Final Marketing Exam yay!!
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what are the three competition oriented approaches
customary pricing ( selling “at its market price” aka setting an equivalent price as the rest of the product category)
Loss-Leader ( retailer uses low-ball price to drive the people into the store)
above-at- below market pricing (exactly what it sounds like - setting the price above, at, or below the market price)
what is price fixing
an illegal conspiracy among firms to set prices
what is price discrimination
the practice of giving different buyers different prices. Legal sometimes; illegal when b2b
what is deceptive pricing
misleading price deals - “bait and switch”
what is predatory pricing
lowballing with the intention of driving out the competitor. Illegal but hard to prove. often practiced by Walmart.
what are marketing channels
they consist of individuals and firms involved in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption by consumer/industrial users
what are direct/indirect marketing channels
direct: producer and buyer deal with each other directly
indirect: intermediaries perform various functions
what is B2B and B2C
business to business (shorter channel length, few buyers)
business to consumer (longer channel length, many buyers)
what is forward and backward integration
forward integration: to own an intermediary downstream towards the buyer (like if the producer owns a retail store)
backward integration: to own an upstream operation towards the producer (like when tiffany’s, a jewelry store, starting producing their own line of jewelry)
what are the three types of target market coverage
intensive distribution (the goal is to be in as many outlets as possible; often used by convenience goods)
exclusive distribution (one retailer; used by specialty goods)
selective distribution (limited # of outlets; used by shopping goods and specialty goods sometimes)
what are logistics / logistics management
trying to get the right amount of the right product to the right place at the right time
what is supply chain / supply chain management
supply chain - a sequence of firms
supply chain management - organizing and integrating information across firms in the supply chain
what is the total logistics cost concept
the goal is to reduce NET cost, not individual.
There are many different expenses in a business (transportation, warehousing, inventory, order processing, etc.). Increasing expenses in one category (like warehousing) may cause a greater decrease in expenses in another category (like transportation), thus reducing NET costs (even though an individual cost went up)
Utilities offered by retailing
time, place, form, and possession (transaction).
what are the levels of service
self service (customer does everything, like a grocery store with self checkout)
limited service (employees available to help if needed)
full service (like wedding dress shopping)
what are the types of merchandise lines
AKA the assortments of goods carried. measured by depth of product line (large selection of each type of item) and breadth of product line (wide variety of items)
specialty outlets
Category killers (dominant retailers in a market, like barnes and nobles)
what does non-store retailing mean and what are the different types of this
outside of the traditional store environment
automatic vending (vending machines. limited selection, high prices, very convenient)
online retailing (convenience, selection, price comparisons)
direct mail/catalogs (good segmentation and targeting, direct channel)
telemarking ( a $500bil business)
Direct selling (door 2 door selling, direct marketing)
what is the promotional mix
tools to inform, persuade, and reinforce
What is IMC
designing marketing communications programs that coordinate all promotional activities - advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, public relations, direct marketing, etc - to provide a consistent message across all audiences
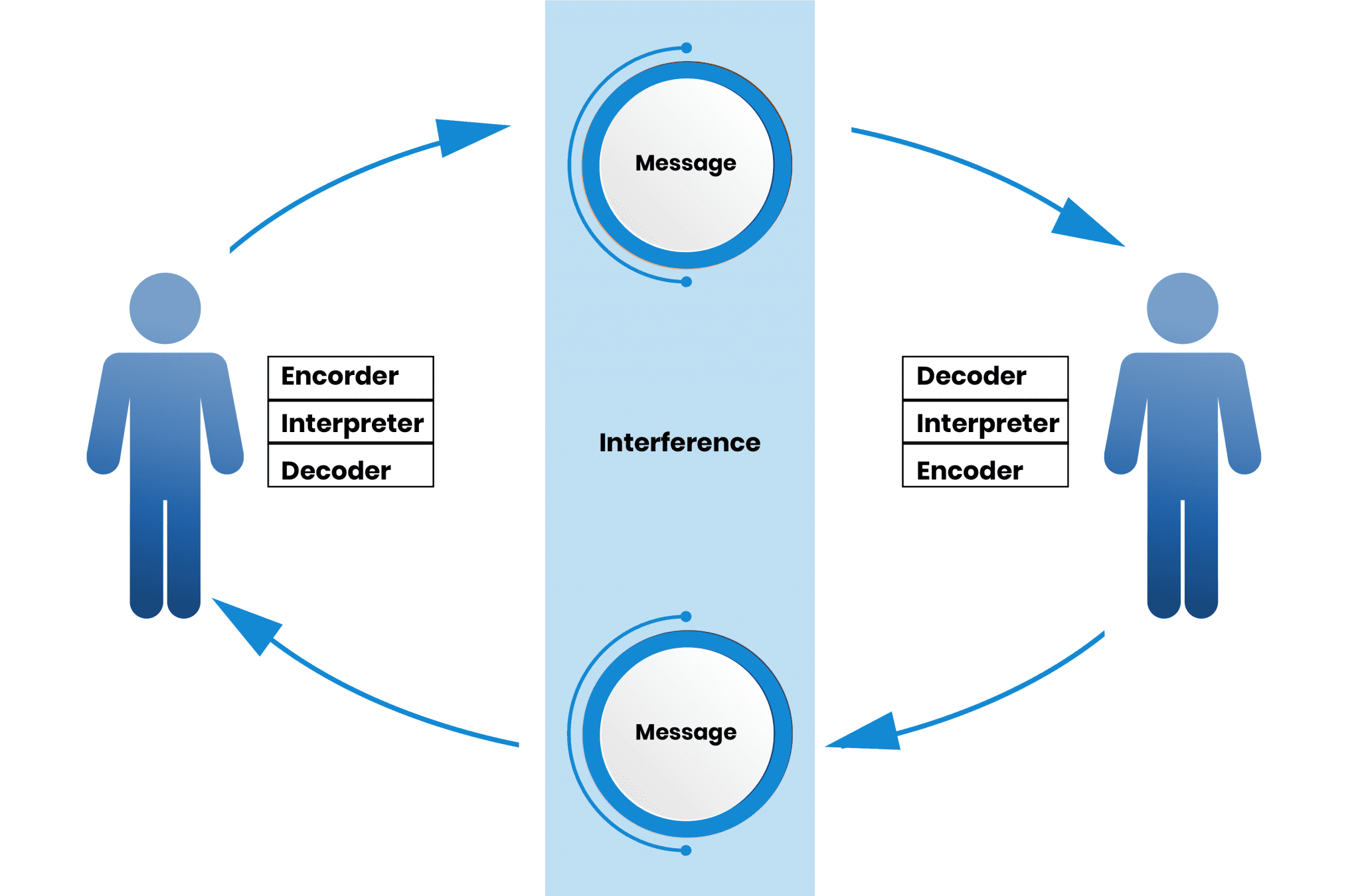
Know the communication model
source (who is conveying the information)
encoding (transforming the idea into a shareable form)
channel (means of conveying the information)
receivers (the information’s recipient)
decoding (the receiver’s interpretation)
Advertising - pros and cons
a paid form of non-personal communication by an identified sponsor. Tv, radio, magazines, newspapers, internet, outdoor, mobile
pros: efficient for reaching a lot of people
cons: high absolute costs, difficult to receive good feedback
personal selling - pros and cons
person to person communication to assist and persuade prospective buyers. flexible and highly customizable
pros: immediate feedback, persuasive, can select audience, can give complex information
cons: extremely expensive, messages may vary between salespeople
Public Relations - pros and cons
attempts to control publicity and also to foster a positive public image. lacks control over message, timing, and audience
often the most credible source in the consumer’s mind
difficult to get media cooperation
Sales promotion - pros and cons
offers an inducement to purchase - influence immediate behavior. Can be directed to consumers or the trade. Includes coupons, premiums, contests, samples, etc. reduce profits if used longterm (promotion trap)
effective at changing behavior in the short run; very flexible
easily abused, can lead to promotion wars, easily duplicated
direct marketing - pros and cons
direct mail, catalogs, email, telemarketing. directly communicate with customers to generate a response. good for direct orders, lead generation, and traffic generation.
messages can be prepared quickly; facilitates relationship with the customer
declining customer response; database management is expensive
what is social media marketing
some call it the 5th P - participation. it’s defining characteristics are web as a platform, user participation, user-generated content, and crowdsourcing. platforms are facebook, twitter (x), pinterest, instagram, snapchat, reddit, etc. can be used to increase customer engagement, brand exposure, and to direct customers to their website.
how does the product life cycle effect the marketing mix
introduction: inform, use all elements/tools to gain awareness
growth: persuade, advertising to differentiate brand, personal selling within the marketing channel
maturity: remind, advertising and sales promotion to maintain market share and customer loyalty
decline: nothing
the three product characteristics to determine when to use personal selling
complexity: does it need an explanation or demonstration
risk: more personal contact alleviates a sense of risk
ancillary services: support after the sale
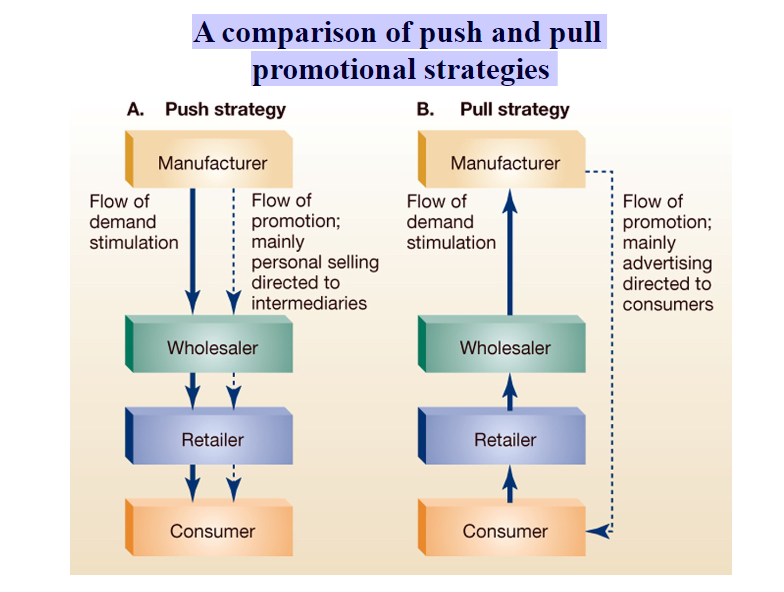
what are the channel strategies?
push strategy: focuses on channel members to stock the product; push the product toward the consumer
Pull strategy: focuses on consumers to increase demand; advertising and sales promotion (customer-oriented). (direct-2-consumer is advertising pharmaceuticals. Those “ask your doctor about…” commercials)
Multichannel marketing
simultaneously offering information, products, services, and support through two or more synchronized channels.
integrating/optimizing across all customer touchpoints
customers addressed through multiple channels tend to be more profitable
multichannel shopping increases satisfaction and loyalty