acid
causes muscle fatigue
In a person with CF, cells lining the lungs and digestive system create too much mucus.
The mucus can:
• block the duct leading from the pancreas to the small intestine
• block the tubes leading to the alveoli in the lungs.
Explain why children with CF grow more slowly than children without CF.
fewer enzymes enter small intestine so enzyme break down less food
therefore less absorption of nutrients
so less glucose can enter blood stream
less glucose available for respiration
less absorption of nutrients so less amino acids can enter the blood stream so less protein is made for growth
less oxygen enters blood stream so less available for aerobic respiration
less energy released for growth
Plants infected with aphids may show symptoms of magnesium deficiency. Magnesium deficiency symptoms include:
• yellow leaves
• stunted growth.
Explain how a deficiency of magnesium could cause these symptoms
yellow leaves due to lack of chlorophyll
less light absorbed
lower rate of photosynthesis
plant makes less glucose
plant converts less glucose into protein so growth is stunted
An aphid feeds by inserting its sharp mouthpiece into the stem of a plant.
Give the reason why the mouthpiece of an aphid contains a high concentration of dissolved sugars after feeding.
aphid had been feeding from the phloem
what condition may be treated using an artificial pacemaker?
irregular heart beat
Compare the structure of an artery with the structure of a vein.
arteries have a thicker layer of muscle
arteries have a thicker layer of elastic tissue
arteries have a narrower lumen
arteries do not have valves but veins have valves
Some athletes train at high altitude. Training at high altitude increases the number of red blood cells per cm3 of blood.
Explain why having more red blood cells per cm3 of blood is an advantage to an athlete.
more haemoglobin
more oxygen can be transported
more aerobic respiration
more energy released for muscles
name 2 other substances, not urea, that is transported in the blood plasma
co2
water
glucose
lactic acid
amino acids
what is an enzyme
chemical which catalyses biological reactions
protein
An axolotl may not be a suitable animal to study when researching regeneration in human tissue.
Suggest one reason why
not a mammal
metabolism processes are too different
Suggest two reasons why the rate of water loss in both plants increased
warmer
light intensity higher
less humid
windier
Describe the transport of water through a plant from the roots to the atmosphere
water is transported in xylem
water evaporates from leaves through the stomata
Water moves from a plant to the atmosphere through the leaves.
How is the volume of water lost from the leaves controlled?
guard cells opening and closing the stomata
Where in the human body are the chemical reactions involved in the normal breakdown of some types box of amino acid inside body cells most likely to occur?
liver
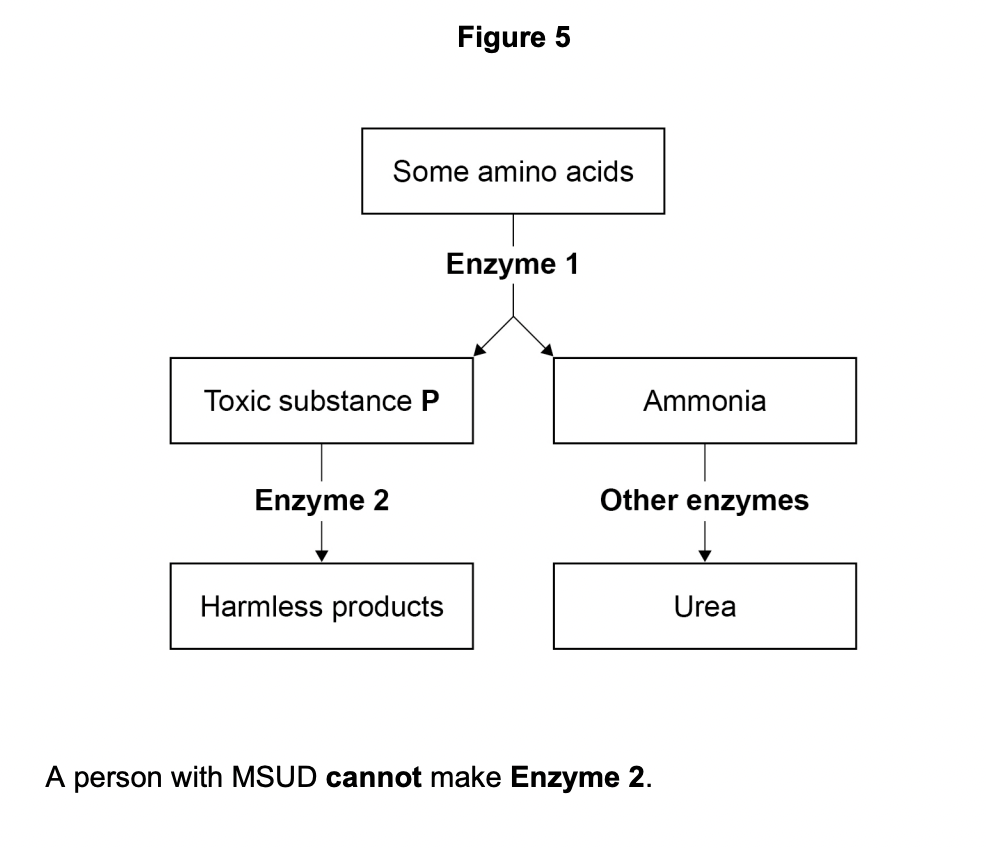
Explain why the blood of a person with MSUD will have a high concentration of toxic substance P.
cannot break down toxic substance
the toxic substance still made
toxic substance diffuses into the blood
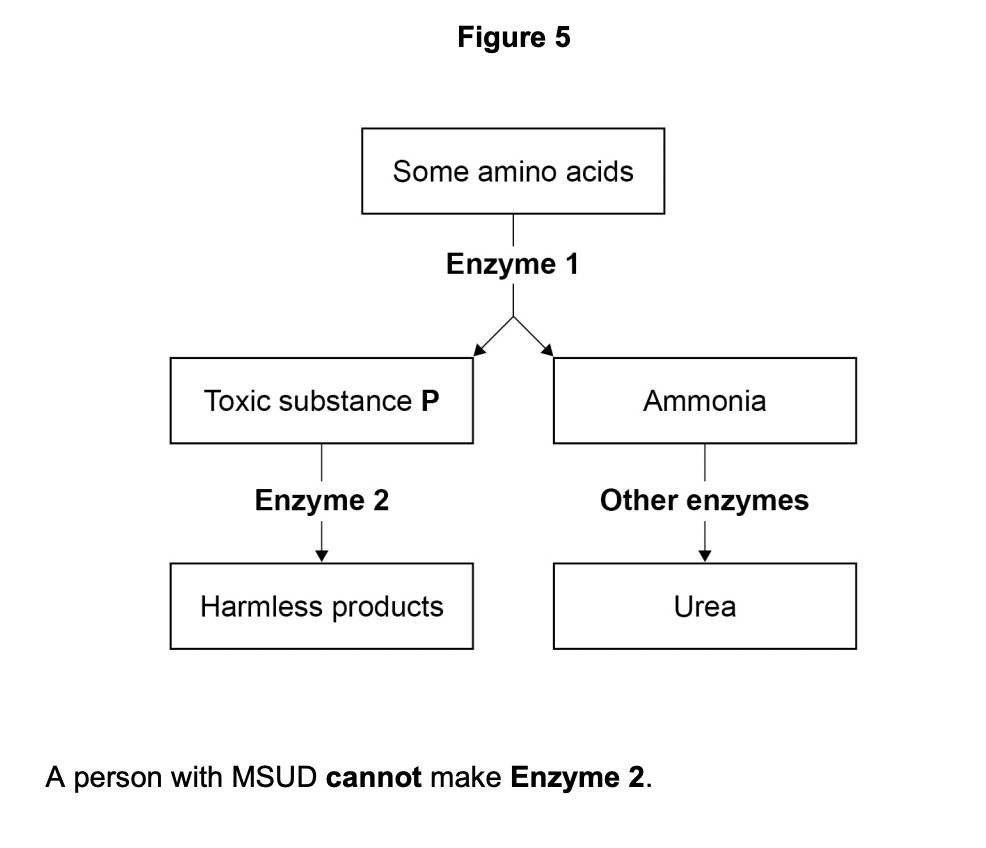
Explain why the urine of a person with MSUD will have a high concentration of toxic substance P.
toxic substance passes through filter in kidney
some not reabsorbed
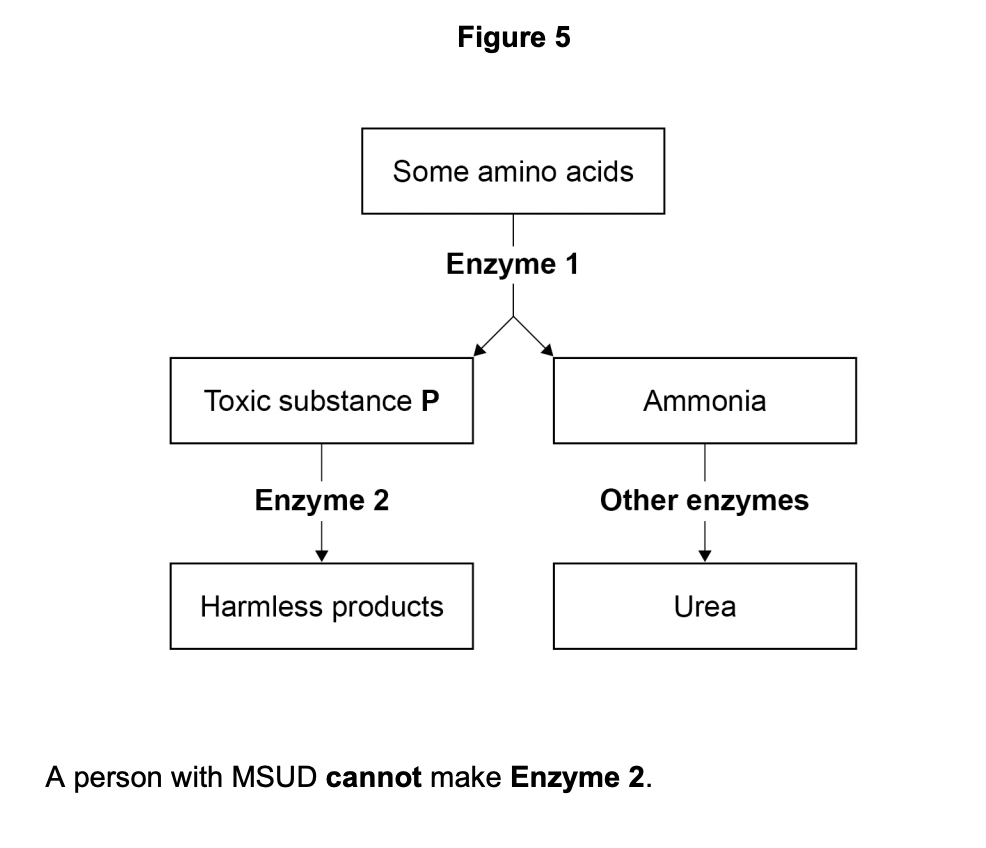
Explain why a person with MSUD must have a low-protein diet.
proteins are made of amino acids
must keep amino acids in low amount
so toxic substance does not build up in body and cause damage to cells
Which environmental conditions would cause the rate of transpiration to be greatest in a plant?
warm with low humidity
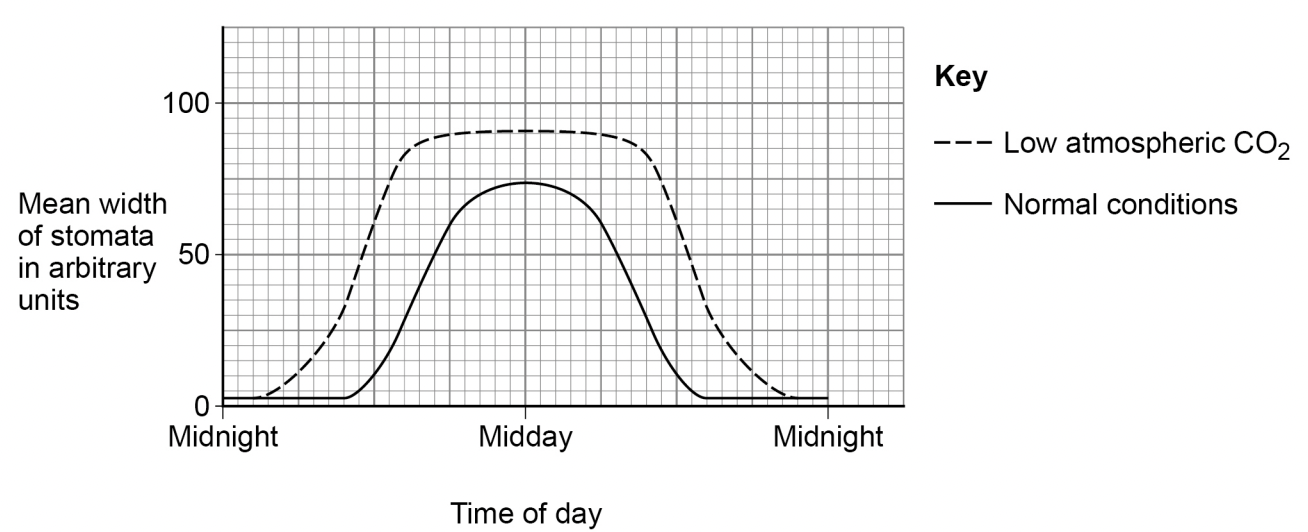
The changes in the mean width of the stomata in normal conditions are an advantage to the plant.
Explain how.
stomata closed at night because there is no light for photosynthesis
closing stomata prevents water loss
stomata open wide at midday at maximum light intensity for photosynthesis
stomata open wide to take in more co2 for photosynthesis
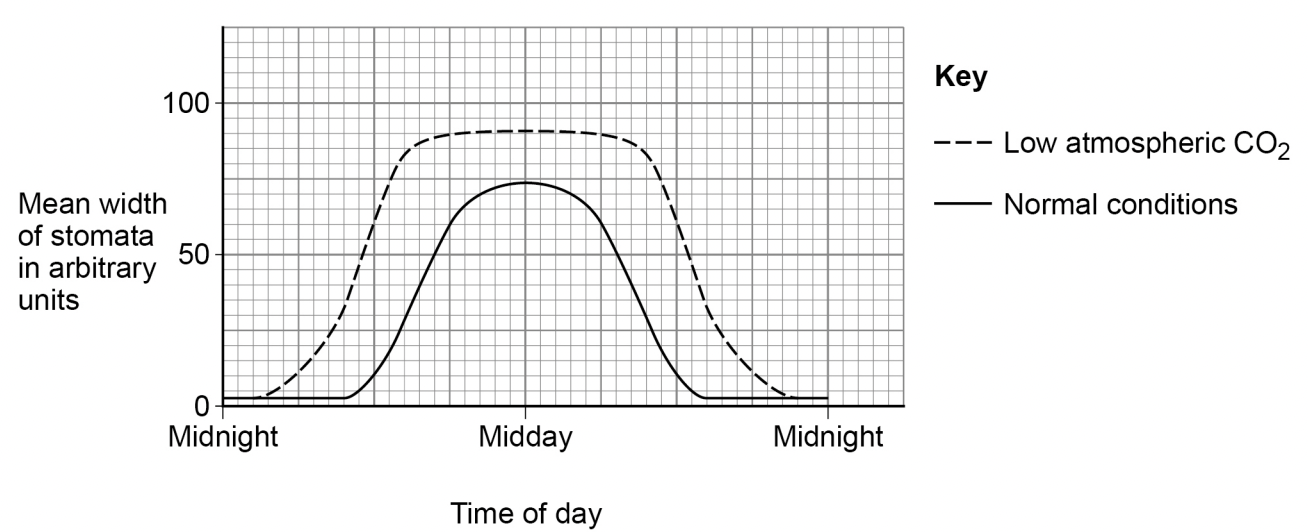
The changes in the mean width of the stomata in low atmospheric carbon dioxide are different from the changes in normal conditions.
Explain how the difference helps the plant to survive in low atmospheric carbon dioxide.
stomata are open wider and for more time
this allows plant to take in more co2 for photosynthesis
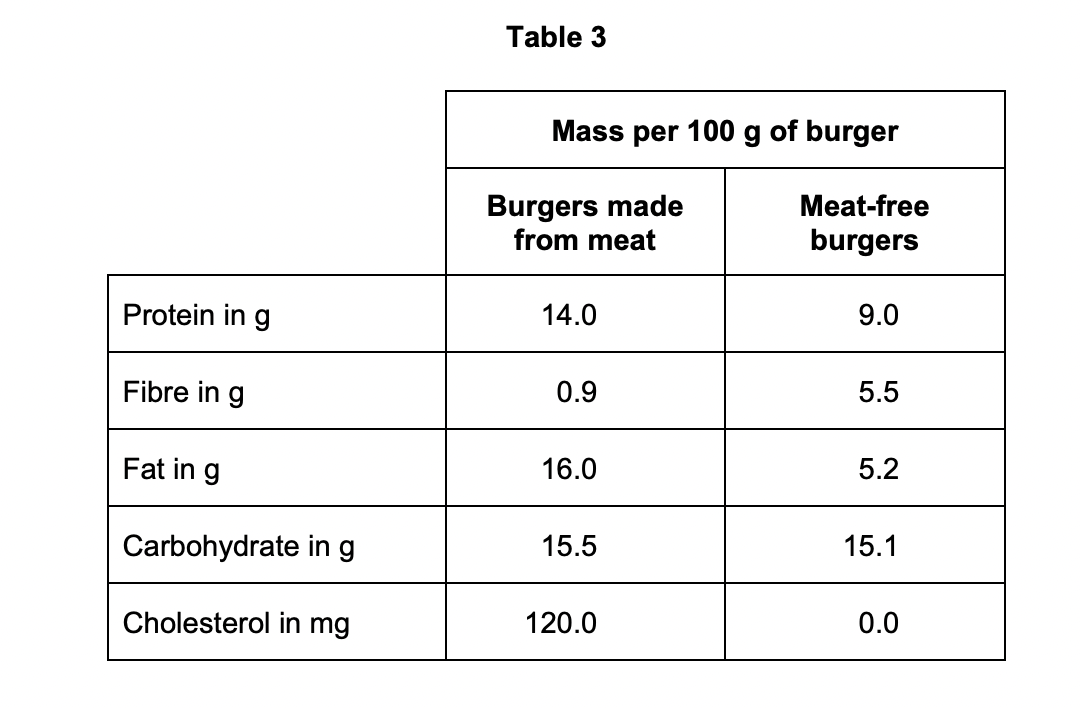
evaluate the use of burgers made from meat compared with meat free burgers in providing humans with a healthy, balanced diet.
meat free burgers contain more fibre which aids digestion
meat burgers contain more protein for growth
meat burgers contain more fat which can cause CHD
may lead to needing stent
may lead to obesity
obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes
meat burgers contain more cholesterol
cause chd
lead to needing a stent
need to take statins
both burgers have similar amounts of carbs which are good for providing energy
no info on vitamins
meat burgers require animals to be farmed which increases methane which contributes to global warming
some people won’t eat meat free burgers because they do not like fungus or prefer taste of meat
where is protein digested in the human digestive system?
stomach
which chemical could be used to test if the burgers contain protein?
biuret reagent
* so starch is not broken down
Name the three parts of the human digestive system that produce amylase.
small intestine
salivary gland
pancreas
The patient then takes one anti-clotting tablet every day.
Anti-clotting drugs:
• are very effective
• can take a week to begin working fully
• have been used for over 60 years
• cost very little to make
• do not work effectively if the patient eats certain types of food.
\
The patient must have their blood tested every few weeks to check that the anti-clotting drugs are working.
\
Evaluate the use of anti-clotting drugs in patients who have had a stent fitted.
* only have to take tablet once a day
* the drug is effective so it is less likely to get a blood clot
\
disadvantages:
* patients could forget to take the drug
* patients could still get a blood clot in the first week
Explain how amylase breaks down starch.
Answer in terms of the ‘lock and key theory’.
substrate binds to active site because the shape of the active site and substrate are complementary. a chemical reaction occurs to produce smaller molecules.
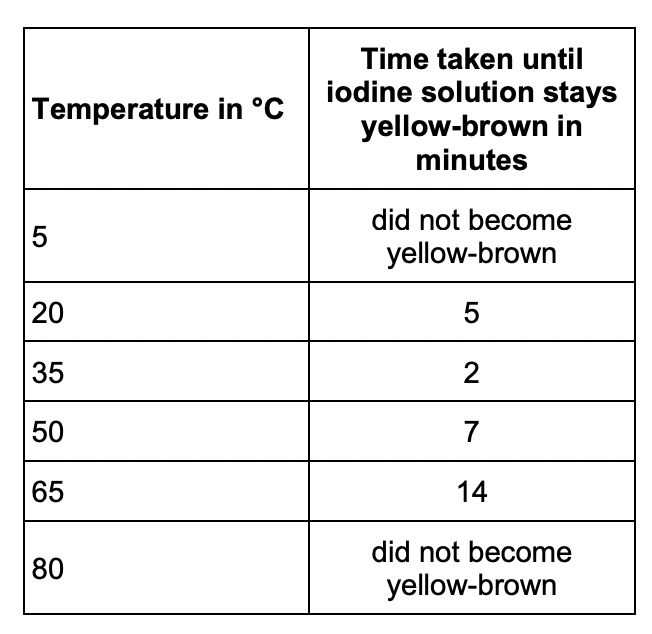
* at 80, the amylase is denatured so the starch can no longer fit
Describe how the student could extend the investigation to determine the effect of a different factor on amylase activity.
\
A person with one of these types of cancer may experience symptoms such as:
• tiredness
• frequent infections
• bleeding that will not stop after the skin is cut.
\
Explain how a very low number of blood components in the body can cause these symptoms.
* fewer rbc so less haemoglobin and therefore there is less oxygen transported around the body
* so less respiration can take place therefore less energy released for metabolic processes
\
frequent infections
* fewer wbc
* so fewer antibodies produce and so fewer pathogens killed
\
bleeding
* fewer platelets so blood does not clot as easily
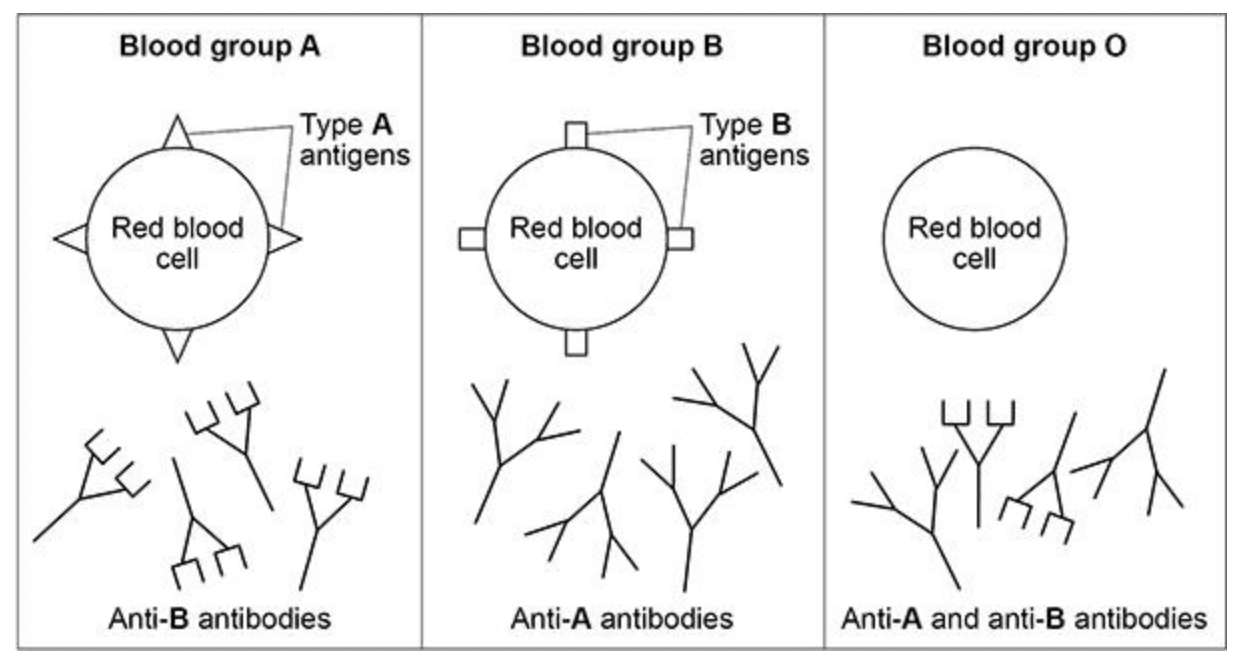
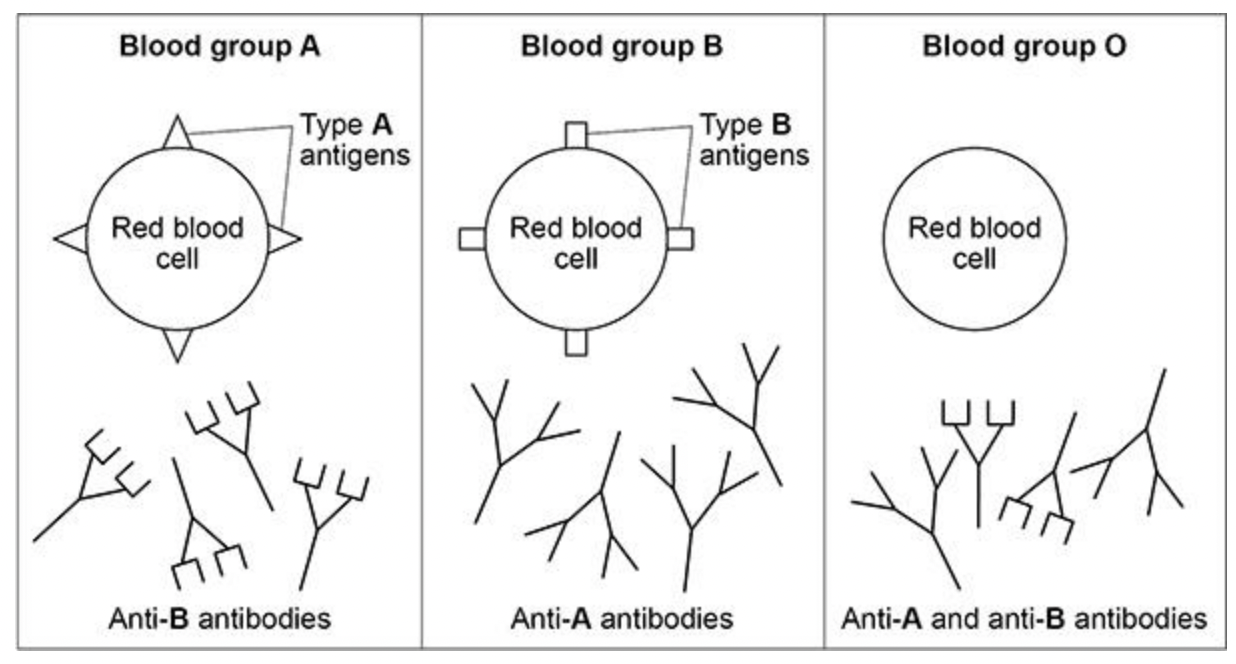
Explain why.
* so rbc clump together and block capillaries
* so cells cannot respire
Explain why this person would have difficulty digesting fat.
* so no emulsification of fat
* so smaller sa for lipase to break down fat
* pH of small intestine is not neutralised
* so lipase is not at its optimum pH to break down fat
* his breathing rate increased so more oxygen is brought to the blood and more carbon dioxide is removed
* more oxygen to muscles is needed for increased respiration to release energy for muscle contraction
* anaerobic respiration occurs due to the lack of oxygen which causes muscle fatigue
Explain how the structure of an artery is related to its function.
thick muscle walls to push blood all around the body
* the capillaries are thin which provides short diffusion path
* breathing moves air in and out to bring oxygen in and to remove carbon dioxide
* therefore maintaining a concentration gradient
* there is a large capillary network around the alveoli meaning it has good blood supply to remove oxygenated blood quickly to bring co2 to the lungs quickly
Nitrate ions need a different method of transport into the root hair cell. Explain how the nitrate ions in Figure 3 are transported into the root hair cell.
active transport because energy is needed to move particles from a lower conc to a higher conc
Which two products are formed when lipids are broken down?
fatty acids and glycerol
Use information from the diagram above in your answer.
1. enzyme binds to the substrate because they are complementary
2. substrate is broken down into products
3. products are released
Why does each different type of lipase act on only one specific type of lipid molecule?
each active site has a specific shape
Describe how the students would find out if the liquid from the leaf contained starch.
add iodine solution
it changes colour to blue from yellow
* if the colour changes from blue to yellow/green/orange/brown/red, glucose is present
* excess glucose is converted into starch
* glucose is used for respiration because there is no light to make more glucose by photosynthesis
Suggest one aspect of the survey which might reduce validity.
may change habits
Describe the effects of liver failure on the human body.
no bile made
fats not emulsified
sa of fats not increased
ph of small intestine will not be alkaline
enzymes will not work effectively
lose weight
lactic acids not broken down
accumulation of lactic acid
lactic acid is toxic
oxygen debt higher
so muscle pain
amino acids will not be broken down
not deaminated
not made into urea or not forming ammonia
if ammonia is formed, it will be toxic
accumulation of amino acids
liver does not break down other toxins
toxins accumulate
body will be poisoned
pain/jaundice/swollen liver
glycogen stores will not be formed
cannot control blood glucose
so diabetes/hyperglycemia
Which type of blood vessel contains valves?
veins
1. no risk of rejection
2. long lasting
Explain why a person with a leaking heart valve has difficulty exercising.
backflow of blood occurs
less blood leaves the heart so less oxygen is supplied to cells
less aerobic respiration
less energy released
less efficient muscle contraction
anaerobic respiration takes place
less removal of lactic acid and therefore oxygen debt occurs and causes muscle fatigue
less efficient removal of co2
Evaluate the use of mechanical replacement heart valves and biological replacement heart valves.
mechanical
longer lasting
blood clots more likely
patient has to take anti clotting medication
medication can lead to excessive bleeding
survival rate at 5 years is slightly higher
lower percentage of deaths due to heart related problems
biological
no additional medication required
ethical issues surrounding the use of animal tissue
valve may harden
more likely to need another valve
more likely to be rejected
more likely to need immunosuppressants
both
both are readily available
little wait time
Define the term double circulatory system
blood is pumped to the lungs by one side of the heart
blood is pumped to the body by the other side of the heart
Explain why having only one ventricle makes the circulatory system less efficient than having two ventricles.
oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mixes therefore less oxygen reaches the body
Explain why an axolotl may die in water with a low concentration of oxygen
concentration gradient is less steep
less oxygen diffuses into blood
less aerobic respiration occurs so less energy released
less metabolism
What is an enzyme?
speeds up reactions in living organisms and is a protein
Name two other organs in the digestive system that produce carbohydrase.
small intestine
salivary gland
Explain how pancreatic cancer may cause a person to lose weight.
reduced enzyme production
food is not broken down fully
less glucose is absorbed
less glucose available for respiration so more fat is used up in metabolism
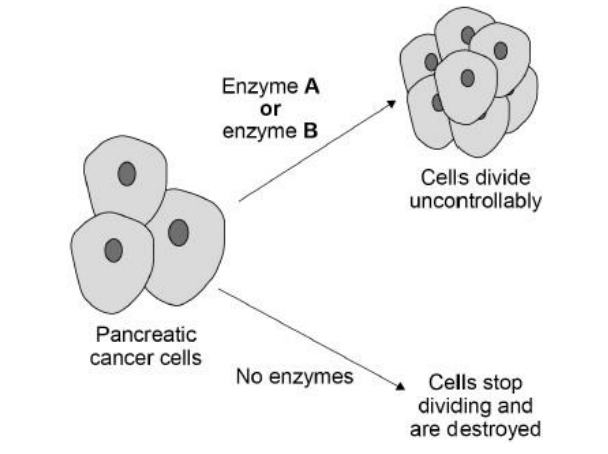
Scientists have developed a drug that inhibits enzyme A.
The drug is given to pancreatic cancer patients who have the gene mutation that stops cancer cells producing enzyme B.
The drug only targets cancer cells.
Explain why the drug can be used to treat pancreatic cancer in patients with the gene mutation. Use information from the figure above
cancer cells cannot divide
tumour does not grow
because enzyme a and b are not working
Give reasons why a placebo and a double-blind trial were used.
placebo = avoid the patients thinking they feel better with the drug
double blind trial = to avoid bias
A monoclonal antibody has been produced to treat pancreatic cancer. Explain how the monoclonal antibody works to treat pancreatic cancer
monoclonal antibody is attached to a radioactive substance
monoclonal antibody will only attach antigen on cancer cells
so radioactive substance will stop them growing
Describe how you would test a sample of food to show it contains protein. Give the reason for any safety precautions you would take.
grind up the food
add biuret reagent to food sample
protein turns solution from blue to purple
wear google to protect eyes
clean up spills immediately because biuret reagent is an irritant
suggest why blood flow through the coronary arteries is lower in people with coronary heart disease.
they are narrower
Describe how a student could test cow’s milk to show whether it contains protein and different types of carbohydrate.
biuret reagent tests for protein
add biuret reagent to milk
solution will turn from blue to lilac if positive
iodine solution tests for starch
add iodine to milk
solution will turn from orange to blue black
benedicts reagent tests for sugars
add benedicts reagent to milk and heat
solution will turn from blue to brick red if positive

Explain why the indicator in both tubes became colourless.
lipase breaks down fat into fatty acids
fatty acids lower the pH
fatty acids cause the pH to be below 10

Explain the difference in the results for the two test tubes in Table 2.
bile emulsifies fats
creates a larger sa of fat
lipase can break down fat to produce fatty acids more quickly
What is a tissue?
a group of cells with a similar function
Name the blood vessel that transports blood from the body to the right atrium.
vena cava
Describe the route taken by oxygenated blood from the lungs to the body cells.
blood travels through the pulmonary vein from the lungs
then enters the left atrium
then enters the left ventricle
the blood leaves the heart via the aorta to the body cells
Explain how the villi and the alveoli are adapted to absorb molecules into the bloodstream.
both have large sa
villi have many microvilli
alveolar walls are not flat
to maximise diffusion
both have many capillaries
to maintain the concentration gradient
both have thin walls
provide short diffusion distance
villi have many mitochondria
provide energy for active transport
cells of the villi have microvilli
further increase sa
Explain how amylase breaks down starch.
substrate fits into the active site
shape of the active site is complementary to substrate
bonds within starch are broken
The concentration of starch in the solution at 20 °C after 1 minute is different from the concentration at 40 °C after 1 minute. Explain why
starch is broken down less quickly at 20C
at 20C enzymes have less energy
Amylase is the enzyme that controls the breakdown of starch to glucose. Describe how the student could investigate the effect of pH on the breakdown of starch by amylase.
range of at least 3 pH values
keep amount of starch and amylase the same
keep temp the same using a water bath
use iodine test to make qualitative observations
observe colour changes at diff temps
do repeats each pH
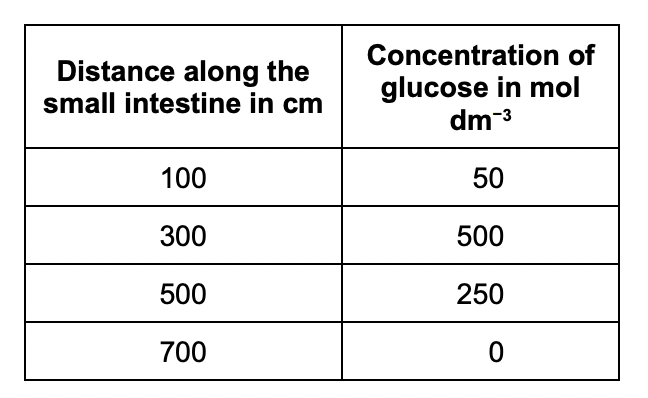
Explain why the concentration of glucose in the small intestine changes between 100 cm and 300 cm.
carbohydrates broken down by carbohydrase or amylase
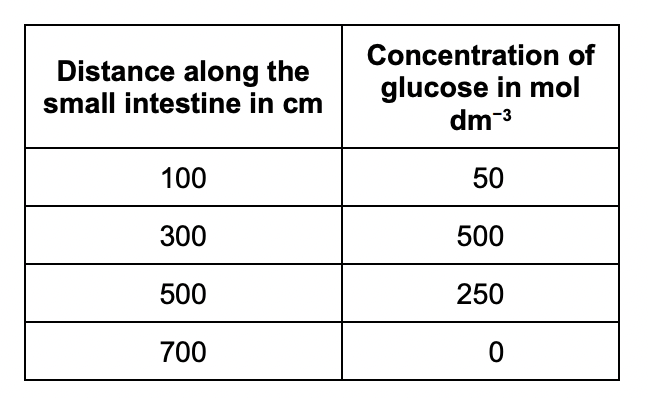
Explain why the concentration of glucose in the small intestine changes between 300 cm and 700 cm.
absorption into blood by active transport
Explain how the human circulatory system is adapted to:
• supply oxygen to the tissues
• remove waste products from tissues.
double circulatory system which means that it has higher blood pressure and a greater flow of blood o tissues
heart pumps blood to lungs in pulmonary artery so that oxygen can diffuse into blood from air in alveoli
blood returns to heart via pulmonary vein where muscles pump blood to the body via the aorta
oxygen carried by rbc which contain haemoglobin to bind oxygen and have no nucleus so there is more space to carry oxygen
thin walls allow for easy diffusion to cells
large sa of capillaries to maximise exchange
blood goes back to the heart in veins which have valves to prevent backflow
In which part of a cell will most enzymes work
cytoplasm
What is the main type of tissue in the heart wall?
muscle
Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
does not have valves
has thicker walls
A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery in the leg and blood taken from a vein in the leg. Give two differences in the composition of the blood
artery has more oxygen
artery has less co2
In your answer you should refer to materials moving upwards in a plant and to materials moving downwards in a plant.
* p is taken up by active transport, this from an area of low to high concentration
* v travels in the xylem
* m travels to the leaves
\
water
* p is taken up by osmosis, it is from an area of low to high concentration
* v travels in the xylem
* m to the leaves
* p travels in the transpiration stream
* movement replaces water as it evaporates from leaves
\
sugar:
* p is made during photosynthesis
* v travels in the phloem
* m to other parts of the plant
In your answer you should:
• give your recommendation
• use information from the table to support your recommendation by making comparisons of the two drugs.
* there are more people in studies so the data is more repeatable
* it reduces cholesterol but aspirin does not
* aspirin may cause bleeding but statins do not
* there is a smaller percentage that suffer side effects
* it is monitored by a doctor and aspirins are not