Terminology
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
A _____ _____ is an equation that contains the derivatives of one or more unknown functions/dependent variables with respect to one or more independent variables
Differential Equation
An _____ _____ _____ is a type of differential equation with only 1 independent variable
Ordinary Differential Equation
A _____ _____ _____ is a type of differential equation involving partial derivatives of two or more independent variables and functions
Partial Differential Equation
Functions are also called ____ ______
Dependent variables
_____ ______ is a way of writing derivatives like dy/dx
Leibniz Notation
_____ ______ is a way of writing derivatives like y’ or y’’
Prime Notation
____ _____ is the last way of writing derivatives by adding dots above the dependent variable
Dot Notation
_____ ______ is a way of writing partial derivatives, by adding subscripts representing the variable being differentiated
Subscript Notation
The _____ _____ _____ ______ ______ is the order of the highest derivative in the equation
Order of a differential equation
A ____ _____ ______ ______ is a differential equation with the order of 1, meaning the highest derivative present is the first derivative
First order differential equation
A ____ _____ ______ ______ is a differential equation with the order of 2, meaning the highest derivative present is the second derivative
Second order differential equation
The _____ _____ is a way of writing a first order DE, represented as M(x,y) dx + N(x,y) dy = 0
Differential Form
Assuming y is a dependent variable, the differential dy is defined in the equation:
dy = y’ dx
The ____ ______ of an ODE is F(x, y, y’, … y^n) = 0
General form
The ____ ______ of an ODE is d^n/ dx^n = f(x, y, y’,… y^n-1)
Normal Form
A ______ _____ ______ ______ is a differential equation that is linear in all dependent functions (y) and their derivatives (y’, y’’, etc.)
Linear ordinary differential equation
The image shows the _____ _____ for an ODE
Linearity Conditions
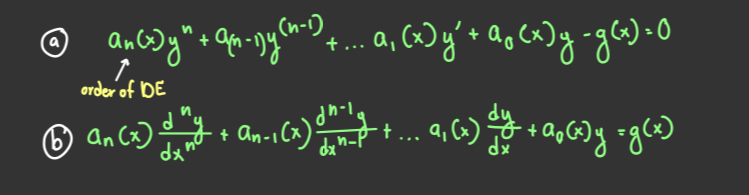
A _______ ______ _______ ______ is an ordinary differential equation that does not satisfy the linearity conditions
Nonlinear ordinary differential equation
A _____ ___ ____ ______ is a function that is continuous on an interval on all derivatives in the order of a DE, that, when substituted, reduces it to an identity
Solution to an ODE
The _____ of the solution is the interval of the independent variable in which the solution of the ODE works
Domain
The domain of the solution is also known as:
1) _____ ___ _____
2) _____ ___ ______
3) _____ ___ _______
Interval of Definition, Interval of Existence, Interval of Validity
A ____ _____ is a solution to an ODE that is identically 0 (zero) on an interval
Trivial Solution
A ______ ______ refers to the graph of a solution to an ODE
Solution Curve
An _____ ______ is a solution to an ODE in which the dependent variable is expressed only in terms of the independent variable and constants
Explicit Solution
An _____ _____ is a solution to an ODE that does not isolate the dependent variable and instead includes all variables in a mix
Implicit Solution
A ______ is a variable representing a constant in a DE, usually obtained with integration
Parameter
A _____ ______ _____ ____ ______ is a family of solutions to a DE parametrized by a single parameter and with an order of 1
One-Parameter family of solutions
An ____ _____ _____ _____ ______ is a family of solutions to a DE with order of n with n parameters
N-parameter family of solutions
A _____ ______ is a parameter given a specific numerical value
Particular Parameter
A _____ _____ is a solution to a DE with no parameters or with particular parameters (the parameters substituted by a number )
Particular Solution
A ____ _____ is a lone solution to an ODE outside of a family of solutions, regardless of the parameters used
Singular Solution
A _____ ____ ______ is a set of two or more ordinary differential equations (involving the derivatives of 2 or more unknown functions of a single independent variables) in the format:
-Dy/dt = f(t, x, y)
-dy/dt = g(t, x, y)
System of ODEs
The _____ ____ ____ _____ ____ ______ is a group of differentiable functions that satisfy the system of ODEs on the same given interval
Solution to a system of ODEs
An ____ _____ is a condition imposed on a solution to a DE at a given value
Initial Condition
An ____ _____ ____ is a problem asking you to find a solution to a DE that satisfies the Initial condition(s)
Initial value problem
A _____ _____ ______ is an initial value problem for a DE of nth order
Nth order IVP
A ____ ____ _____ is an initial value problem for a first order DE
First order IVP
A ____ ____ _____ is an initial value problem for a second order DE
Second order IVP
The _____ ___ ___ _____ _____ occurs when a function of x and y and the first partial with respect to y of this function are both continuous in a region R
Existence of a unique solution
A _____ ____ is a mathematical description of a system of phenomenon
Mathematical Model
The _____ ____ ____ _____ is the solution of a mathematical model for a system that involves time t
State of the System
A ____ ____ ____ is a chemical reaction DE whose rate is proportional to the concentration of a single reactant
First-Order Reaction
A ____ ____ _____ is a chemical reaction whose rate is dependent on one reactant squared or two separate reactants
Second-Order Reaction
Tan(a) is equivalent to _____
Dy/dx
A ____ ____ is a first order DE in normal form, or in the format dy/dx = f(x,y)
Slope Function
A slope function is also known as a ____ _____
Rate function
A ____ _____ is a line representing the slope magnitude at a specific point of a solution curve
Linear element
A ____ _____ or _____ _____ is a graphical representation of slopes at specified points using lineal elements
Slope field, direction field
An _____ ____ ____ ______ is an ODE of first order in which the independent variable does not appear explicitly
Autonomous 1st order ODE
____ _____ are values of the dependent variable y that make an autonomous function [ dy/dx = f(y)] equal 0
Critical Points
A ____ _____ is a critical point of an AUTONOMOUS DE, equivalent to a constant and a solution to the ODE
Constant solution
An _____ _____ is a critical point of an AUTONOMOUS 1ST ORDER ODE, equivalent to a constant and a solution to the ODE
Equilibrium Solution
A ____ ____ _____ _____ is a graphical representation of the trajectory of a dependent variable in an autonomous function, making the dependent variable the axis
One dimensional phase portrait
A _____ ____ is the vertical line in the phase portrait representing the dependent variable
Phase line
A _____ _____ is a function that is either always increasing or always decreasing
Monotonic Function
If a region for y of an autonomous DE is _____ ______ then it has a critical point that bounds it from above only
Bounded above
A ____ _____ is a region of y in an autonomous DE that is bounded by above and below
Bounded region