Digital Addiction and Internet Use Disorders Overview
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
What is Problematic Internet Use (PIU)?
A global social issue characterized by an inability to control one's Internet use, leading to negative consequences in daily life.
Why is the definition and diagnosis of PIU unclear?
There are no widely accepted diagnostic criteria, and it is not included in official diagnostic systems like the DSM-V.
What factors may contribute to the development of PIU?
Genetic, personality, and self-regulation factors.
What are some potential treatments for PIU?
Pharmacological approaches like Escitalopram and Naltrexone, and psychotherapeutic approaches such as cognitive behavior therapy.
What self-report instruments are used to assess PIU?
The Internet Addiction Test and Young's Diagnostic Questionnaire.
What is the prevalence rate of PIU in the general population?
Rates range from 0.7% to 1.0%.
In which populations are higher rates of PIU found?
Adolescents and international university student samples.
What psychiatric disorders are often comorbid with PIU?
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), depression, problem gambling, social anxiety disorder, and substance use disorders.
What pharmacological treatments have shown effectiveness for PIU?
Escitalopram, Naltrexone, and Methylphenidate.
What psychotherapeutic approach has shown preliminary evidence of effectiveness for PIU?
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT).
What is the relationship between psychiatric disorders and PIU?
Comorbid psychiatric disorders may cause or exacerbate PIU.
What is Nomophobia?
The fear of being without a mobile phone or being unable to use it.
What is Internet Gaming Disorder?
Characterized by persistent and recurrent use of the internet to engage in games leading to significant daily impairment.
What is the Cognitive Behavioural Model in relation to PIU?
It suggests that problematic internet use is the result of maladaptive thoughts and behaviours.
What are the two types of Problematic Internet Use?
Generalized (excessive emailing, etc.) and Specific (gaming, social media, porn, etc.).
What is the I-PACE model?
A theoretical framework used to understand the factors influencing Internet use and addiction.
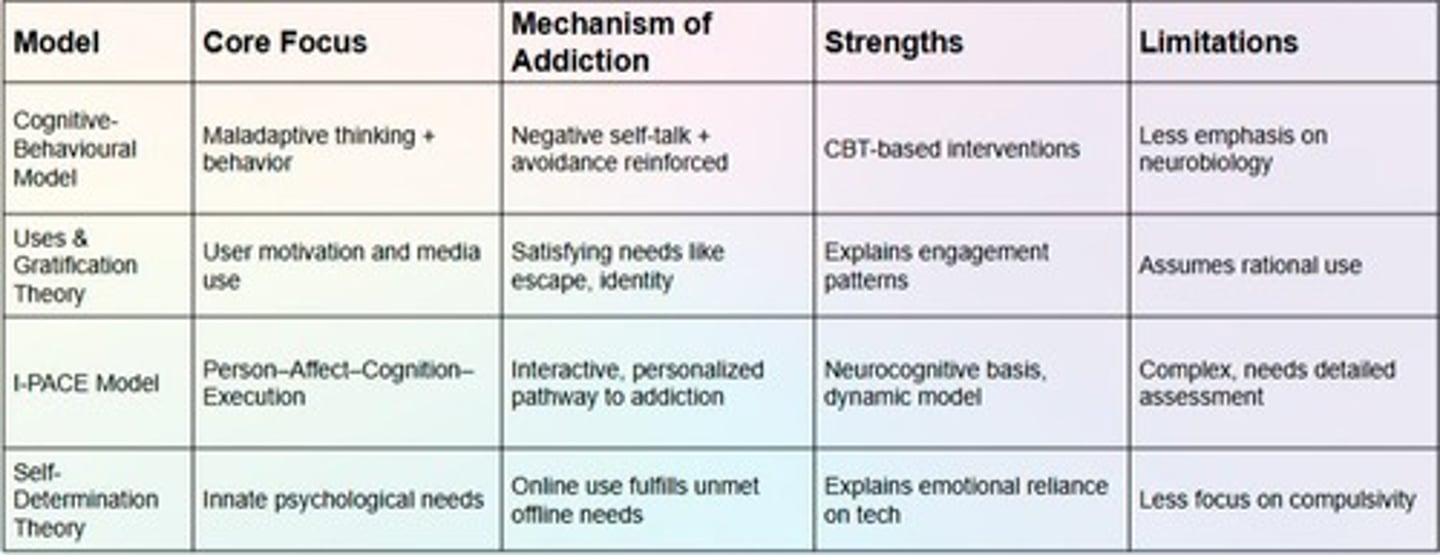
What does the Uses and Gratifications Theory suggest?
It posits that individuals use media to fulfill specific needs and desires.
What is the Self-Determination Theory?
A theory that focuses on the motivation behind choices that people make without external influence.
What are some psychological effects of Internet addiction?
Associations with various psychiatric symptoms, including ADHD, depression, and social phobia.
Who are some researchers that have investigated Internet addiction?
Young, Yen, Spada, Widyanto, Griffiths, and Yau.
What is the significance of further research on Internet addiction?
To clarify the effects on psychological functioning, mental health, and well-being.
What is the main concern regarding excessive and compulsive use of digital technologies?
It leads to impairments in daily functioning.
What is the role of comorbidity in treating PIU?
Treatment should address comorbid psychiatric disorders as they may exacerbate PIU.
What are the two types of causes distinguished in models of digital addiction?
Distal cause (e.g., depression, anxiety) and proximal cause (e.g., cognitive distortions).
What are some examples of cognitive distortions related to digital addiction?
Examples include 'I can only make friends online' and 'People like me better online than in person.'
What are maladaptive cognitions?
Thought patterns such as low self-esteem that can contribute to digital addiction.
What is a reinforcement loop in the context of digital addiction?
It involves negative reinforcement (removing something bad) and positive reinforcement (adding something positive, like likes and comments).
How does reinforcement explain differing levels of internet addiction among individuals?
Not everyone is addicted to the internet; some use it as a coping mechanism.
What does Uses and Gratification Theory focus on?
It examines why individuals actively seek out specific media to satisfy needs such as entertainment and escape.
What are the five main psychological and social needs identified in Uses and Gratification Theory?
Cognitive (info seeking), affective (emotional satisfaction), personal identity (self-reflection), social (connection), and escapism (diversion).
What is a criticism of Uses and Gratification Theory?
It does not address long-term consequences or compulsivity and assumes actions are rational and goal-directed.
What does the I-PACE model explain?
It explains how the interaction of a person affects cognitive execution and the development of digital addictions over time.
What are the key components of the I-PACE model?
Person (traits like impulsivity), affect (mood states), cognition (biased expectations), and executive functions (inhibitory control).
How does Self-Determination Theory relate to digital addiction?
It emphasizes autonomy, competence, and relatedness in motivation, which can lead to seeking fulfillment through digital means.
What is autonomy in the context of Self-Determination Theory?
Feeling in control of one's actions, such as having the freedom to choose content online.
What is competence as described in Self-Determination Theory?
Feeling effective and capable, often measured by feedback and achievements in digital contexts.
What is relatedness in Self-Determination Theory?
Feeling connected to others, which can be fulfilled through digital interactions like likes and messages.
What is a criticism of Self-Determination Theory?
It focuses on motivation rather than compulsion and does not account for neurological and behavioral dependence.
What are some examples of types of digital addictions?
Pornography addiction, cybersex addiction, online shopping addiction, information overload, internet gaming disorder, social media addiction, smartphone addiction, online gambling disorder, and streaming/content-binging addiction.
What is generalized problematic Internet use?
An overarching pattern of excessive or maladaptive internet use that interferes with everyday life.
What psychological frameworks are associated with generalized problematic Internet use?
Cognitive behavioral model and social compensation hypothesis.
What comorbidities are often associated with digital addiction?
Anxiety, depression, and ADHD.
What is the estimated prevalence of digital addiction worldwide?
Around 6-7%, with higher rates in Middle Eastern and Asian countries.
What are some diagnostic criteria for Internet Gaming Disorder?
Continued excessive use despite problems, deceiving others about gaming, and gaming to escape negative moods.
What is the DSM-5 criteria for gaming disorder?
Five of the following symptoms must be present over 12 months: preoccupation with gaming, withdrawal symptoms, tolerance, unsuccessful attempts to control gaming, and loss of interest in other activities.
What percentage of the global population is affected by digital addictions?
About 2.5-3% worldwide, with rates varying from 0.3% to 14.9% across studies.
What are the core features of social media addiction?
Mood modification, salience, tolerance, withdrawal, conflict, and relapse.
What psychological mechanisms contribute to social media addiction?
FOMO (fear of missing out), variable ratio reinforcement, social comparison, and validation seeking.
What is the prevalence of social media addiction globally?
Approximately 24% are affected, highest in Asia (31%) and lowest in Western/Northern Europe (8%). Among university students, it's around 18%.
What are key indicators of smartphone addiction?
Phantom vibration syndrome, nomophobia (fear of not having a phone), sleep disturbances, and distracted behavior.
What psychological mechanisms are associated with smartphone addiction?
Instant gratification, attachment theory, and conditioned habits.
What is the prevalence of smartphone addiction worldwide?
Around 28%, with severity measured by scales like SAS (mean score ~90) or SAS-Short Version (mean score ~30).
What defines online gambling disorder?
Compulsive engagement with digital gambling platforms resulting in financial loss, emotional distress, and impaired functioning.
What psychological mechanisms are involved in online gambling disorder?
Intermittent reinforcement, illusion of control, escapism, mood regulation, and ties to impulsivity, depression, and substance use.
What unique risks are associated with online gambling?
24/7 access, anonymity, fast-paced betting, and digital payments that reduce the perceived loss.
What is the prevalence of problematic online gambling among adolescents?
0.77% to 57.5% show some problematic online gambling, with about 0.89% to 1% having an online gambling disorder.
What characterizes streaming/content binging addiction?
Excessive viewing of digital content in a single session or habitually consuming digital videos negatively impacting daily life.
What psychological mechanisms contribute to streaming/content binging addiction?
Autoplay features, infinite scroll, narrative transportation, escapism, procrastination, and habit loops.
What percentage of people binge-watch TV?
About 72% binge-watch, with 28% reporting problematic use, which increased significantly during COVID-19.
What is the prevalence of problematic video game streaming?
Around 6% report problematic video game streaming.
What defines pornography addiction?
Compulsive and problematic use of online porn material leading to impairment in daily life, relationships, or emotional well-being.
What psychological mechanisms are involved in pornography addiction?
Operant conditioning, mood regulation, and cue reactivity.
What is the prevalence of problematic internet sexual use?
Around 5% of women and 13% of men report some problems; 2% of women and 5% of men report serious problems.
What distinguishes cybersex addiction from pornography addiction?
Cybersex addiction involves interactive and relational aspects, including emotional intimacy and role-playing.
What types of activities are included in cybersex addiction?
Compulsive use of online sexual activities such as erotic chat rooms, webcam interactions, virtual sex, and sexting.
What is cybersex addiction?
Compulsive use of online sexual activities such as erotic chat rooms, webcam interactions, virtual sex, and sexting, often detrimental to personal, social, or professional life.
How does cybersex addiction differ from porn addiction?
Cybersex addiction is more interactive and relational, involving emotional intimacy and role-playing aspects.
What are some associated risks with cybersex addiction?
Relationship conflict, risky sexual behavior, and legal and ethical issues.
What percentage of American college students show signs of risky cybersex addiction?
About 10%.
What is onimania?
A term referring to compulsive online purchasing behaviors, used as a cue to remember online shopping addiction.
What psychological drivers contribute to online shopping addiction?
Instant gratification, cognitive distortions, and advertising algorithms.
What is the prevalence of compulsive online buying among Paris university students?
Around 16%.
What is doomscrolling?
Compulsive consumption of negative or distressing online news, often leading to increased anxiety, stress, and insomnia.
What psychological mechanisms contribute to doomscrolling?
Negativity bias, fear of missing out (FOMO), and anxiety reinforcement loops.
What contextual triggers can lead to information overload or doomscrolling?
Health crises, political instability, war, and natural disasters.
What screening tools are used for assessing digital addiction?
Internet addiction test, smartphone addiction scale, mobile phone problem use questionnaire, binge-watching engagement and symptoms questionnaire, Bergan social media addiction scale, and social media disorder scale.
What are some mental health impacts of digital addiction?
Increased symptoms of depression, anxiety disorders, ADHD, and OCD.
How does excessive social media use correlate with depression?
It is associated with social comparison, sleep deprivation, and reduced in-person socialization.
What physical health impacts are associated with digital addiction?
Sleep disturbances, visual health issues, musculoskeletal problems, and a sedentary lifestyle.
What academic impairments can result from digital addiction?
Lower GPA, increased absenteeism, and reduced study time.
What occupational impairments can result from digital addiction?
Impaired concentration, impaired task completion, and reduced cognitive efficiency.
What social impacts can digital addiction have?
Decreased face-to-face interactions, relationship conflict, feelings of loneliness, and the 'alone-together' phenomenon.
What neurobiological findings are associated with digital addiction?
Similar brain patterns to those with substance addictions, including increased dopamine and reduced gray matter.
What are some prevention and treatment strategies for digital addiction?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, digital detoxes, pharmacological interventions, psychoeducational and family therapy, and harm reduction strategies.
What is the 'alone-together' phenomenon?
A concept by Sherry Turkle (2011) describing how people can feel lonely while being together due to digital distractions.
What is the relationship between excessive digital use and ADHD?
Excessive digital use worsens attention problems and individuals with ADHD are more susceptible to digital addictions.
What are some visual health issues caused by digital addiction?
Eyestrain, dry eyes, and computer vision syndrome.
What musculoskeletal problems can arise from excessive screen time?
Tech neck, shoulder tension, and lower back pain.