Chapter 22-23: Fiscal and Monetary Policy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Public Sector Net Borrowing (PSNB)
governments fund their spending when it exceeds tax revenue by issuing bonds that people and institutions buy, lending money to the government and adding to the national debt
Public Sector Net Cash Requirement (PSNCR)
a more immediate cash-flow focussed measure of government borrowing, accounting for not just planned spending, but also things like loan repayments
fiscal stance
the overall impact of a government’s budget on the economy
automatic stabilisers
built in features of the tax and benefit system which automatically dampen economic swings
fiscal drag
when the economy is recovering but automatic stabilisers pull it back by increasing tax revenue and reducing welfare too quickly, potentially hindering growth
discretionary fiscal policy
when the government actively changes tax rates or spending levels to try and influence the economy
challenges to fiscal policy
timing
magnitude
Keynesian view on crowding out
crowding out is minimal, especially during recessions when there is spare capacity in the economy. They argue interest rates won’t rise much and investment isn’t that sensitive to interest rate changes
Monetarist view on Crowding out
crowding out is a serious concern, they believe government borrowing significantly increases interest rates, which chokes off private investment
central bank tools to influence the money supply
reserve requirements
open market operations
central bank lending
reserve requirements
mandating that banks hold a certain percentage of their deposits as reserves
open market operations
buying or selling government bonds to influence the amount of money in circulation
central bank lending
adjusting the interest rate at which they lend to commercial banks
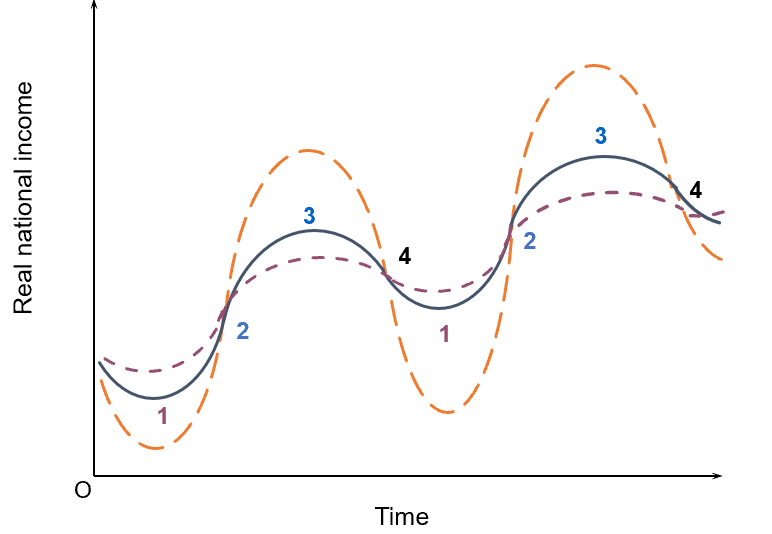
stabilising or destabilising fiscal policy
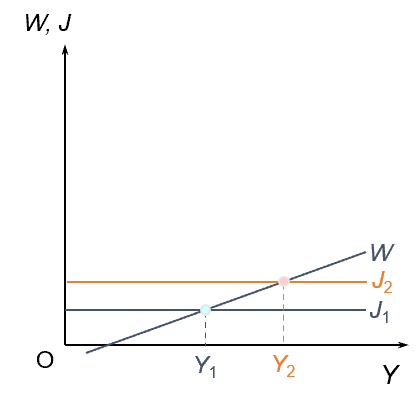
monetary effects of expansionary fiscal policy on the goods market
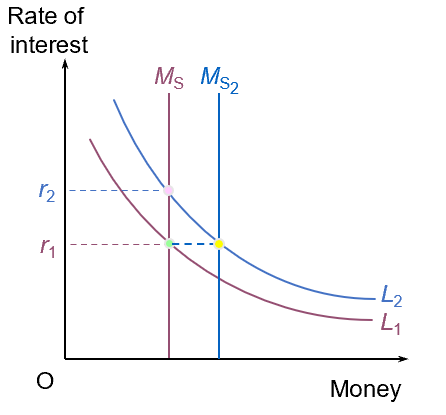
monetary effects of expansionary fiscal policy on the money market
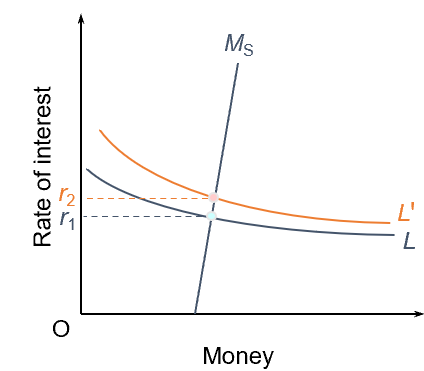
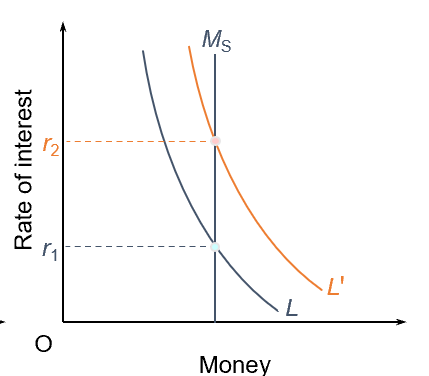
Keynesian view on the demand for money
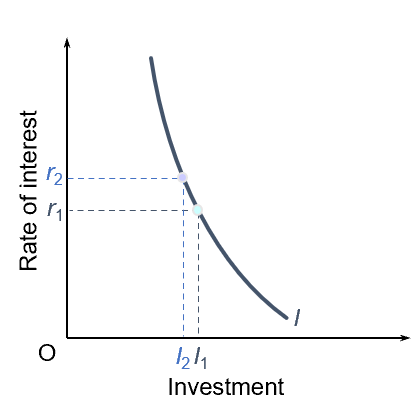
monetarist view on the demand for money
Keynesian view on the demand for investment
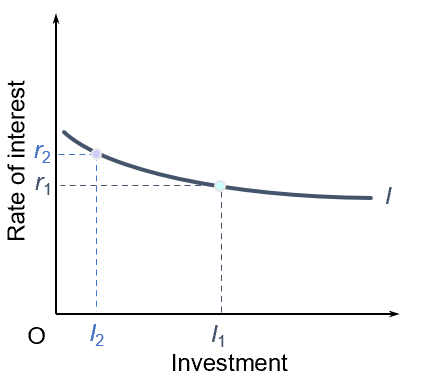
Monetarist view on the demand for investment