Ch. 1 Mendel's Principles of Heredity Practice Problems
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
An albino corn snake is crossed with a caramel colored corn snake. The offspring are all caramel colored. When these first generation progeny snakes are crossed among themselves, they produce 32 caramel colored snakes and 10 albino snakes.
Which phenotype is controlled by the dominant allele?
caramel (because it is the phenotype observed in the F1 hybrid)
An albino corn snake is crossed with a caramel colored corn snake. The offspring are all caramel colored. When these first generation progeny snakes are crossed among themselves, they produce 32 caramel colored snakes and 10 albino snakes.
What are the genotypes of the parents?
AA, aa (F2 ratio is approximately 3:1, therefore, F1 must be heterozygotes (Aa))
An albino corn snake is crossed with a caramel colored corn snake. The offspring are all caramel colored. When these first generation progeny snakes are crossed among themselves, they produce 32 caramel colored snakes and 10 albino snakes.
A caramel colored female snake of unknown genotype is involved in a test cross with an albino snake. This cross produces 10 caramel colored snakes and 11 albino snakes. What is the genotype of the caramel colored parent snake?
Aa (1:1 ratio of Aa (caramel) and aa (albino)
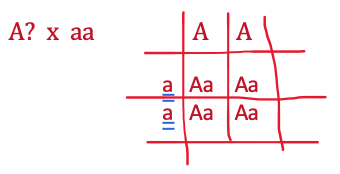
What is the probability of an Aa father and Aa mother having an aa child?
In other words, what is the probability of a child inheriting a AND a?
1/4
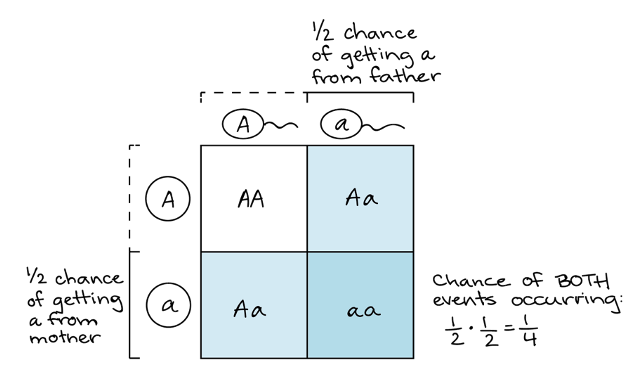
What is the probability of an Aa father and Aa mother having a child with a dominant phenotype?
Since a dominant phenotype can be seen in a heterozygous or homozygous genotype, we are asking what is the probability of a child having the genotype Aa, aA OR AA?
¾
first, we can apply the product rule for each of these genotypes: AA, Aa, aa
then, we can apply the sum rule: ¼ AA, ¼ Aa, ¼ aa
¼ + ¼ + ¼ = ¾
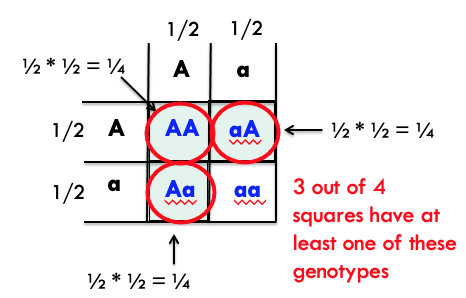
What is the possibility of getting Yy Rr progeny in F2?
P: YY RR x yy rr
F1: Yy Rr (all identical)
¼
break down into two questions:
what is the probability of getting Yy?
what is the probability og getting Rr?
use the punnett square to calculate each separately and then multiply the two answers
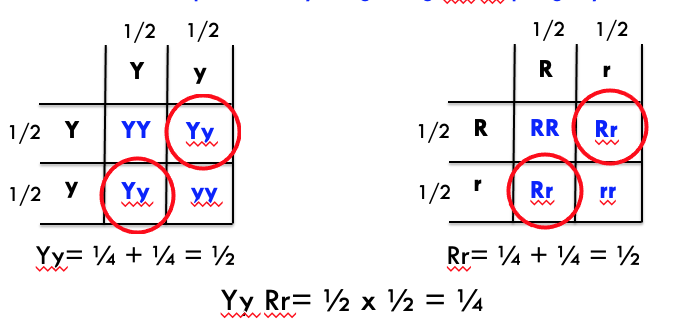
cross Aa Bb Cc Dd x Aa Bb Cc Dd
what proportion of progeny will be AA bb Cc Dd?
1/64
Aa x Aa → ¼ AA
Bb x Bb → ¼ bb
Cc x Cc → ½ Cc
Dd x Dd → ½ Dd
¼ x ¼ x ½ x ½ = 1/64
cross Aa Bb Cc Dd x Aa Bb Cc Dd
how many progeny will show the dominant traits for A, C, and D and the recessive trait for B?
27/256
Aa x Aa → ¾ A-
Bb x Bb → bb
Cc x Cc → ¾ C-
Dd x Dd → ¾ D-
¾ x ¼ x ¾ x ¾ = 27/256
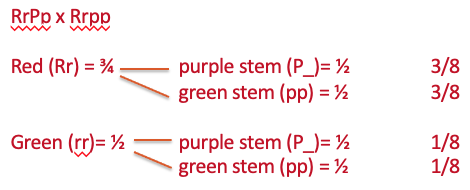
In tomatoes, red fruit is dominant to yellow fruit and purple stems are dominant to green stems. The progeny from one mating consists of:
305 red fruit, purple stem plants
328 red fruit, green stem plants
110 yellow fruit, purple stem plants
97 yellow fruit, green stem plants
What were the genotypes of the parents in this cross?
RrPp x Rrpp
For the following cross: AA Bb Cc Dd x Aa Bb cc DD
How many different types of gametes are possible for the parent on the left?
8
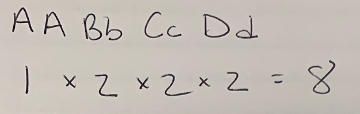
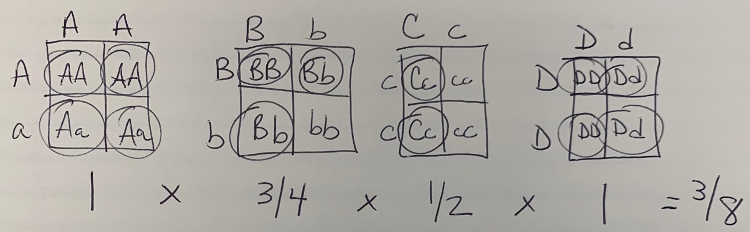
For the following cross: AA Bb Cc Dd x Aa Bb cc DD
What is the probability of having a child that phenotypically resembles the parent on the left?
3/8
Huntington’s Disease is a rare fatal, degenerative neurological disease in which individuals start to show symptoms in their 40s. It is caused by a dominant allele. Joe, a man in his 20s, just learned his father has the disease.
What is the probability that Joe will develop the disease?
½
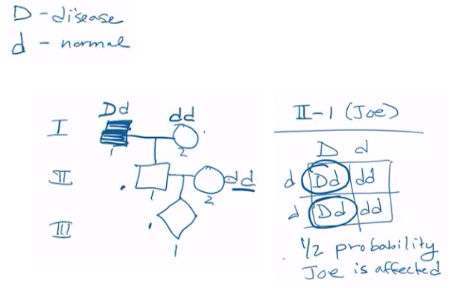
Huntington’s Disease is a rare fatal, degenerative neurological disease in which individuals start to show symptoms in their 40s. It is caused by a dominant allele. Joe, a man in his 20s, just learned his father has the disease.
What is the probability that Joe’s first child will also develop the disease?
¼

Tay-Sachs disease is a recessive early-onset neurodegenerative disease. The disease is rare in a population overall, but is found at a relatively high frequency in Ashkenazi Jews from eastern Europe. A woman whose maternal uncle had the disease is trying to determine the probability that she and her husband could have an affected child. Her father does not come from a high-risk population, but her husband’s sister died of the disease at a young age.
What is the probability of their first child being affected by the disease?
1/18
three steps:
calculate probability of a person being a carrier
calculate probability of passing it to their offspring if they are a carrier
use product rule to multiply the above probability together
see ppt