Chapter 5 Membrane Transport & Cell Signaling
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Selective permeability
A property of cell membrane: substances are filtered and let through via proteins spanned throughout the membrane
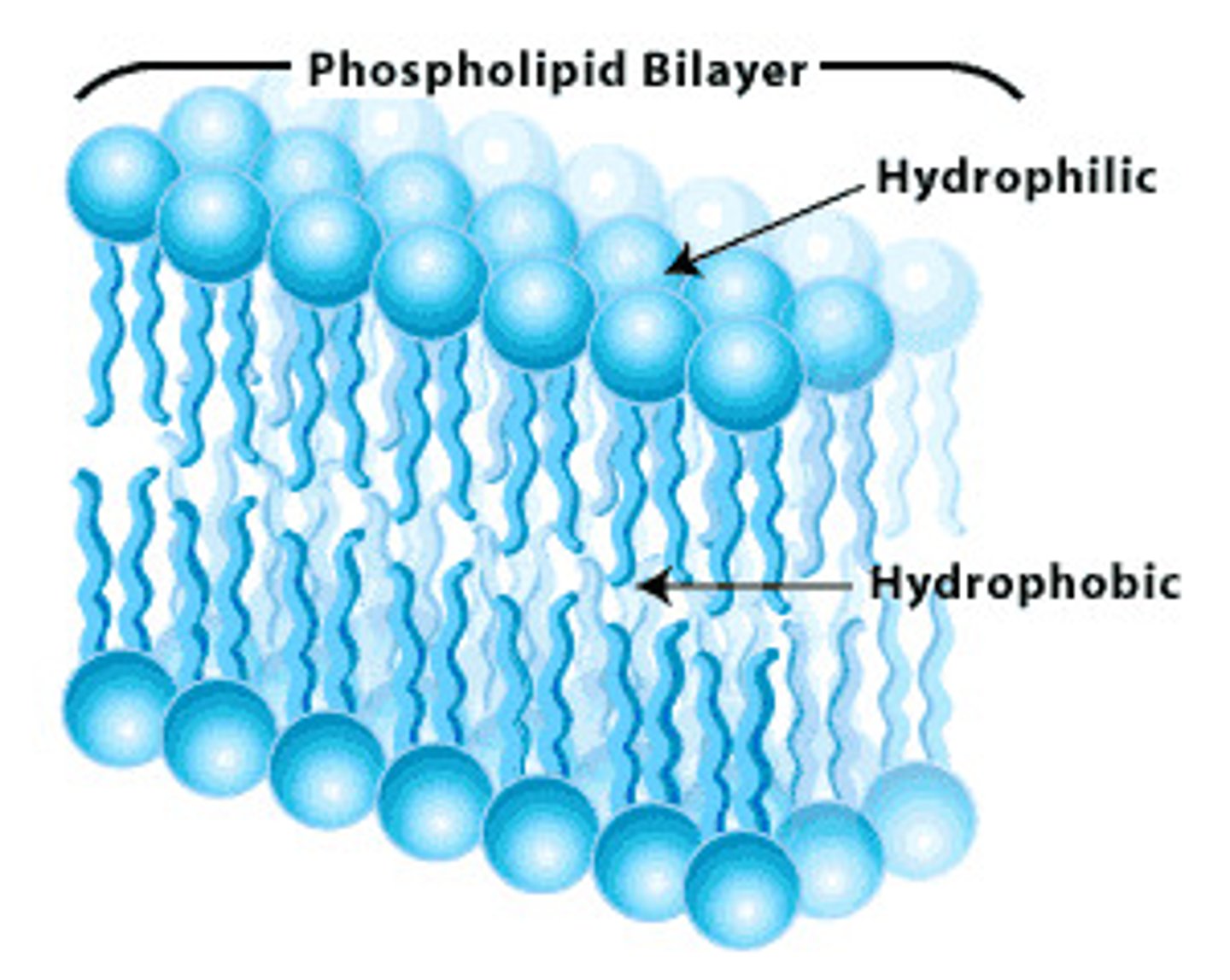
amphipathic
Pertains to a molecule containing both hydrophilic polar (water-soluble) and hydrophobic nonpolar (not water-soluble) portions in its structure
fluid mosaic model
A model conceived by S.J. Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972 to describe the structural features of biological membranes
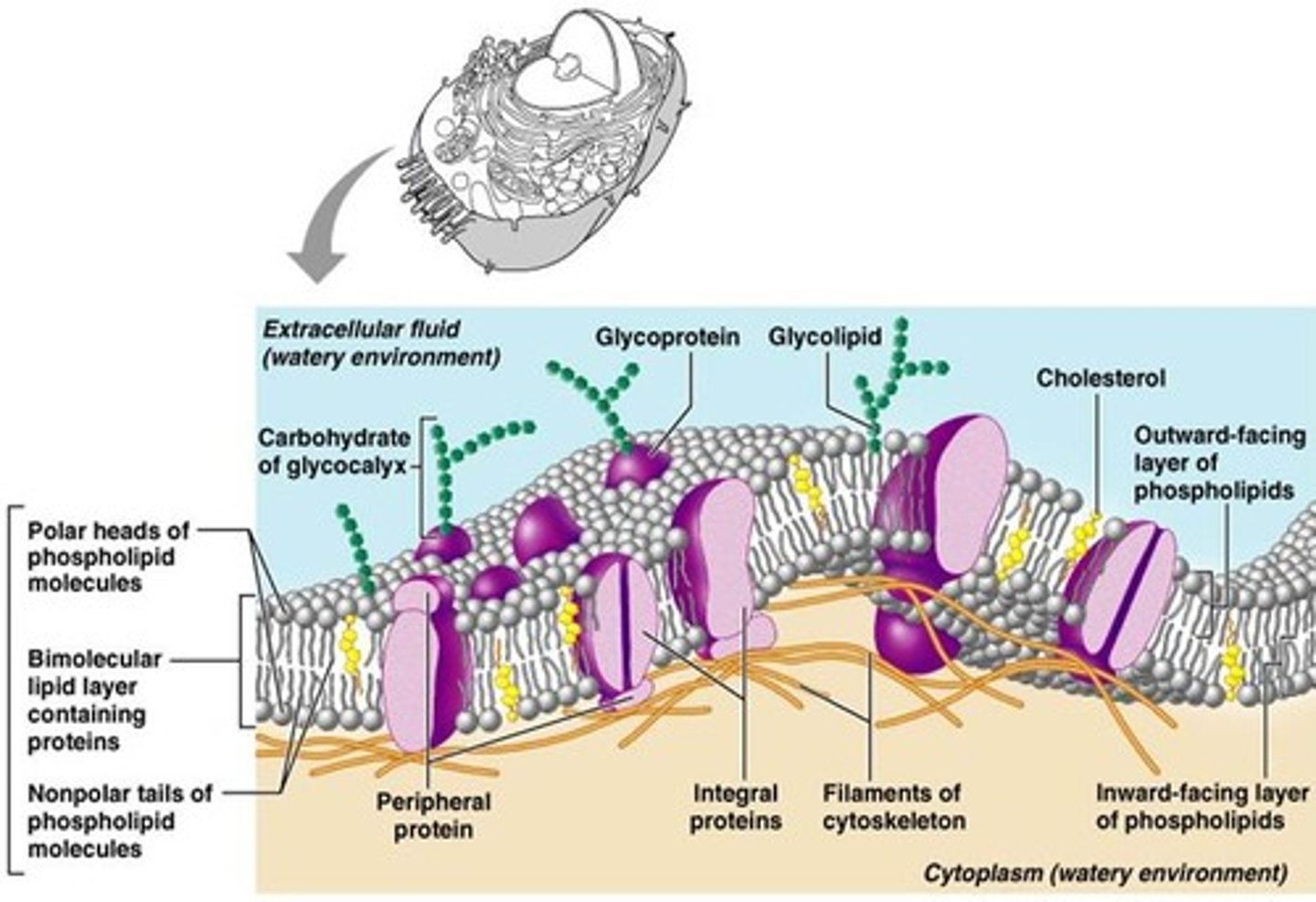
integral proteins
A protein molecule or protein assembly permanently attached in biological membrane
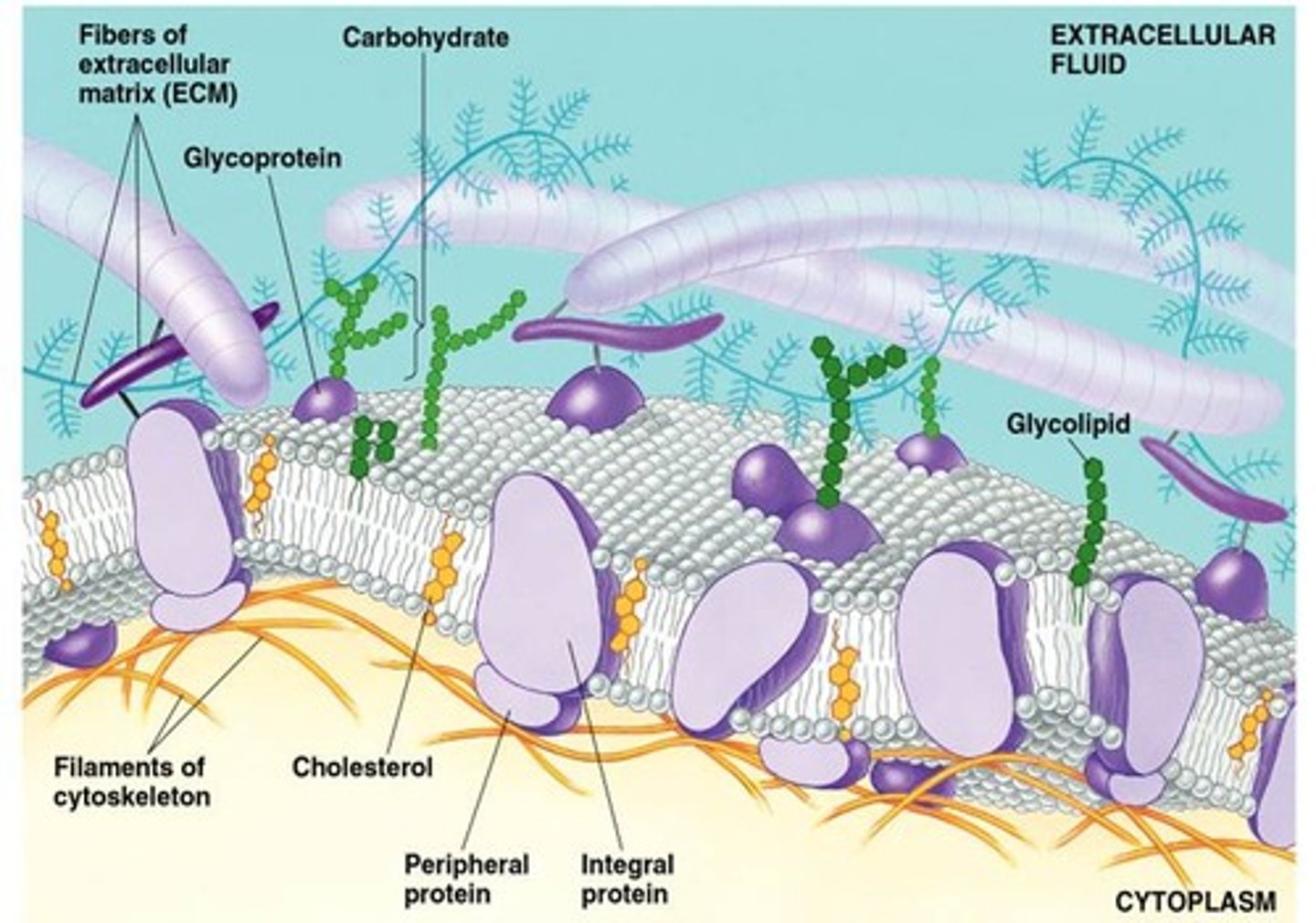
peripheral proteins
Membrane proteins that are bound to the surface of the membrane and not integrated into the hydrophobic region
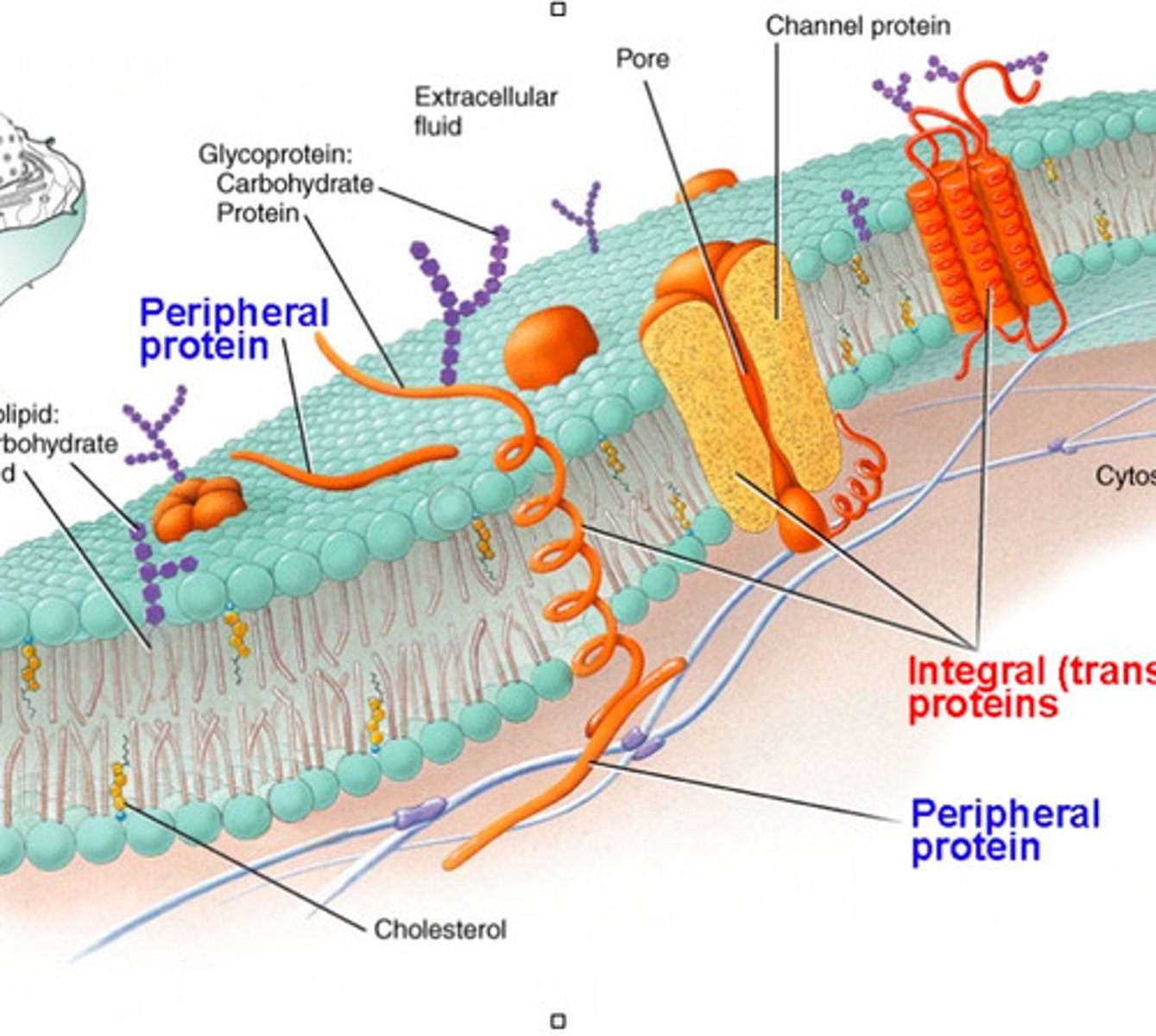
glycoproteins
Proteins that have sugars in them (?)
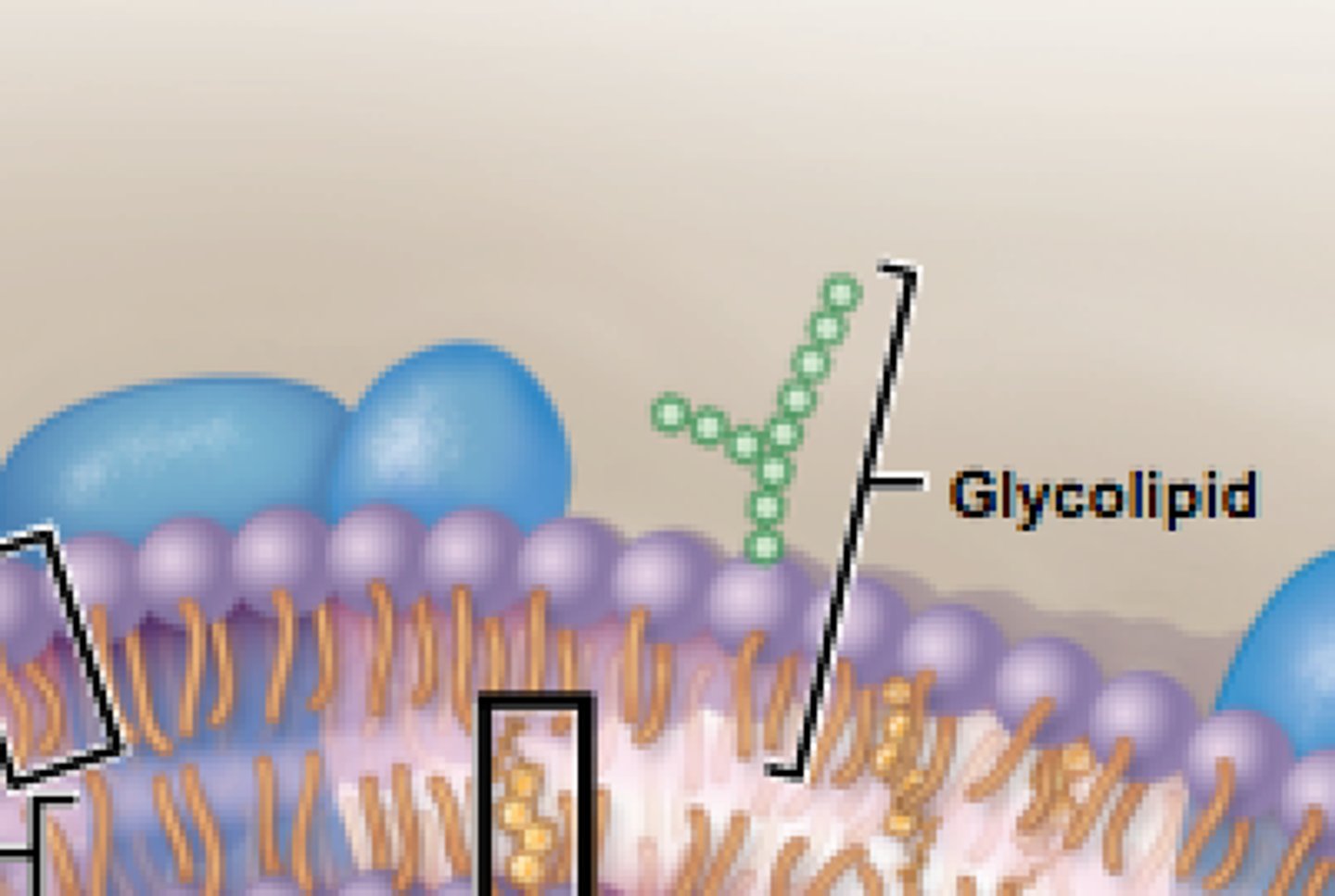
glycolipids
Lipids that have carbohydrates attached to it; found in the fluid mosaic model.
transport proteins
A type of protein located in the membrane and specifically allow some particles to get through.

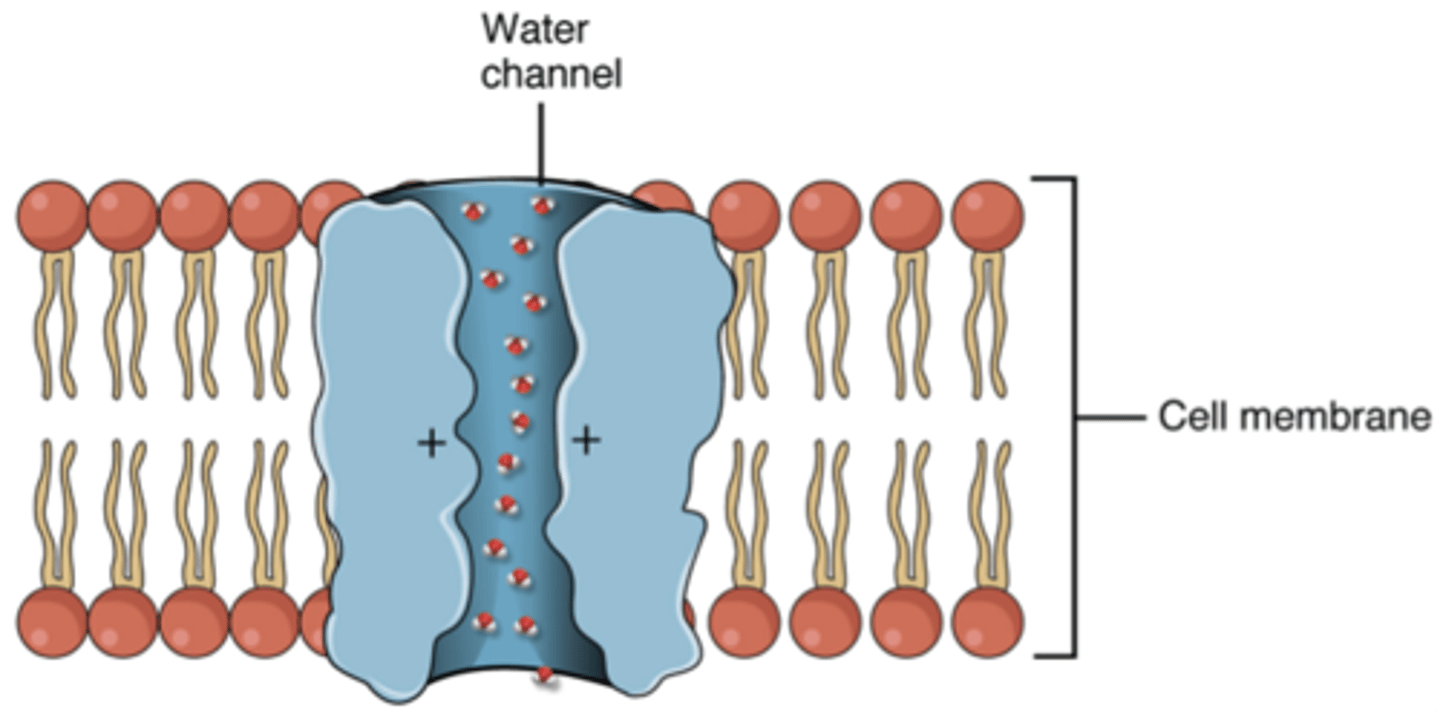
aquaporins
integral membrane proteins from a larger family of major intrinsic proteins (MIP) that form pores in the membrane of biological cells
diffusion
The passive movement of molecules or particles along a concentration gradient, or from regions of higher to regions of lower concentration
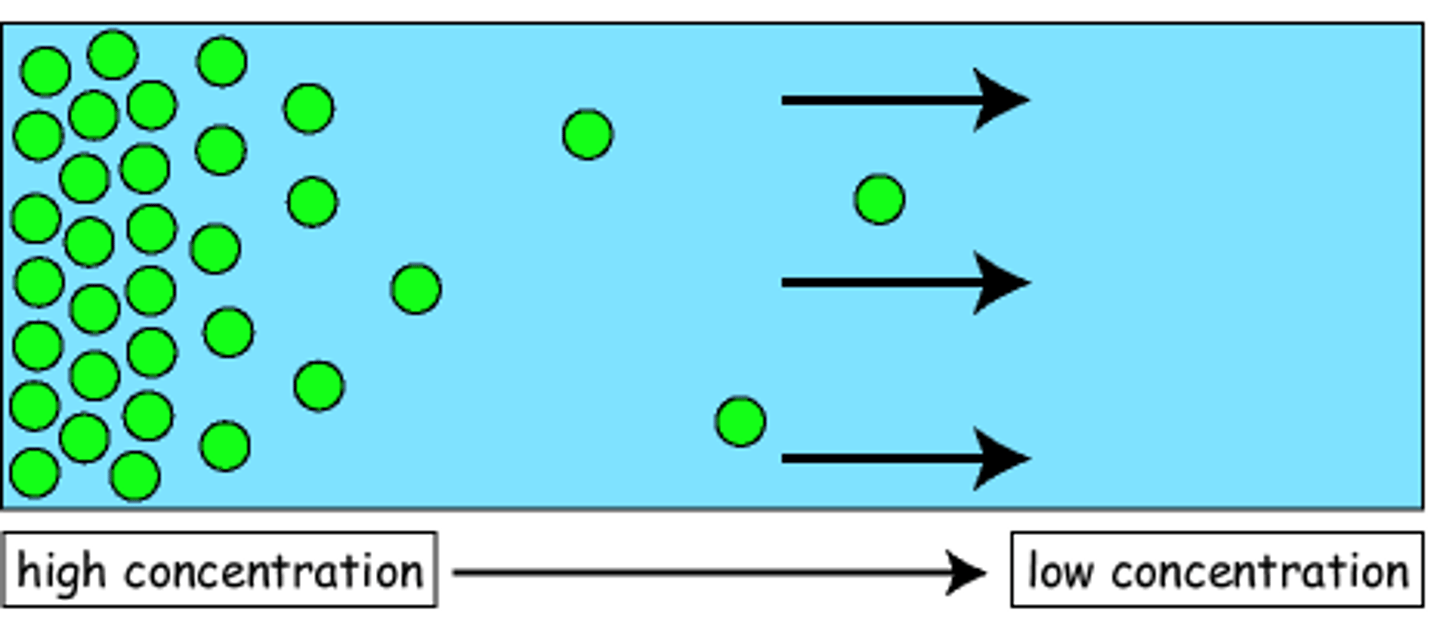
concentration gradient
a gradual change in the concentration of solutes in a solution as a function of distance through a solution
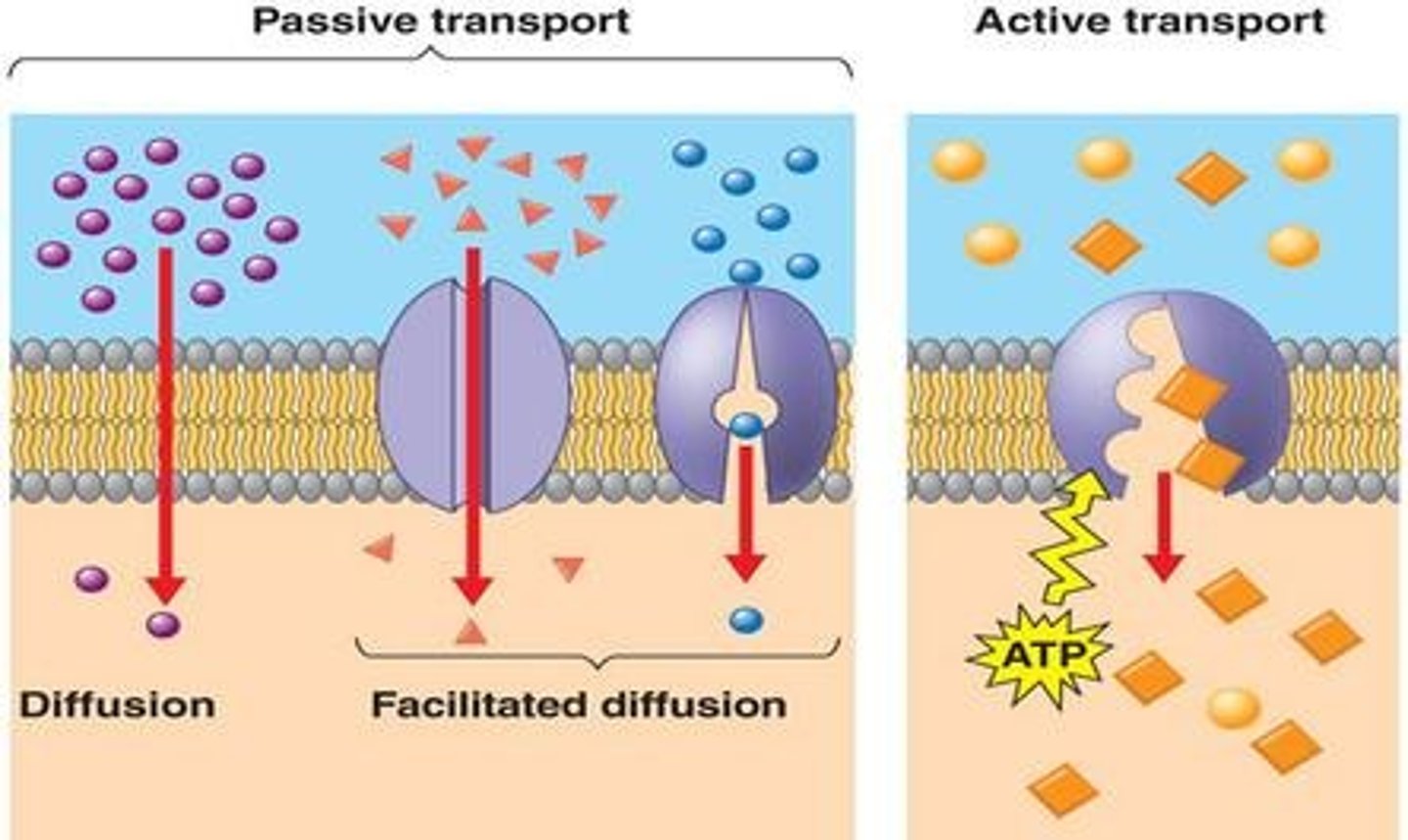
passive transport
The movement of a chemical substance across the cell membrane without using any energy; diffusion
tonicity
The ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain or lose water.
isotonic
A solution having the same osmotic pressure as some other solution, especially one in a cell or a body fluid.
hypertonic
A solution having a higer osmotic pressure than a particular fluid, (hyper means "more").
hypotonic
A solution having a lower osmotic pressure than a particular fluid (hypo means "lower").
osmoregulation,
the process which cells and single celluar organisms use to maintain fluid and control their water balance with the enviornment
turgid
The state when a cell is very firm because the cell wall is experiencing a back pressure to stop further water taking
flaccid
The state when a cell is very flat because it is surrounded by an isotonic environment and therefore can not take water in
plasmolysis
When plants are surrouned by isotonic environment, their cells shivels with its plasma membrane pulled away from the wall
facilitated diffusion
mechanism in which a transport protein speeds up the diffusion in accordance to the concentration gradient
ion channels
channel proteins that transport ion
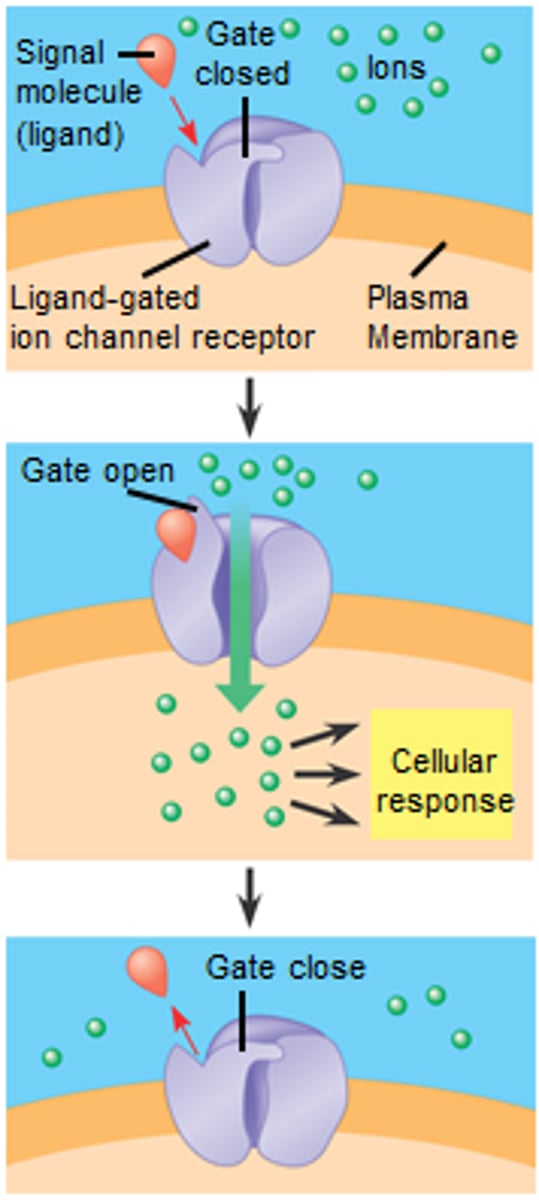
gated channels
ion channels that open or close in response to a stimulus (ref.42. ion-gated ion channel)
active transport
The transportation of molecules following or against the concentration gradient, requires energy.
membrane potential
Range of voltage in and around membrane
electrochemical gradient
The interaction of chemical force(ion concentration) and electrical force(membrane potential) with cell membrane.
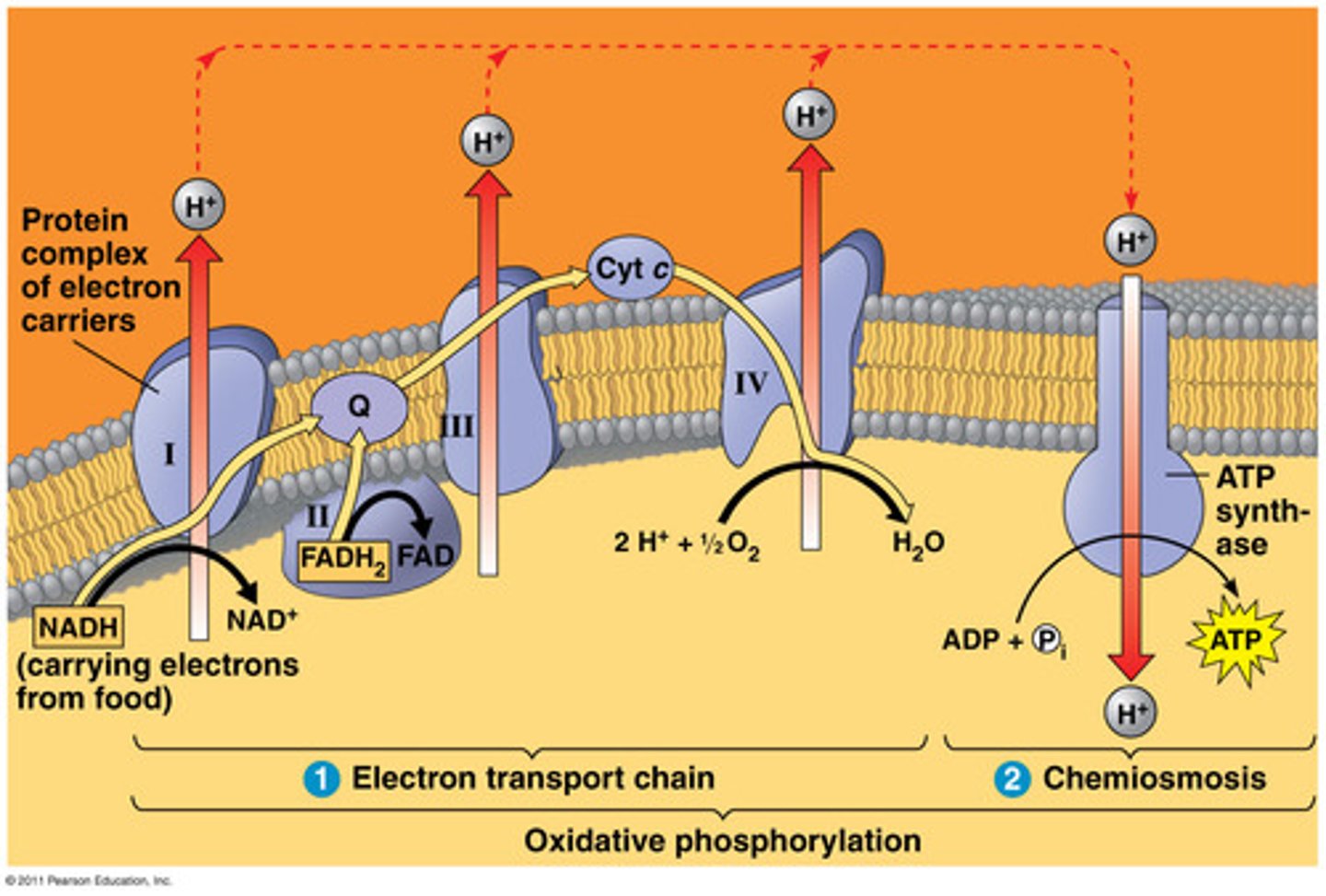
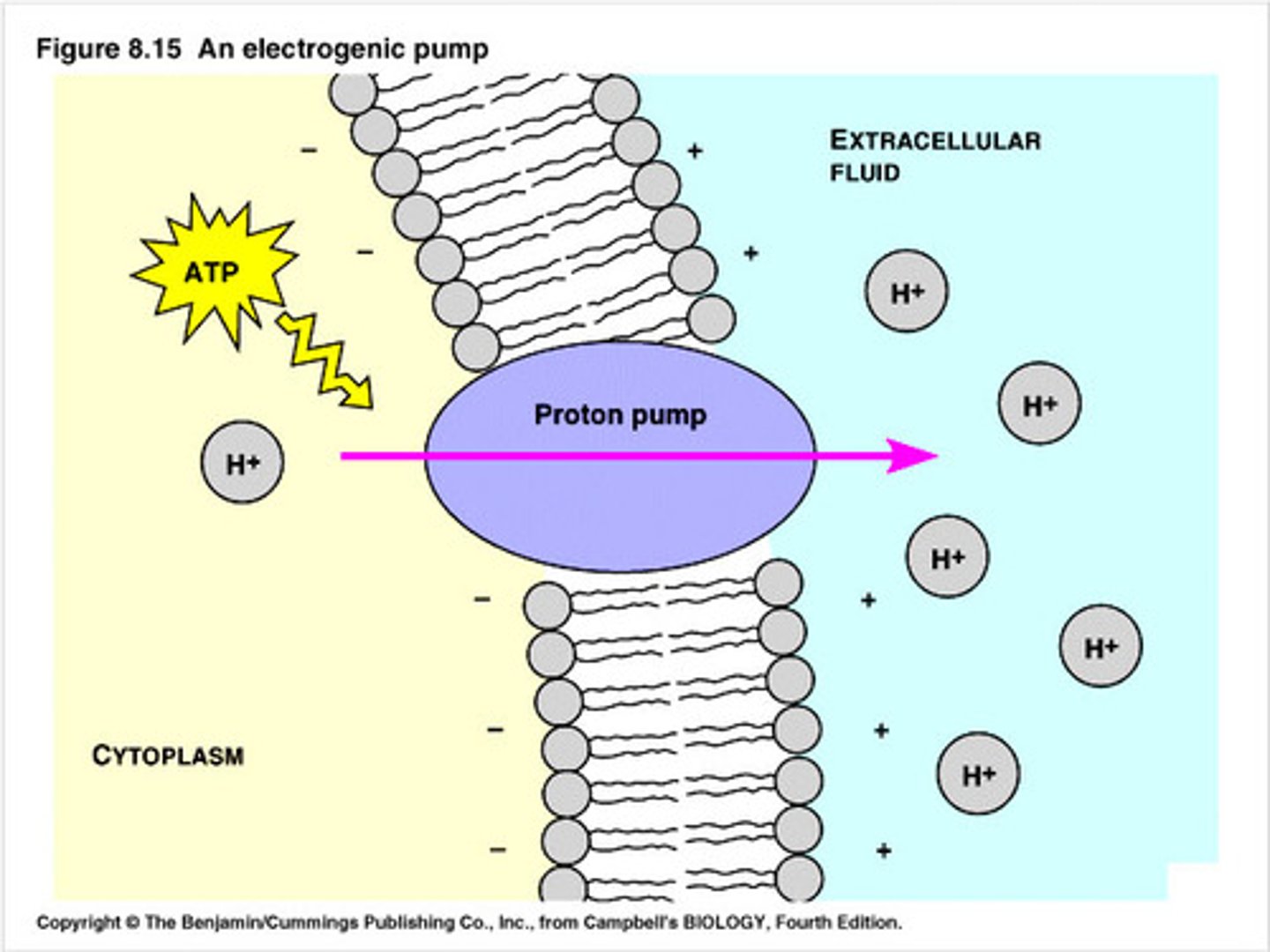
electrogenic pump
a transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane
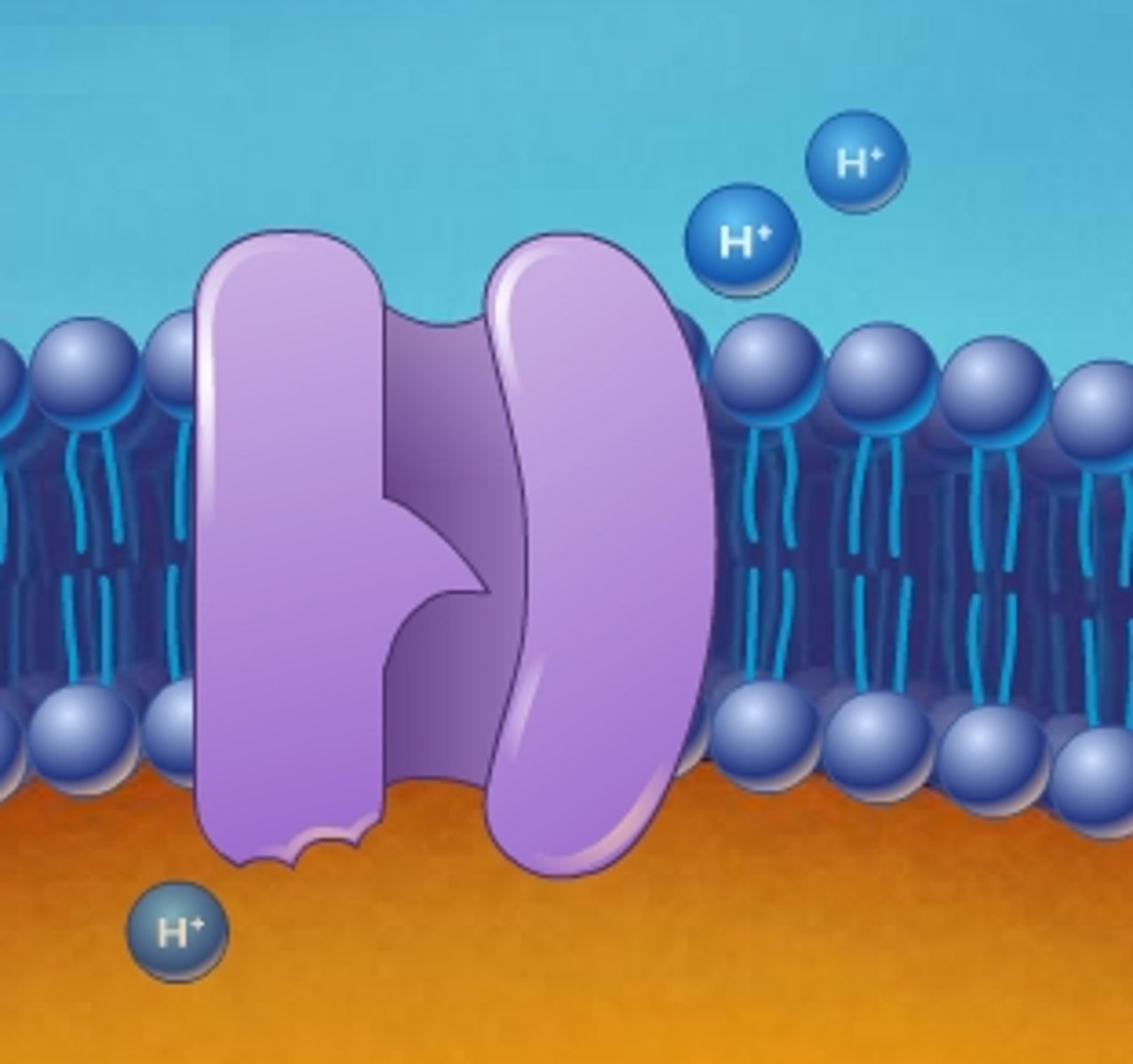
proton pump
a protein embedded in a biological membrane that moves protons (H+) across the membrane, creating a proton gradient. These pumps are crucial for various cellular processes, including energy production, pH regulation, and nutrient transport.
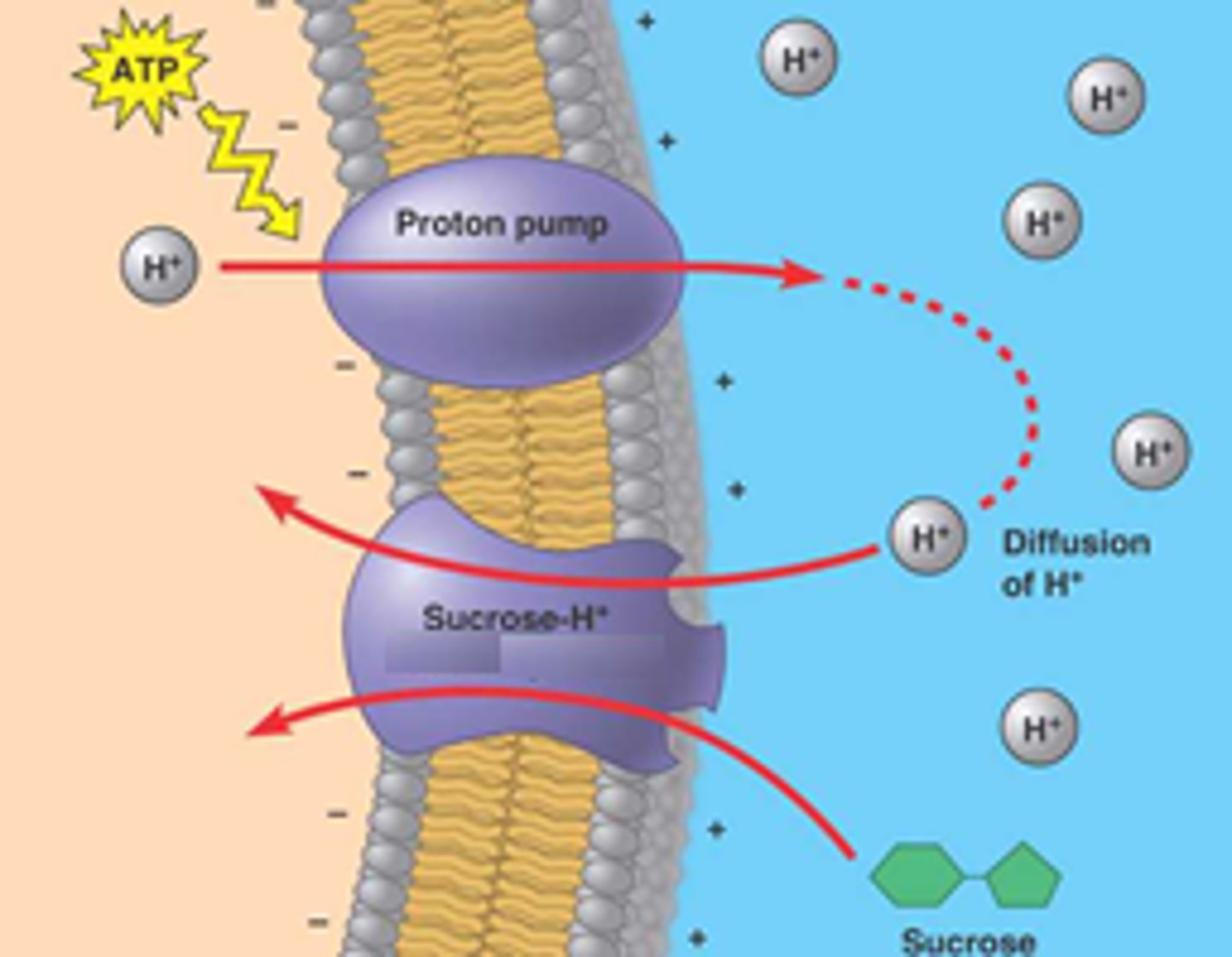
cotransport
the mechanism in which a ATP-powered pump that transports a specific solute can indirectly drive the active transport of several other solutes.
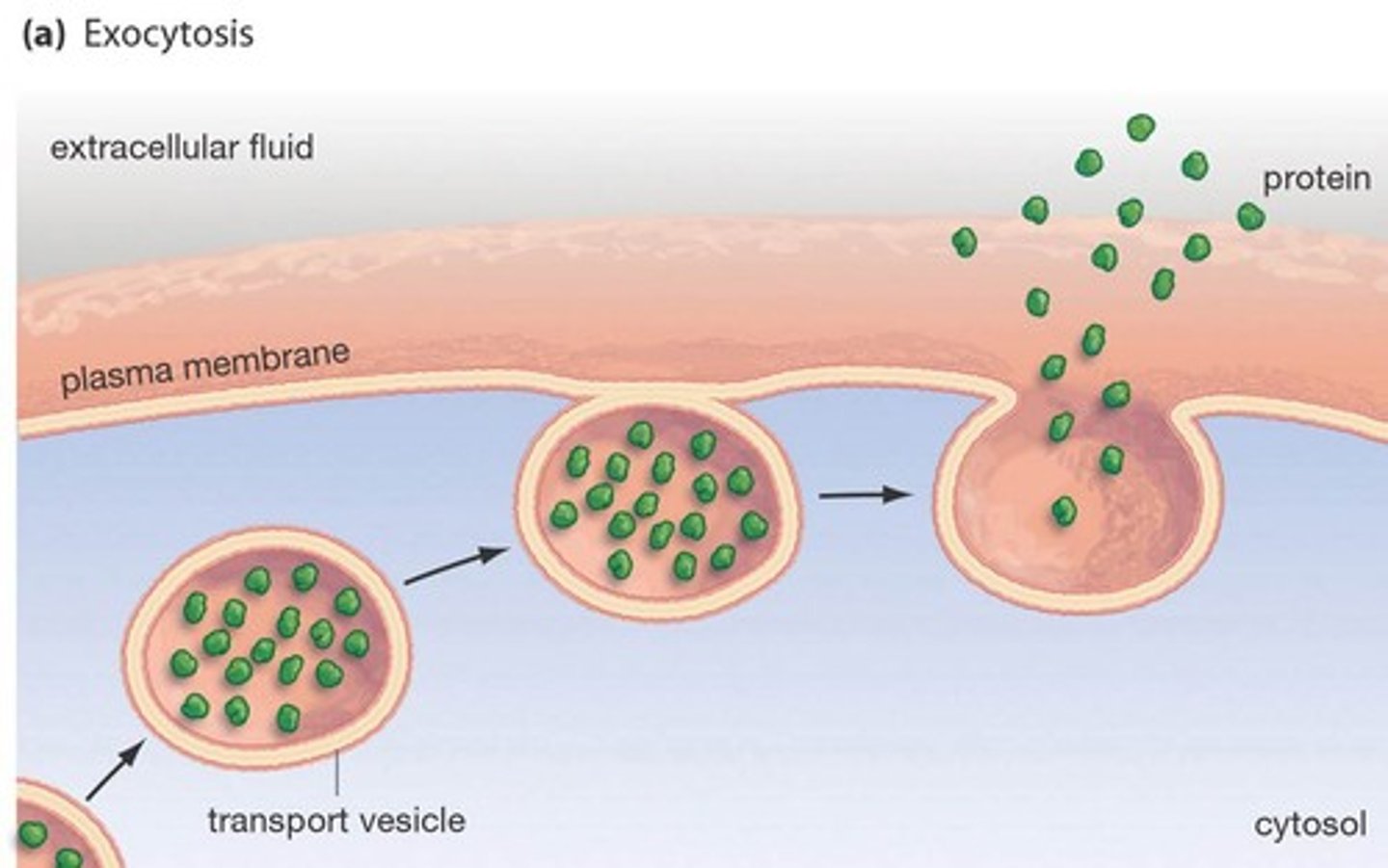
exocytosis
The process of transport vesicles migrate to and fuse with membrane, then releasing their contents
endocytosis
The intake of molecules by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane
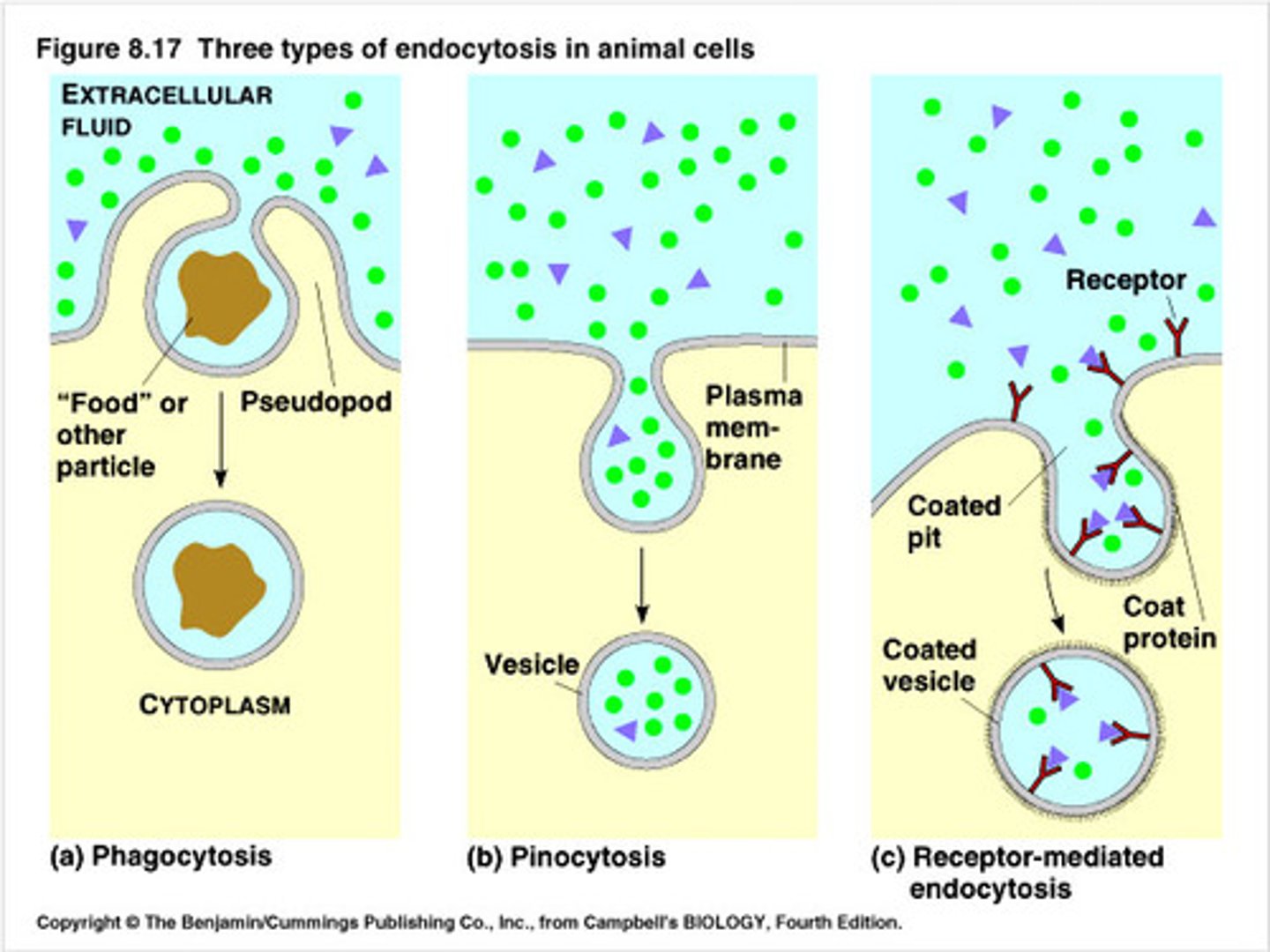
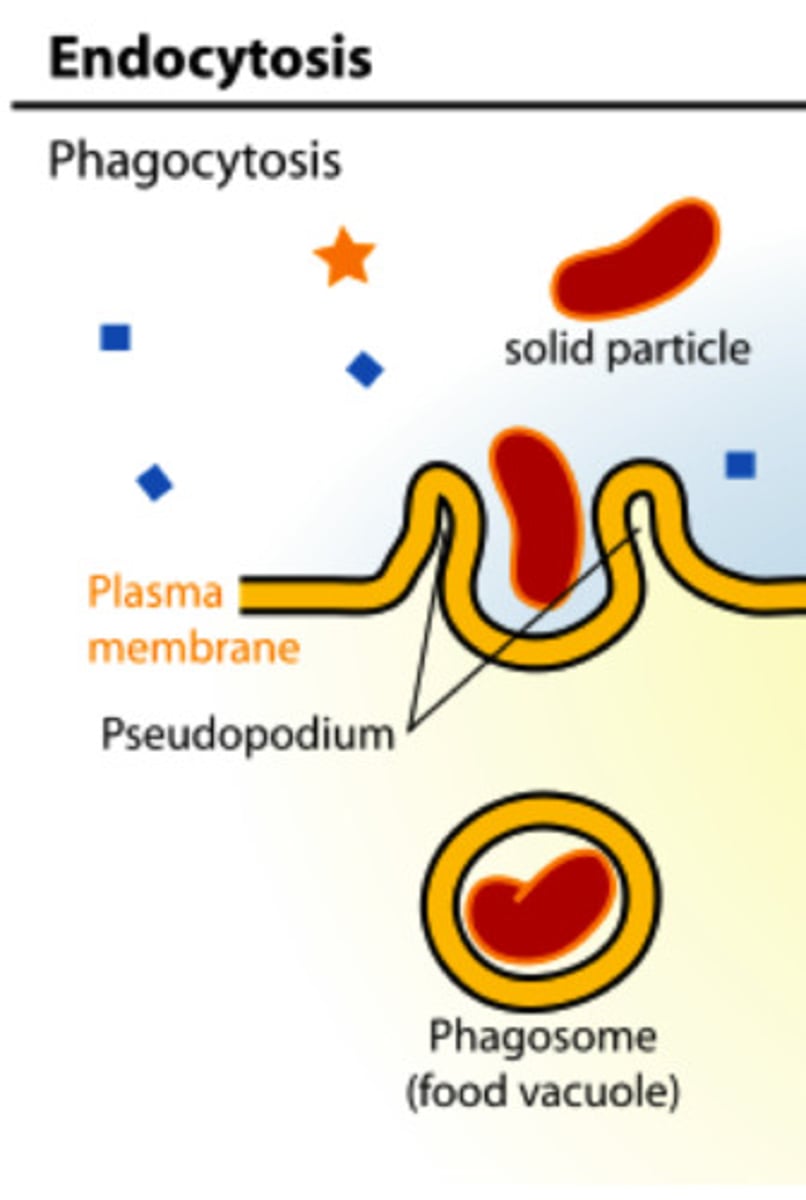
phagocytosis
cellular "eating"
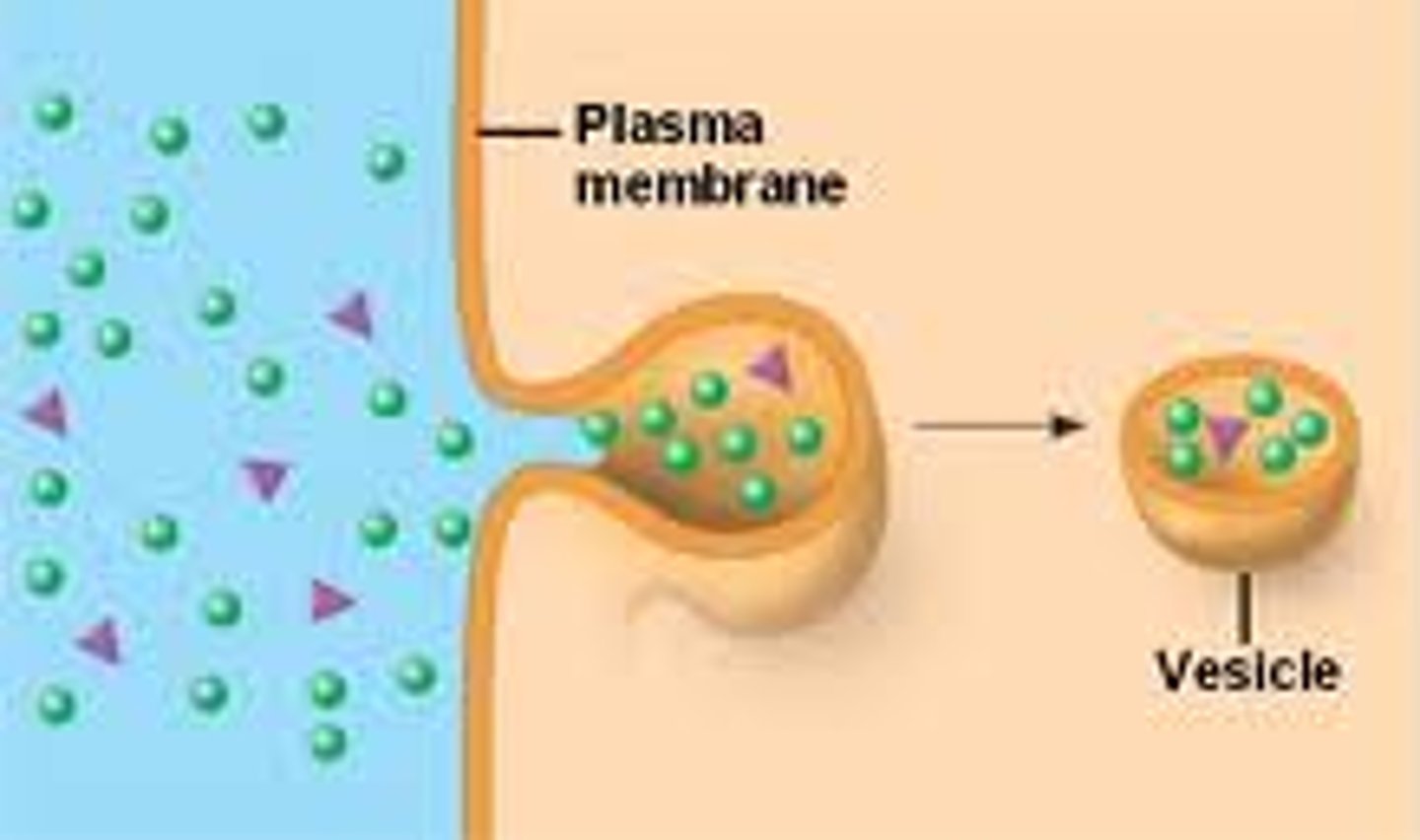
pinocytosis
cellular "drinking"
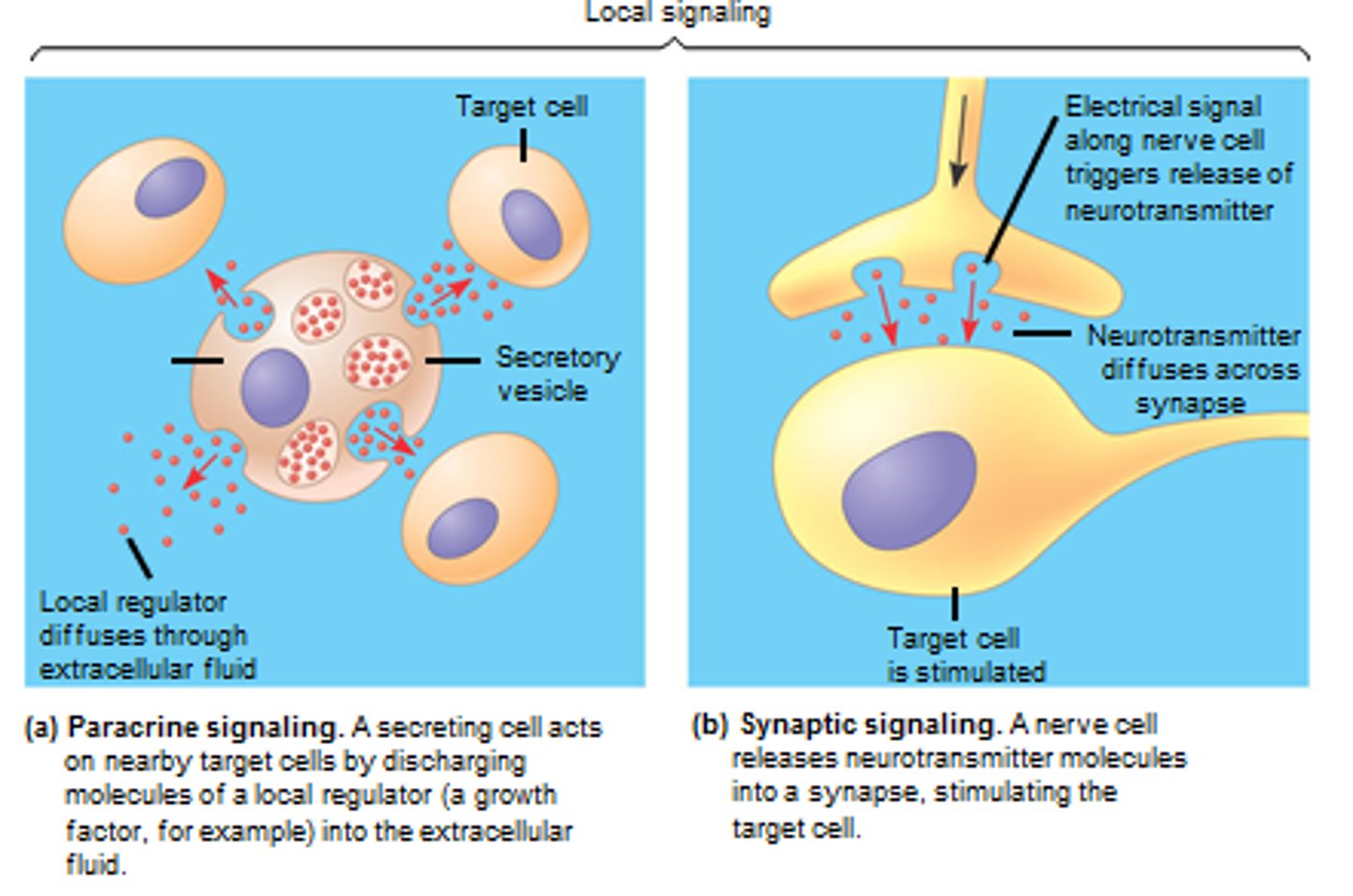
local regulators
messenger molecules secreted by signaling cell
hormones
The chemical signal the endocrine system send to the rest of body; could be steroids or proteins. | discovered by Earl W. Sutherland who later suggested the 3 processes of signaling
reception
receptor triggers changes when signal molecule ( ligand) binds to it
transduction
step of series of steps that converts the signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response
signal transduction pathway
a sequence of changes in a series of molecules during transduction
response
any cellular activities
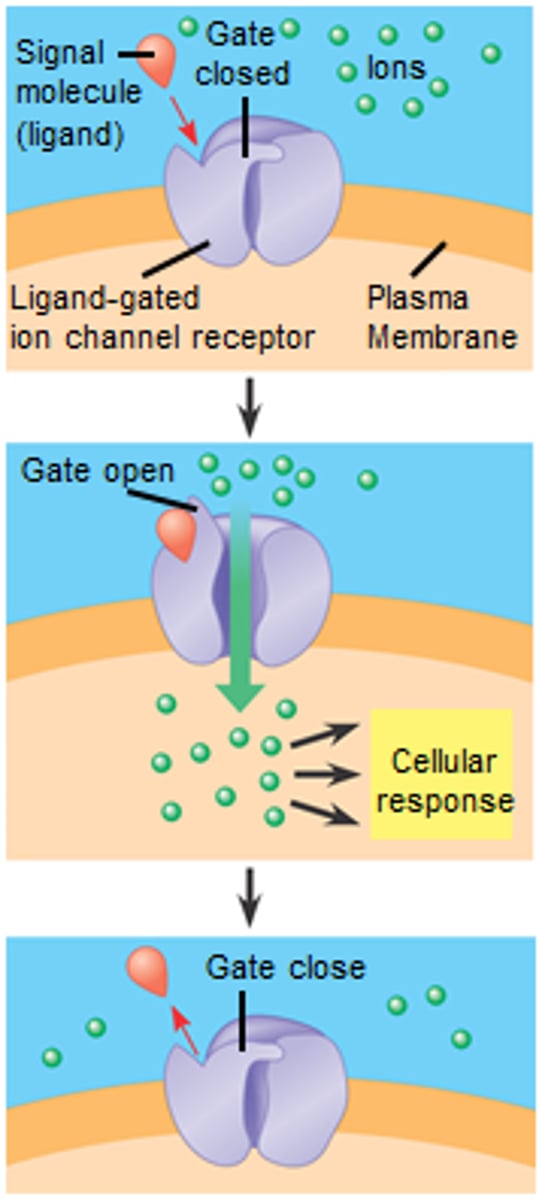
ligand
a signal molecule that specifically binds to another molecule
G protein-couples receptor (GPCR)
receptors that work with help of G proteins which bind to energy-rich molecules GTP
ligand-gated ion channel
a membrane receptor that acts as a gate, allowing ions to pass through when a specific molecule (ligand) binds to it and causes a conformational change. This change opens the channel, enabling ions to flow across the cell membrane