final operating systems
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
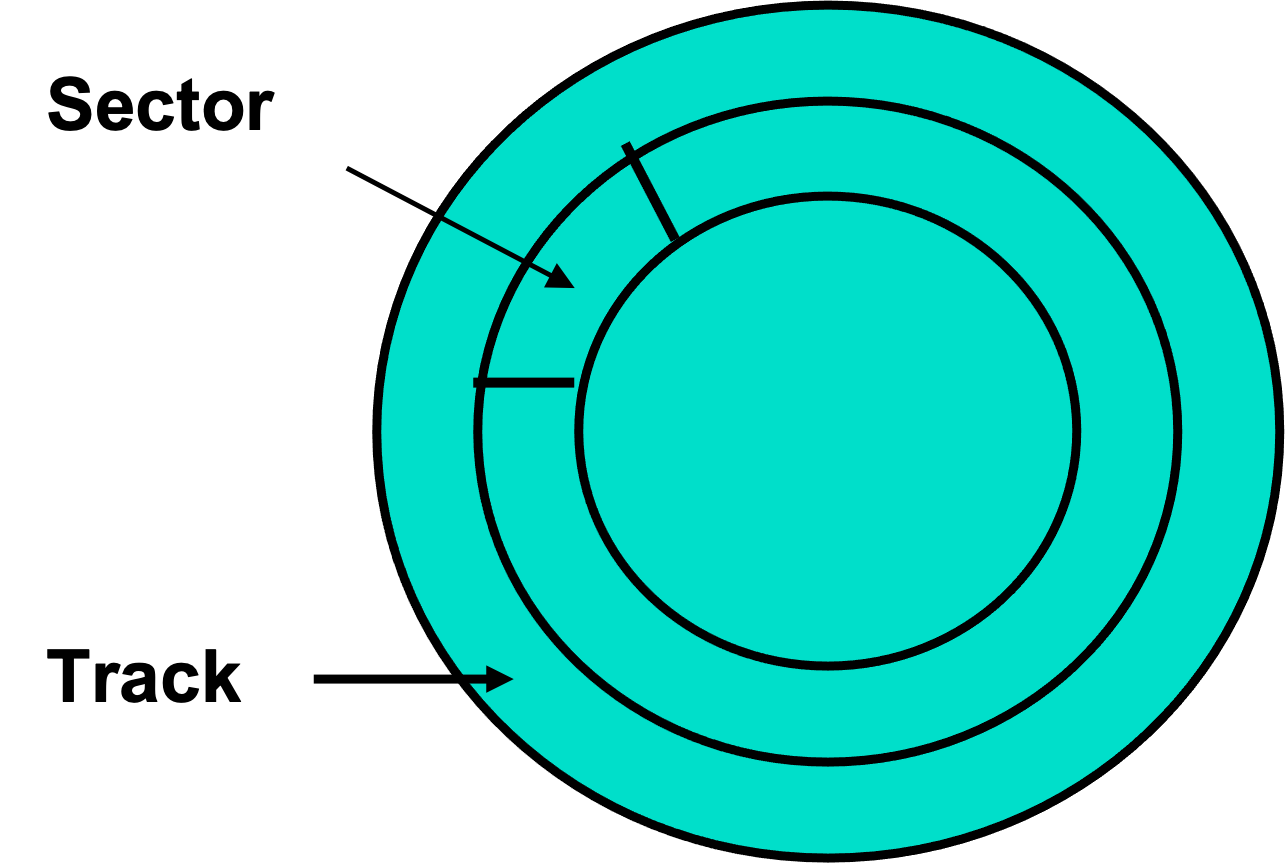
Explain the structure of a hard disk
the hard disk is separated into rings that are called tracks. tracks are divided into sectors/blocks
2
New cards
How does ssd write new data when the pages are almost full
1. find a block with enough pages marked unused
2.record pages that are necessary in that block
3. reset every page in the block
4.rewrite the necessary pages into the freshly reset block
5. fill the remaining pages with the new data
2.record pages that are necessary in that block
3. reset every page in the block
4.rewrite the necessary pages into the freshly reset block
5. fill the remaining pages with the new data
3
New cards
can an ssd overwrite pages?
no , they must be reset
4
New cards
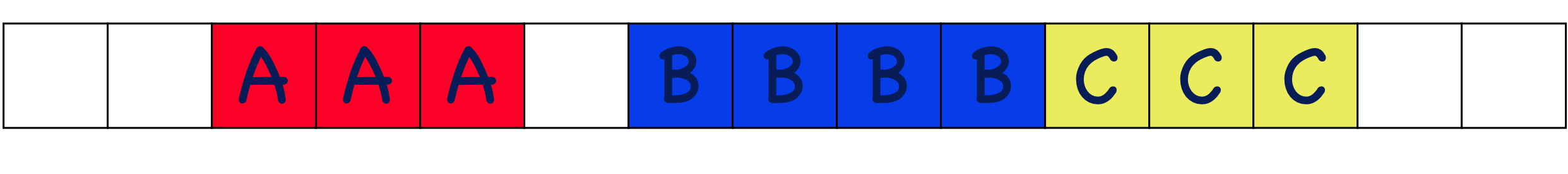
Contiguous allocation
each file is allocated to contiguous blocks on the disk. The files are placed in blocks that have enough free space to hold the file
5
New cards
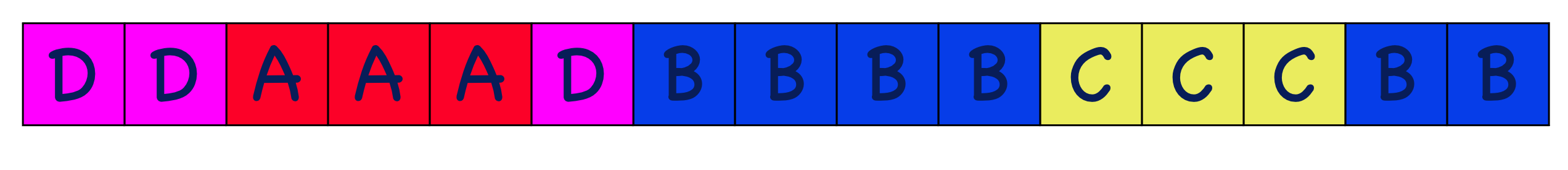
Extent based allocation
Allocate multiple contiguous regions (called extents) for files. This solves the problem of not having enough space for the files to expand that happens with contiguous allocation
6
New cards

Linked Allocation
Allocate fixed sized blocks that are connected as a linked list. Each block points to the next block.
7
New cards
File Allocation table
Variation of linked allocation that keeps the information for the files in a table on the disk.
8
New cards
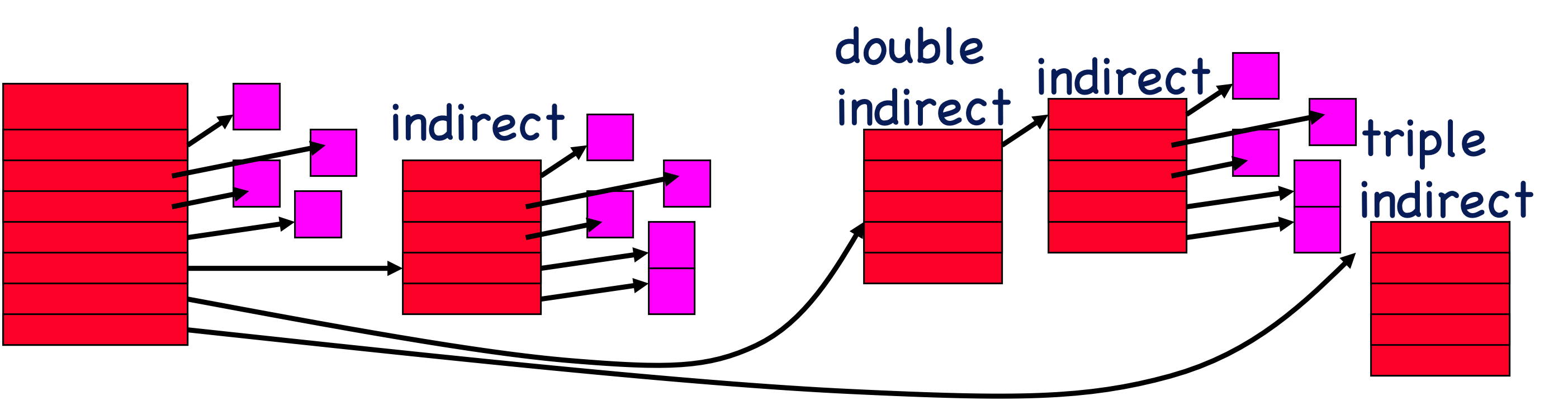
Multi-level indexed files
dynamically allocate hierarchy of pointers to blocks as needed
9
New cards
what are pros of contiguous allocation?
Little overhead for meta-data
Excellent performance for sequential accesses
Simple to calculate random addresses
Excellent performance for sequential accesses
Simple to calculate random addresses
10
New cards
what are the cons for contiguous allocation
Horrible external fragmentation (Requires periodic compaction)
May not be able to grow file without moving it
May not be able to grow file without moving it
11
New cards
What are the pros of Extent-Based Allocation?
improvement of contiguous allocation
File can grow over time (until run out of extents)
Helps with external fragmentation
File can grow over time (until run out of extents)
Helps with external fragmentation
12
New cards
what are the cons of extent based allocation?
External fragmentation can still be a problem
Not able to grow file when run out of extents
Not able to grow file when run out of extents
13
New cards
what are the pros of linked based allocation
no external fragmentation
Files can be easily grown, with no limit
Files can be easily grown, with no limit
14
New cards
what are the cons of linked based allocation
Cannot calculate random addresses w/o reading previous blocks
Sequential bandwidth may not be good
Sequential bandwidth may not be good
15
New cards
What are pros of File-Allocation Table
no external fragmentation
Files can be easily grown, with no limit
Files can be easily grown, with no limit
16
New cards
What are cons of File-Allocation Table
has to Read from two disk locations for every data read
17
New cards
where should file allocation table be kept to improve random access?
cache in main memory
18
New cards
Direct pointer (multilevel index file)
a pointer that points directly to the data on the disk
19
New cards
indirect pointer (multilevel index)
a pointer that points to a block that contains either another indirect pointer or a direct pointer.
20
New cards
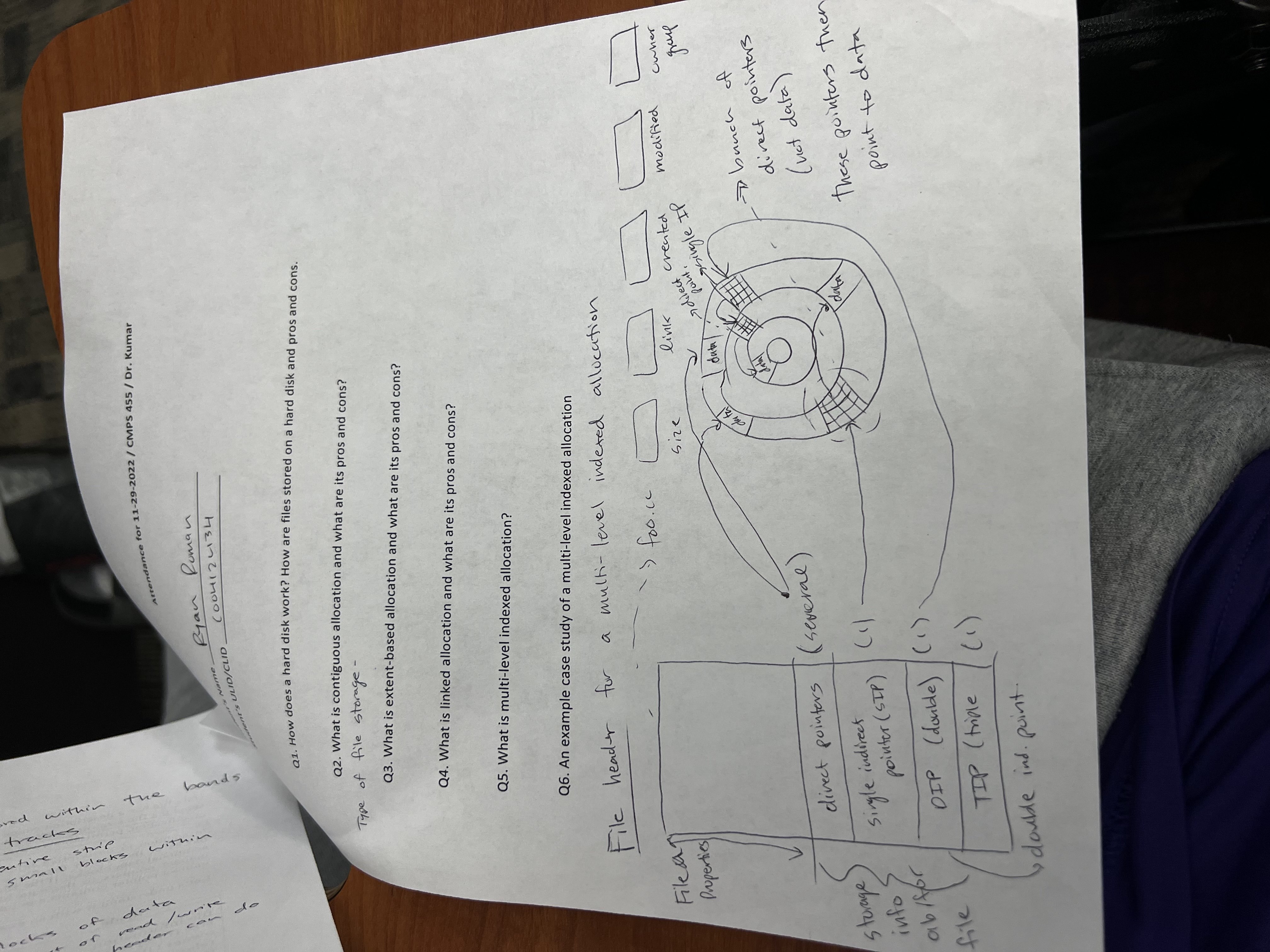
example
yes
21
New cards
what is inode
a description stored in a unix file structure that contains file size, location, owner, creation time, last access time, last modified time, permissions, and more. The inode also contains pointers to first few data blocks of file
22
New cards

read this
ok
23
New cards
explain 2 level paging
In two level paging, there are two levels of page tables: one, with one outer page table and a second level that has many page tables. The entries in the outer page table point to a page table in the second level. The page number is divided into 2, with the first half corresponding to the entry in outer page table, which points to the specific table in the second level. The second half of the number points to the entry in the second level table (the table that is found based off the first half of the page number). The frame number is stored in the second level page table. And the offset is then used to get the physical address in memory.
24
New cards
explain multilevel paging
In multilevel paging, the page number is divided into an equal number of bits per the number of levels. In the case of 3 level paging, the page number is divided into 3. The first level page number contains the entry of the second level page table. The second level page number contains the entry of the third level page table. The third level page number contains the entry that has the frame number of the physical address. Then, you combine the frame number with the offset to get the physical address in memory.
25
New cards
how to calculate bankers
First you must calculate the need matrix by subtracting the allocation from the claim. Then, you compare the need to the available. If the need is less than the available, then you can allocate the number of resources for that process. You will add the available and the allocation for that process to get the new available matrix. Then move on to the next process and check again. If the need is more than the available, move to the next process and check without changing the available matrix. The safe sequence is the order of the completed processes that updated the available matrix.
26
New cards
you should practice a bankers problem
okay
27
New cards