General Psychology Midterm
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
General Psychology Midterm / Pittsburgh Institute of Mortuary Science / Exam Date: 10/31/24 {EXAM INCLUDES ALL PAST FLASHCARDS} {VOCAB FROM BOOK INCLUDED}
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Motivation
Defined as the process that initiates, directs, and sustains behavior
Usually satisfying the physiological or psychological needs
It's the reason or purpose, referred to as motive
Drive reduction theory
People are motivated to take action in order to reduce the internal tension that is caused by unmet needs
Motivation arises to maintain homeostasis
Being hungry, cold, thirsty, tired, or hot
Arousal theory
People take certain actions to either decrease or increase their levels of arousal
People seek optimal levels of arousal
When arousal is too low a person may go for a job, when arousal is too high a person may meditate
Expectancy theory
People are motivated to do things because of external rewards
People are drawn to the positive and repelled by the negative outcomes
Focus on incentives
Goal setting theory
People are propelled strongly by the use of goals
Increase performance
Goals must be specific, challenging, and attainable
Feedback aids progress
Three components of motive
Activation
Persistence
Intensity
Extrinsic motivations
Engaing in behvaior in order to obtain an external reward or avoid a penalty or other undesirable consequences
Motivation that arises from outside of the individual and often involve rewards
Accolades (enticement maintains interest)
Intrinsic motivation
Engaging in behavior simply for the feelings of pleasure, satisfaction, or sense of competence or independence it brings
Motivation that arises within the individual
Autonomy, mastery, and purpose
Abraham Maslow
Most notable humanistic psychologist of the 20th century
People do not blindly react to situations
Studied exemplary people
Created the hierarchy of needs (pyramid of needs)
The hierarchy of needs (pyramid of needs)
The arrangement of needs from most basic to those at the highest levels
Physiological → safety → love/belonging → self-esteem → self-actualization
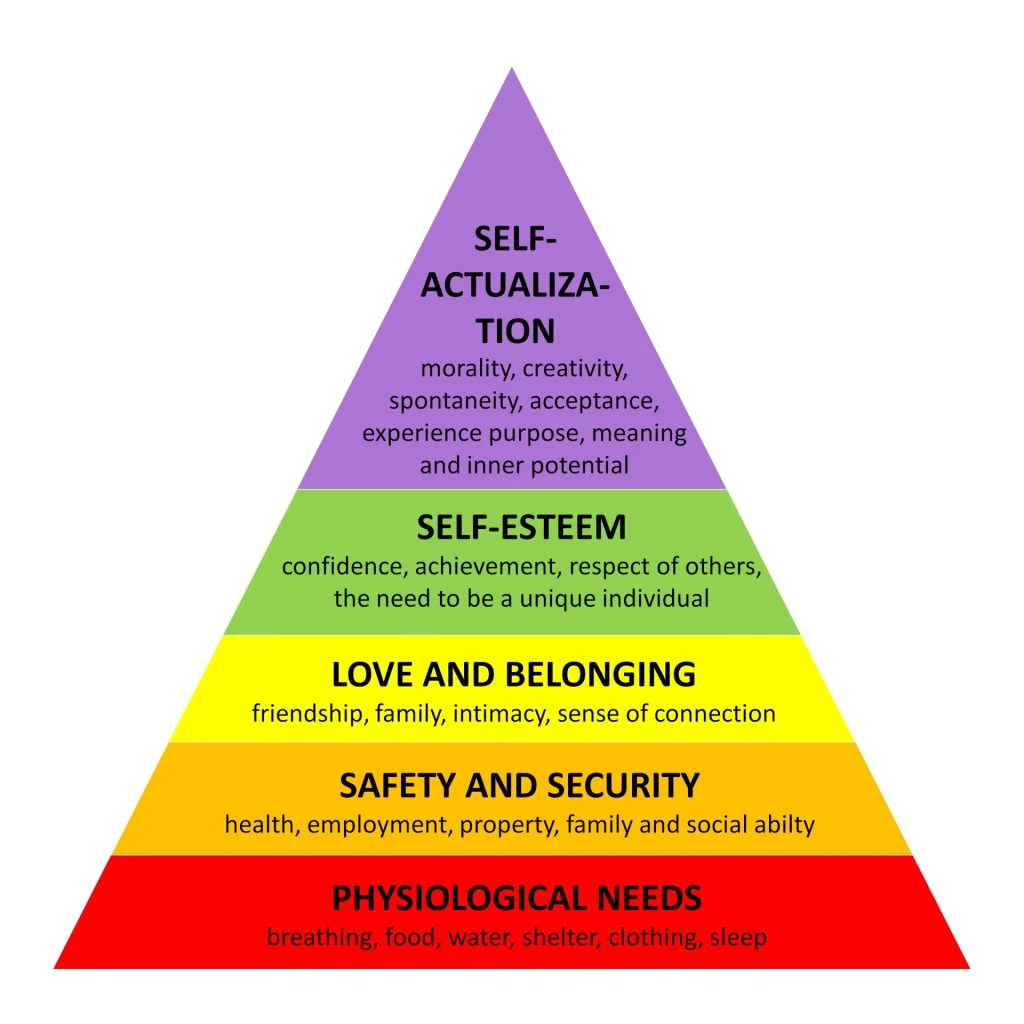
Physiological (hierarchy of needs)
Breathing, food, water, sex, sleep, homeostasis, excretion
Safety (hierarchy of needs)
Security of: body, employment, resources, the family, health, property
Love and Belonging (hierarchy of needs)
Friendship, family, sexual intimacy
Self Actualization (hierarchy of needs)
Morality, creativity, spontaneity, problem solving, lack of prejudice, acceptance of facts
Hunger motivation
The desire to obtain and consume food
The most powerful motivator
The brain controls the sensation to start or stop our hunger drive but many other factors become involved
Binge eating disorder
Recurring episodes of binge eating occur, feeling out of control while binging, feeling guilt and shame afterwards
Anorexia nervosa
Eating disorder characterized by an obsessive fear of gaining weight
Bulimia nervosa
Eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging
Sexual motivation
The desire to engage in various forms of sexual relations
The most intimate motive
Used in advertising to attract attention to products
Achievement motivation
Desire to accomplish difficult tasks and meet standards of excellence
Characteristics of high achievement motivation
Prefer difficulty, clear expectations, feedback, competition, responsibility and having to persevere
McGregor’s X & Y theory
Created in the 1960s for business development
Describing two contrasting models of workforce motivation
Theory X
Management believes employees are lazy, will avoid work if they can and that employees dislike work
Micromanagers
Theory Y
Management assumes employees are ambitious, self-motivated, exercise self-control, and believe that employees enjoy their work duties
Herzberg’s two factor theory
Contain factors exist in the workplace that cause job satisfaction, while a separate set of factors cause dissatisfaction which both factors operate independently
Developed in Pittsburgh
Composed of two categories of factors:
Hygiene
Salary, job security, fringe benefits
Motivators
Challenging work &/or recognition
Emotions
Defined as the outward displays or expressions of mood or feelings
Typically learned from your culture
Characteristics of emotions (7)
Temporary
Subjective
Positive or negative (or a mix)
Intensity varies
Triggered partially by thoughts
Alters thought process
Felt regardless of desire
Grief
The internal reaction
Involves the process of many emotions
Mourning
The external process
‘Grief gone public’
Bereavement
The event or state causes by a loss
Actually means to be torn away
Cannon’s bard theory (central theory)
Events simultaneously produce the subjective reaction labeled as emotion
Emotion starts in the brain
Information goes first to the thalamus—>autonomic nervous system & cerebral cortex, where emotion becomes conscious
Create experience of fear while at the same time sending message to heart, lungs, and legs to get you out of the situation
Arousal and emotion occur at the same time
James lang theory
Events cause the subjective reaction of emotion but the person must recognize the physical symptoms first
You are afraid because you run from bear
Experience emotions only by percieving or physiological response to an event
Without physiological responses, nothing remains of emotional experience
Emotions occur after arousal
Schacter and singer theory
The subjective reaction of emotion is determined by the cognitive label we attach to the feeling
Emotions result from a combination of feedback from the body’s responses and or interpretation of what caused those responses
Arousal first occurs then the reaction must be identified and finally the emotion is labeled
Nonverbal gestures
Outward signs of emotional states
Body language, eye contact, & facial expressions
Body language
The body posture or movement of the body in reaction to emotional events
Eye contact
Nonverbal means of conveying and ascertaining emotional information or mood status
Facial expressions
The use of the face to illustrate a person’s emotional state
6 universal facial expressions
Anger
Fear
Surprise/shock
Sadness
Happiness
Disgust
Evolutionary theory
A view that emphasizes the inherited, adaptive aspects of behavior and mental processes
Incentive theory
A theory that people are pulled toward behaviors that offer positive incentives and pushed away from behaviors associated with negative incentives
Hypothalamus
A structure in the forebrain that regulates hunger, thirst, and sex drive
Thalamus
A forebrain structure that relays signals from most sense organs to higher levels in the brain and plays an important role in processing and making sense out of this information
Parasympathetic nervous system
The subsystem of the autonomic nervous system that typically influences activity related to the protection, nourishment, and growth of the body
Sympathetic nervous system
The subsystem of the autonomic nervous system that readies the body for vigorous activity
Ventromedial nucleus
Important in the regulation of female sexual behavior, feeding, energy balance, and cardiovascular function
Lets the body know to stop eating
Lateral hypothalamus
Controls many behaviors, including feeding, energy balance, sleep-wake states, and motivated behavior
Tells animal to start eating
Paraventricular nucleus
Reduces food intake when stimulated
Approach-avoidance conflict
Arises when we must decide wether to do something that has both positive and negative consequences
Instinctive behaviors
Innate, automatic dispositions to respond in particular ways to specific stimuli
Instinct doctrine
A view that behavior is motivated by automatic, involuntary and unlearned responses
Androgens
Masculine hormones that circulate in the bloodstream
Progestational hormones
Feminine hormones that circulate in the bloodstream
Excitation transfer theory
The theory that physiological arousal stemming from one situation is carried over to and enhances emotional experience in an independent situation
Lazarus’s cognitive appraisal theory
The process of cognitive appraisal begins when we decide whether an event matters to us
Unlikely to have an emotional experience when it doesn't matter
If event is relative to health, well-being, staus, self-esteem, goals, or finances, we will probably have a significant emotional reaction to it
Darwin’s universal rules
Some facial expressions are genetically determined, passed on biologically from one generation to the next
Social referencing
A process where people, especially infants, use emotional information from others to guide their behavior, particularly in uncertain situations