StemUp: AQA A level Biology 3.6.3 Skeletal muscles
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is the mechanism in which muscles work? (3)
- Act in antagonistic pairs
- Where one will contract whilst other relaxes
- Against an incompressible skeleton
What is the overview of the structure of skeletal muscles? (6)
Skeletal muscles -> Bundle of fibers -> Muscle Fiber -> Myofibrils -> Sarcomeres -> Actin and Myosin
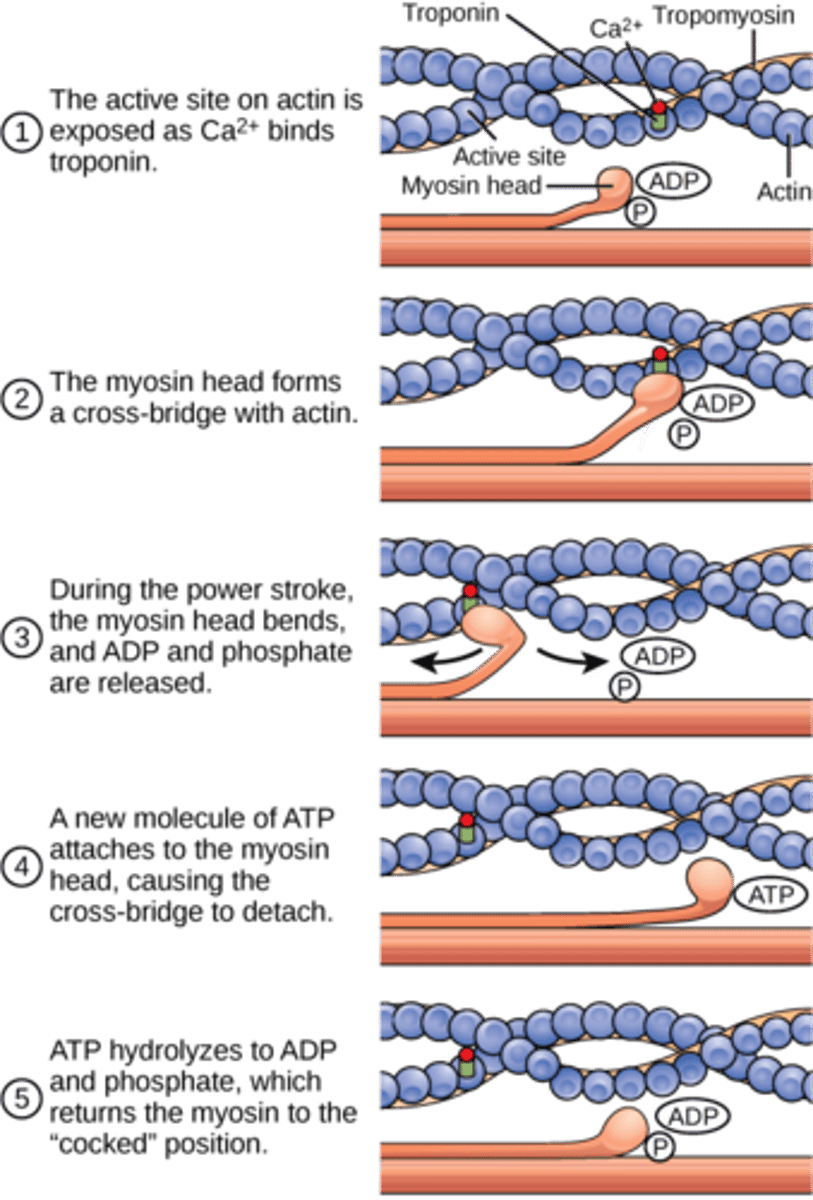
Draw a diagram to showcase a summary of myofibril contraction (6)
What is actin? (1)
Thin filaments (proteins) that are involved in myofibril contraction
What is the role of actin in myofibril contraction? (2)
- They provide the binding sites for myosin heads to bind
- Which enables the formation of actin-myosin cross-bridges
What is myosin? (1)
Thick filaments with moveable heads
What is the role of myosin in myofibril contraction? (4)
- Myosin heads attach to the binding sites on actin
- This enables the formation of actin-myosin cross-bridges
- Myosin heads move, pulling actin along
- They then detach from the binding site and moves to original position
Where are calcium ions released from during myofibril contraction? (1)
From the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is the role of calcium ions in myofibril contraction? (6)
1. Binds to a protein that is attached to tropomyosin on the actin filament
2. This causes the protein to change shape
3. This changes the position of tropomyosin on actin
4. Which exposes the myosin binding site
5. So that muscle contraction can occur
6. This activated ATP hydrolase to release energy
What is the role of ATP in myofibril contraction? (5)
1. ATP binds to bound myosin head and in which it gets hydrolysed
3. This releases energy for the myosin head bending
4. This causes myosin head to detach and reattach further along
5. ATP also provides energy for calcium ions to be actively transported back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is the collective role of calcium ions and tropomyosin in the cycle of actin-myosin cross-bridge formation? (2)
1. Before contraction, they cover the myosin binding sites on actin molecules
2. This prevents myosin heads from binding
3. Calcium ions cause tropomyosin proteins to change position on actin filaments
What is the role of phosphocreatine in muscle contraction? (3)
- Releases high energy phosphates
- To recycle unbound ATP
- As the reformation of ATP requires phosphate molecules
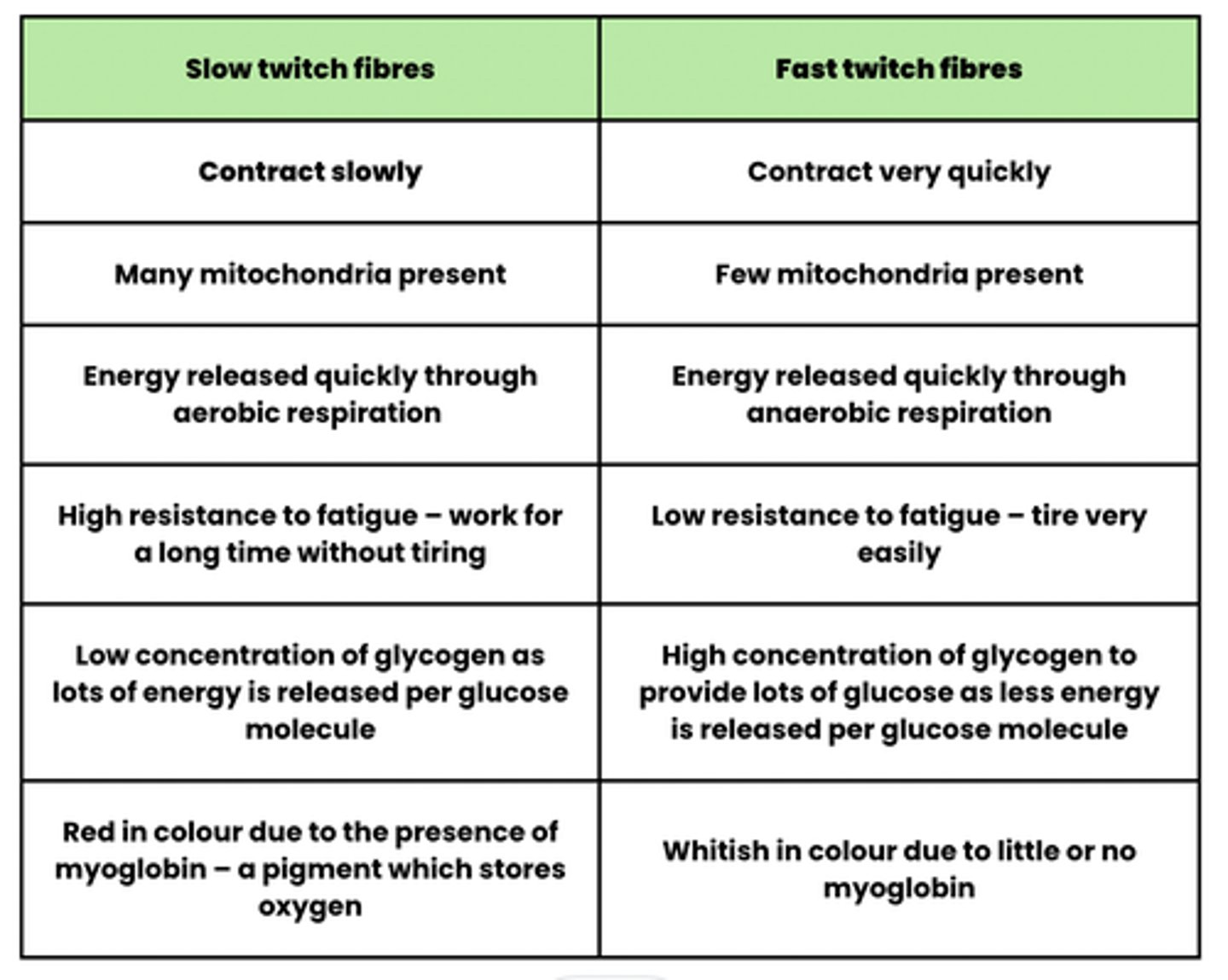
Compare slow vs fast twitch fibers (10)