Digestive System Quiz Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:22 PM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
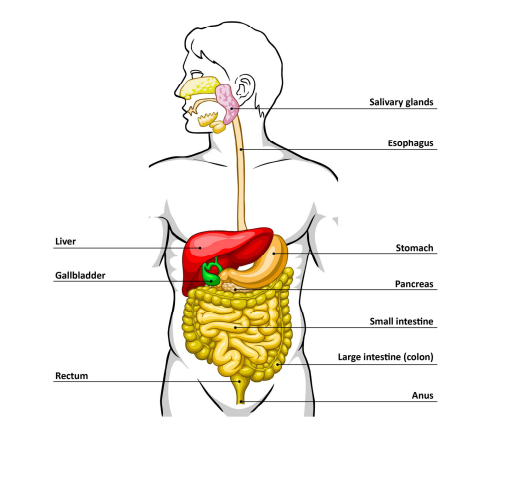
**Identify parts of the digestive system from a diagram**
2
New cards
**Define the four processes of the digestive process, where in the alimentary canal they occur, and which accessory organs help with each**
**Move onto the next cards.**
3
New cards
Ingestion
Taking food in
**Organs involved:**
**Mouth**-Teeth chew and tongue mixes food to increase
its surface area and prepare it for swallowing
**Pharynx**-Propels food toward the stomach through
peristalsis
**Esophagus-**
Propels food toward the stomach through
peristalsis
\
\
\
\
**Organs involved:**
**Mouth**-Teeth chew and tongue mixes food to increase
its surface area and prepare it for swallowing
**Pharynx**-Propels food toward the stomach through
peristalsis
**Esophagus-**
Propels food toward the stomach through
peristalsis
\
\
\
\
4
New cards
Digestion
Breaking food down into absorbable and/or usable molecules
**Organs involved:**
**Salivary glands**-Contains digestive enzymes
**Stomach**-Cells secrete acid and enzymes that start
chemical digestion of proteins
**Small intestine (Duodenum)** -Continues chemical digestion and uses its large surface area to absorb nutrients
**Liver**-Produces bile, which breaks down large fat
globules into smaller ones, increasing their
surface area
**Pancreas**-
Produces pancreatic juice containing digestive
enzymes
**Organs involved:**
**Salivary glands**-Contains digestive enzymes
**Stomach**-Cells secrete acid and enzymes that start
chemical digestion of proteins
**Small intestine (Duodenum)** -Continues chemical digestion and uses its large surface area to absorb nutrients
**Liver**-Produces bile, which breaks down large fat
globules into smaller ones, increasing their
surface area
**Pancreas**-
Produces pancreatic juice containing digestive
enzymes
5
New cards
Absorption
Getting usable molecules from the digestive tract into the bloodstream
**Organs Involved:**
**Small intestine (Jejunum and Ileum)**-
Nutrients and water pass through the cells in the
villi and from there into the nearby capillaries
**Organs Involved:**
**Small intestine (Jejunum and Ileum)**-
Nutrients and water pass through the cells in the
villi and from there into the nearby capillaries
6
New cards
Defecation
Getting rid of wastes
**Organs Involved:**
**Large intestine-**Prepares feces to be removed from the body by absorbing water from them and getting rid of bile, bacteria, and indigestible food
**Rectum**-Feces move into the rectum and the brain gets a
signal that they’re there
**Anus**-The brain consciously decides to open the
voluntary sphincter, and peristalsis pushes the
feces out
**Organs Involved:**
**Large intestine-**Prepares feces to be removed from the body by absorbing water from them and getting rid of bile, bacteria, and indigestible food
**Rectum**-Feces move into the rectum and the brain gets a
signal that they’re there
**Anus**-The brain consciously decides to open the
voluntary sphincter, and peristalsis pushes the
feces out
7
New cards
**Micronutrients and their roles in the body**
move onto the next cards.
8
New cards
Fat Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins dissolve in fat, and your body is able to store them in fatty tissues, hydrophobic. (Vitamin A, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K) Have too much and it become toxic.
9
New cards
Water Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins dissolve in your body fluids; you lose some each day and must replace them through the food you eat, hydrophilic. (B Vitamins, Vitamin C)
10
New cards
Minerals
Are inorganic substances, often ions of a particular element, that are as vital as vitamins are to your body’s functions, and work with vitamins to make important reactions happen in your body. Are absorbed by the body better if they’re consumed in your food rather than as supplements.
11
New cards
**Macronutrients and their roles in the body**
move onto the next cards.
12
New cards
Carbohydrates
The main source of energy for everything your body does. All your tissues can use this source for energy and are the only molecule our brains can use.
13
New cards
Fiber
Made of plant material called cellulose that is in fresh fruits and vegetables. Prevent sugar spikes, because it’s a type of carbohydrate that the body doesn’t digest; however, doesn’t provide any energy, it’s vital for moving waste through the large intestine, and a high-fiber diet can decrease the risk for heart disease, obesity, and colon cancer.
14
New cards
Glucose
The body converts all carbohydrates to glucose, and once it’s broken down chemically inside a cell, it makes energy for the cell to use.
15
New cards
Protein
Provide the building blocks for new proteins and enzymes that make many of your cellular functions possible.
16
New cards
Amino Acids
Are used to build new proteins and to make some hormones, such as epinephrine and insulin.
17
New cards
Fats
Become stored energy but can also become parts of cell membranes and protective tissues.
18
New cards
Triglycerides
Is the main lipid that we take in as part of our diet, and packages fatty acid so that there isn’t too many fatty acids around. Tri- are the three long chains of carbon (fatty acid) and glycerol is the back bone for those hydrocarbons.
19
New cards
Cholesterol
Helps the cell membrane hold its shape and keeps small molecules from passing through and is the starting substance for steroid hormones such as your sex hormones. Also transports fats. HDL (High density) cholesterol is good and LDL is bad (Low Density).
20
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acid
Reduce a person’s blood cholesterol and help keep his or her blood sugar under control. Has a double bond and doesn’t have hydrogen.
21
New cards
Saturated fatty acid
Raise your cholesterol levels because the body packages these fats together with cholesterol into a molecule called low-density lipoprotein, or LDL. (You will learn about the other kind of cholesterol you may have heard of, HDL, later in this lesson.) Has hydrogen.
22
New cards
Water
The mucus that lines your respiratory and digestive tracts is mostly water. Fluid surrounding your brain and spine cushion and protect them. Your body uses water to control blood pressure and body temperature. Your blood plasma is mostly water, and it’s that solution that carries out much of the vital transport of body products, wastes, and toxins.
23
New cards
**How your digestive system functions to process each macronutrient.**
move onto the next cards.
24
New cards
Digestion of carbohydrates
1. Starts in the the mouth ( Salivary Amylase)
2. Continues in stomach with HCl and peristalsis
3. Small intestine (duodenum) takes chyme from stomach and mixes with Pancreatic Amylase
4. Small intestine absorbs glucose into the bloodstream
25
New cards
Digestion of Proteins
1. Starts in the stomach with HCL and Pepsin
2. Small intestine (duodenum) takes chyme from the stomach and mixes with carboxypeptidase from the pancreas.
3. Small intestine absorb amino acids in to the bloodstream
26
New cards
Digestion of Fats
1. Starts in the the mouth (Lingual Lipase)
2. Continues in stomach with HCl and peristalsis
3. Small intestine (duodenum) takes chyme from the stomach and mixes with pancreatic lipase.
4. Small intestine absorb fats (Mainly triglyceride) into the lymphatic system to the liver