anatomy and physiology: connective tissues
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
connective tissue components
-specialized cells,
-extracellular protein fibers
-ground substance
connective tissue function
-provide structural support
-fills internal spaces
-stores energy
-transport materials
-blood supply can be vascular or avascular
extracellular matrix
-Non-living material that surrounds living cells
-ground substance and fibers
-determines special function
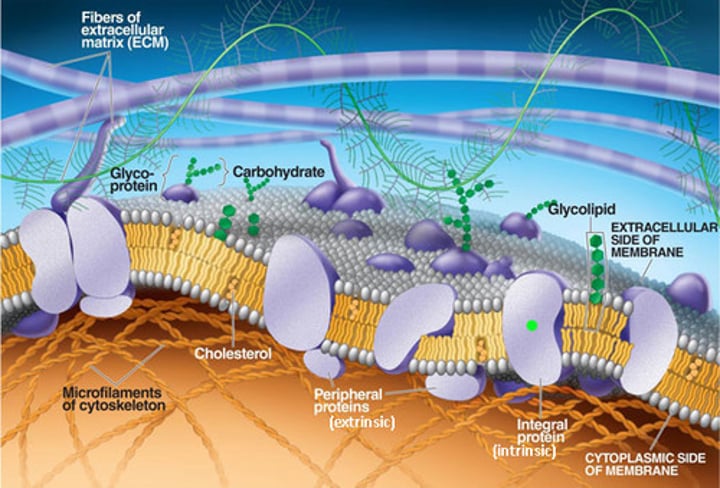
Ground substance
-mostly water along with adhesion proteins and polysaccharide molecules
-clear, colorless, and viscous
-fills cell space and slow pathogen movement
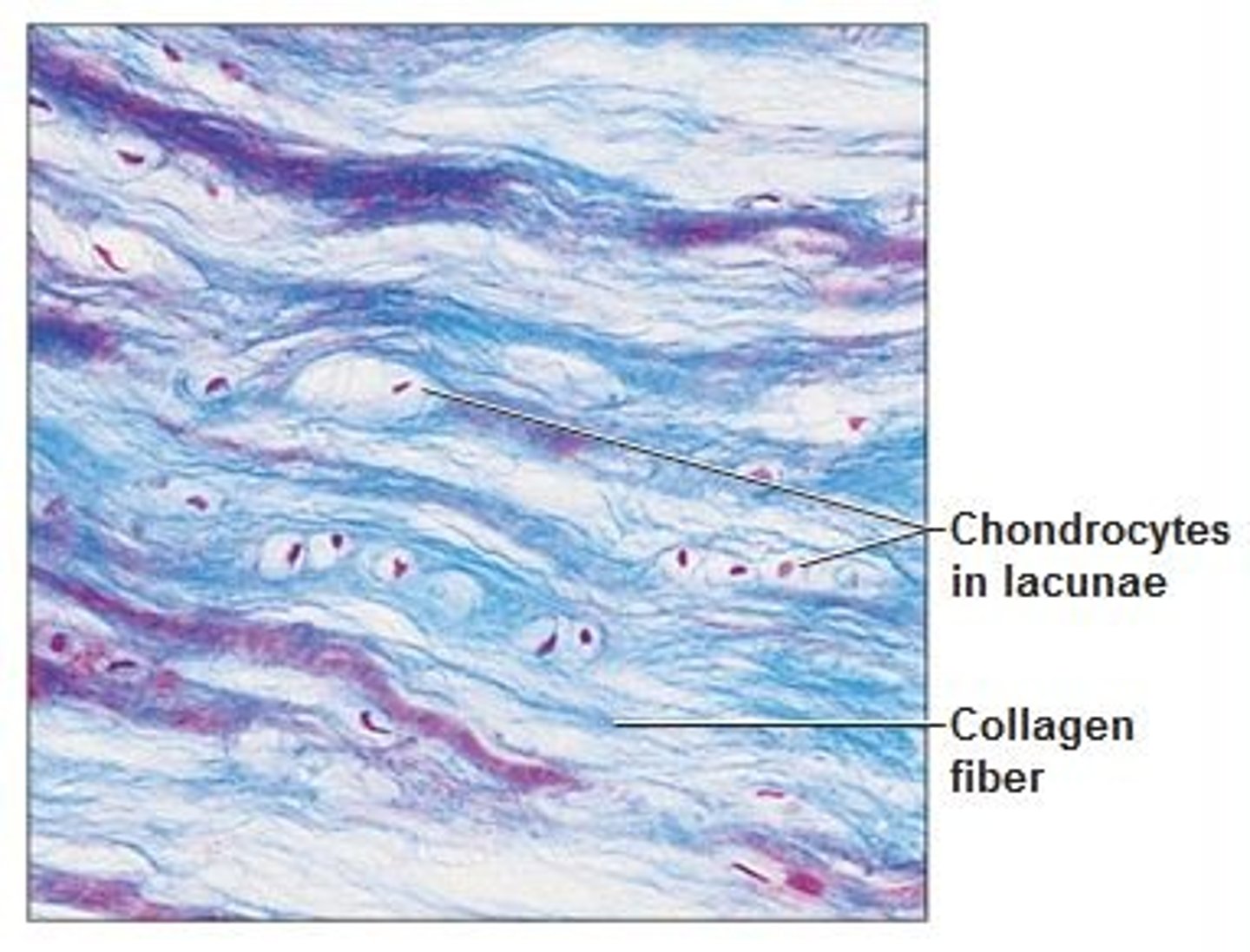
fibers
-produced by cells
-collagen (white)
-elastic (yellow)
-reticular
collagen fiber
-Strongest and most abundant type (flexible)
-long, straight, unbranched
-Provides high tensile strength
-resist force in one direction
elastic fiber
-Long, thin fibers that form branching networks
-branched and wacky elastin
-allows them to stretch and recoil.
reticular fibers
-short, fine and highly branched collagenous fibers.
-network of interwoven fibers
-resist force in many directions
-strong and flexible
connective tissues categories
-proper: connect and protect
-fluid: transport
-supporting: structural strength
proper connective tissue: loose
-more ground substance, fewer fiber
-packing materials
-areolar
-adipose
-reticular
areolar connective tissue function
-soft packing material web wraps and cushions organs
-support permits independent movement
-can soak excess fluid
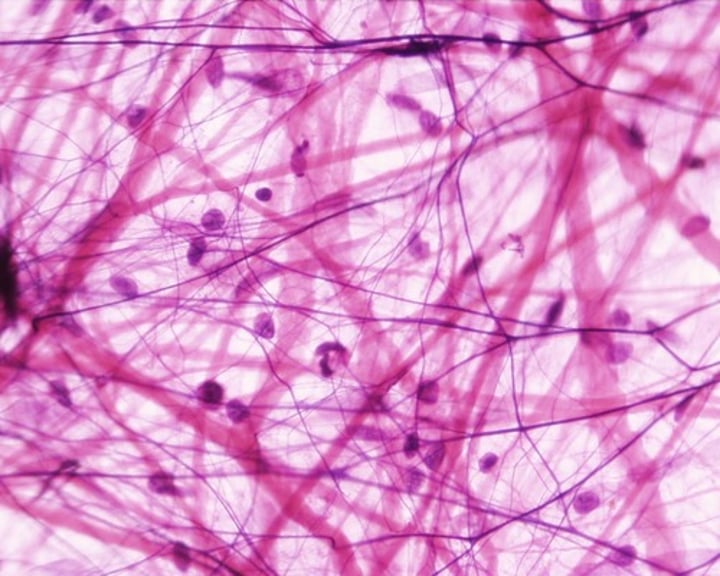
areolar connective tissue location
widely distributed under epithelia of body
reticular connective tissue
-Delicate network of interwoven fibers
-Forms stroma (internal supporting network) of lymphoid organs
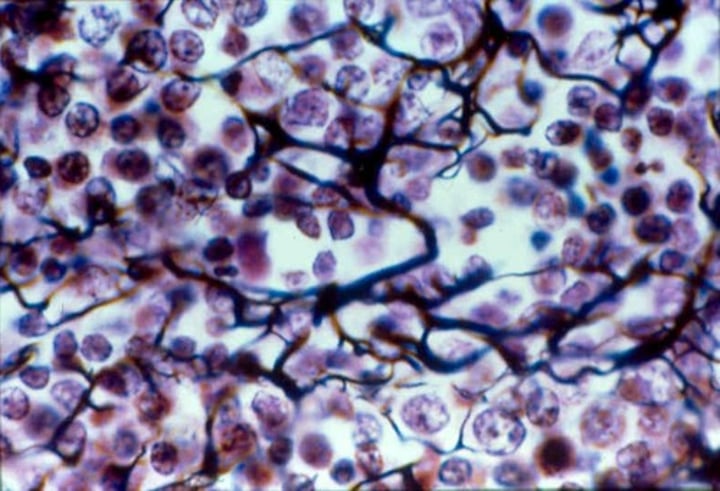
reticular connective tissue location
lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, liver and kidney
adipose connective tissue
-Acts as a storage depot for fat (expand and shrinks)
-provide insulation against heat loss
-padding and cushions shocks
-mesenchymal cells divide & differentiate for more fat & storage
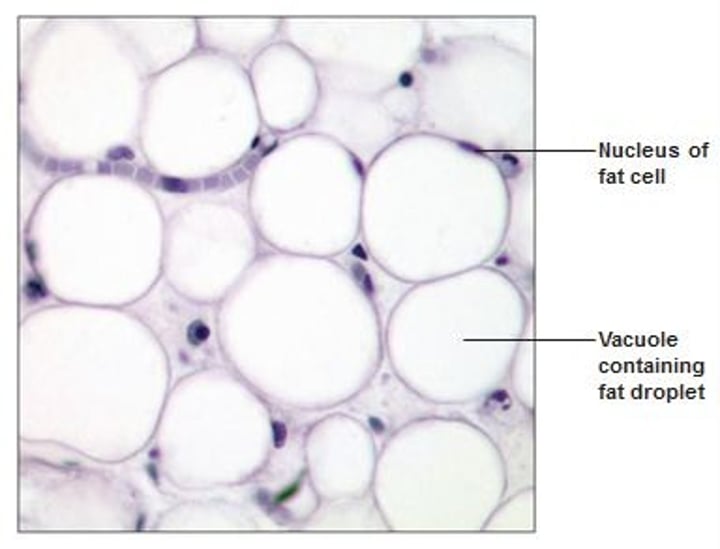
adipose connective tissue location
-under skin
-around kidneys and eyeballs;
-butttocks and breasts
Blood (vascular tissue)
-fluid matrix called blood plasma
-Fibers are visible during clotting
-transport vehicle for materials
-found in blood vessels
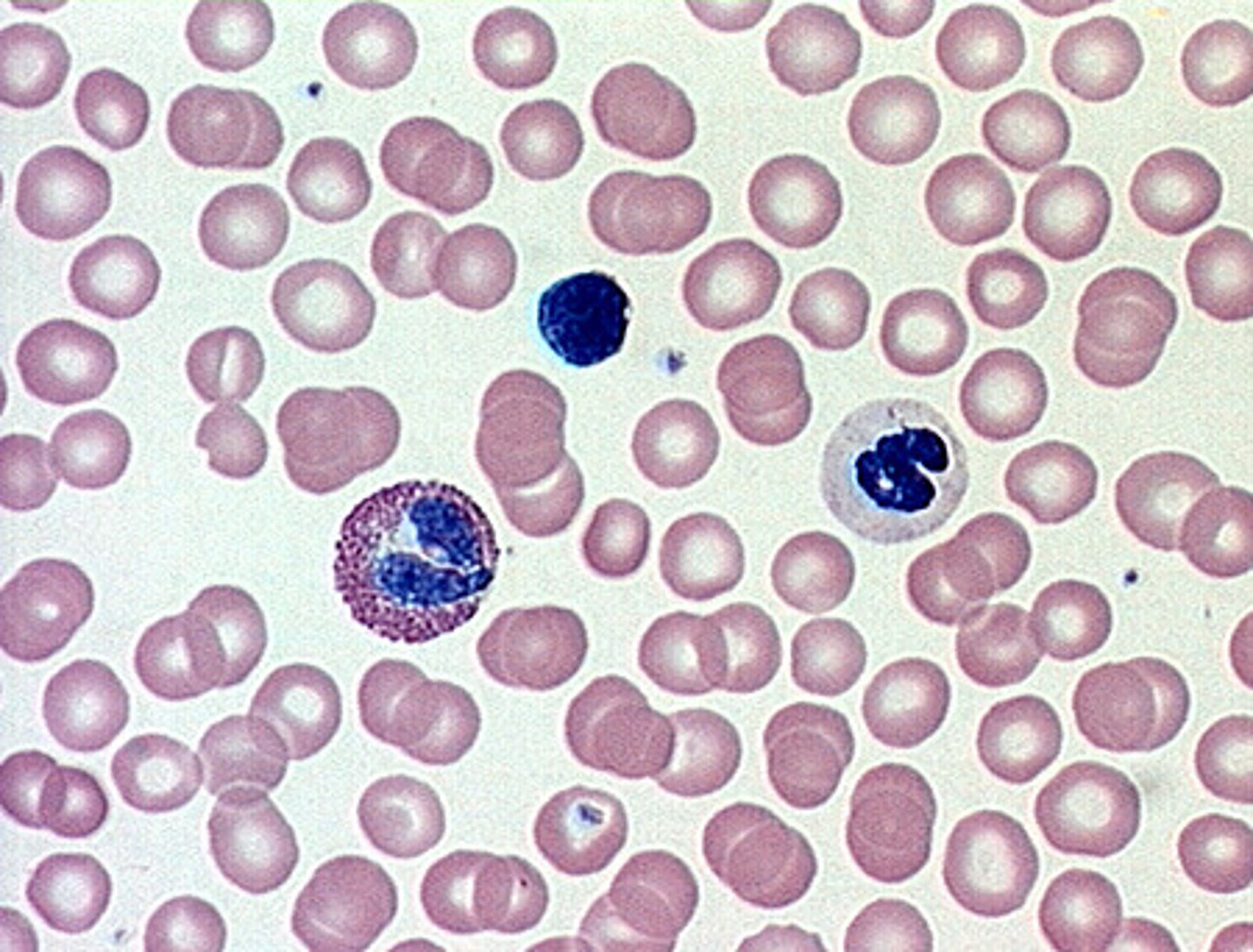
red blood cells (erythrocytes)
-transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
-no nucleus
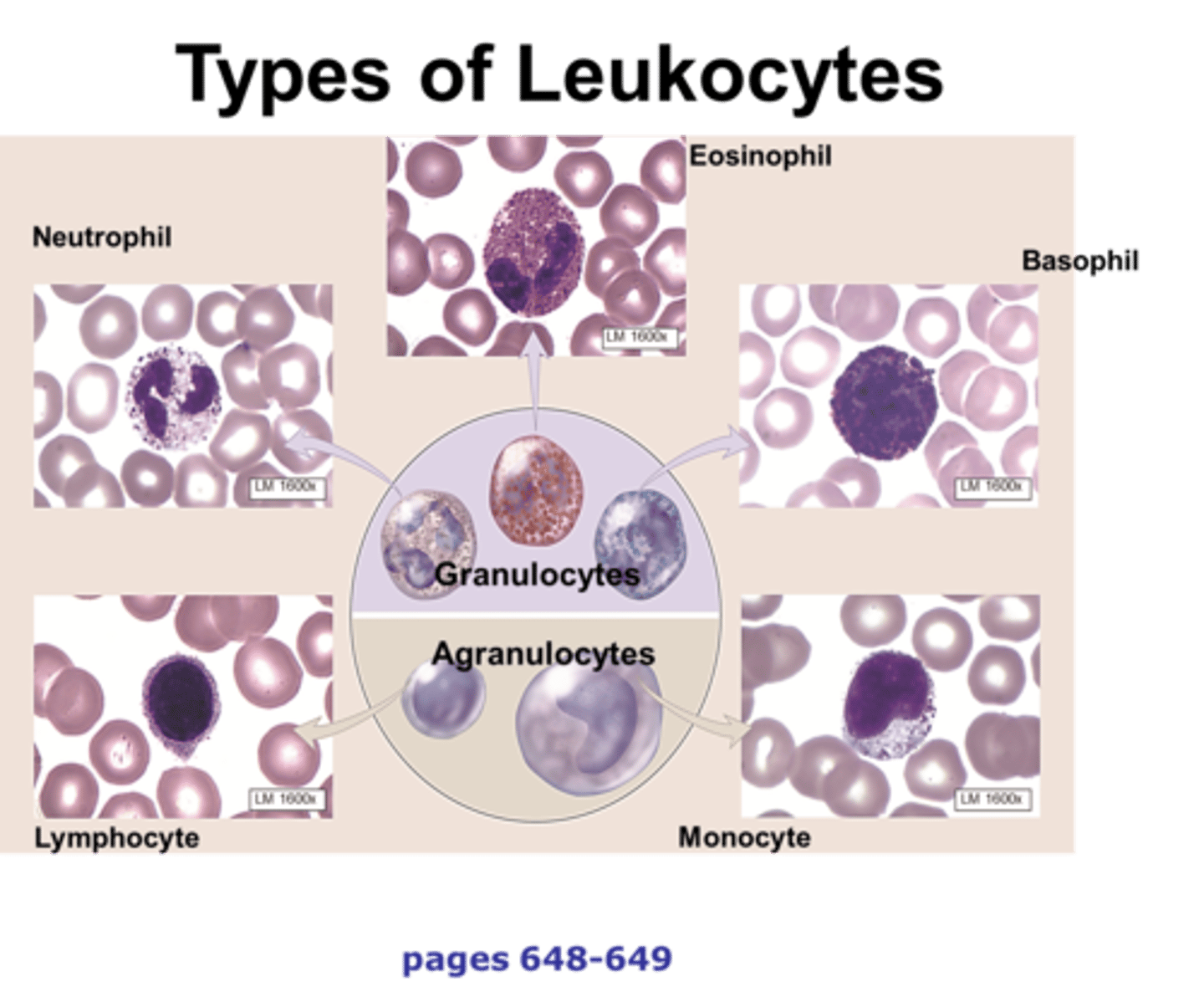
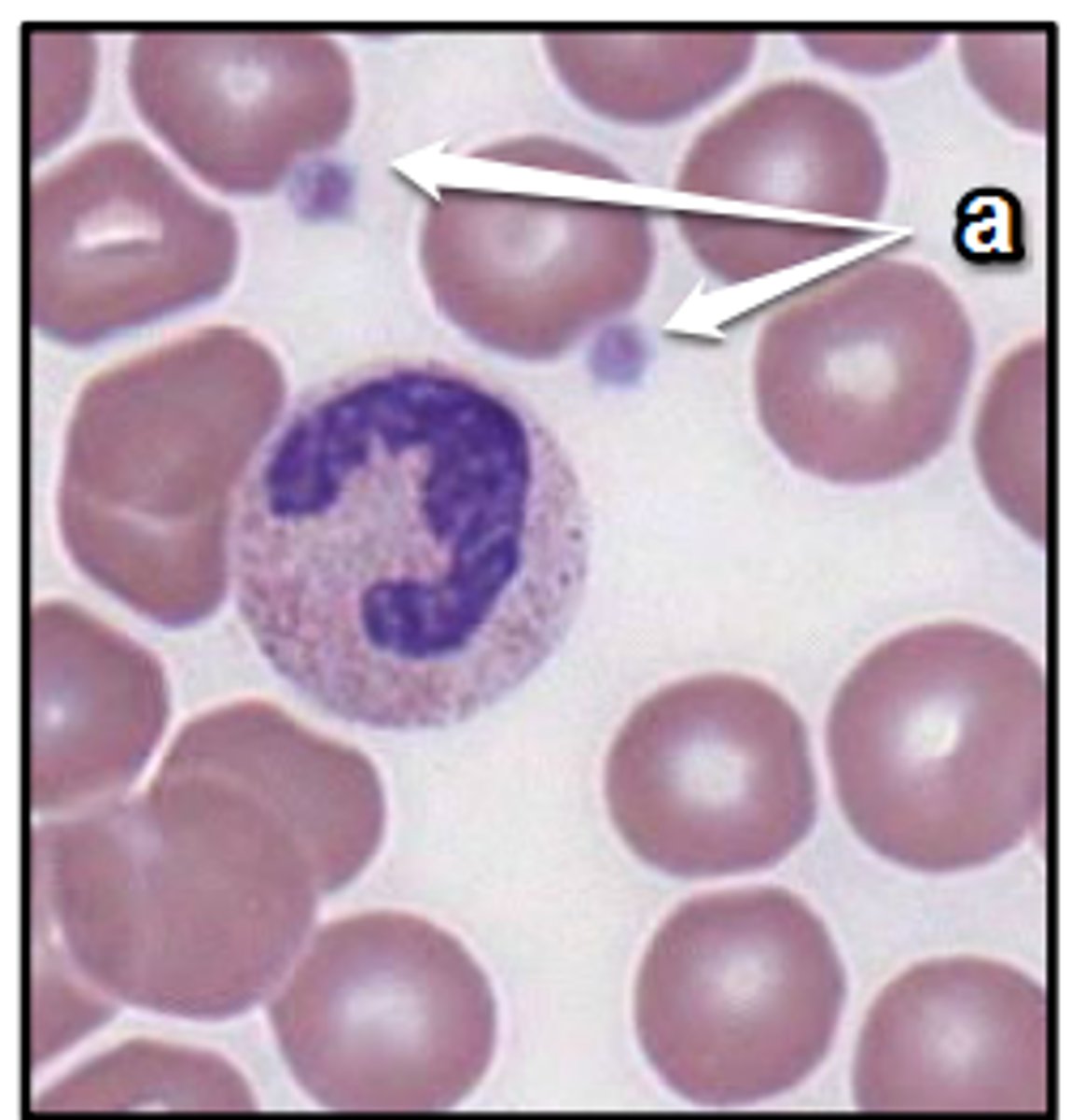
white blood cells (leukocytes)
-respond to injury or infection
-nucleus
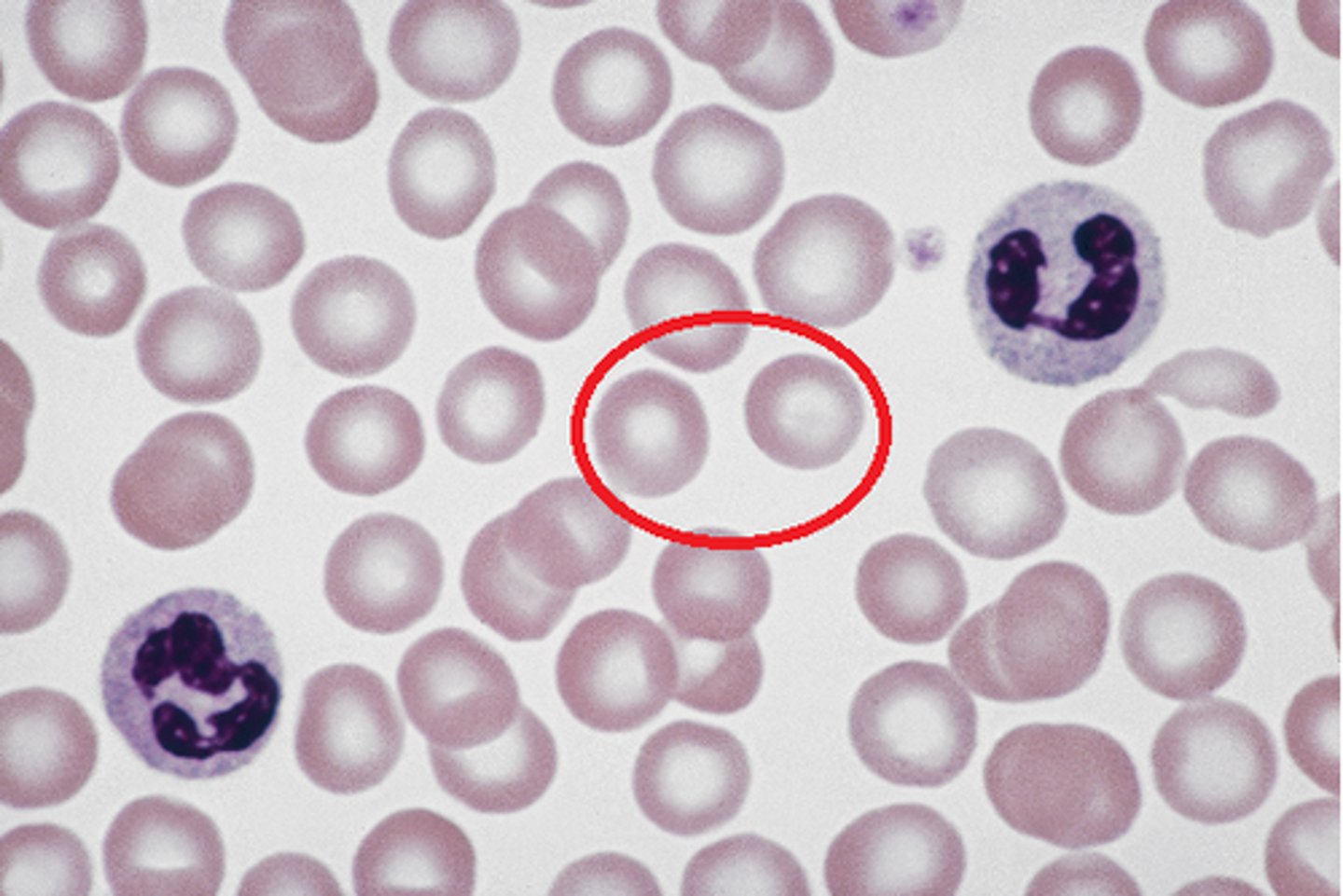
Platelets (thrombocytes)
blood clotting
proper connective tissue: dense
-more fibers, less ground substance
-COLLAGEN
-regular
-irregular
-elastic
dense regular connective tissue
-Tightly packed, PARALLEL collagen fibers
-FIRM attachment and stability
-reduce muscle friction
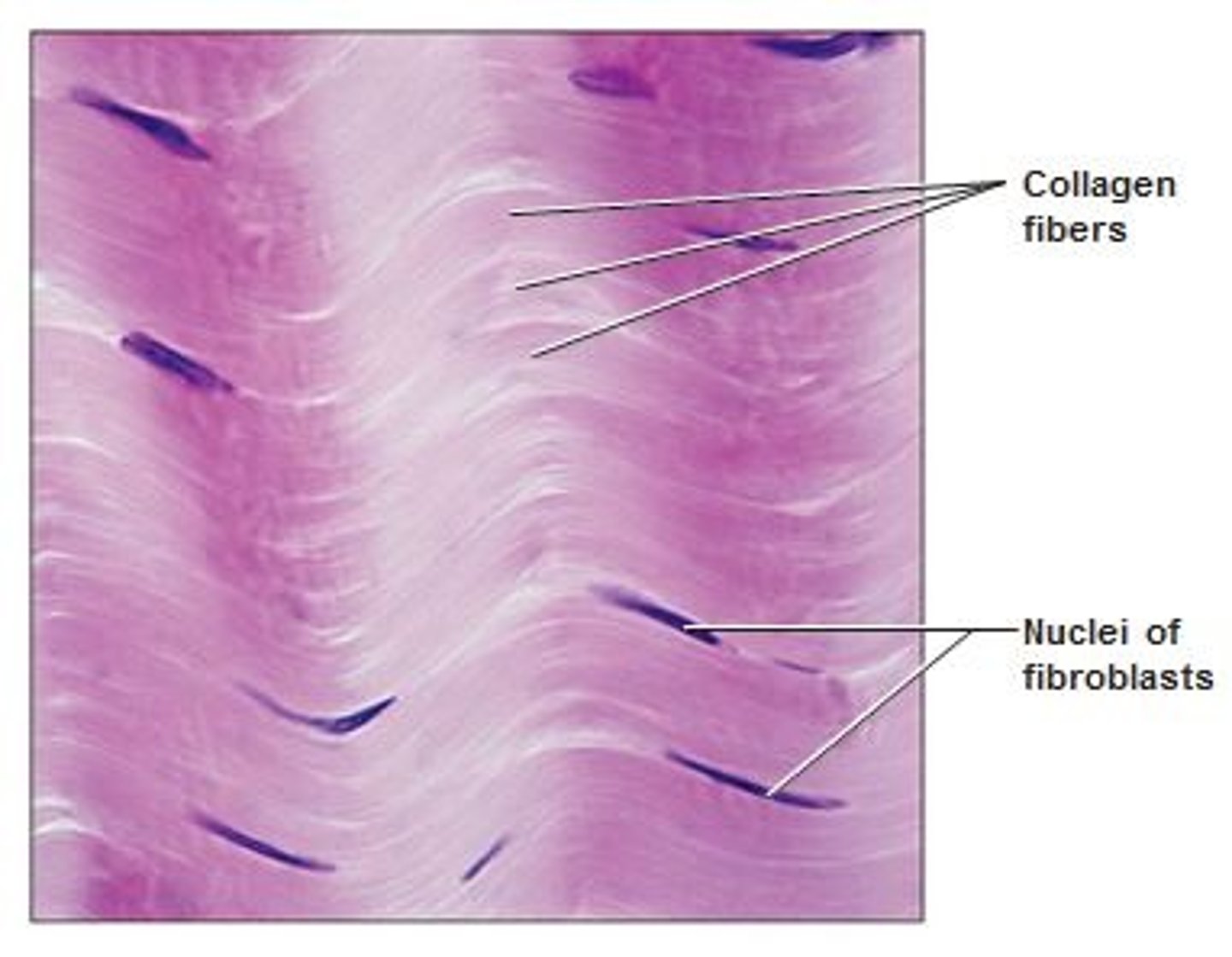
dense regular connective tissue location
-TENDONS: attach muscles to bones
-LIGAMENTS: connect bone to bone and stabilize organs
-APONEUROSES: attach in sheets to large, flat muscles
-DERMIS: lower skin layers
dense irregular connective tissue
Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
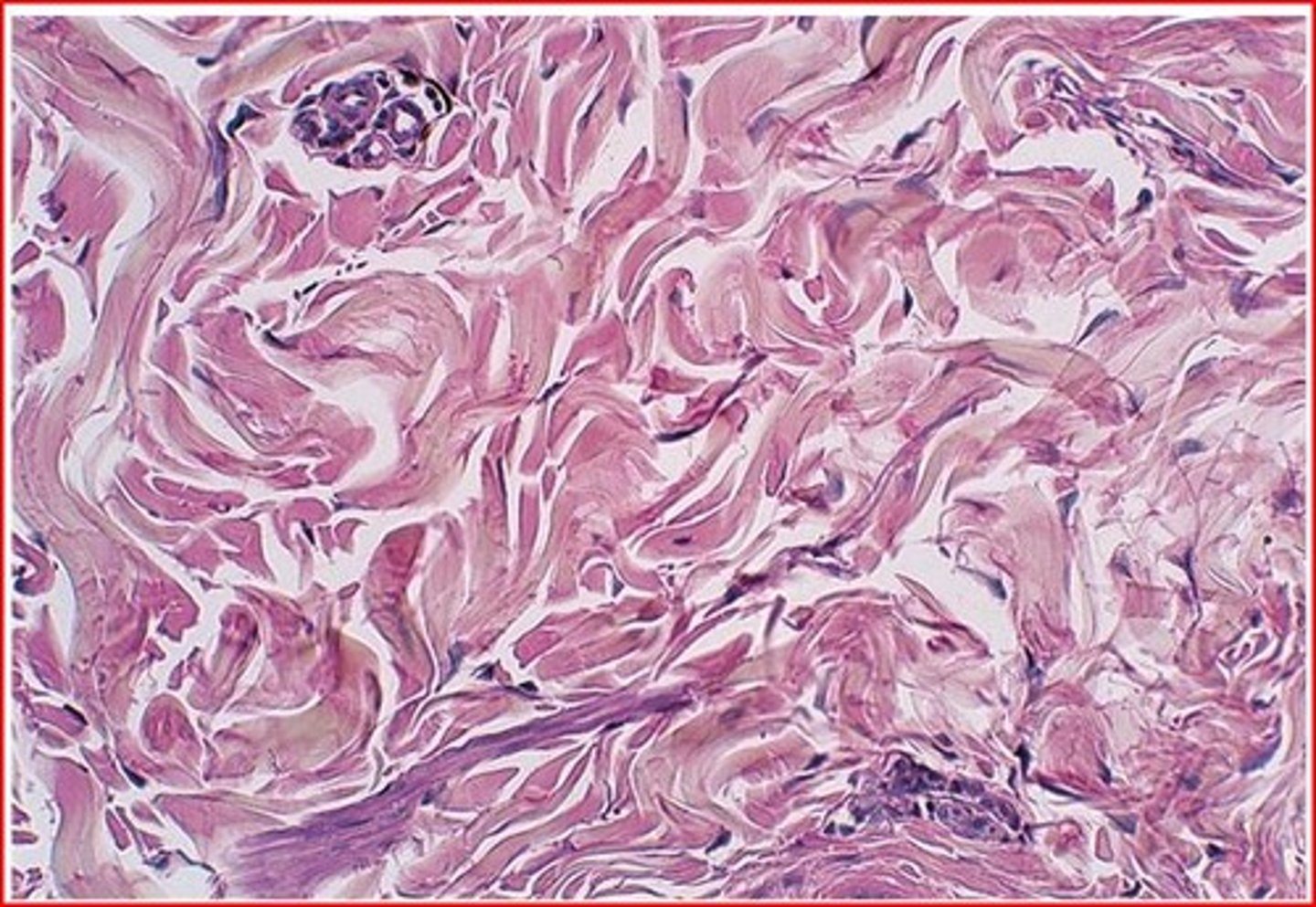
dense irregular connective tissue location
fibrous capsules of organs and of joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract
elastic dense connective tissue
elastic fibers allows recoil after stretching; allows blood flow
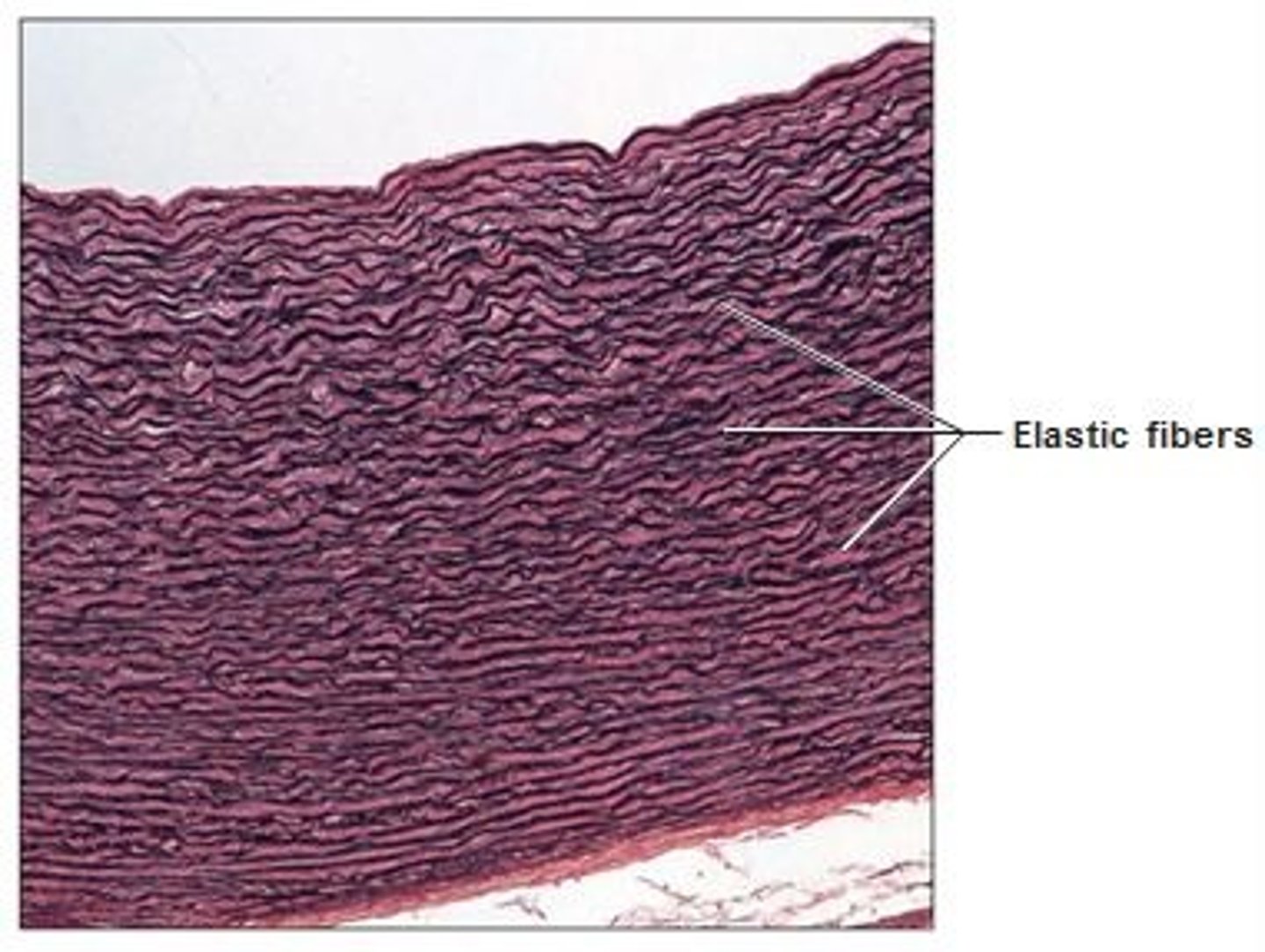
elastic dense connective tissue location
Walls of large arteries and walls of bronchial tubes
fibroblast cell
-abundant cell type
-secrete proteins and hyaluronan (cellular cement)
-all proper connective tissue
hematopoietic
pertaining to the formation of blood cells
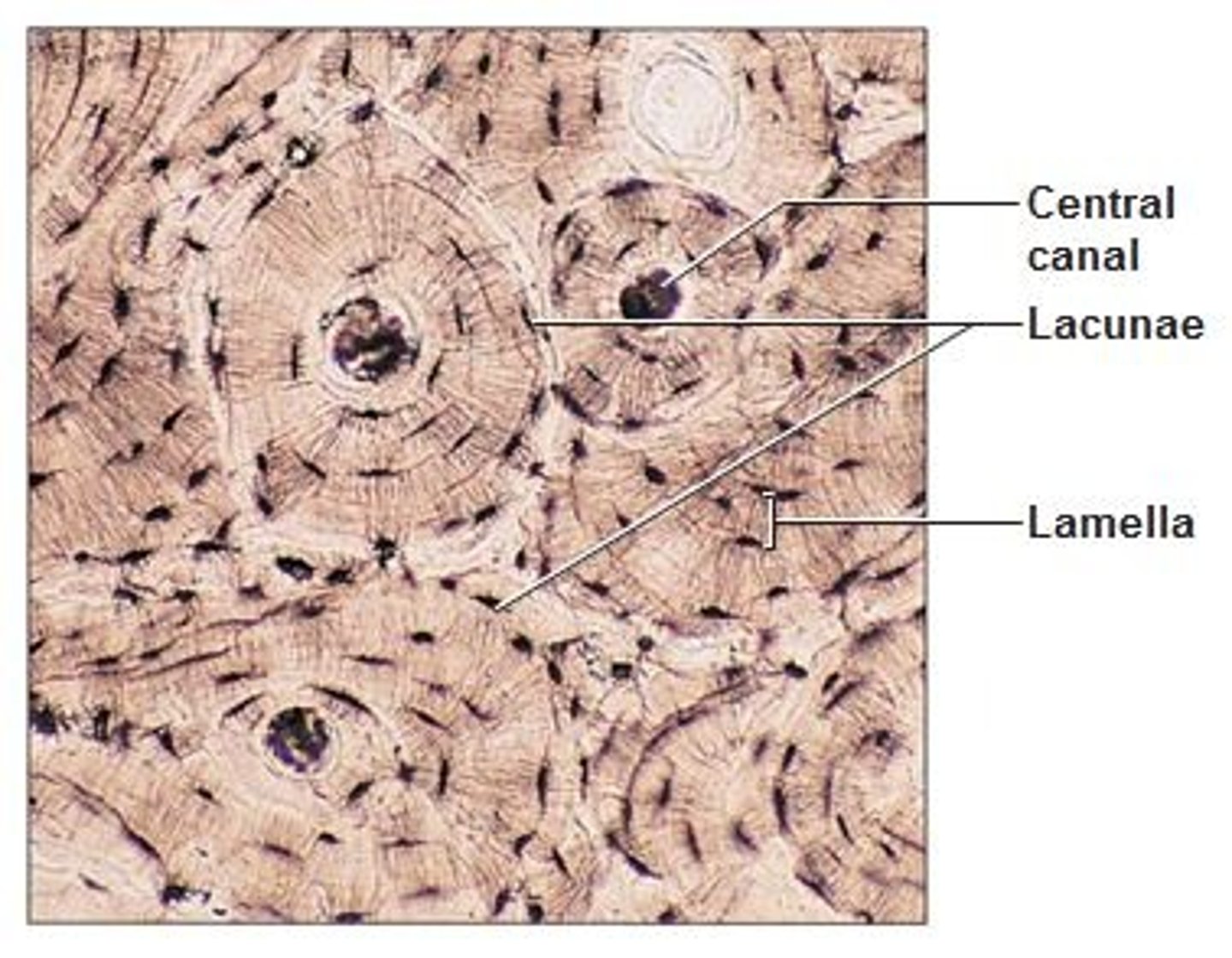
lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes (bone cells)
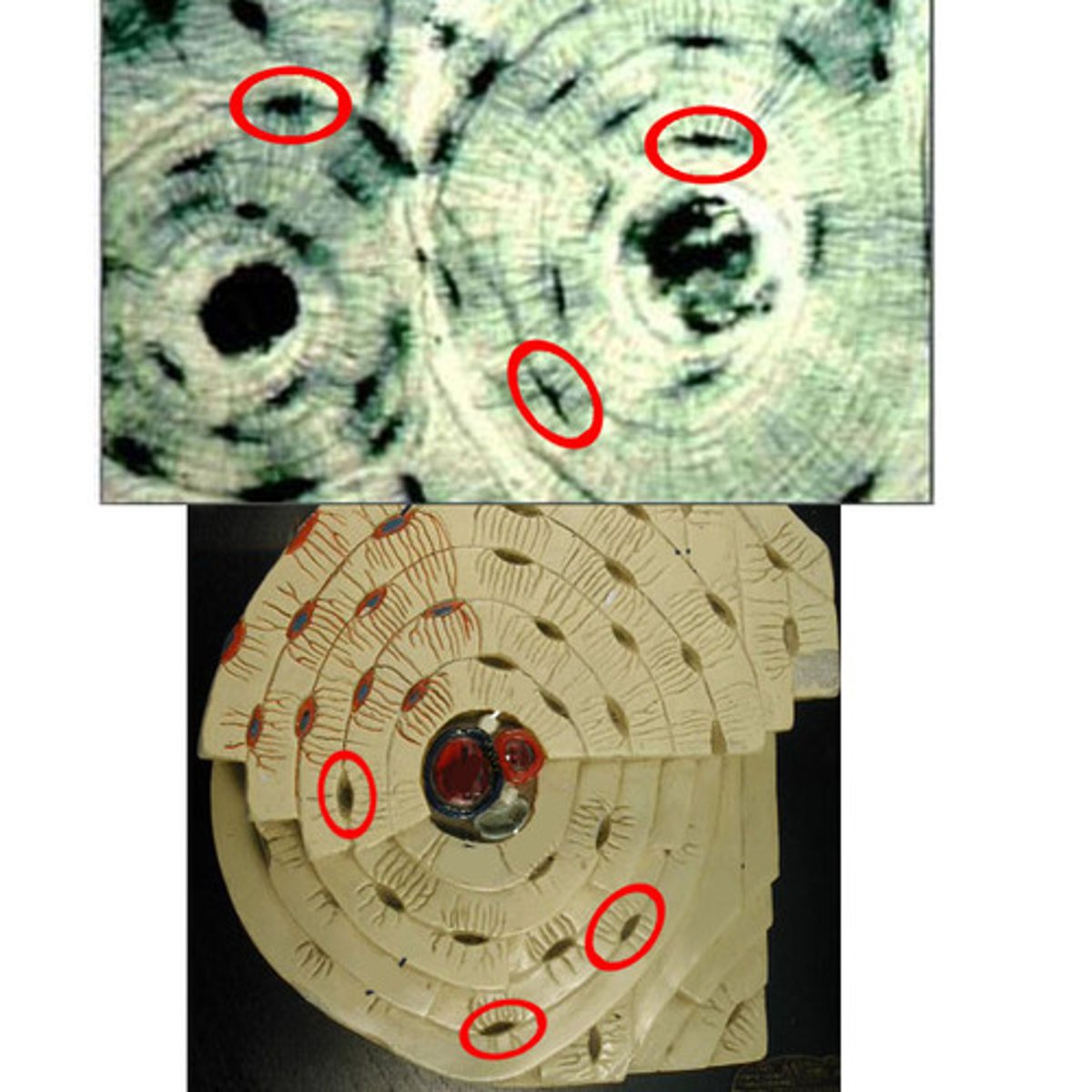
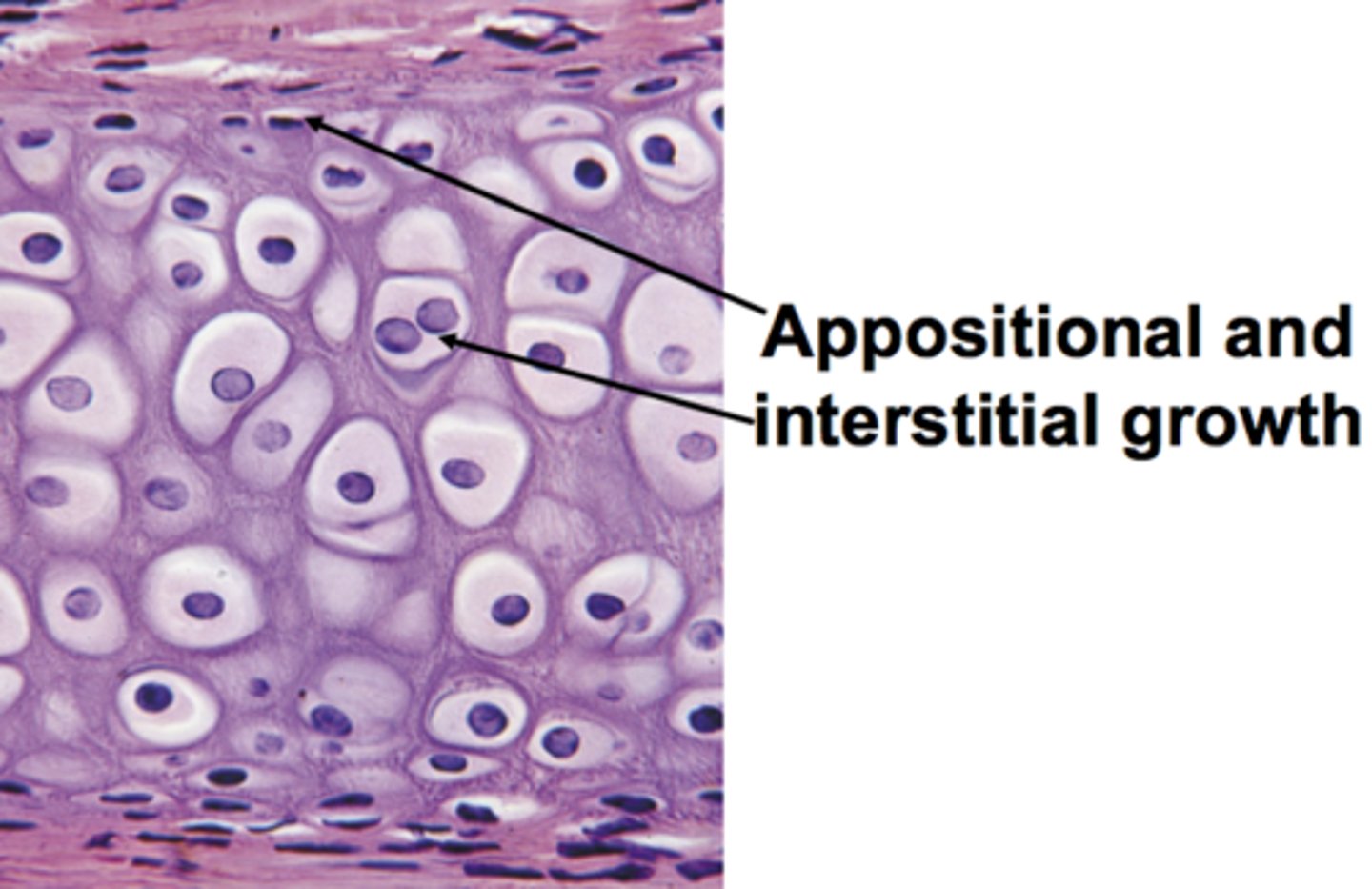
hyaline cartilage
-Most common type of cartilage
-reduce bone friction
-stiff but somewhat flexibility
hyaline cartilage location
ends of long bones, ribs, and nose
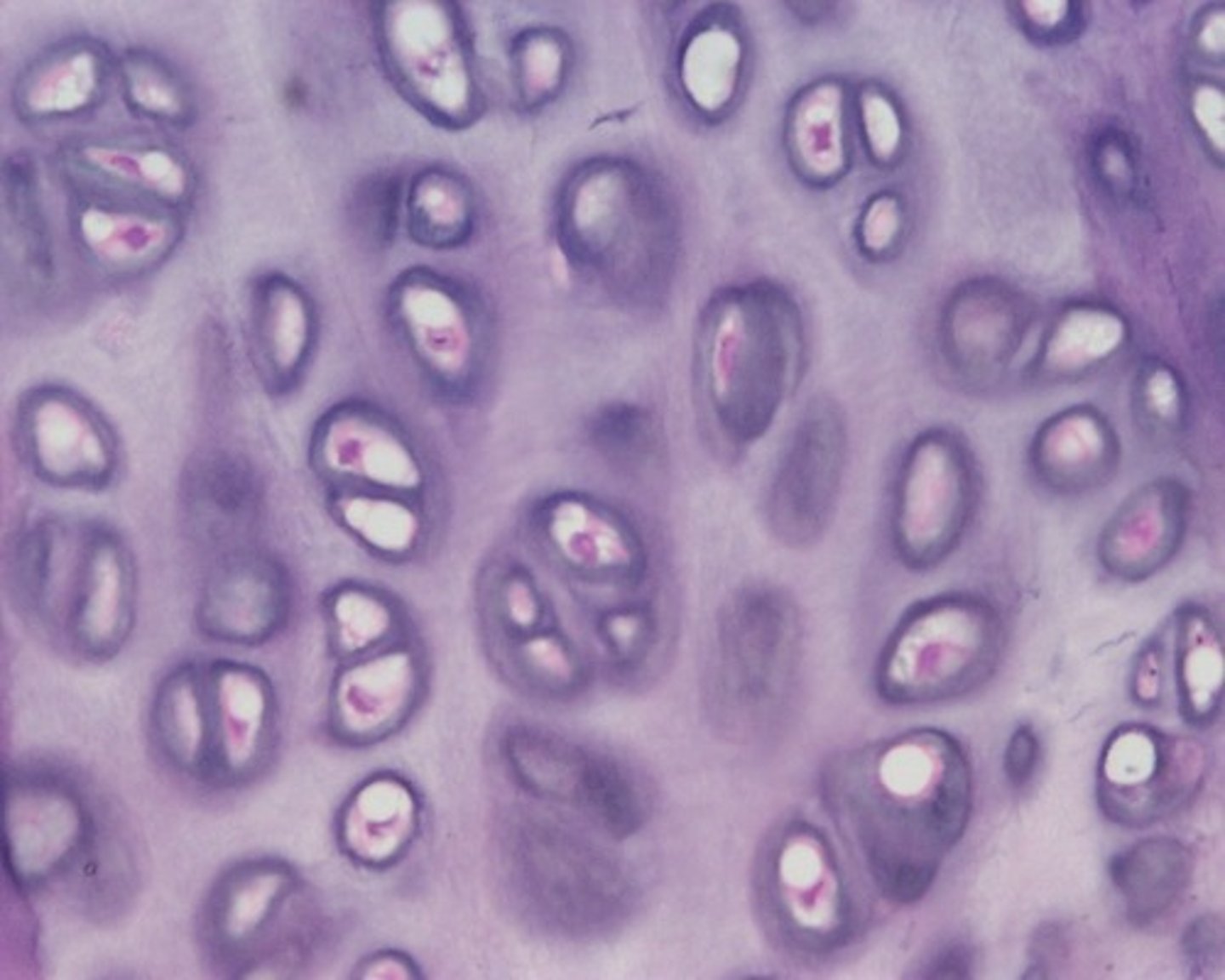
elastic cartilage function
maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
elastic cartilage location
external ear, epiglottis
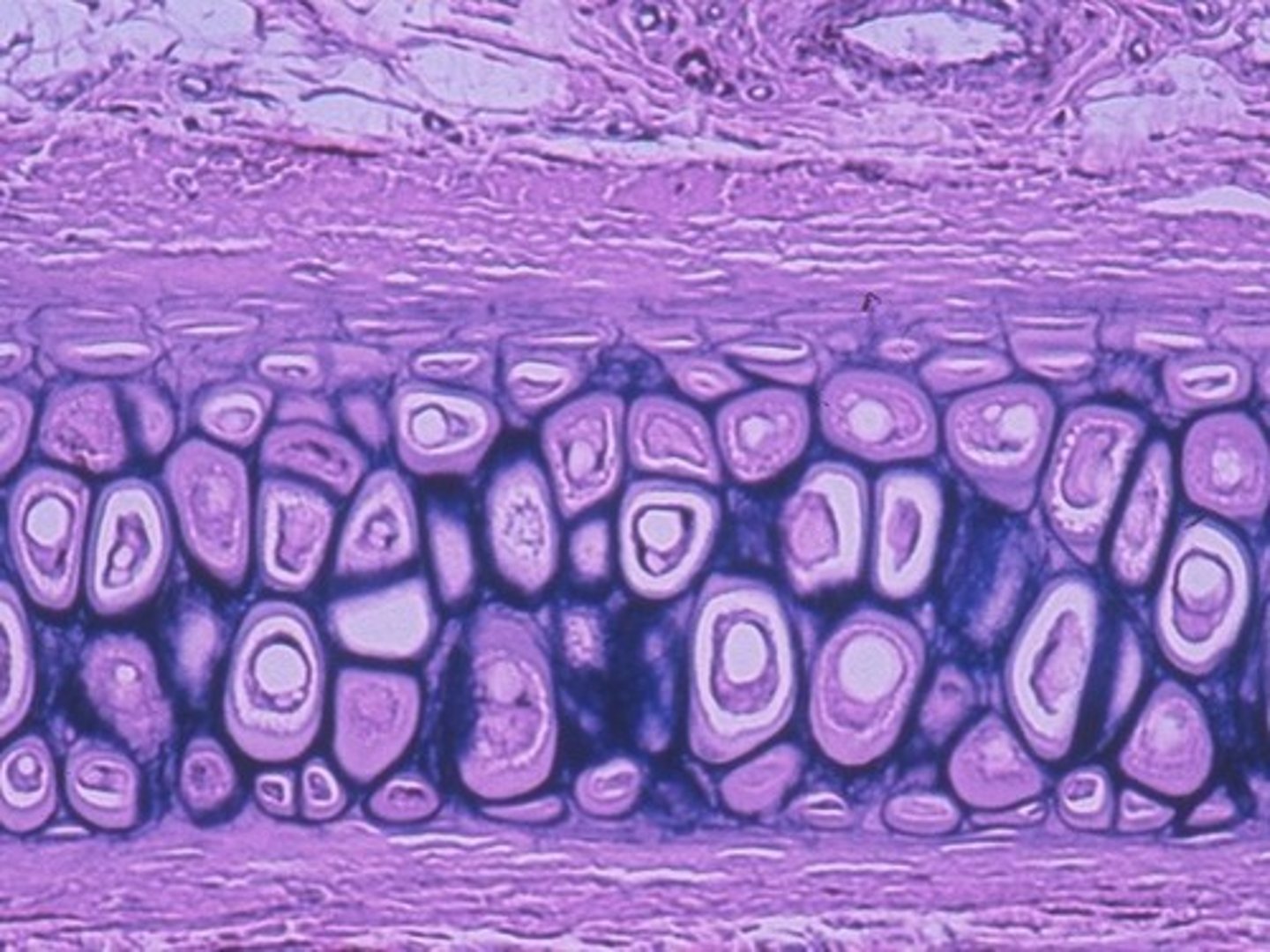
fibrocartilage function
-tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
-prevents bone to bone contact
fibrocartilage location
intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint
cartilage growth
-Interstitial: enlarges cartilages INSIDE
-Appositional: cartilage growth OUTSIDE
bone (osseous tissue)
-bone cells (osteocytes) in lacunae
-hard matrix of calcium salts
-protect and support the body
-periosteum: cover bone (fibrous outer/cellular inner)
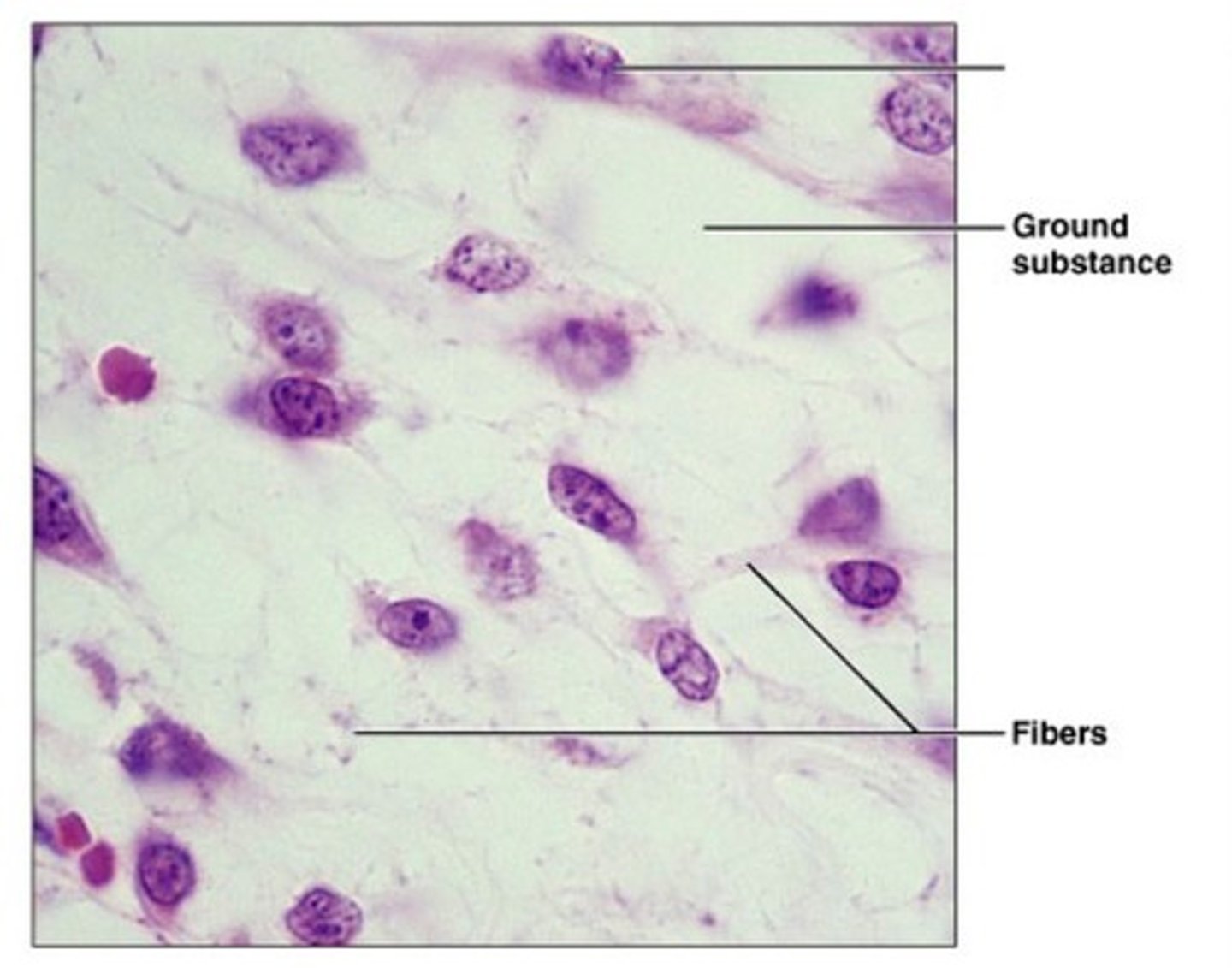
mesenchyme cells
-stem cells that respond to injury or infection
-first embryonic connective tissue
-differentiate into fibroblasts and macrophages
mast cells
-respond to injury, infection, or allergy
-releases heparin and histamine
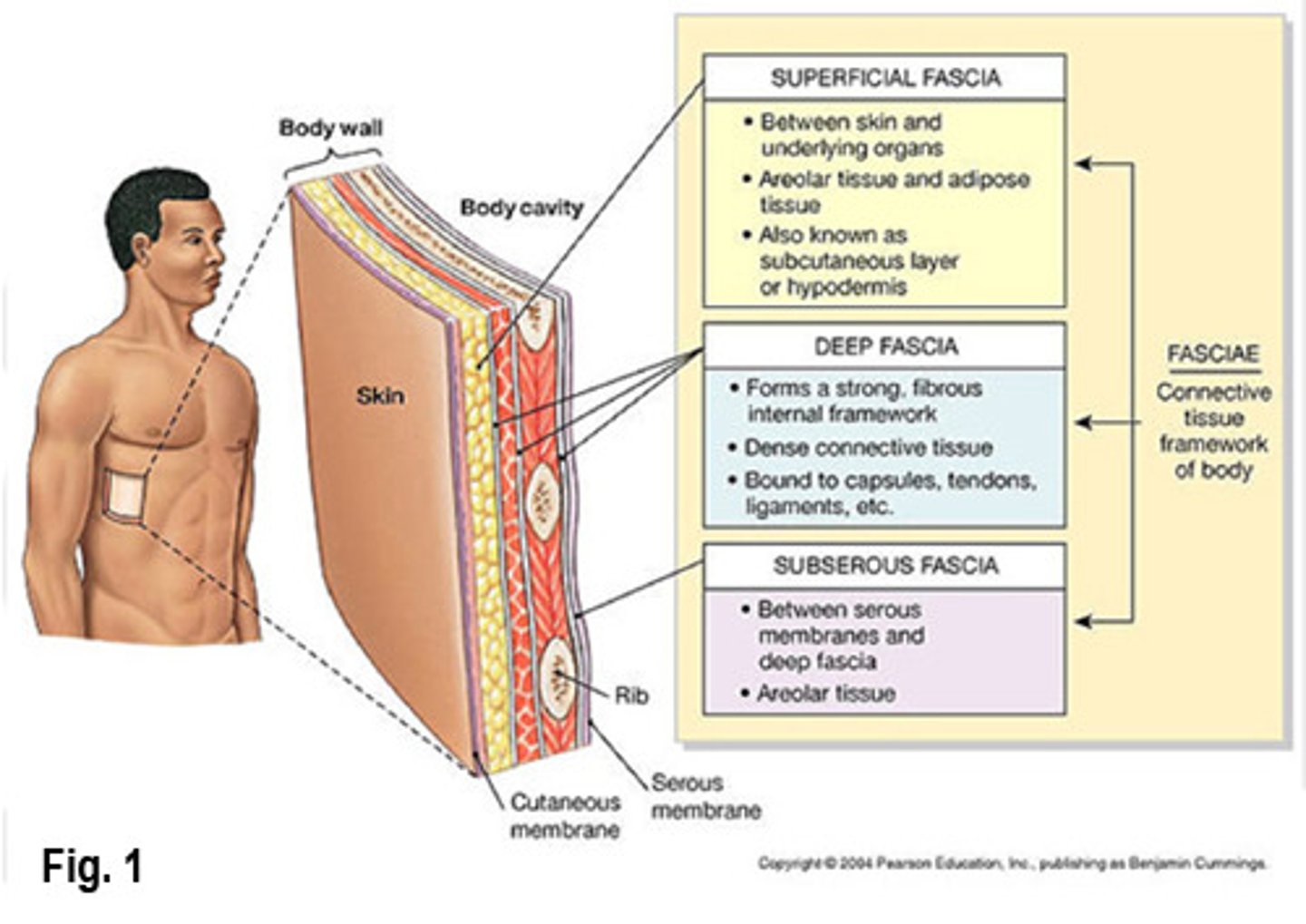
superficial fascia
Separates skin from underlying tissues
deep fascia
Sheets of dense regular connective tissue
subserous fascia
between serous membranes and deep fascia that lines body cavities
fasciae
connective tissue layers and wrappings that support and surround organs