Psych 9C, Chapter 10: Stress and Health
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Health Psychology
field that investigates links among behavior, cognition, and physical health
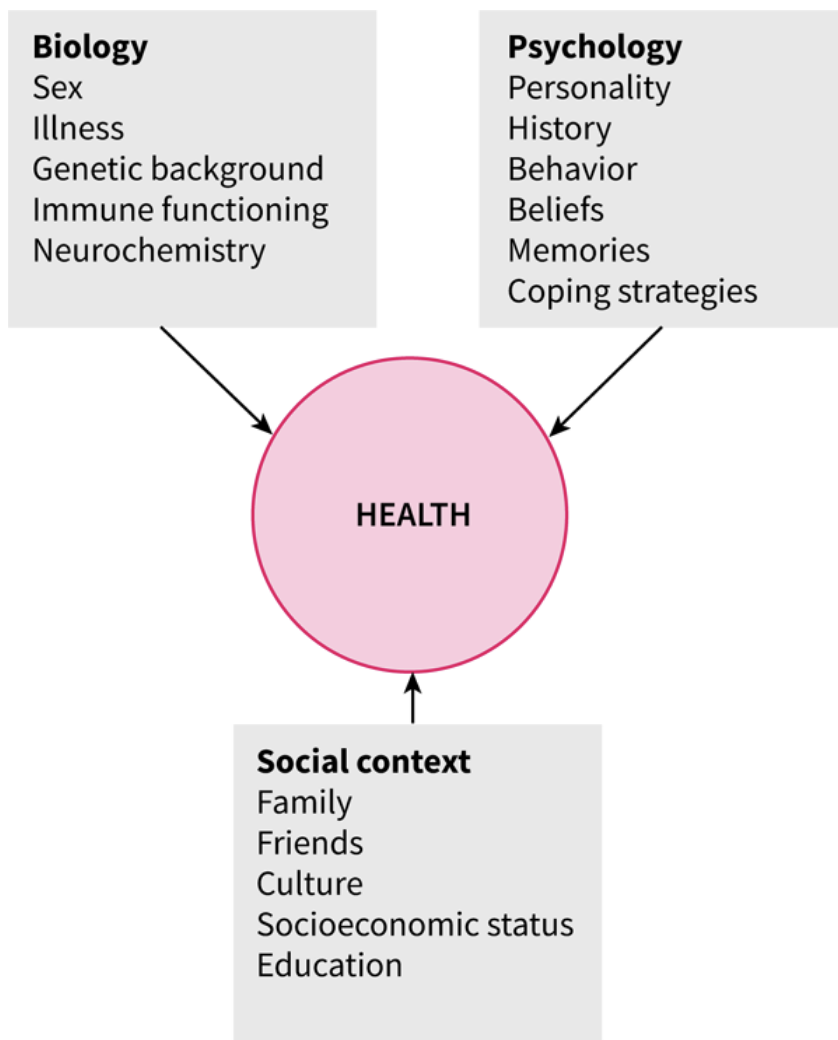
Biopsychosocial model
understanding what makes us health requires a recognition that biology, psychology and social context are closely interconnected in health outcomes
Components of biopsychocosial model
biology, psychology, and social context
stress
physiological response to some type of environmental event
three categories of stressors
catastrophic events, major life events, and daily hassles
major life event examples
divorce, marriage, move, etc.
daily hassles example
paper cuts, minor problems, over the course of a day
primary appraisal
our perception of the demands in a given situation
Secondary Appraisal
the evaluation of resources to cope with the stressful situation perceived in primary appraisal
Hans Selye
discovered link between stress and health
general adaptation syndrome
when posed with stress, the body sends out an all hands on deck response which has 3 stages
3 phases of general adaptation syndrome
alarm reaction → resistance stage → exhaustion stage
alarm stage
emergency reaction, initial shock, release of cortisol and epinepherine
resistence stage
defenses are maximized, cannot last overtime
exhaustion stage
systems begin to fail
sympathetic-adreno-medullary axis (SAM)
immediate or acute response to stress, impulsive superhero
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
more methodical sidekick, acts as hormone alarm call
Corticotrophic-releasing hormone (CRH)
alarm call utilized by HPA
challenge reactivity
sympathetic arousal which leads the heart to beat faster, blood vessels dilate

threat reactivity
blood vessels constrict rather than dilating
allostatic load
the sustained elevation of neuroendocrine response to stress which creates wear and tear on body
cytokines
molecules that cause fever and inflammation
alcohol myopia
focus of attention narrows and impulses are impaires
Type A personality
highly competitive, driven, etc.
Type B personality
more reflective, creative, etc.
Who is more likely to have a heart attack type A or B?
Type A
gene x environment interactions
stressful events affect some people more severely than others as a function of how genes and the environment interact
diathesis-stress model
genes we are both with can give us an inherent susceptibility for a given health outcome
differential sensitivities hypothesis
some poeple might simply have a genetic predisposition to being more strongly affected by their environment
perceived control
precieving that you have control even if you do not, can reduce stress
problem focused coping
emotion focused coping
broaden and build function
opening your mind for exploration
social support
support from others around them
flow
when people have such strong attention on a task that self-awareness disappears
implementation intentions
conscious and specific if-then thoughts designed to cognitively connect a desired action to triggering events or stimulus