mmbio review exam 1 yay !!
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
Edward Jenner
Developed smallpox immunization using cowpox agent
Paul Ehrlich
sought a magic bullet to destory pathogens and not the host
Alexander Fleming
discovered penicillin
Joseph Lister
Pioneered aseptic surgery (phenol mists)
John Snow
Father of Epidemiology (working with cholera in London)
Ignaz Semmelweis
Pioneered asepsis by discovering that hand washing prevented streptococcal infections
in obstetric patients
Robert Koch
Pioneered the cultivation of bacteria on solid media
Louis Pasteur
Disproved the theory of spontaneous generation of microorganisms with swan-necked
flasks
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
First person to see bacteria using a primitive microscope
Francesco Redi
Disproved the theory of spontaneous generation of flies from meat; father of the
scientific method
Which of the following microorganisms is known for, and classified by, its variety of
locomotive structures
Protozoa
Types of Fungi
yeasts, are eukaryotic, can be molds
Carl Woese
The person who proposed that all cellular life belongs to one of three domains
(Bacteria, Archaea, or Eukarya), based upon rRNA gene sequences
To which of the following substances would a typical cell membrane be least
permeable
Sodium ion Na+
Which organisms are responsible for red tides and shellfish poisoning
Algae
All of the following statements concerning prokaryotic flagella are true except
They are composed of tubulin
Which of the following substances is not associated with bacterial cell walls
chitin
Cells of the genus Mycoplasma lack?
Peptidoglycan
Short, numerous, non-motile projections used for adherence
Fimbriae
Made of tubulin in eukaryotes
Flagella
Responsible for motility in spirochetes
Axial filaments
Have a central role in bacterial conjugation
Pili
Means “sugar cup”;
most often composed of polysaccharides Glycocalyx
The endosymbiotic theory explains it’s origin in the cell
Mitochondrion
Composed of RNA and protein; major role in protein synthesis
Ribosomes
Polysaccharide chains cross-linked by short peptides
Peptidoglycan
The most significant permeability barrier of the cell
Cell membrane
Resting structure built for survival in harsh conditions
endospore
Teichoic acids
gram positive bacteria only
Lipopolysaccharide
Gram-negative bacteria only
Peptidoglycan
Gram+, Gram – and Acid fast
Mycolic acids
Acid-fast bacteria only
Lipid A
Gram-negative bacteria only
Will appear blue after an acid-fast stain
Gram+ and Gram-
A red blood cell (RBC) is placed into a HYPERTONIC solution… what happens?
crenation (it shrinks)
An RBC is placed into a HYPOTONIC solution.. what happens?
swell then burst (lysis)
A plant cell is placed into a hypertonic solution
Plasmolysis
A plant cell is placed into a hypotonic solution
nothing happens
An RBC is placed into an isotonic solution
nothing happens
Plasmolysis
(the process where a living plant cell loses water and its cytoplasm shrinks)
An object measures 0.5 μm. This is equivalent to… in nm?
500 nm
Empty magnification results from increasing magnification without increasing
the…
resolution
Assume that a bacterial cell has established a typical proton gradient. When
this gradient is used to power the transport of lactose into the cell, the
protein involved is most correctly termed….
symport
Which of the following types of microscopy is capable of generating a three-
dimensional image of a specimen?
confocal
differential interference contrast
scanning electron
Gram-positive cells immediately following the primary stain
purple
Gram-negative cells immediately following decolorization
colorless
Gram-negative cells immediately following the counterstain
pink
Gram-positive cells immediately following the counterstain
purple
Glucose goes in; pyruvate, ATP, and NADH come out
glycolysis
Acetyl-Co-A goes in; NADH, FADH2, and GTP come out
krebs cycle
Hydrogen atom “juicing”; a proton gradient is formed
Electron transport chain
Lactic acid is produced
fermentation
Fatty acids are broken down, 2 carbons at a time
Beta oxidation
Consists of cytochromes and iron-sulfur proteins
Electron transport chain
Ethyl alcohol and CO2 are produced
fermentation
Malachite green is associated with which of the following staining procedures
endospore stain
The reason visible light is relatively limited in its usefulness for microscopy is
its wavelength is too long to enable high resolution of very small objects
Most stains that stain bacteria well are classified as
-Basic (positively-charged chromophores)
The molecule upon which an enzyme acts is known as its
substrate
Carbon dioxide is, or can be, a by-product of which of the following
the krebs cycle, fermentation
The synthesis of acetyl-Co-A from pyruvate is a bridge step between which 2 pathways
glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
Anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration in
the nature of the terminal electron acceptor
Proteins are polymers of
amino acids
The Krebs cycle performs which important functions
removes H atoms from organic
compounds and places them onto NAD + and FAD.
Catalase
is one of the fastest enzymes known
NAD and FAD are most correctly classified as
hydrogen atom carriers
Most bacterial capsules are composed of
polysaccharides
Blood agar to which antibiotics inhibitory to gram-negative bacteria have been added is
Selective
Differential
Complex
A fatty acid containing 14 carbons is metabolized for energy by an aerobic bacterium. What is the
total net number of ATP equivalents that this fatty acid is worth
112
Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation
do not affect electron flow, act by dissipating the proton
gradient, are hydrophobic substances like dinitrophenol and dicumarol.
Which of the following ingredients is characteristic of a complex medium
beef extract
How many times more acid is a tomato (pH=4.3) than blood (pH=7.3)-
1000 times
Net ATP by a lactic acid bacterium (they can only perform this fermentation)
2
Net ATP (aerobic bacterium) from substrate-level phosphorylation only
4
Net ATP from oxidative phosphorylation only, in most eukaryotic cells
32
The number of ethanol molecules produced during fermentation
2
The number of phosphates in ATP
3
The number of fatty acids in a phospholipid
2
The number of CO2 molecules released from the complete oxidation of one pyruvate molecule
3
The number of mitochondrial protons required to produce 1 cytoplasmic ATP in a eukaryotic cell
4
The number of ATP equivalents produced from one turn of the Krebs cycle, starting with acetyl-CoA
12
Capnophiles grow best in
higher concentrations of CO2
Forty organisms with a generation time of 20 min are allowed to multiply for 6
hours. How many organisms are present?
One organism develops into 1.07 × 10 9 organisms in 6 hours. What is the
generation time?
During the lag phase, organisms are
synthesizing necessary enzymes without dividing much.
Water activity of a substance is lowered by:
adding salt
adding sugar
removing water
For a mesophile, the optimum temperature of an organism is
always closer to its maximum than its minimum.
Obligate halophiles require
increased concentrations of NaCl.
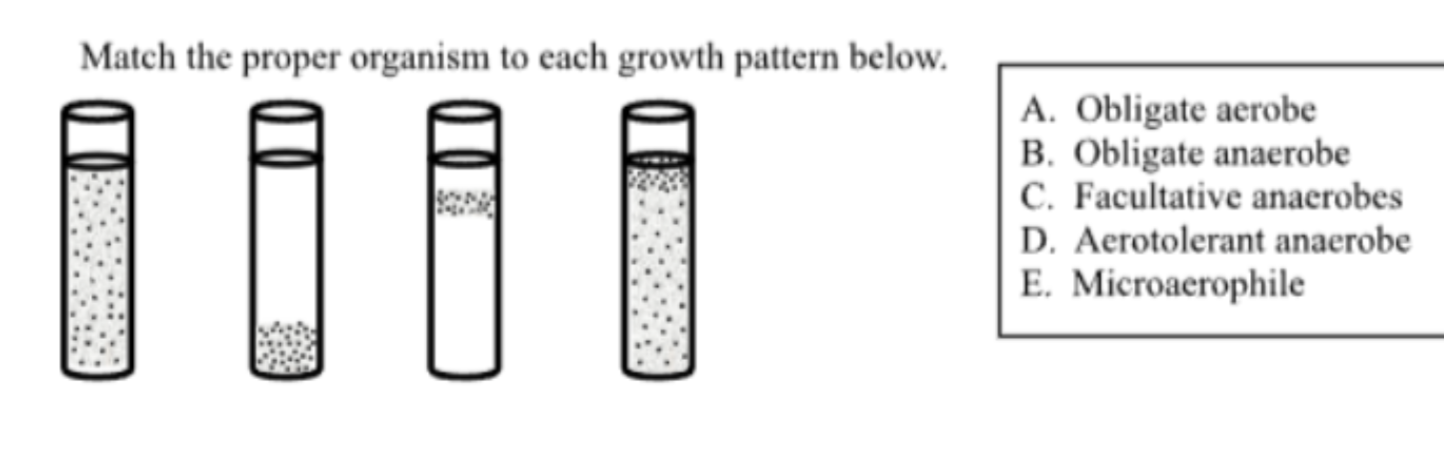
Match the proper organism to each growth pattern (A)
aerotolerant anaerobe (oxygen does not affect them)
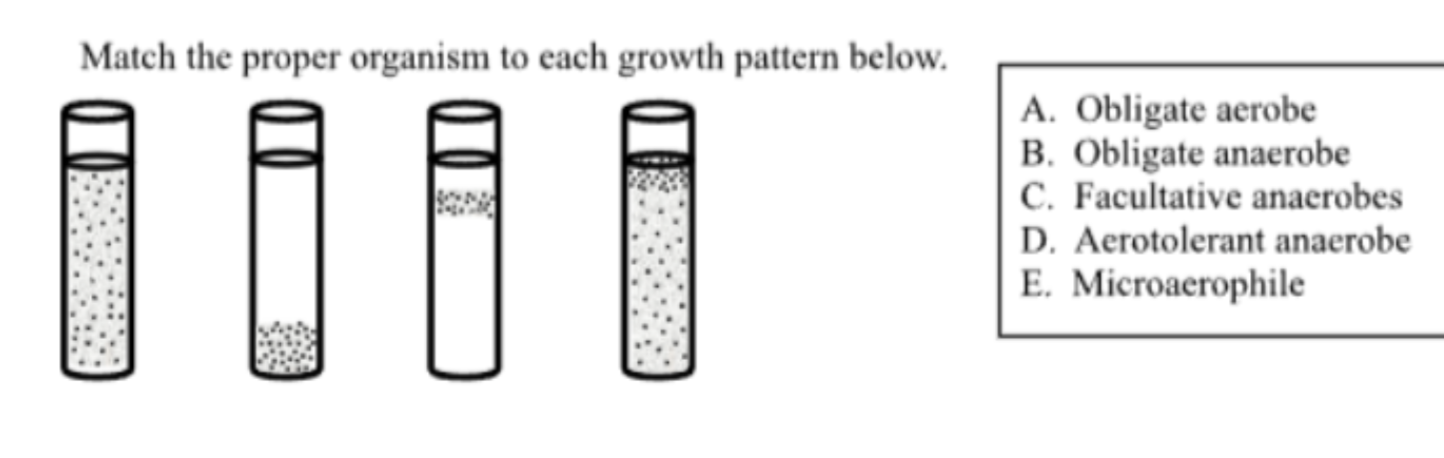
Match the proper organism to each growth pattern (B)
obligate anaerobe (oxygen is toxic to them so at bottom)
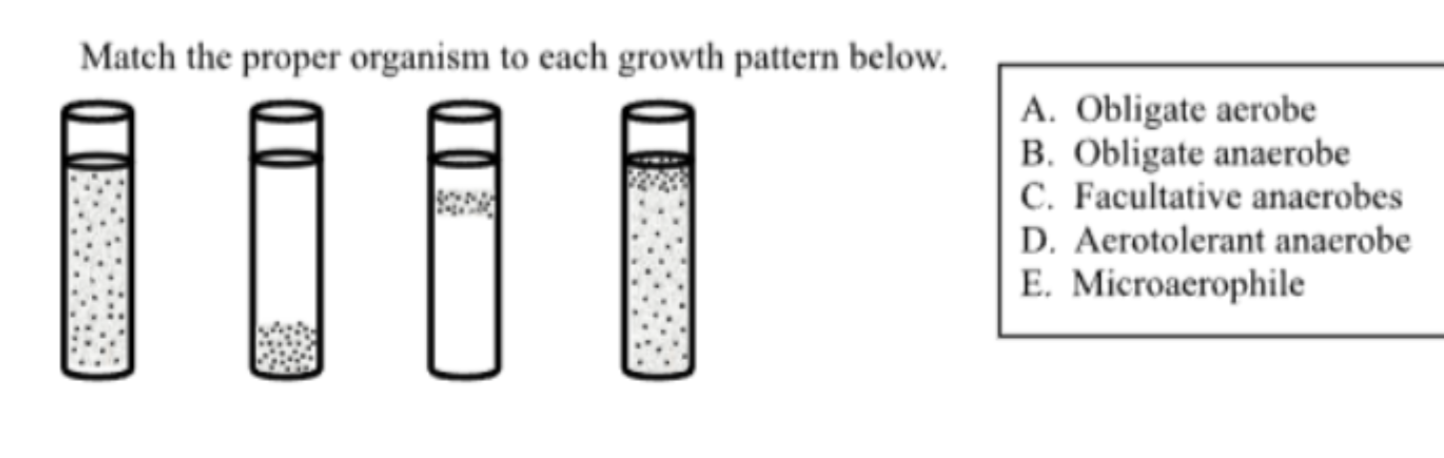
Match the proper organism to each growth pattern (C)
facultative anerobe (prefer oxygen so heavy growth at the top)
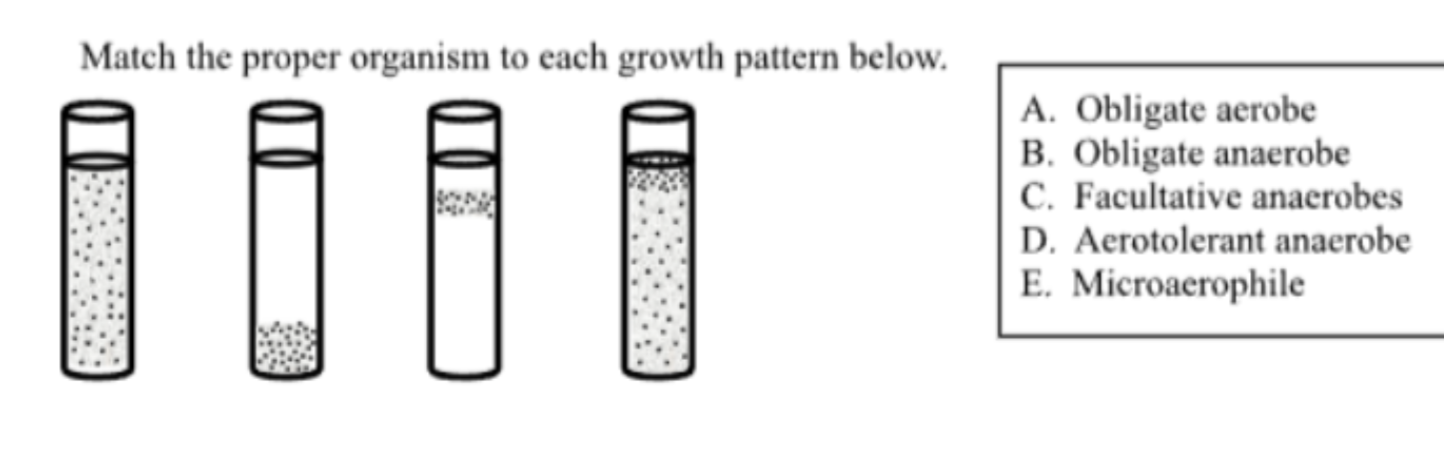
Match the proper organism to each growth pattern (D)
microaerophile (need a little oxygen but not too much at the surface is toxic)
Which type of cell wall has the most peptidoglycan?
gram positive
Bacterial flagella are
composed mostly of a globular protein called flagellin
hollow rigged structures responsible for motility
composed of three parts … a filament, a hook, and a basal body
Peptidoglycan are….
covelantly crosslinked with short peptides
is composed of polysaccharide chains containing N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid
and ONLY found in bacteria
A bundle of internal flagella found in spirochetes is called
AXIAL FILAMENT
Which of the followinh structures are present in eukaryots but are ABSENT in prokaryotes?
mitochondria
Antiport
membrane protein that participates in an active process in which two chemicals are simultaneously transported across a membrane in OPPOSITE directions
osmosis
the passive diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane
symport
membrane protein that participates in an active process in which two chemicals are simultaneously transported across a membrane in the same direction