Unit 4: Political Patterns and Processes (copy)
1/92
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Country
An identifiable land area.
Nation
A population with a single culture, also known as a culture group.
State
A population under a single government, implying sovereign territory.
Nation-state
A single culture under a single government, sometimes representing a singular contemporary culture.
Sovereignty
Full independence from outside control, holding territory, and having international recognition.
Multi-national states
Made up of different nations represented by various culture groups.
Nationalism
Derives from an existing culture group desiring political representation or independence.
Stateless nations
Culture groups not included or allowed a share in the state political process.
Federal states & confederations
Provide military protection, administer foreign diplomacy, and regulate trade.
Microstates
Sovereign states with a small size but holding the same position as larger states.
Autonomous regions
Parts of nations granted freedom from central authority for various reasons.
Semi-autonomous regions
Have the same freedom as autonomous regions but to a lesser degree.
Supranationalism
Two or more sovereign states aligned together for a common purpose.
Supranational organizations
Formed for trade alliances, military cooperation, and diplomacy.
Territoriality
The expression of political control over space.
Citizenship
The legal identity of a person based on the state where they were born or naturalized.
Political boundaries
Expressions of political control that must be definable and clear.
Enclave
A minority culture group concentrated inside a country dominated by a different, larger culture group.
Exclave
A fragmented piece of sovereign territory separated by land from the main part of the state's territory.
UNCLOS
United Nations Conference on the Law of the Seas, standardizing oceanic boundaries.
Territorial sea
Sovereign territory from shore out to the 12-nautical-mile limit.
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
Exclusive economic rights from shore out to the 200-nautical-mile limit.
Physical border
Natural boundaries such as rivers, lakes, oceans, mountains, or deserts.
Cultural border
Estimated boundaries between nations, ethnic groups, or tribes.
Geometric border
Boundaries surveyed mostly along lines of latitude and longitude.
Frontier
Open and undefined territory.
State morphology
The shape of a country impacting its society and external relations.
Annexation
Addition of territory as a result of a land purchase or when a territorical claim is extended through incorporation
Capitals
Seat of government where political power is centered.
Suffrage
Voting rights (which have varied historically from state to state).
Gerrymandering
Irregularly shaped districts designed to manipulate voting outcomes.
types:
cracking : dispersing a group into several districts to prevent a majority
packing : combining like-minded voters into one district so other districts aren’t affected
stacking : diluting a minority-populated district with majority populations
hijacking : redrawing 2 districts in order to force 2 elected reps of the same party to run against each other
kidnapping : moving an area where an elected representative has support to an area without support
Feudalism
Political economy with aristocracy controlling land and wealth, and peasants working the land.
Absolute monarchy
Supreme aristocrat serving as both head of state and head of government.
Constitutional monarchy
A form of government where the supreme aristocrat remains head of state, but the leader of the elected parliament is the head of government.
Prime minister (premier)
The leader of the elected parliament who appoints senior members of parliament to be ministers or secretaries of executive-branch departments.
Free-market democracies
Countries with elected-representative parliamentary systems, commonwealth countries, and other constitutional monarchies or republics that rely upon balancing the relationship between the elected-representative government, its citizens, and business interests.
Republics
Governments free of aristocracy or monarchical control and are fully under the control of the "common" people, as opposed to hereditary monarchy.
Separation of powers
Where the executive, legislative, and judicial branches of government are held by separate groups of people that keep each other in check.
Marxism
Karl Marx's political-economic theories aimed at creating a class-free society with no inequalities in terms of wealth or power.
Communism
A political-economic system where the state owns all land and industry, and the government directs economic productivity, aiming for equal distribution of wealth.
Planned economy
An economy that does not rely on supply and demand like capitalism, but rather the central government calculates the economic needs and sets quotas for production.
Centripetal forces
Factors that hold together the social and political fabric of the state.
Centrifugal forces
Factors that tear apart the social and political fabric of the state.
Balkanization
The political landscape going from a larger state to several smaller states.
Neocolonialism
A contemporary form of colonialism based on economic pressure rather than political control.
Buffer states
Lands that protect hostile countries by creating a surrounding buffer of sympathetic countries.
Terrorism
Planned violent attacks on people and places to provoke fear and cause a change in government policy.
State terrorism
When governments use violence and intimidation to control their own people.
Primary Commodity of Conflict
The resource that countries are willing to fight over.
Definitional Dispute
When border treaties are interpreted two different ways by states.
Locational Dispute
Dispute caused by movement of a natural border.
Operational Dispute
When borders are agreed on but passage across the border is a problem.
Allocational Dispute
When a dispute is caused by a resource lying directly on the border accessible by both sides.
Antecedent Boundary
created before heavy development of the cultural landscape
ex. boundary of the pyranees mountains established between spain and france
based off landforms
Relic Boundary
Former political border that no longer serves as a boundary due to changes in political or territorial divisions.
Subsequent Boundary
Boundary that is established after the settlement of an area, often resulting from political or social changes.
drawn to accommodate religious, ethnic, linguistic, or economic differences
changes as cultural landscape changes
drawn to accomodate developments due to a certain event
ex. Yugoslavia was separated into different states because of political and economic unrest
Superimposed Boundary
Boundary created by outside forces, often disregarding existing cultural or ethnic divisions.
Delimitation Process
Borders are put on the map
Demarcation Process
Markers are placed on the ground to show where borders lie.
Expatriate Population
Citizens living outside of their borders.
Free-trade union
No taxes charged on goods and services flowing between member states.
Open-border policy
No border-control between member states.
multistate nations
when a nation has a state of its own but stretches across borrs of other states
berlin conference
representatives from europe met to create claims to form state boundaries in africa
boundaries showed little regard to the ethno-linguistic, cultural, and political boundaries already existing
the cold war
period of diplomatic, political, and military rivalry between the USA and USSR
satellite states
state dominated by another politcally and economially
devolution
when one or more regions are given increased autonomy by the central political unit
imperialism
broader concept that includes a variety of ways of influencing another country or group of people by direct conquest, economic control, or cultural dominance
consequent boundary
a type of subsequent boundary that takes into account already existing cultural or physical landscapes
geometric boundary
a straight line or arc drawn by people that does not follow any physical feature
irredentism
A political movement seeking to reclaim and unify a territory inhabited by people who share a common history, culture, or ethnicity.
operational/functional boundary dispute
disagreements on how a boundary functions
allocational/resource boundary dispute
when a boundary separates natural resources that may be used by both countries
shatterbelt
a place located between two very different and contentious regions
under constant stress
may face instability or fragmentation
united nations convention on the law of the sea (unclos)
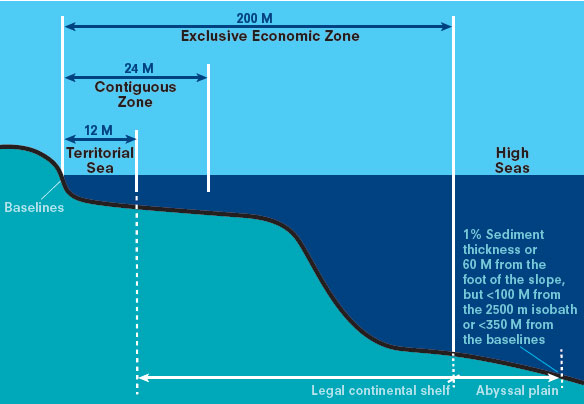
territorial sea-
extends up to 12 nautical miles
commercial vessels may pass
noncommercial vessels may be challenged
exclusive economic zones (EEZs)
sea zone over which a state has special rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources
coastal states can explore, extract minerals, and manage natural resources up to 200 nautical miles
contiguous zone
coastal states have limited sovereignty for up to 24 nautical miles where they can enforce laws on customs, immigration, and sanitation
high seas
water beyond any country’s eez that is open to all states
small island developing states (sids)
control nearly 30% of all oceans and seas
EEZ is much larger than their landmass
200-mile eez is very valuable
demarcated boundary
identified by physical objects placed on the landscape, may be as simple as a sign or complex as a set of fences and walls
delimited boundary
drawn on a map by a cartographer to show the limits of a space
defined boundary
established by a legal document, such as a treaty
militarized boundary
heavily guarded and discourages crossing
open boundary
unguarded and easy to cross
redistricting
state committees/legislatures redraw district boundaries so that each district contains roughly the same # of ppl
electorate
ppl who are eligible to vote
ethnic separatism
advocacy of full political separation from the larger group along cultural, ethnic, tribal, or governmental lines
ethnic cleansing
policy designed by one religious/ethnic group to violently remove another ethnic/religious group from certain geography
federal states
power is shared between the central govt and regional govts
can offer more support for minority groups and react quicker
decisions are made at the local and national level
unitary states
power is located in central or national government (little power is given to regional and local governments)
hosts a national identity
certain cultural groups may not be a part of decisionmaking
most of these states are smaller and are more homogenous (nation-state)
causes of devolution
physical geography
ethnic separatism
ethnic cleansing
terrorism
economic/social problems
irredentism
democratization
a process through which a political regime becomes more democratic