Female Reproductive System
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
The ovaries are suspended in the pelvic cavity by multiple _____.
ligaments
Describe the pre-ovulatory part of the follicular phase.
closer to day 14
several follicles continue maturing, but only the dominant ova is released
The growing follicle secretes more estrogen
Increased amounts of estrogen has a negative feedback on FSH (prevents too many follicles from maturing)
Estrogen causes the endometrial lining to thickenDuring the pre-ovulatory phase, several follicles mature, but only the dominant follicle is selected for ovulation around day 14. The growing follicle secretes increasing amounts of estrogen, which has a negative feedback effect on FSH, preventing the maturation of multiple follicles, and leads to the thickening of the endometrial lining.
Describe ovulation.
the rise in LH levels stimulate ovulation on Day 14
Ovulation: a mature egg is released from the ovaries
LH and FSH levels are high
the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum under LH stimulation
Describe the luteal phase.
the corpus luteum produces progesterone
Increased progesterone and estrogen inhibit LH and FSH release
The endometrium becomes thicker and more glandular to support a potential embryo
If fertilization does not occur the corpus luteum degrades into the corpus albicans.
This causes progesterone levels to drop and initiates bleeding
What does FSH do?
it goes directly to the follicle and stimulates development
Estrogen, Progesterone, and inhibin inhibit _____ production. Which…
GnRH
decreases FSH and LH levels
What are the two layers of the fallopian tubes?
inner mucosa: lined with ciliated cells that move the egg
Smooth muscle: contracts to move the ova and sperm
What are the two layers of the endometrium?
superficial functionalis and deep stratum basalis
Superficial functionalis
the outer part of the endometrium that sheds monthly
Deep Stratum Basalis
the inner layer of the endometrium that attaches to the myometrium and remains constant
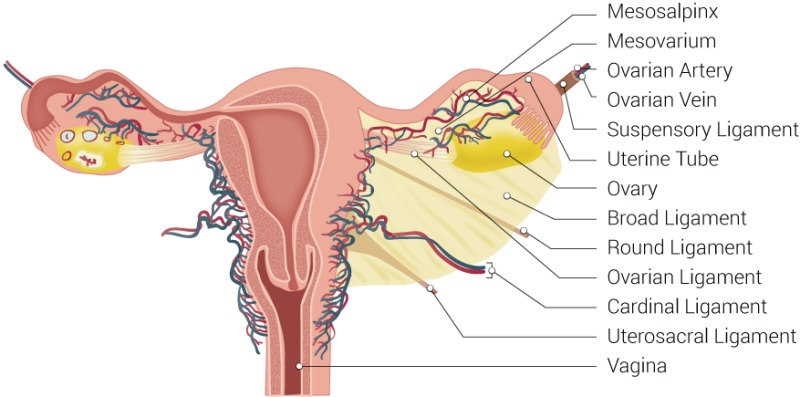
Ovarian Ligament
the ligament that attaches the ovary to the body of the uterus and holds the ovary in place
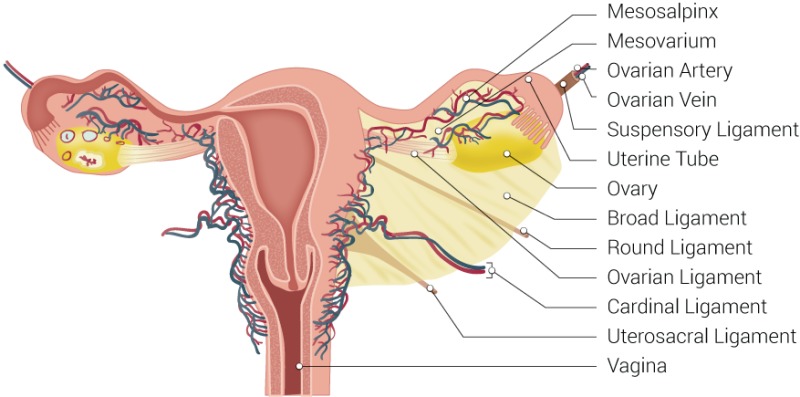
Broad Ligament
a large peritoneal fold that drapes over the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes
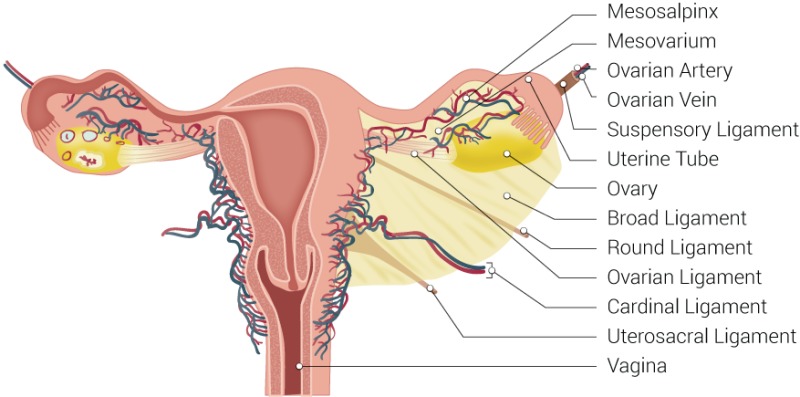
Suspensory Ligament
a specific part of the Broad Ligament that connects the upper ovary to the pelvic wall
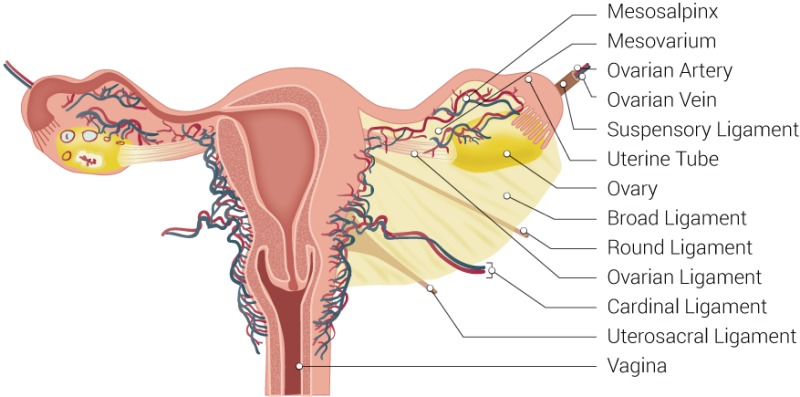
Round Ligament
a ligament that helps the uterus maintain a forward motion during pregnancy

What does the Cardinal Transverse, Uterosacral, and Pubocervical ligaments do?
they support the pelvic floor