8.1 Human population dynamics
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Fertility rate
The number of births per thousand women of child beraring age.
Crude birth rate (CBR)
The number of births per thousand individuals in a population per year.
Crude death rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per thousand individuals in a population per year
Natural increase rate
The rate of human growth expressed as a percentage change per year.
Natural increase rate
(Crude birth rate - crude death rate) / 10
Doubling time (DT)
The time in years that it takes for a population to double in size
Natural increase rate of 1% will double a population in 70 years.
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children each woman has over her lifetime.
Human Development Index (HDI)
A measure of the well being of a country, measuring health, wealth and education.
Malthusian theory
The theory that population growth is potentially exponential. While food production is linear, as population growth will be exponential, we will run out of food. This would limit maximum human population.
Limited due to the various other reasons why a shortage of food may occur such as the ppor distribution of resources.
Bosserup’s theory
A belief that an increase in population woudl stimulate technologists to increase food production and thus allow for food production to be sustained in relation to the population.
Limited in the fact that overpulation can lead to unsuitable farming practices
Overpopulation country
When the population is aboe the optimum population for the highest economic return per capita.
Reasons for large families
High infant and childhood mortality (insurance to reach adulthood), security in old age, economic asset, status of women, unavailability of contraceptives.
Ways to reduce family size
Provide education, improve health, make contraceptives available, enhance income, increase resource management.
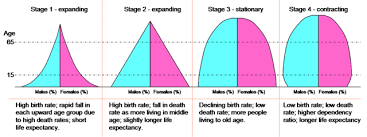
Demographic transition model (DTM)
The pattern of decline in mortality and fertility of a country as a result of social and economic development. Done in 5 stages.
Stage 1: High birth rate, high infant mortality, high death rate
Stage 2: Early expanding (LEDC), death rate drops as sanitation inproves, reduced disease, birth rate high, child mortality decreases.
Stage 3: Wealthier LEDC, lower borth rates, improve healdhcare, leveling off population.
Stage 4: Low birth and death rates, industralized countries, stable population size.
Stage 5: Low fertility rate.