Alkenes and Alkynes
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Alkene
1+ C-C double bond
Alkyne
1+ C-C triple bond
Nomenclature
Name Parent Compound
longest chain containing double or triple bond
-ene or -yne ending
if multiple double/triple bonds, indicate # w/ numerical prefix (diene, triene)
# C atoms in main chain so that multiple bonds have lowest #s
Write full name
assign #s to branching attachments
list substituents alphabetically
indicate position of multiple bonds by giving # of first C — if multiple then use commas and appropriate prefix
Common names
HC=CH — acetylene
H2C=CH2 — ethylene
CH3CH=CH2 — propylene
Bond angles of alkenes and alkynes
alkene: 120
alkyne: 180
Cis-Trans isomerism
same formula & connections btwn atoms, but diff 3d structures since double bonds do not allow rotation around bonds, creates rigidity and possibility for different structures
cis: groups are on the same side of the double bond
trans: groups are on opposite sides of the double bond
Properties
nonpolar
insoluble in water
less dense than water
flammable
nontoxic
multiple bonds are chemically reactive
Types of reactions
Addition
Reagant X-Y
Hydrogenation
Halogenation
Hydrohalogenation
Hydration
Elimination
Substitution
Rearrangement
Reagant X-Y addition
reagant X-Y adds to multiple bond in unsaturated reactant to yield saturated product w/ only saturated bonds
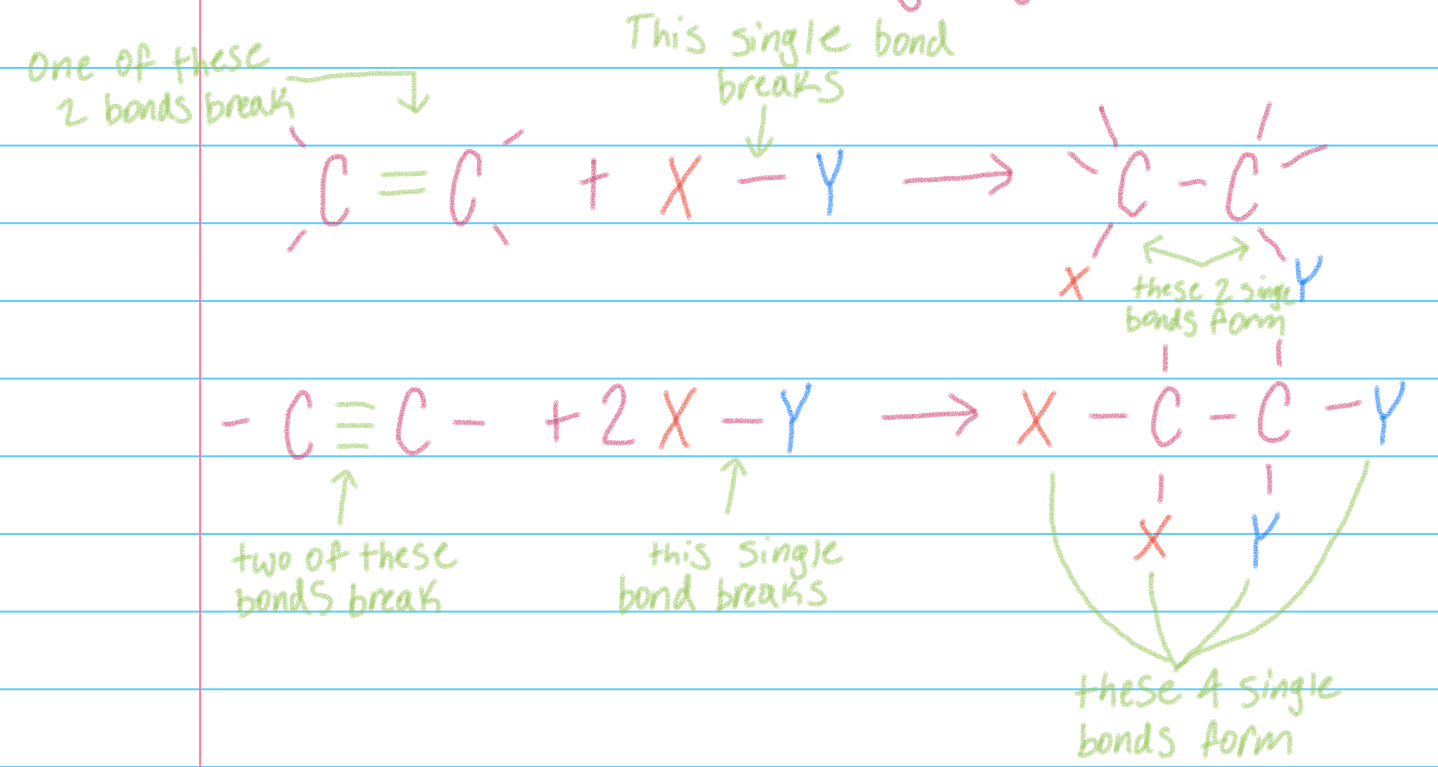
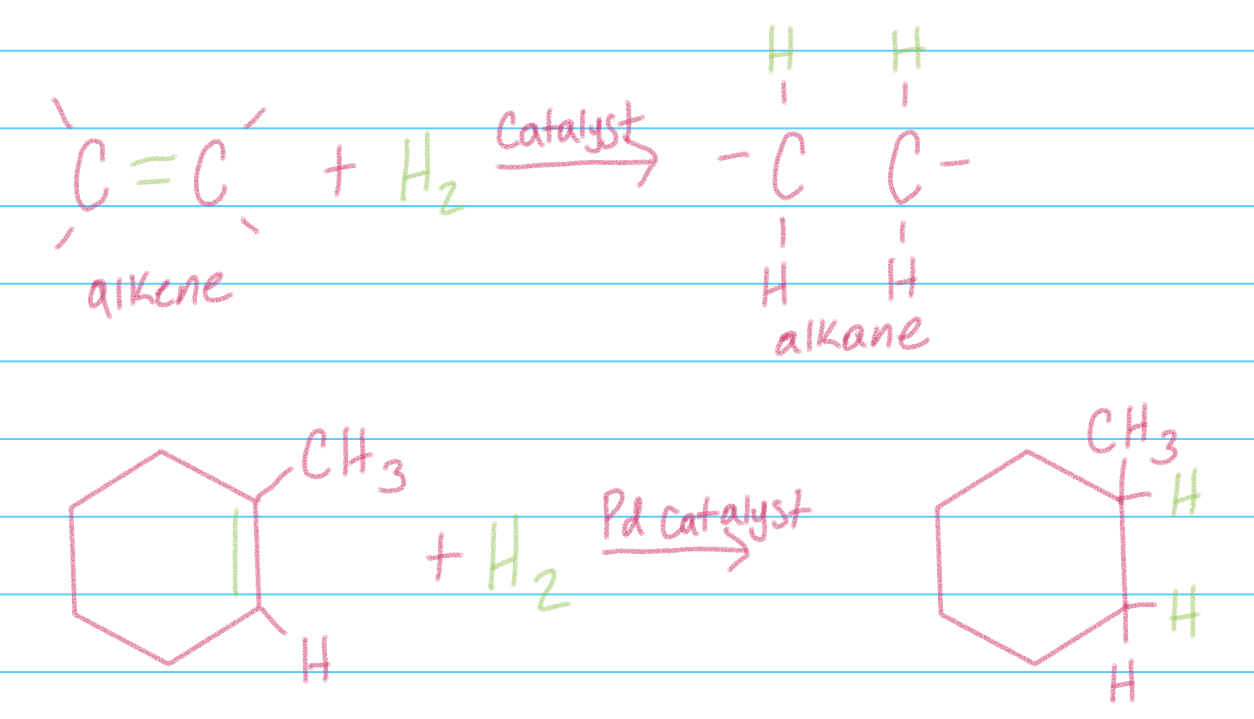
Hydrogenation addition
Addition of H2 to Alkenes in presence of a solid state metal catalyst (Pd,Pt,Au), yields corresponding alkane product
Halogenation addition
Addition of Cl2 or Br2 to alkenes, use UV and heat
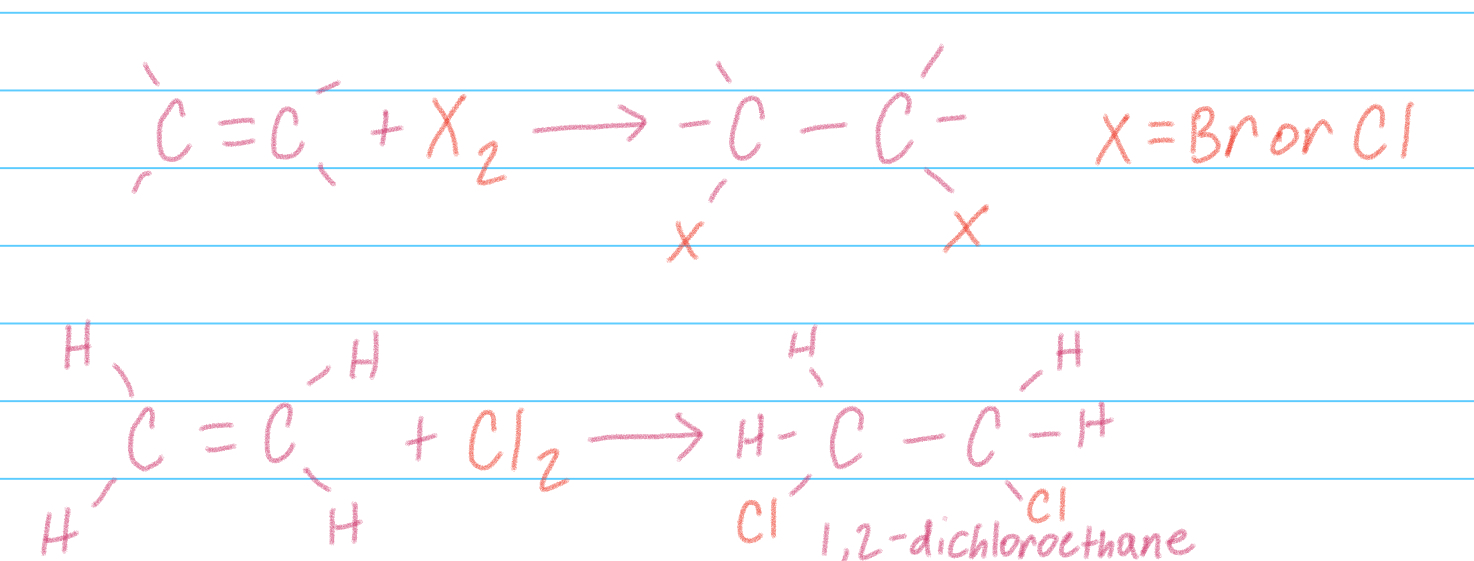
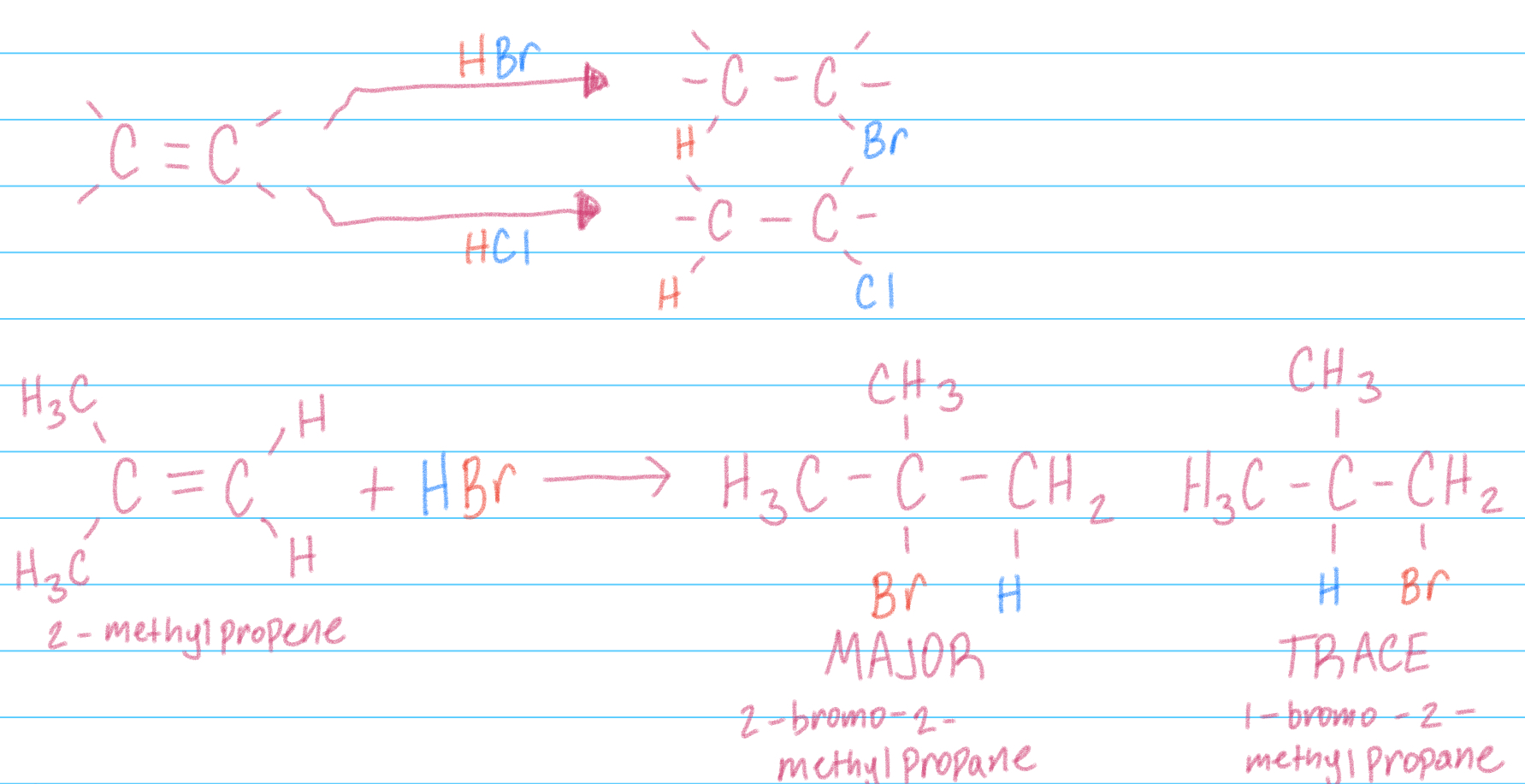
Hydrohalogenation addition
Addition of HBr or HCl to Alkenes to yield alkyl bromides/chlorides
Can have a major product—> use Markovnikov’s rule to determine
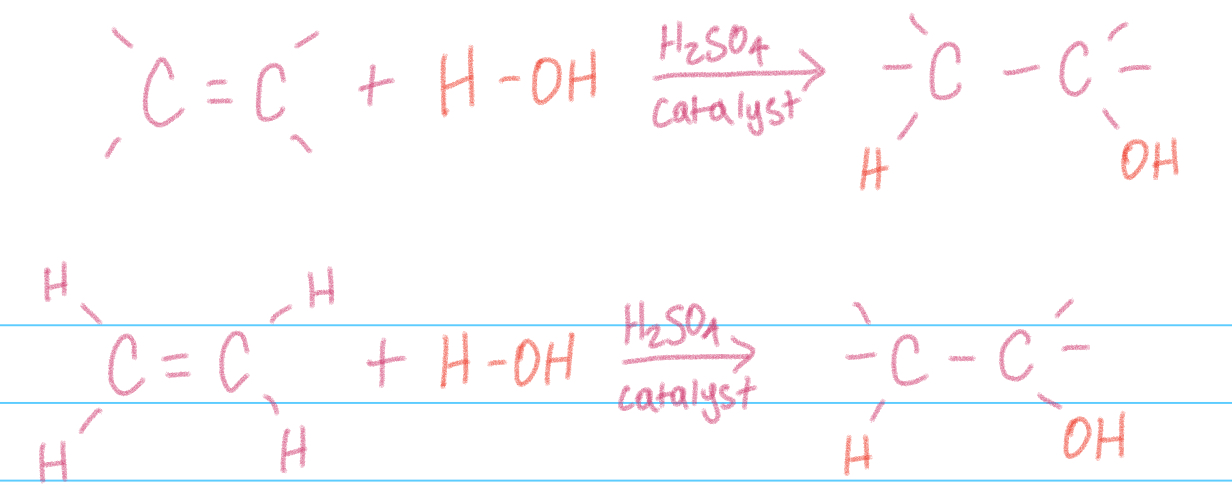
Hydration addition
Addition of water to alkenes
think of water as H-OH
Not the same as X-Y addition, alkene will not react with pure water alone —> needs a strong acid catalyst (H2SO4)
Yields an alcohol (R-OH)
Can have a major product —> use Markovnikov’s rule to determine
Elimination Reaction
single reactant splits into 2+ products
converts starting material to product w/ 2 fewer single bonds & a C-C multiple bond in their place +XY
If Hydrogens— needs a solid state catalyst and yields an alkene + H2
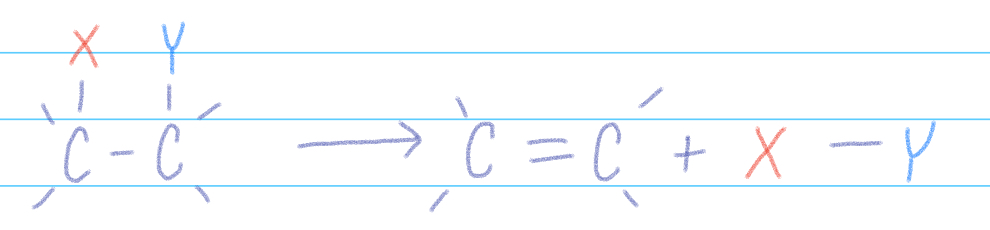
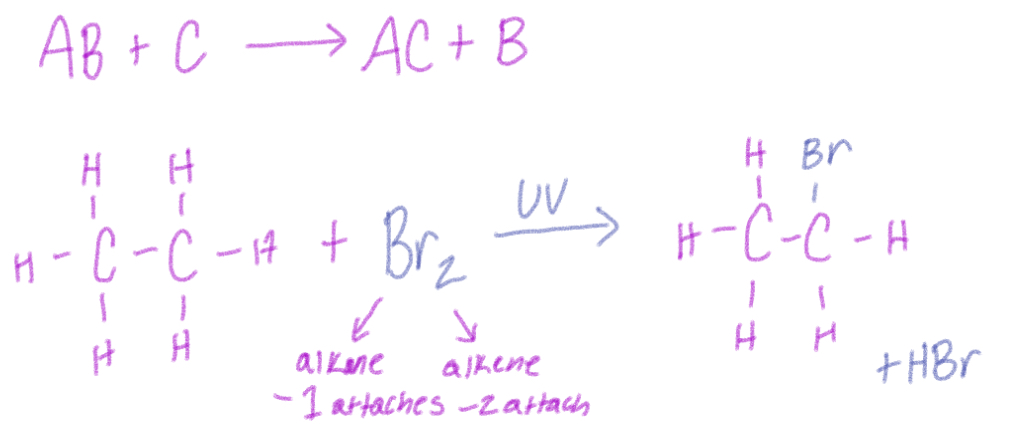
Substitution Reaction
2 reactants exchange parts to give 2 new products, uses UV and heat
Br2 (less reactive, more selective) or Cl2 (more reactive, less selective)
If reactant is alkane—one attaches and yields new product + HBr/Cl
If reactant is alkene—two attach and yields new product + H2
Rearrangement reaction
bonds and atoms in reactant are rearranged to yield single product that is an isomer of reactant
breaks, rotates, and reforms the =
uses H2SO4 catalyst
Can switch cis and trans

Markovnikov’s Rule
When adding HX to an alkene—major product has H attaching to = C with larger # H atoms directly attached, and X attaches to C with smallest # H atoms directly attached
Only happens in with molecules that are asymmetrical for hydrogen
Symmetrical for H: each = C has the same # H directly attached—> products form in equal amounts
Asymmetrical for H: one = C has more H directly attached than the other—> forms a major product