Science Y10: Heredity, Pedigrees and Punnet Squares
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Gene
A Gene is a segment of DNA that contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Genes are passed from parents to offspring and determine traits like eye color and hair texture.
Genes are sections of homologous chromosomes that code for specific instructions such as characteristics
Genotype
A genotype is an organisms entire set of genes with their alleles .
Phenotype
A phenotype is the set of genes organism carries e.g code for blonde hair. Can be affected by environmental/nutritional/chemical exposure. (Observable characteristics)
Traits
Traits are categories of characteristics you have. E.g hair colour, eye colour, height.
Allele
Alleles are alternative forms of the same gene.
Sex Chromosome
A sex chromosome is one of two chromosomes that determine an organisms biological sex.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is NOT a sex chromosome.
Sex linked gene
Genes located on sex chromosomes (usually X or Y) whose inheritance patterns differ from autosomal (non-sex chromosome) genes.
X-linked = on the X chromosome. Y-linked = on the Y chromosome.
Males are hemizygous for X: they have one X and one Y (so one X allele → any X allele shows in males).
Females have two Xs → can be homozygous, heterozygous (carrier), or affected depending on dominance.
Carrier
A carrier is a heterozygous individual that inherited a recessive allele for a genotype disorder but does not display symptoms of that disorder.
Autosomal vs sex-linked traits
Autosomal are traits that are shown in the first 22 pairs of chromosomes and show equally within females and males (basically non sex linked traits) and sex linked traits are traits that show only in the last pair of chromosomes which determine an organisms gender.
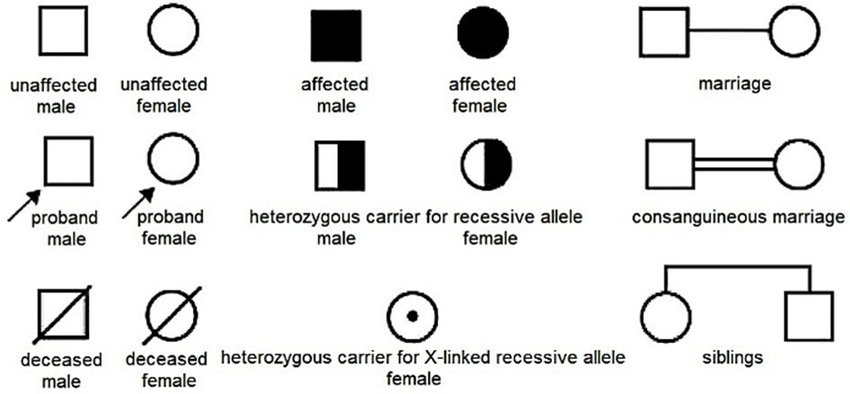
Pedigrees
A pedigree chart shows a family’s entire genetic history over a few generations, used to spot and identify diseases and where they began within the family tree
Heterozygous
Heterozygous alleles have two different alleles: e.g Aa
Homozygous
Homozygous alleles have two of the same alleles: e.g AA or aa
Dominant Allele
Dominant alleles always show their trait when present; e.g Aa (trait will be seen)
Expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy is present (AA or Aa).
Masks the effect of the recessive allele.
Example: Brown eyes (B) dominant over blue (b).
Recessive Allele
Recessive alleles only show when both alleles are recessive. E.g aa will be shown.
Only expressed if two copies are present (aa).
Hidden when a dominant allele is present.
Example: Blue eyes (bb).
Sex Linked Punnet square
A punnet square shwoing inhertiance of traits on the X or Y chromose