IvyTech - A&P 101 Midterm
1/728
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
729 Terms
Anatomy and Physiology
study of the structure of human body and how it works
Append
to hang something
Cardi
heart
Cerebr
brain
Cran
helmet
Dors
back
Homeo
same
-logy
the study of
Meta
change
Nas
nose
Orb
circle
Pariet
wall
Pelv
basin
Peri
around
Pleur
rib
-stasis
standing still
super
above
-tomy
cutting
Anatomy
examines structure or morphology of body parts, their forms organization
Physiology
studies the functions of body parts, what they do and how they do it
Why is it difficult to separate topics of anatomy and physiology?
anatomical structures make possible their functions
Human Organism
body parts from a well-organized unit
All materials are made up of what?
chemicals
chemicals are composed of ?
atoms
atoms are composed of ?
subatomic particles
atoms join together to form?
molecules
small molecules combine and form?
macromolecules
cells of complex organisms contain what? what do they carry out?
organelles; carry out specific activities
organelles are composed of?
macromolecules (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbs)
tissue
group of cells
organ
group of different tissues with specialized functions
organ system
group of organs that function closely together
organism
interacting organ systems
cell
basic unit of life
List the levels of organization from lowest level to highest level.
subatomic particles, atom, molecule, macromolecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
all living things consist of what?
cells
List and explain the characteristics of life
Growth: increase in cell number and size and increase in body size
Reproduction: production of new cells and organisms
Responsiveness: reaction to a change inside or outside the body
Movement: change in body position or location; motion of internal organs
Metabolism: sum of all chemical reactions in a living system (energy and nutrient cycling)
What are the four processes of metabolism?
Respiration: acquiring energy; moat organisms do it by taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide
Digestion: breaking down food into usable nutrients for absorption into the blood
Circulation: moving of chemicals and cells through body fluids
Excretion: removing waste products
List the environmental factors which are requirements of organisms
chemicals = water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, food
heat = energy
pressure = force
homeostasis
the body’s ability to keep its internal conditions stable, such that its cells cna survive
why is homeostasis important?
it maintains a stable internal environment necessary for cells and organisms to function optimally
What systems control homeostasis? How do they control it?
self-regulating systems called homeostatic mechanisms based on feedback loops
Name the 3 parts of a homeostatic mechanism
receptors: provide info about specific conditions (stimuli) in internal environment
control center: decision maker; contains set point (body temp of 37ºC or 98.6ºC)
effectors: act and cause appropriate responses (muscles / glands)
list the steps of homeostasis components in correct order
stimulus → receptors → control center (set point) → effectors → response
negative feedback
deviation from the set point is corrected (moves in opposite or negative direction) and the correction reduces the response of the effectors
why is negative feedback important?
crucial for maintaining homeostasis; prevents excessive fluctuations that could be harmful or even fatal
give example of negative feedback in the body
When body temperature rises, the body sweats to cool down
When it gets too cold, the body shivers to generate heat
Positive feedback
a change is not reversed, but intensified, and the effector activity is initially increased rather than turned off
why is positive feedback not common in the human body
Usually produces unstable conditions which might not seem compatible with homeostasis
give example of positive feedback in the body
childbirth, where the pressure of the baby's head on the cervix stimulates the release of oxytocin, which in turn increases the strength of uterine contractions
human body consists of 2 main portions
Axial: head, neck, trunk
Appendicular: upper and lower limbs
Cranial Cavity
houses brain

what cavity is this?
cranial cavity
Vertebral Canal (Spinal Cavity)
contains spinal cord and surrounded by vertebrae
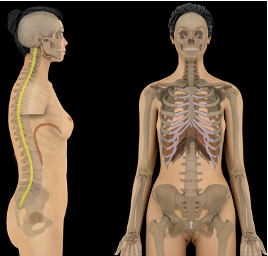
what cavity is this?
vertebral canal (spinal cavity)
Thoracic Cavity
houses the lungs and thoracic viscera
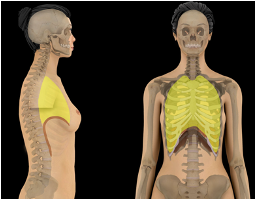
what cavity is this?
Thoracic Cavity
Abdominopelvic Cavity
contains abdominal and pelvic viscera
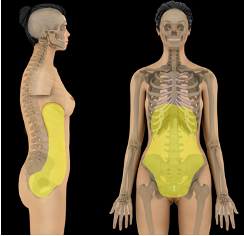
what cavity is this?
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Abdominal Cavity
extends from diaphragm to top of pelvis and contains stomach, liver, spleen, kidneys, small intestine, most of large intestine
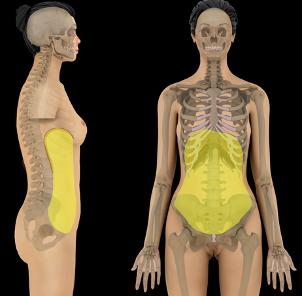
What cavity is this?
Abdominal Cavity
Pelvic Cavity
enclosed by pelvic bones and contains ends of large intestine, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs
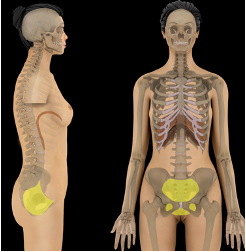
what cavity is this?
Pelvic Cavity
where is the diaphragm located?
muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
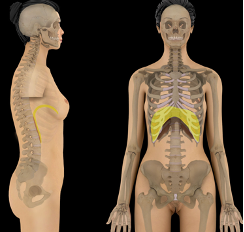
what cavity is this?
Diaphragm
where is the mediastinum located?
region between the lungs and thoracic cavity which contains heart, esophagus, trachea, thymus gland
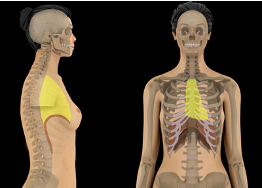
what cavity is this?
mediastinum
Serous Membrane
double layered membrane that lines the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities that secrete serous fluid (prevents friction between layers)
Explain the difference between a visceral layer and a parietal layer of a serous membrane
Visceral Layer: inner layer, which covers organs
Parietal Layer: outer layer, which lines wall of cavity
Describe where the visceral and parietal pleura, visceral and parietal pericardium, and visceral and parietal peritoneum are located
Visceral and parietal pleura (around lungs in thorax)
Visceral and parietal pericardium (around heart in thorax)
Visceral and parietal peritoneum (around abdominopelvic organs)
Explain basic functions of all body systems
Integumentary: body covering, protection, body temp regulation, sensory reception, production of vitamin D (body covering, support, movement)
Skeletal: support and movement, framework, protection, attachment sites, storage of inorganic salts, production of blood cells (body covering, support, movement)
Muscular: support and movement, main source of body heat and posture (body covering, support, movement)
Nervous: integration and coordination (nerve impulses / neurotransmitters)
Endocrine: integration and coordination (chemical messengers / hormones)
Cardiovascular: transportation of gases, nutrients, blood cells, hormones, wastes (transport)
Lymphatic: transportation of fluids, carries fats, defends body against infection (transport)
Digestive: receives food, breaks it down, absorbs digestion products, excretes waste (absorption and excretion)
Respiratory: moves air in and out of body, exchange gases, absorbs oxygen (absorption and excretion)
Urinary: removes blood wastes, regulates water balance and blood pressure, produces urine and excretes by transporting outside body (absorption and excretion)
Reproduction: systems produce and transport sex cells, produce hormones, and produce new organisms
anatomical position
Standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward
Superior vs Inferior
above
below
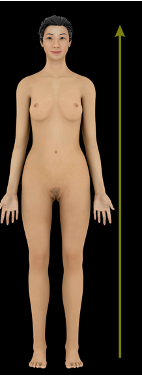
what direction is this?
superior

what direction is this?
inferior
Anterior / Ventral vs Posterior / Dorsal
toward the front
toward the back

what direction is this?
anterior / ventral
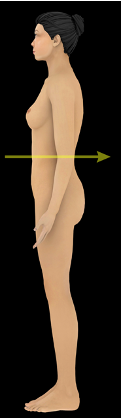
what direction is this?
posterior / dorsal
Medial vs Lateral
toward the midline
away from the midline
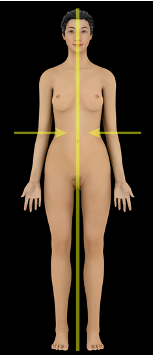
what direction is this?
medial
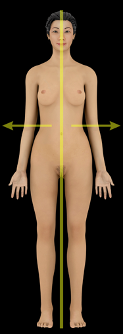
what direction is this?
lateral
Bilateral
paired structures; on both sides
Ipsilateral vs Contralateral
same side
opposite side
Proximal vs Distal
close to point of attachment to trunk
farther from point of attachment to trunk
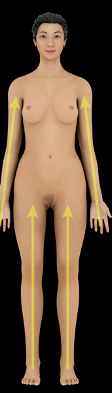
what direction is this?
proximal
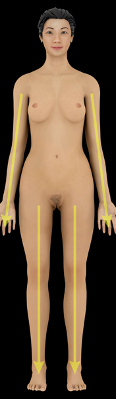
what direction is this?
distal
Superficial vs Deep
close to body surface
more internal
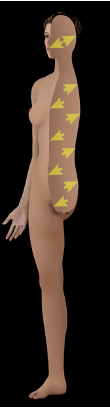
what direction is this?
superficial
Sagittal Section
longitudinal cut that divides the body into left and right portions
Mid-Sagittal / Median Section
divides the body into equal left and right portions
Parasagittal Section
sagittal section lateral to midline that divides body into unequal left and right portions
Transverse or Horizontal Section
divides the body into superior and inferior portions
Coronal or Frontal section
longitudinal cut that divides body into anterior and posterior portions
Cross Section
a cut across the structure
oblique section
an angular cut
longitudinal section
a lengthwise cut
Epigastric Region
upper middle portion
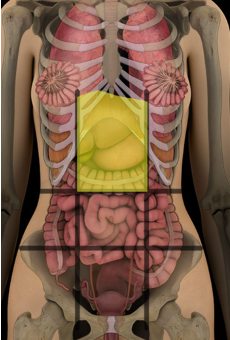
what abdominal region is this?
epigastric region
Right and Left hypochondriac regions
right and left side of the epigastric region
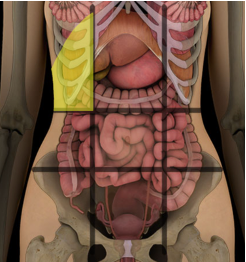
what abdominal region is this?
right hypochondriac region