
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
what is mastitis?
inflammation / infection in the udder
painful to animal
costly
what are the clinical changes seen with mastitis?
changes in milk - seen with grade 1
changes in udder - seen with grade 2 (in addition to milk changes)
changes in cow - seen with grade 3 (in addition to milk and udder changes)
what is subclinical mastitis?
infection present
no visible clinical signs
changes in somatic cell count, milk quality and milk yield
what is somatic cell count (SCC)?
number of cells per ml of milk (mainly epithelial and white blood cells)
how do contagious pathogens cause mastitis?
obligate parasites
main source is other infected cows
spread from cow to cow during milking via fomites
how do environmental pathogens cause mastitis?
live in slurry, bedding, soil, feed and water
infection between milking times and during milking
what are the main UK mastitis pathogens?
staphylococcus aureus (contagious)
streptococcus uberis (environmental but some adapted to be contagious)
coliforms e.g. E. coli (environmental)
streptococcus dysgalactaie (contagious)
streptococcus agalactiae (contagious)
coagulase negative staphylococcus spp (contagious)
Mycoplasma spp (contagious)
how can we identify mastitis bacteria?
culture
grow the bacteria
bacteria must be alive and must be shedding on day of sampling
can’t use antibiotics at least 7 days prior
PCR
detects bacterial DNA
can be dead or alive
can be done before, during or after antibiotics
why may samples fail with bacterial identification for mastitis?
contamination
testing panel
not shedding
poor storage or handling
unknown pathogen
fastidious
what is staphylococcus aureus?
gram positive cocci
coagulase positive
on agar - white colonies with a ring of haemolysis
what is the source of infection of staph aureus?
cows and fomites
spread amongst heifers pre-calving by teat sucking
fly spread
why is staph aureus difficult to treat?
intracellular - limits number of antibiotics we can use
also lives in biofilms
damages duct system and can cause abscesses in udder
often responsible for recurrent persistent chronic infections
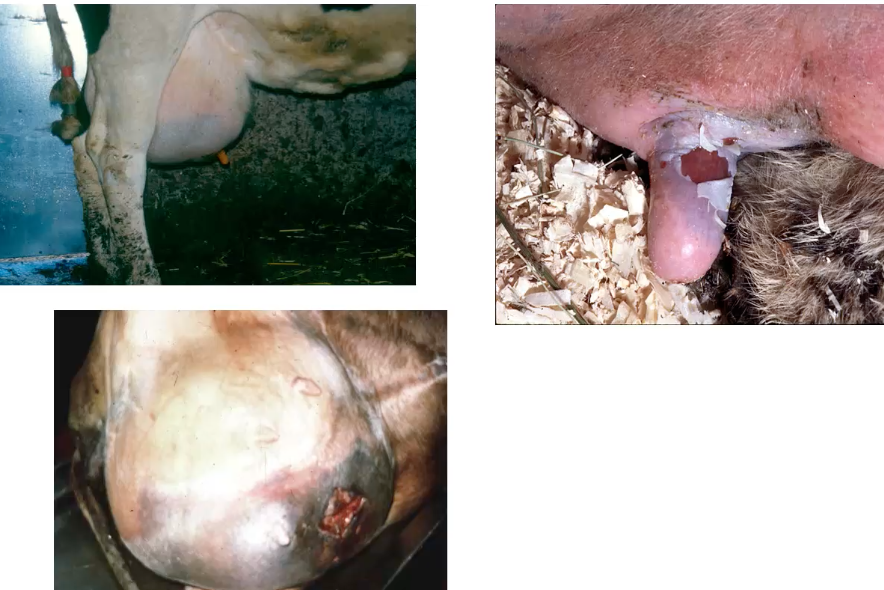
what is this and what pathogen is mostly likely to cause it?
gangrenous mastitis —> caused by staph aureus
how can we control staph aureus (and for other mastitis pathogens)?
prevent introduction of new infections - care with buying in cows
reduce existing infection - treat cases, cull chronic cases, dry cow therapy
prevent spread within herd - wear gloves, early detection and treatment, post milking disinfection, maintain milking machine correctly
what is streptococcus agalactiae?
gram positive cocci
non haemolytic
very small pin prick colonies on culture
what is the source of infection of strep agalactiae?
contagious
failure of parlour hygiene or introduced by brought in animal
what antibiotics are used to treat strep agalactiae or dysgalactiae?
responds well to penicillin
what is streptococcus dysgalactiae?
gram positive coccus
small pin point colonies on Edwards Medium Partial Haemolysis Green Zone
alpha haemolysis
what is the source of infection of strep dysgallactiae?
between udder and tonsils
cows and heifers licking each others teats
what can mycoplasma bovis cause?
mastitis
infertility
metritis
otitis media
arthritis
keratoconjunctivitis
pneumonia
why are mycoplasma spp difficult to treat?
highly contagious in parlour
aerosol spread and haematogenous
lack cell wall - non-responsive to beta-lactams
what is Esherishia coli?
environmental
blood agar forms creamy white colonies
can be haemolytic and non haemolytic
gram negative rods
what is the source of infection of E. coli?
bovine faeces
housed cows - risk factor
often acquired during dry period and peri-parturiently
if there is inadequate or too slow neutrophil influx after E. coli infection, what is the result?
cow will develop endotoxaemia —> often fatal
what are the clinical signs of E. coli in the different stages of mastitis?
grade 1 - clots in milk
grade 2A - clots in milk and hard, hot, painful quarter
grade 3 - very sick cow, endotoxaemic shock, udder may be hot or cold, hard or soft, milk varies from clots to blood
what is E. coli mastitis a differential for?
downer cow post calving
how do we control E. coli infections?
pre milking teat prep - remove the muck
loafing times post milking - don’t let them lie down for 30 mins after milking (ensures teats closed)
dry cow therapy
vaccine - Startvac reduces severity of clinical disease but will not eliminate disease
what is streptococcus uberus?
environmental
non haemolytic
brown colonies on Edwards medium
gram positive
what is the source of strep uberis?
bovine faeces
straw yard housing
straw bedded cubicles
muddy fields at the end of summer
what type of mastitis does strep uberis usually cause?
grade 1 or 2 - rarely grade 3
often see persistent sub-clinical infection
recurrent clinical cases common
why is strep uberis difficult to treat?
intracellular
has protective shell which prevents attachment of antibodies
some strains can resist killing by neutrophils
how do we control strep uberis?
infection common during dry period
improve housing hygiene
pre-milking teat prep
cull chronic cases
dry cow therapy
what animals are usually affected by summer mastitis?
dry cows and heifers out doors in summer
how is summer mastitis spread?
Hydrotea irritans - sheep head fly
what are clinical signs of summer mastitis?
hot, hard, swollen, very painful udder
thick purulent secretion
cow may also be lame and systemically ill
how can we use a milking order to minimise transmission of mastitis?
1st parity heifers first
healthy cows next (low SCC)
high SCC cows after
cows with clinical mastitis last