Chapter 28 - Plant Reproduction
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
advantages of gamete and offspring dispersal
1. Outcrossing/genetic diversity
2. nutrient supply(less competition for resources)
3. Pathogen/parasite avoidance by spreading out the population.
two parts of plant repro
fertilization and dispersal
sporopollenin
a complex of polymers that protect the spore from stressors such as dessication
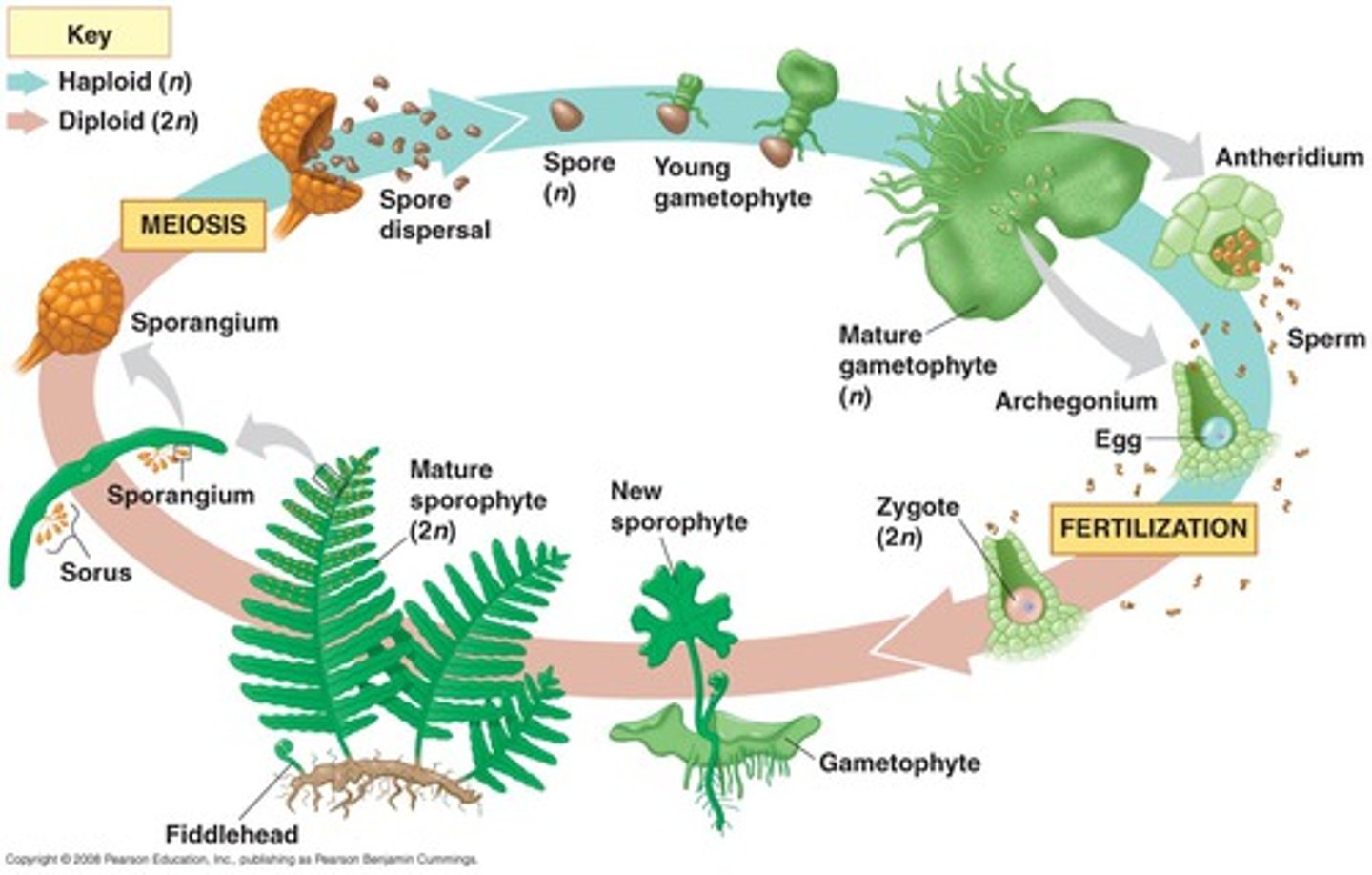
life cycle of the fern
- sperm is released when moisture is present
- the sporophyte is initially supplied with nutrients by the gametophyte
- vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) allow sporophyte generation to grow tall and become physiologically independent of the gametophyte
- spores are released into air. those that land in a suitable site will germinate and grow into new gametophytes
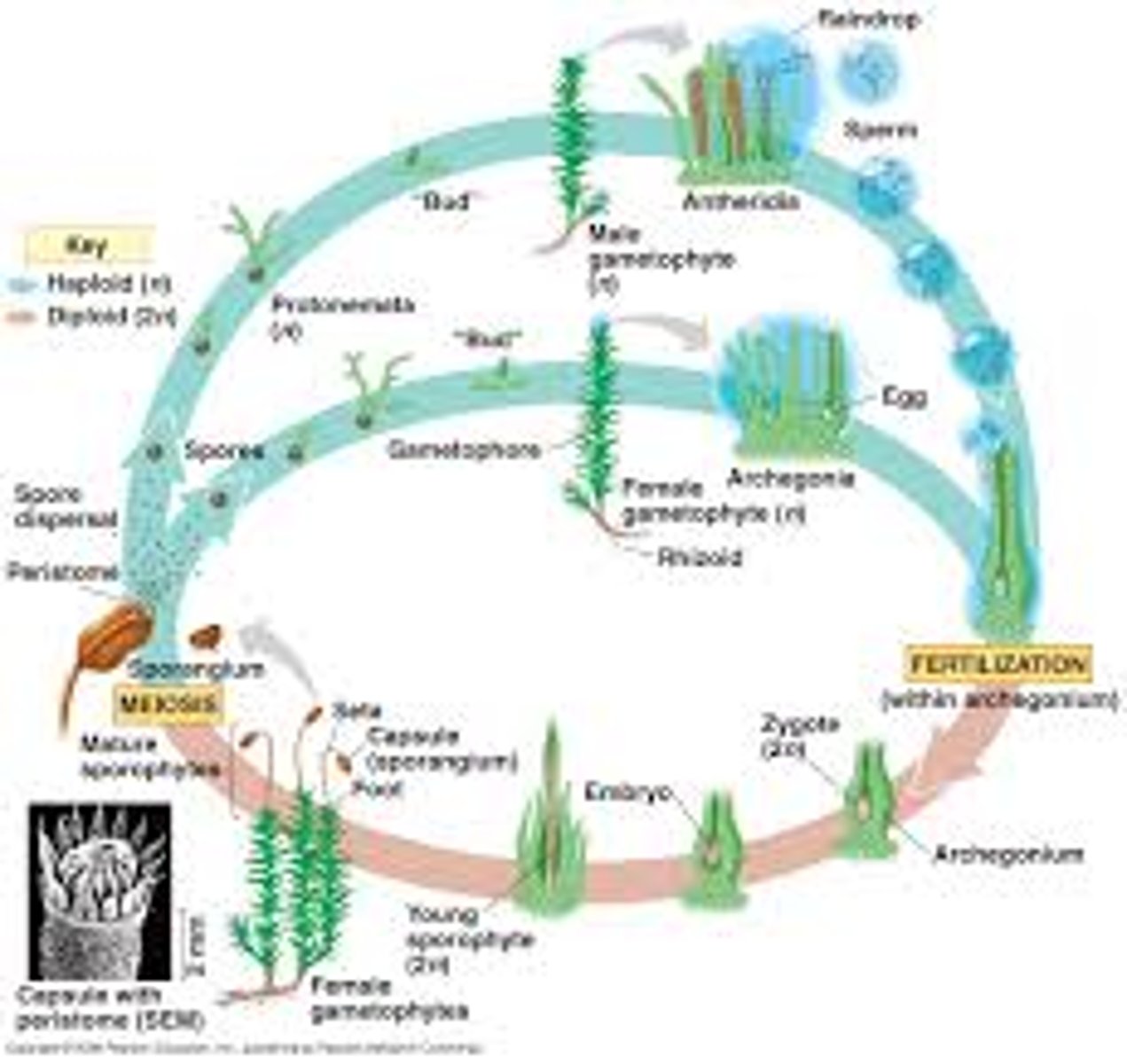
life cycle of moss
- sperm release is stimulated by raindrops
- diploid zygote is retained and the sporophyte develops in place, supported mechanically and nutritionally by the gametophyte
- multicellular sporophyte produces thousands of haploid spores by meiosis
- haploid spores are released into the air. those that land in a suitable site will germinate to form a new gametophyte generation
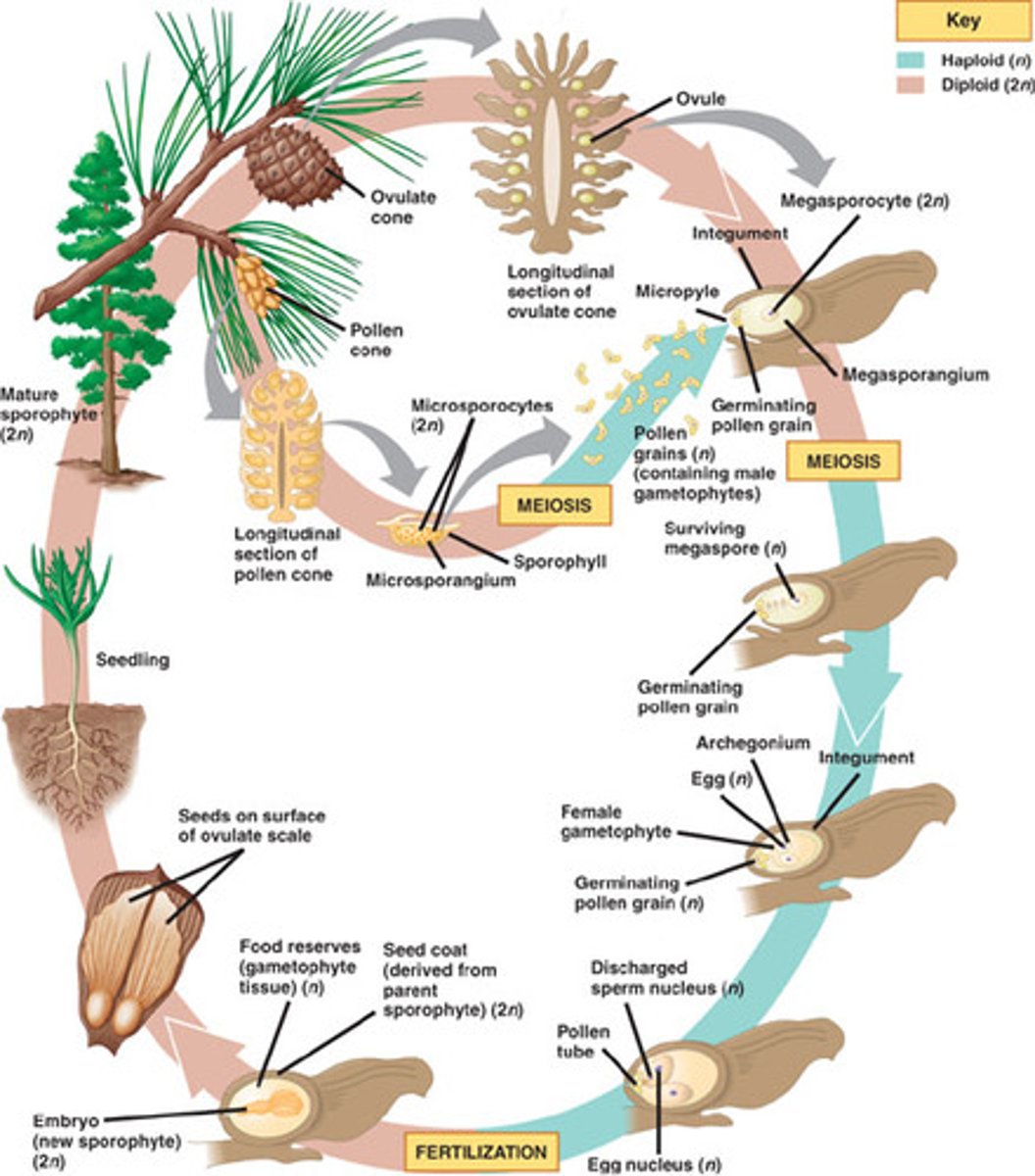
life cycle of pines
- pollen is released into the air and transported by wind; some land on ovule cones
- before fertilization can occur, pollen must germinate and pollen tube must grow towards the female gametophyte
- fertilized ovule develops into a seed
female gametophytes develop within ovule cones
- seeds that land in a suitable site can grow into new sporophytes
- male gametophytes develop with pollen cones
characteristics of seed producing plants
- male gametes are never exposed to the environment (pollen)
- the relationship between sporophyte and gametophyte is reversed from that in bryophytes: the gametophyte is reduced to a few cells dependent on the sporophyte.
- seeds are produced, which are able to disperse away from the parent plant.
flower organization
- Sepals: Most leaflike, protect flower bud
- Petals: Attract pollinators
- Stamen: Produces pollen
- Pistil: Bears ovules, ovules produce embryo sac
- Floral organs arranged in whorls
angiosperm life cycle
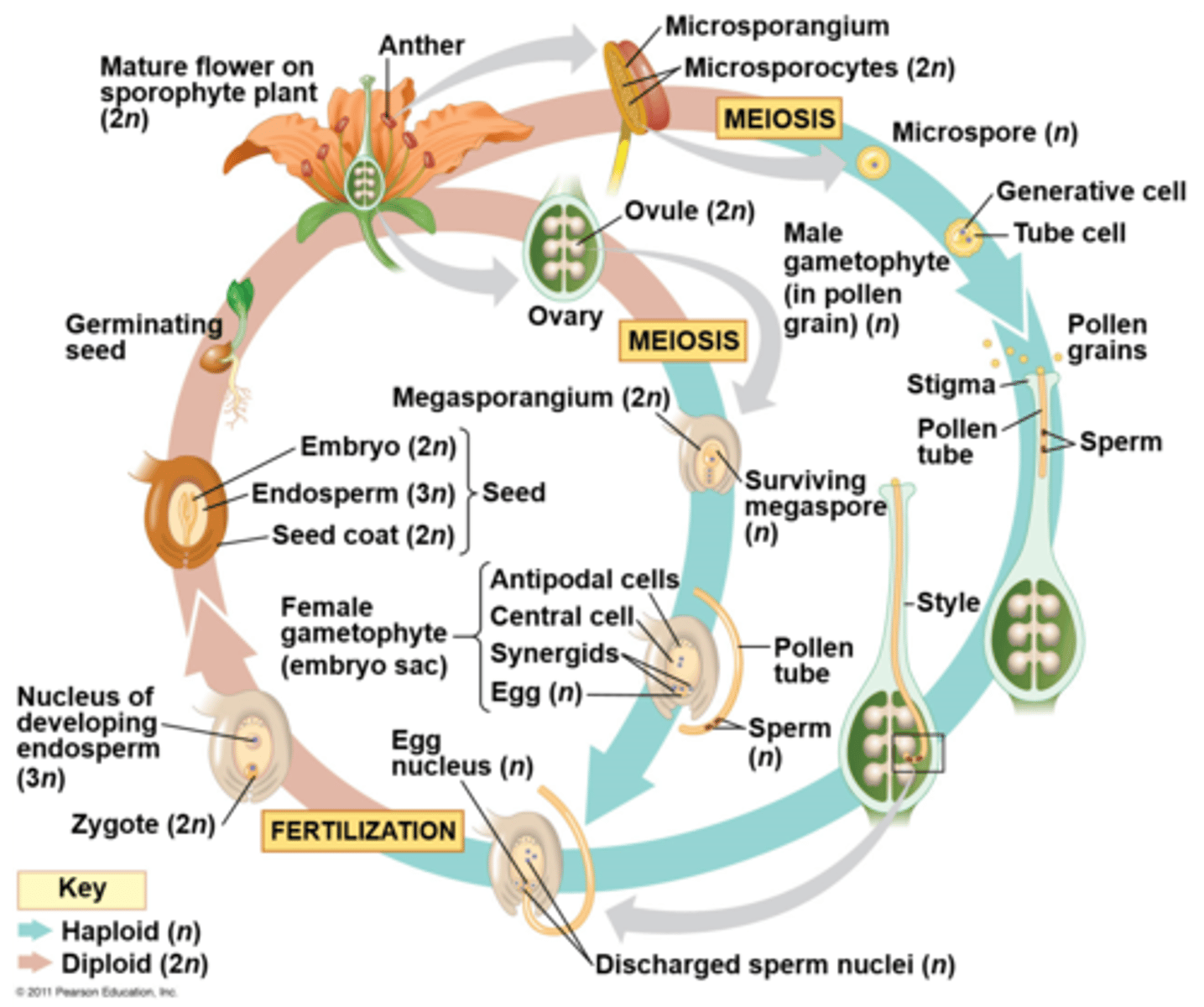
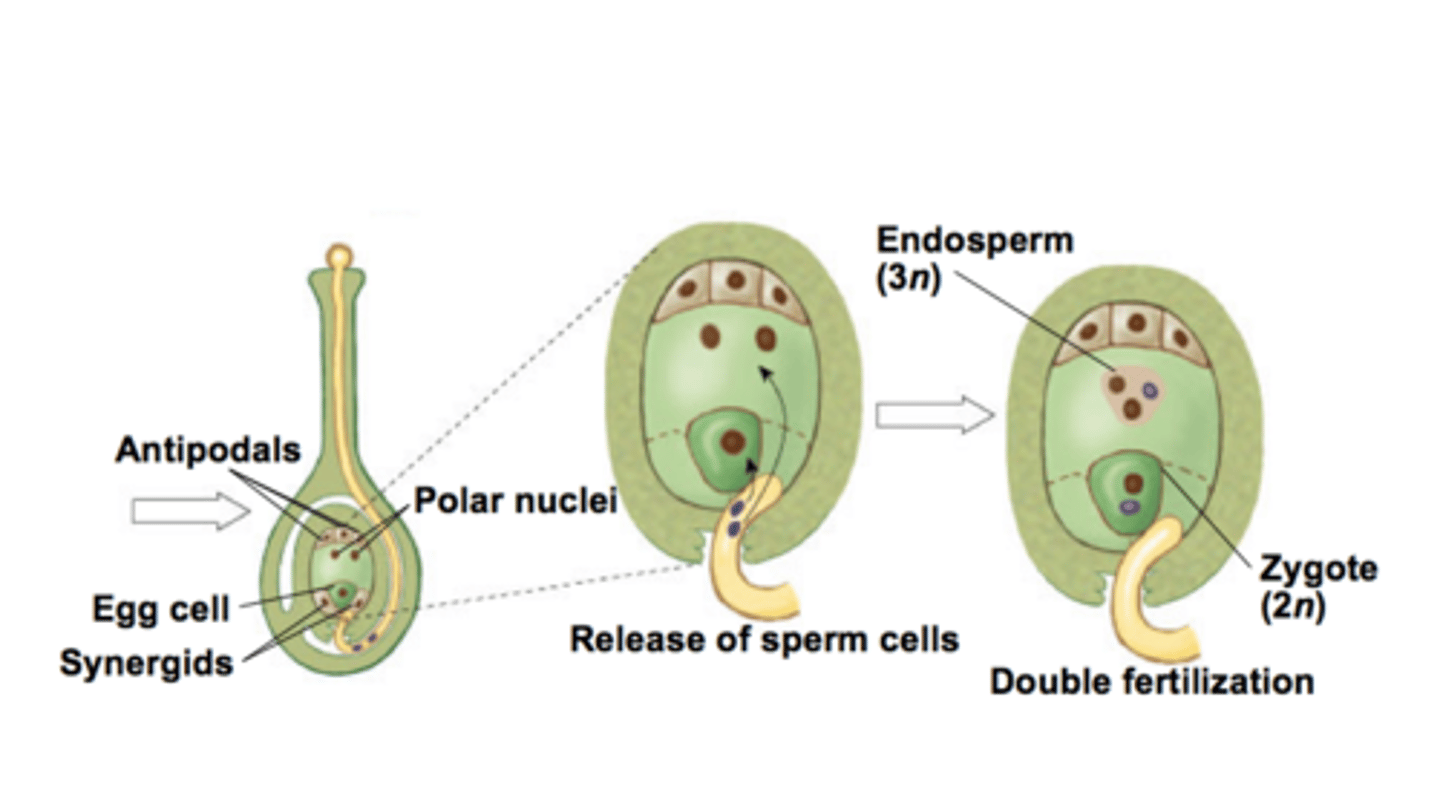
double fertilization
one nucleus from the male gametophyte fuses with the egg, forming the zygote. The other unites with the diploid cell of the female gametophyte to form a triploid cell that gives rise to endosperm
endosperm
In angiosperms, a nutrient-rich tissue formed by the union of a sperm with two polar nuclei during double fertilization. Provides nourishment to the developing embryo in angiosperm seeds.
methods of fruit and seed dispersal
- Animals
- Gravity
- Water
- Explosion
mangroves
angiosperm trees from a number of genera that live in salt water
photoperiodism
Short-day plants
- Flower when day length does not exceed some critical threshold
- Too long a light period = leaves but no flowers
Long-day plants
- Flower only when photoperiod reaches or exceeds a certain threshold
Day-neutral plants
- Ignore day length as a flowering signal
vernalization
Prevents flowering until the plant has been exposed to a prolonged period of cold temperatures
what can seed dormancy be controlled by
Toughness of seed coat
The embryo... which induces germination through:
• Exposure to cold
• Exposure to light
phytochrome
The photoreceptor responsible for keeping track of the length of day and night; there are two forms of this, Pr (red light absorbing) and Pfr (infrared light absorbing)
detecting shading by phytochrome
- in open environments, 60% of phytochrome is in the active P-fr form
- in the forest understory, as little as 10% of phytochrome is in the active P-fr form
- the absorption of red light by chlorophyll means that the light in the understory has a greater amount of far-red light than red light