cognition
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
recall
retrieving info that is not currently in conscious awareness, but was learned earlier
recognition
identifying items previously learned
relearning
learning something more quickly when learned a second time
central executive
focuses attention and pulls information from long term, helps encode, switches between tasks
chunking
organizing information into meaningful units (letters, words, phrase)
mnemonics
memory aids, especially techniques that use imagery and organization
hierarchies
few broad concepts divided and subdivided into levels
spacing effect
tendency for distributed study to yield better long term retention
testing effect
taking a test on material improves long term retention of that material more efficiently than simply reviewing
hippocampus
temporal lobe neural center, save button for explicit memories, loading dock to temporarily hold until moved to long term
cerebellum
forming and storing implicit memories
basal ganglia
motor movement, procedural memories for skills
amygdala
emotion processing and encoding
memory consolidation
neural storage of long term memory (during sleep)
infantile amnesia
conscious memory of first 4 years is blank (hippocampus isn’t mature enough)
long term potentiation
increase in cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation, neural basis for learning and memory
imagination inflation
memory distortion that occurs when a person becomes more confident that an event happened after imagining
anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories
retrograde amnesia
inability to retrieve info from past
repression
defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety arousing thoughts, feelings, memories (rarely occurs)
misinformation effect
occurs when misleading info has distorted one’s memory of an event (influence later attitude and behavior)
source amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where info was learned and imagined (can create false memories or deja vu)
cognition
mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
concept
mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
prototype
mental image or best example of category, developed and hypothetical stereotype
convergent thinking
narrowing available problem solutions to determine single best solution, analytical thinking to converge on best solution
divergent thinking
expanding number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions, novel alternatives
algorithm
methodical procedure that guarantees to solve a problem, takes a while
creativity
produce new, novel, and valuable ideas
heuristic
short cuts, solve problems efficiently, more prone to errors, exclude rare combinations and group most common
mental set
tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, usually a successful way in past
fixation
inability to see problem from new perspective; obstacle to problem solving, hindering solution
functional fixedness
thinking of things in terms of typical uses and functions
achievement test
test designed to assess what a person has learned (reflect)
aptitude test
test designed to predict a person’s future performance; capacity to learn (predict)
learning
the process of acquiring new information or behaviors through experience
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding storage and retrieval of information
multistore model
sensory, short term, long term
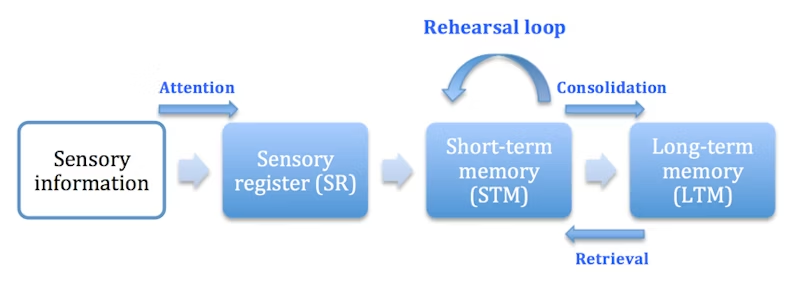
sensory
collects and transforms material (iconic 1 second and echoic 3-4 seconds, large capacity)
short term memory
temporarily holds material (20-30 seconds, capacity 7)
long term memory
more permanently retains material and recalls it as needed (>30 seconds, capacity limitless)
iconic memory
visual
echoic memory
audio
maintenance rehearsal
repeating info to keep in short term
automatic processing
performing tasks rapidly with little effort
encoding
putting in new information
storage
organize information
retrieval
pull out information
selective attention
focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus from among all sensory input
inattentional blindness
failing to see objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the visual environment
cocktail party effect
focusing on a specific conversation or sound in a noisy environment, such as a party, while filtering out a multitude of other sounds
prosopagnosia
neurocognitive disorder involving the inability to recognize faces (perceptual problem, impacts fusiform gyrus in right temporal lobe)
sensation
process by which the sensory systems and nervous system receive information from the environment
bottom up processing
information processing that analyzes raw sensory data
perception
process of organizing and interpreting incoming sensory information
top down processing
information processing that draws on our experiences and expectations to interpret incoming sensations (prior knowledge)
shallow processing
encoding on based on superficial characteristics
structural encoding
when we encode based on the physical qualities or appearance of something (appearance of letters)
phonemic encoding
when we encode based on how something sounds (rhymes, pronunciation)
deep processing
encoding semantically, based on meaning of the words rather than perceptual characteristics; tends to yield stronger, longer-lasting memories
semantic encoding
when we encode based on the meaning of something (visualize)
elaborative rehearsal
process of interpreting new information by relating it to other knowledge
levels of processing model
assumes information that is more deeply processed info will be remembered efficiently and for a longer period of time
priming
unconsciously activating particular associations in memory
recency effect
good recall of the last items from list
primacy effect
best recall of the first items of list
mood congruent memory
during positive mood states tendency to retrieve pleasant memories, negative moods states tendency to retrieve negative memories
context dependent memory
contextual association facilitates retrieval; recall is better when the external/physical are the same as when the information was encoded
state dependent memory
biological or physiological association facilitates retrieval; recalls is better when the person’s biological and psychological sate is the same as when information was encoded
retrieval cues
stimulus for remembering
serial position effect
effect of an item’s position in a list
tip of the tongue phenomenon
temporary inability to retrieve a word or name despite strong feeling that information is known
explicit memory
conscious recall of facts or events
semantic memory
general knowledge and facts
episodic memory
memory of personal experiences and specific events
prospective memory
remembering to perform a task in the future
implicit memory
unconscious recall of skills and routines
procedural memory
memory of how to perform tasks, skills, and actions
working memory model
explains how short term memory works as an active system uses to temporarily store and manipulate information
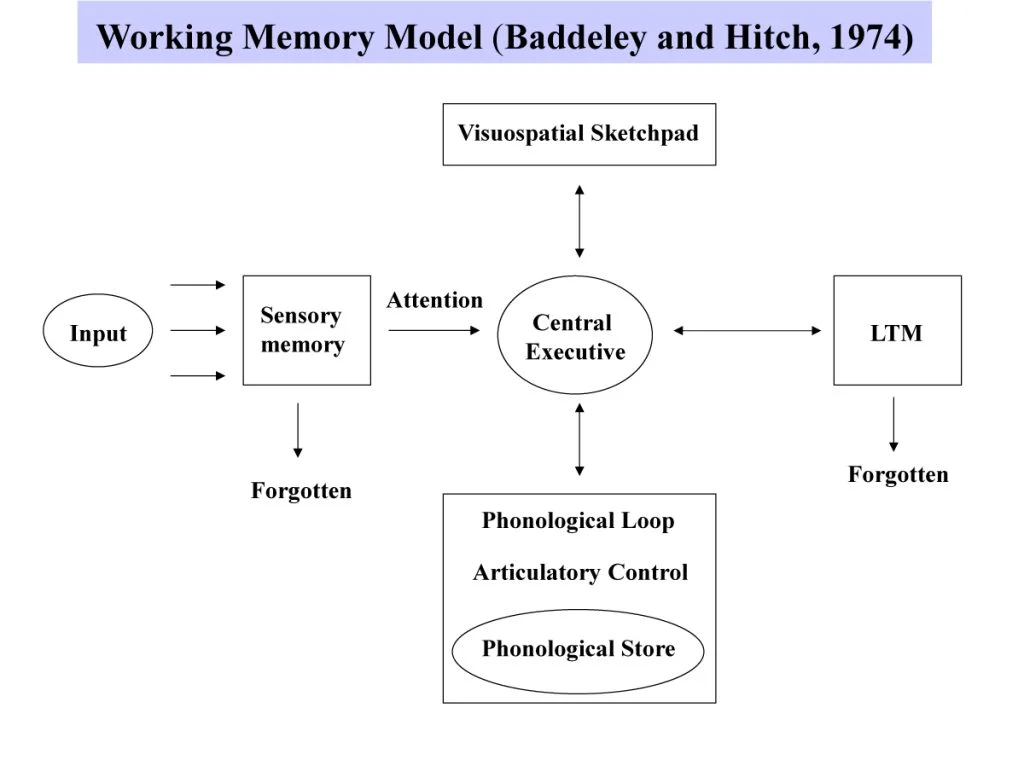
phonological loop
stores and processes spoken and written information allowing us to repeat information on a loop
visuospatial sketchpad
stores and processes visual and spatial information, allowing us to picture things in our mind
episodic buffer
combines different types of information into a single memory
method of loci
visualization of familiar spaces to assist with memorization
constructive memory
how the brain creates memories based on past memories
encoding failure
much of what we sense we never pay attention to, and what we fail to encode we will not remember
storage decay
memory for new information fades quickly especially without rehearsal but levels out over time
retrieval failure
important information can defy our attempts to access it
proactive interference
when the old stuff you learned previously is getting in the way of new stuff you are trying to remember now
retroactive interference
when the new stuff you’ve learned makes it hard to remember the old stuff
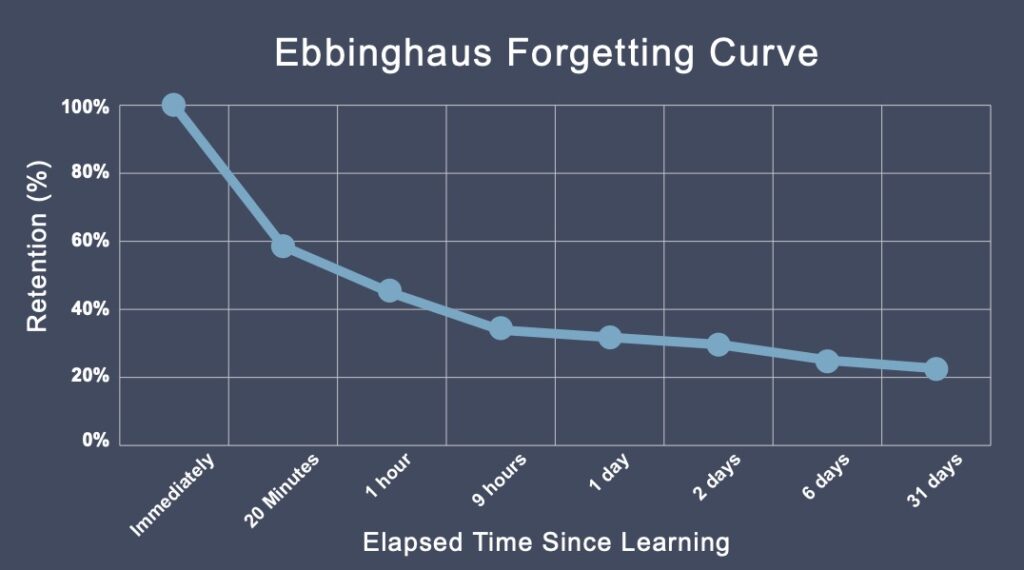
forgetting curve
tests of recognition and of time spent relearning demonstrate that we remember more than we recall
availability heuristic
process of judging the likelihood or frequency of an event by the ease with which instances come to mind
representativeness heuristic
process of estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent or match particular prototypes which may lead us to ignore other relevant information
sunk cost fallacy
tendency to continue investing time, money, or effort into a decision or activity, even when its no longer beneficial simply because of the resources that have already been committed
gamblers fallacy
cognitive bias where people mistakenly believe that they likelihood of a random event is influences by previous outcomes
single intelligence/general ability
describes broad mental capacity, can be measured by an iq test
multiple abilities
divides human intelligence into independent modalities
intelligence
the ability to acquire and apply knowledge and skills
confirmation bias
seeking out information that agrees with you and dismissing anything that doesn’t
flynn effect
new generations test better to environmental factors