Biochemistry Class 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are four types of macromolecules?
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and neucleic acids
How are macromolecules made?
Via polymerization reactions using polymerases (aka condensation reaction, dehydration synthesis reactions)
Adds them together via removal of water
Makes polymers out of monomers
What are acidic amino acids?
Aspartate, glutamate
What are basic amino acids?
Lysine, arginine, histidine (kinda)
What are polar amino acids?
Serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, tyrosine, cysteine
What are the non-polar amino acids?
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, proline, phenylalanine, tryptophan
What are neutral amino acids?
Serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, cysteine, tyrosine
Histidine can be
pKa of amino acid R groups and charge at physiological temperature
1 and 3 letter abreviations
How is a peptide bond formed?
Amino group attacks carboxylic acid group → loose a water
What direction are proteins synthesized in?
N → C
What is primary structure? Secondary? Tertiary? Quaternary?
sequence of amino acids
interactions between the backbone (alpha helix, beta sheet)
hydrogen bonds
interactions between R groups
non covalent bonds
covalent disulfide bridge
more than one peptide whose side chains interact
What is hydrolysis?
Use a water to break a molecule
What is the monomer of carbohydrates? Formula?
Monosaccharides
CnH2nOn
What is glucose structure?
What is fructose structure?
What is galactose structure?
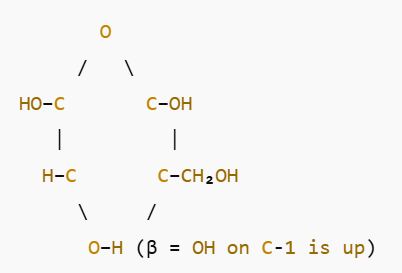
What is ribose structure?
see image
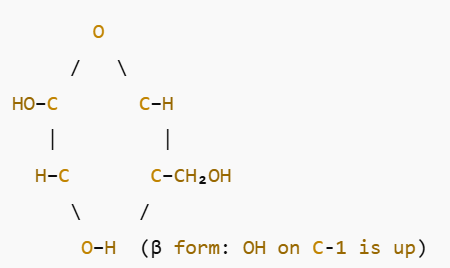
What is deoxyribose sugar?
see image
What is maltose made of?
Two glucoses
What is sucrose made of?
Glucose + fructose
What is lactose made of?
Glucose + galactose
What is glycogen?
Chain of glucose for storage in animals
Humans can digest it
Polar, so it carries water with it
What is starch?
Chain of glucose for storage in plants
Humans can digest it
What is cellulose?
Plant structure
Not digestable by humans
How are carbs primarily used?
Energy, cell surface markers, adhesion (in unicellular organisms mainly)
What are fatty acids?
Hydrocarbon with an acid on the end
What are properties of saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated: solid at room temp
Unsaturated: liquid at room temp
What are triglycerides?
Three fatty acids attached to glycerol via dehydration synthesis
How fats are stored
What are phospholipids?
Two fatty acids and a phosphate group bound to glycerol
Phospholipid is polar
What are terpenes?
Made of isoprene units (at least two)
Precursor to cholesterol, steroids, ear wax
Precursor to vitamin A (a terpenoid)
What is isoprene?
Monomer of a terpene
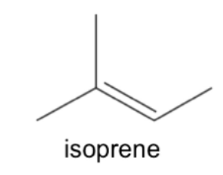
How are terpenes named?
The number of sets of two isoprene units they have
Called a terpenoid if something else is added to it
What are cholesterols?
3 six carbon rings and 1 five carbon ring
Used in membranes, bile salts
Precursor to vitamin D and steroids
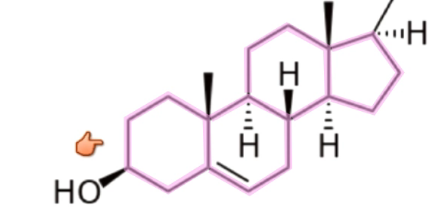
What are monomers of lipids?
Hydrocarbons
What is gibbs free energy?
delta G = delta H - T(delta S)
G = gibbs free energy
H = enthalpy = potential energy
T(delta S) = kinetic energy
When is a reaction spontaneous?
Negative delta G
Kinetic energy must be greater than potential energy
When is a reaction at equilibrium? In terms of free energy
Delta G = 0
Why are endergonic reactions sometimes coupled to exergonic ones?
The exergonic reaction releases energy the endergonic one can use
What is delta G of ATP hydrolysis? kcal/mol
-12 kcal/mol
What is kinetics?
How fast a reaction proceeds
How is reaction rate and energy of activation related?
Inverse of one another
What is delta G on an RCD?
Energy difference between reactants and products
Constant for a given reaction
What is the rate determining step in a reaction?
Reactants → transition state
How do catalysts work?
Stabilize transition state, thus lowering its energy
Reduce energy of activation
What are three characteristics of enzymes?
Increase rate of reaction
Not used up by reaction
Specific for a particular reaction
How are enzymes activated/deactivated?
Phosphorylation (#1 way to regulate them)
Allosteric regulation (#2 way)
What kind of feedback is most common in the body?
Negative/inhibition feedback
How is positive feedback used?
Neurons firing
Birthing
Both have external regulators (action potential, baby is birthed)
How does the V vs S plot look when S « E, S = E, S » E
S « E: linear
S = E: parabolic and levels off
S » E: levels off
What is V max? What does it depend on?
Max velocity of an enzyme
Depends on enzyme concentration and which enzyme is being used
What is Km? How does it relate to enzyme affinity?
Substrate concentration needed to reach ½ V max
Enzymes with higher affinity have lower Km
What are types of enzyme inhibition?
Competitive: binds at active site and blocks substrate
Non-competitive: bind at allosteric site of enzyme
Uncompetitive: binds to allosteric site of enzyme-substrate complex
Mixed: bind to allosteric site of enzyme alone or enzyme-substrate complex
How do mixed inhibitors affect V vs S?
V max decreases
Km varies
What is V vs S of uncompetitive inhibition?
Shifts left and down
Km decreases
V max decreases
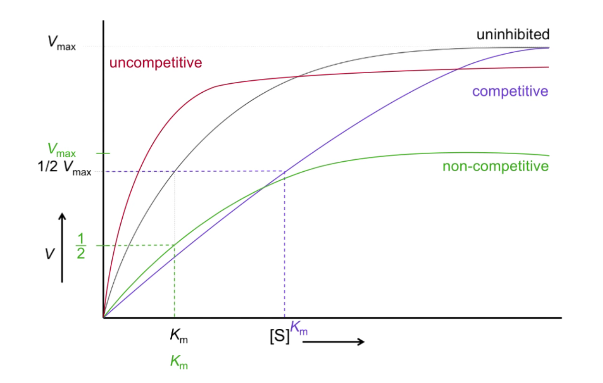
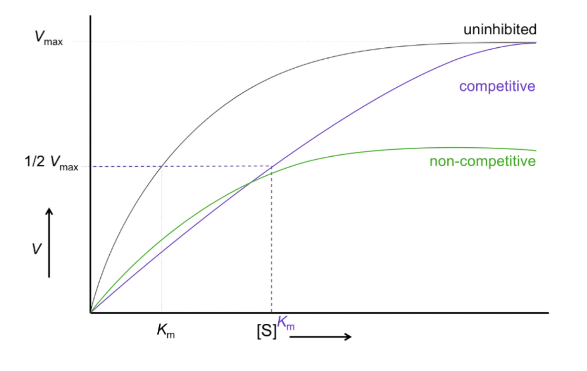
What is V vs S of non-competitive inhibitor?
Curve shifts down
Km is constant
V max decreases
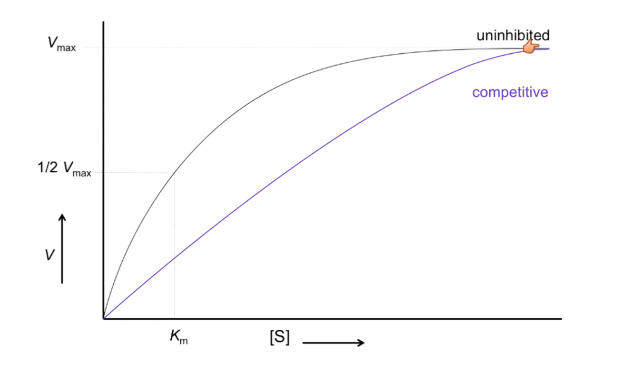
What is V vs S of competitive inhibition?
Curve shifted right
V max stays the same
Km increases
What causes changes in Km?
Affecting the ability of substrate to bind to the enzyme (ex: competitive inhibitor, uncompetitive)
What causes change in V max?
Allosteric regulation (non-competitive and uncompetitive0
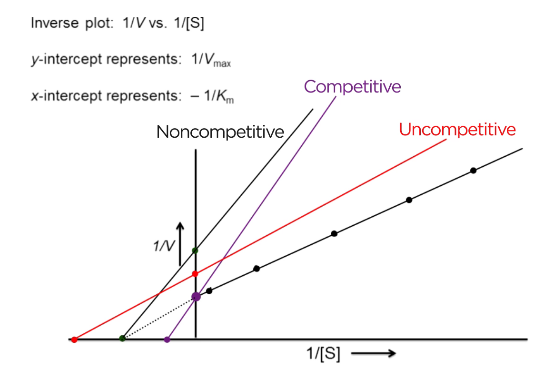
What is an LB plot?
1/V vs 1/S
Y-intercept: 1/V max
X-intercept: -1/Km
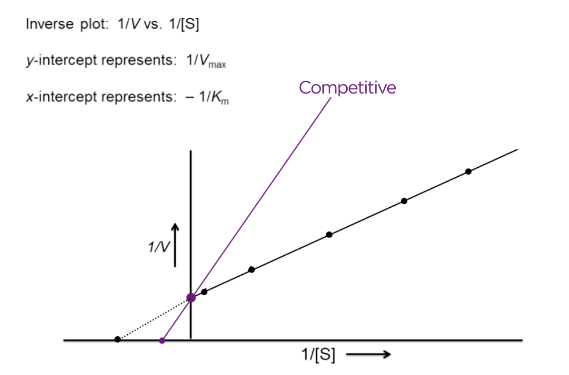
What does competitive inhibition look like on an LB plot?
V-max same = y-intercept the same
Km increases = x-intercept approaches zero
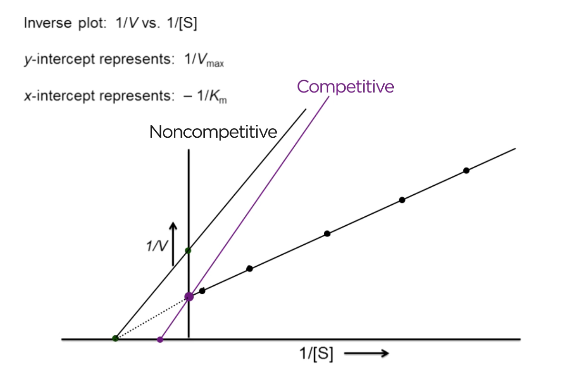
What does non-competitive inhibition look like on an LB plot?
V max decreases = y-intercept is further from zero
Km constant = x- intercept is constant
What does uncompetitive inhibition look like on an LB plot?
V max decreases = y-intercept goes further from zero
Km decreases = x-intercept goes further from zero