(Part 4) Solubility
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Define the term solubility of a solute
The solubility of a solute is the maximum quantity of solute that can dissolve in a certain quantity of solvent at a specified temperature
What factors affect the solubility of a solvent
The nature of the solvent and solute
Temperature
Pressure
Explain how the nature of the solvent and solute affects the solubility of a solute
When the solvent and solute have similar chemical natures, solubility increases
Explain how temperature affects the solubility of a solute
o For most solutions, as temperature increases, so does the solubility of the solid solute: This is because higher temperatures provide more energy, allowing the solvent molecules to more effectively break the intermolecular forces holding the solute particles together.
o But for all gases, when temperature increases, solubility decreases This is because higher temperatures, there is more kinetic energy which give gas molecules more energy to move around faster and break intermolecular bonds and escape from the solution into the air, making them less likely to stay dissolved.
How does pressure affect the solubility of a solvent
o For solid and liquid solutes, changes in pressure have practically no effect on solubility
o However, for gaseous solutes, an increase in pressure → increase in solubility and vice versa
What are the factors that affect how fast a solute dissolves in a solvent
Particle size — Smaller particles dissolve faster because they have a larger surface area.
Stirring — Stirring helps by constantly bringing fresh solvent to the solute.
Amount already dissolved — Dissolving is faster when little solute is dissolved; it slows down as the solution gets closer to saturation.
Temperature —
Solids/liquids: Higher temperature = faster dissolving.
Gases: Higher temperature = slower dissolving.
What is a saturated solution
A solution in which no more solute will dissolve in at a given temperature
How can you get a saturated solution to dissolve more solute
Heating it
What do these two terms mean
Dilute
Concentrated
o Dilute: A solution where there is a relatively small amount of solute dissolved in the solution
o Concentrated: A solution which contains a relatively large amount of solute dissolved in the solution
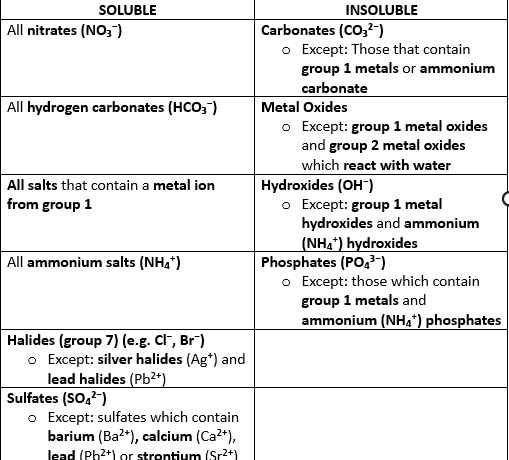
Name the solubility rules of substances in water at room temperature (taken at 25C)
What do graphs of solubility show
show the how solubility of a substance in a solvent varies with temperature
What are these graphs called
Solubility curves