3.9 - Further Organic Analysis (Chromatography + NMR)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is the Rf value?
The ratio for how far a substance travels up the stationary phase relative to the solvent front
What are the 3 factors of Rf?
Solubility of sample in solvent
Retention of sample in the Stationary phase
Relative affinities between stationary and mobile phases
How do we observe invisible components of a sample? (2)
Spray ninhydrin to dye the samples to a purple hue to make them visible
Mix fluorescent substance with stationary phase then shine UV on the dried plate to see invisible spots
Describe the features of Column Chromatography
Mobile phase (Eluent)
Sample
Stationary phase (at the bottom)
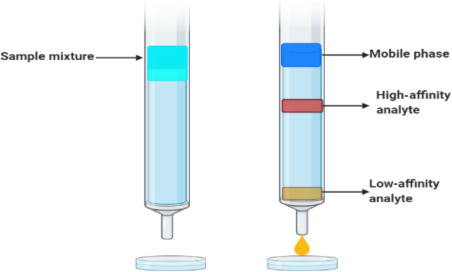
What 2 conditions are needed for the movement of the sample(s)?
Low retention
High solubility
What type of Stationary + Mobile phases are needed to a polar sample?
High solubility = Polar solvent
Low retention = Non polar stationary phase
Gas Chromatography
Gas Chromatography
What are the 3 types of Chromatography? (uses)
TLC = Identification
Column = Separation
Gas = Both
Describe a Gas Chromatography setup
Phases
A thin tube of 0.5 mm width and 100m length is coiled and heated in an oven, where the sample is fed through the tube and detected via chromatography:
Stationary phase = Powder coated with viscous liquid (like oil) in the tube
Mobile phase = Non-dissolved Inert gas (He or N)
Why is the Mobile phase an inert gas? (2 reasons)
No affinity, we only consider the affinity of samples + stationary phase:
Ensures complete separation of sample ONLY
Avoids separation interference from samples which contain various substances with different retention times
Describe the process of Gas Chromatography
Sample is vaporised + injected into the tube
The sample then separates in the tube within the oven and travels to the detector
Samples then contact the detector and forms a gas chromatogram once all samples have reached the end of the tube
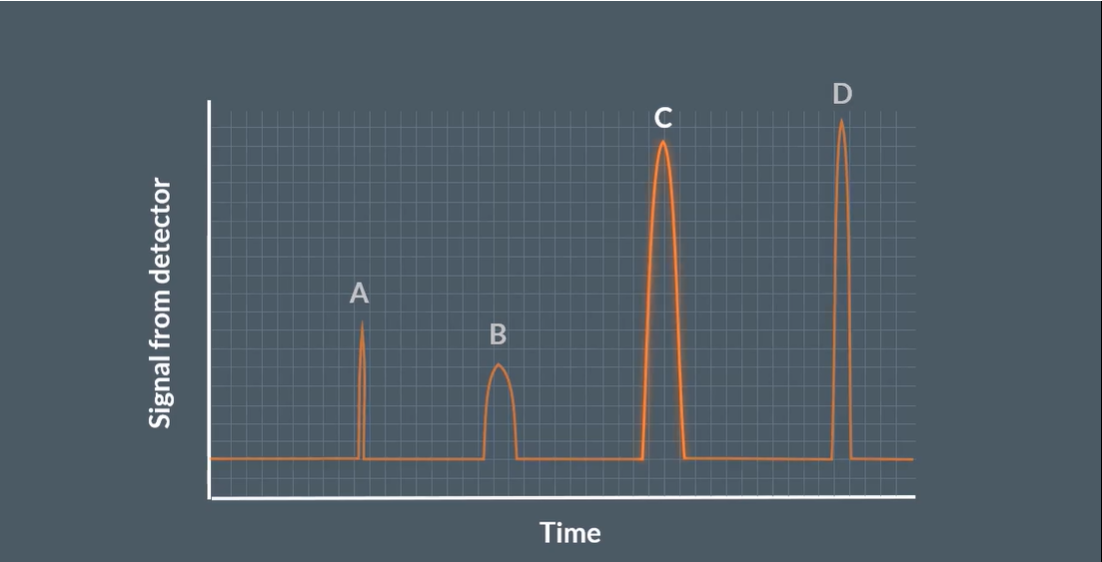
How do we determine which is the most abundant in a Gas Chromatogram?
Axis on the graph
The peak with the greatest area under it (not just height or width but a mixture of both):
x-axis = Signal from detector
y-axis = Time
What is Retention Time?
2 factors
What is this for Gas + Column methods
The time taken for how long each component was held back by the stationary phase:
Mobile phase solubility
Retention in the stationary phase
Gas = Time taken for sample(s) to reach the detector
Column = Time taken for sample(s) to elute
What is acts as the Detector for Gas chromatography?
HRMS (High-Res Mass Spectrometer)
NMR Environments
NMR Environments
What are the 2 rules when finding the Number of Carbon environments?
Look for symmetry (when single bonds are involved you can rotate then to make a molecule symmetrical)
Identical surroundings for atoms
In NMR spectra what do the following indicate:
Number of Peaks
Peak height
Peak shape
Number of Peaks = No of Carbon environments
Peak height = No relevance
Peak shape = No relevance
Define Nuclear Spin (cause)
The overall spin of a nucleus in a magnetic field due to a difference in the number of protons and neutrons, causing a difference in energy:
The difference in energy forms an energy gap in the field
What are the 2 factors of Nuclear Spin?
Magnetic field strength
Atoms bonded to the Carbons
Comment on the difference in spin between atoms in the same Carbon environment
No difference, atoms in the same Carbon environment have the same spin
What is the effect on ionising on Nuclear spin? (how)
Increases Spin = Ionising an atom increases spin, decreases shielding effect which decreases the effect of a magnetic field on nuclei
What is the relation between Charge density and Energy gap?
Charge density ∝ 1/Energy gap
Give 2 factors which increase Energy split
Increase number of identical atoms in the environment
Increase number of different electronetgative atoms
What is the physical process where we determine a substances different environments?
Cast radio waves in a magnetic field + record the frequency that interacts with the sample causing it to switch spin states from lower to higher
What is the spin of C-12?
0, since the number of protons = neutrons
How can spin be detected despite C-12 being abundant?
The few C-13 (1000s) are detected amongst the abundant C-12 (1 million), since C-13 has more protons than neutrons it interacts with radio waves to switch spin states from lower to higher
What are the Graph axis for NMR spec?
x-axis = Frequency
y-axis = Intensity
What are the differences in NMR graphs produced from:
Strong magnets
Weak magnets
Conclusion
Strong = Higher frequencies of interaction
Weak = Lower frequencies of interaction
The same sample can product different graphs from magnet strength
How do we get Weak + Strong magnets to give the same values?
We use a standard + plot x values as PPM to calculate the different in shift → making the percentage difference the same
What are Peaks measured in?
PPM (parts per million)
What standard is used for NMR?
Structure
TMS (Tetramethylsilane):
Central Silicon atom bonded to 4 methyl molecules
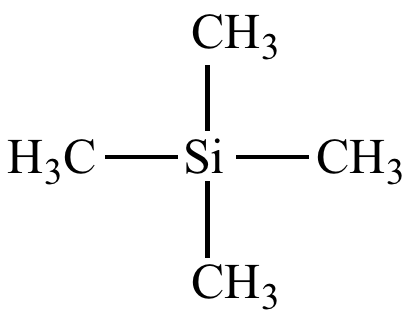
Give 5 reasons why TMS is used as a standard
Uncreative with samples
Contains one Carbon environment with a low shifted peak
Doesn’t interfere with graph due to very low shift value
Low BP → Easy to remove
Non toxic
When making a structural formula from the following info what 2 things should we remember?
Number of peaks < Carbon in the molecular formula
Branching is in the molecule
The molecule may be cyclical (ringed)
In Carbon NMR what do we look for in a molecule’s structure?
We look for “complete” units which are shown in the data booklet
***READ NOTES ON UNKNOWN MOLECULE IDENTIFICATION IN CHEM NOTES 1***
***READ NOTES ON UNKNOWN MOLECULE IDENTIFICATION IN CHEM NOTES 1***
Hydrogen NMR
Hydrogen NMR
What isotope(s) of Hydrogen are detected by NMR?
1H
How is 1H detected in Hydrogen-NMR?
When in a magnetic field, Hydrogen-1 nuclei aligns with or against the magnetic field lines giving different alignments causing an energy gap where radio waves promote nuclei to higher energy levels where the frequencies of the waves are absorbed by different hydrogen environments
Give 3 reasons why we use Hydrogen NMR
1H is abundant
Greater analysis of molecule via splitting
Less of a sample needed due to high abundance of Hydrogen-1 isotope
What are the 4 rules of Hydrogen-NMR?
Hydrogens bonded to the same carbon are in the same environment
Hydrogens bonded to carbon in the same carbon environments are in the same environment
Hydrogens bonded to Carbon in different Carbon environments are in different environments
Hydrogen bonded to O-H once is in its own environment
For Low Res Hydrogen-NMR, what are the following shown from by NMR spectograms:
No of peaks
No of Hydrogen atoms in an environment
No of peaks = No of hydrogen environments
No of H-atoms = Ratio of areas under the peaks
***PREDICTING ENVIRONMENTS, NO OF PEAK ANALYSIS, AREAS (BOTH) IN CHEM NOTES 1***
***PREDICTING ENVIRONMENTS, NO OF PEAK ANALYSIS, AREAS (BOTH) IN CHEM NOTES 1***
What is the difference between High + Low Res NMR?
High res gives lines not peaks with an area under it
What are the peak names, shapes + ratios for High Res Mass Spec?
Singlet = 1 line
Doublet = 2 lines (1:1)
Triplet = 3 lines (1:2:1)
Quartet = 4 lines (1:3:3:1)
Multiplet = 5 lines (N/A)
***IDENTIFYING SPLITTING + H-NEIGHBOURS IN NOTES 1***
***IDENTIFYING SPLITTING + H-NEIGHBOURS IN NOTES 1***
What is the n+1 rule?
Where the n= number of neighbouring H and we add 1 to get the number of peaks shown for that hydrogen environment
How many Hydrogens are in the following:
Singlet
Doublet
Triplet
Quartet
Multiplet
Singlet = 0
Doublet = 1
Triplet = 2
Quartet = 3
Multiplet = 4+
***SPLITTING WITH EQUIV H IN CHEM NOTES 1***
***SPLITTING WITH EQUIV H IN CHEM NOTES 1***
What type of Splitting do N-H and O-H observe?
Singlets
***EXAM TECH IN CHEM NOTES 1***
***EXAM TECH IN CHEM NOTES 1***
What is the Standard used in H-NMR?
How is it processed to be useable? (2)
TMS:
Dissolve the TMS in a solvent to:
1. Give clear peaks
2. Use less of the TMS
What are the 3 conditions when Using TMS in H-NMR?
Liquid
Inert + not Hydrogen atoms in sample
Solvent can have deuterium (Hydrogen-2 isotope 2H) which is non spin active