Biology Lecture 2010 Exam 2 Austin Peay
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
1) Regulation
2) Protection
3) Sensation
4) Communication
5) Excretion
6) Immunity
7) Dermis is a significant blood reservoir
8) Synthesis of Vitamin D
What are the skin functions?
1.5mm - 4mm
What is the Variable Thickness of the skin?
Epidermis and Dermis
What are the 2 principal portions of the skin?
Hypodermis (Beneath the dermis)
What is the Subcutaneous layer?
Epithelial tissue
What tissue is the epidermis made of?
Areolar connective tissue and dense irregular connective tissue
What tissues make up the dermis?
Keratinocytes, melanocytes, langerhans cells, and merkel cells
What are the four cells types in the stratified squamous epithelium?
water proof barrier, and filled with keratin (protein)
What are some details of keratinocytes?
Produce melanin (pigment), protects against UV light, and passes melanin to keratinocytes.
What is the function of melanocytes?
Phagocytes (from immune system), help fight bacteria
what is the function of Langerhans cells?
UV light
What easily damages langerhans cells?
Sensory transduction (touch), works for nervous system, and has nerves attached
What is the function of Merkel cells?
Stratum Corneum
Stratum Lucidum (only found in thick skin; palms and feet)
Stratum Granulosum
Stratum Spinosum
Stratum Basale
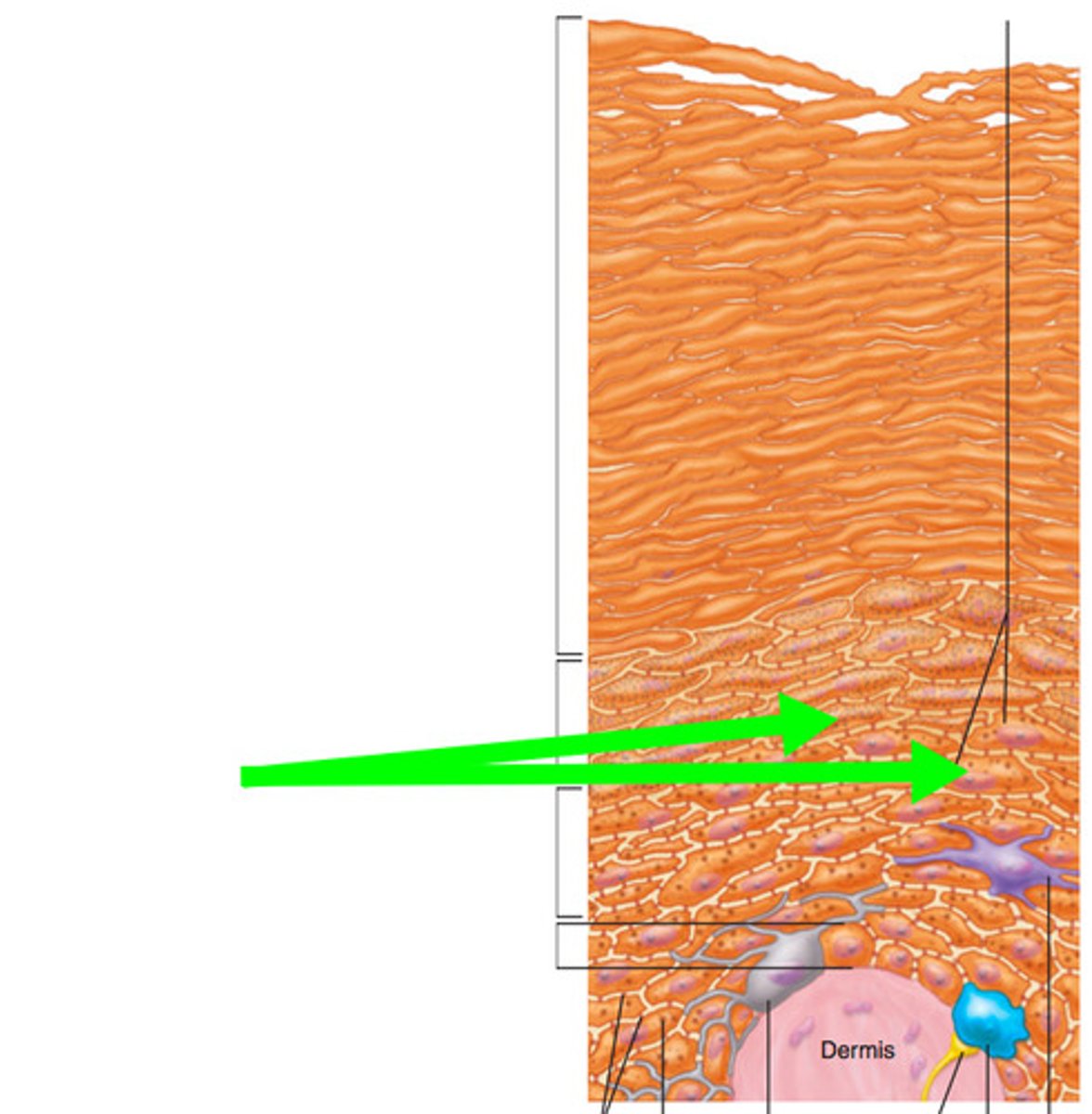
Identify the layers of the skin form superior to inferior.
Stratum Basale
In what layer do you find melanocytes?
Stratum Spinosum
In what layer do you find Langerhans cells?
Stratum Basale (Hairless skin)
In what layer do you find Merkel cells?
Langerhans cell
Identify cell
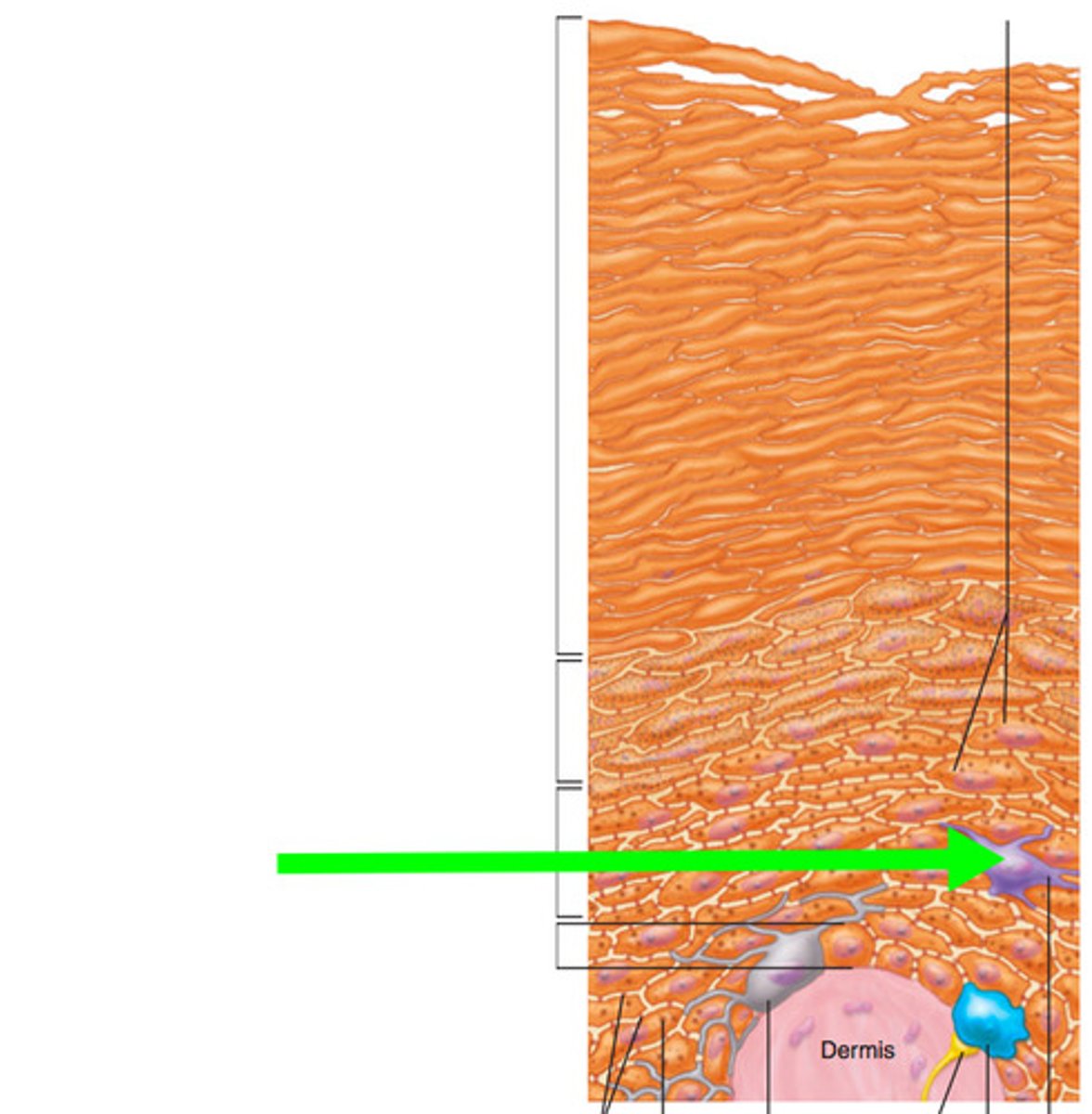
Merkel cell
Identify cell
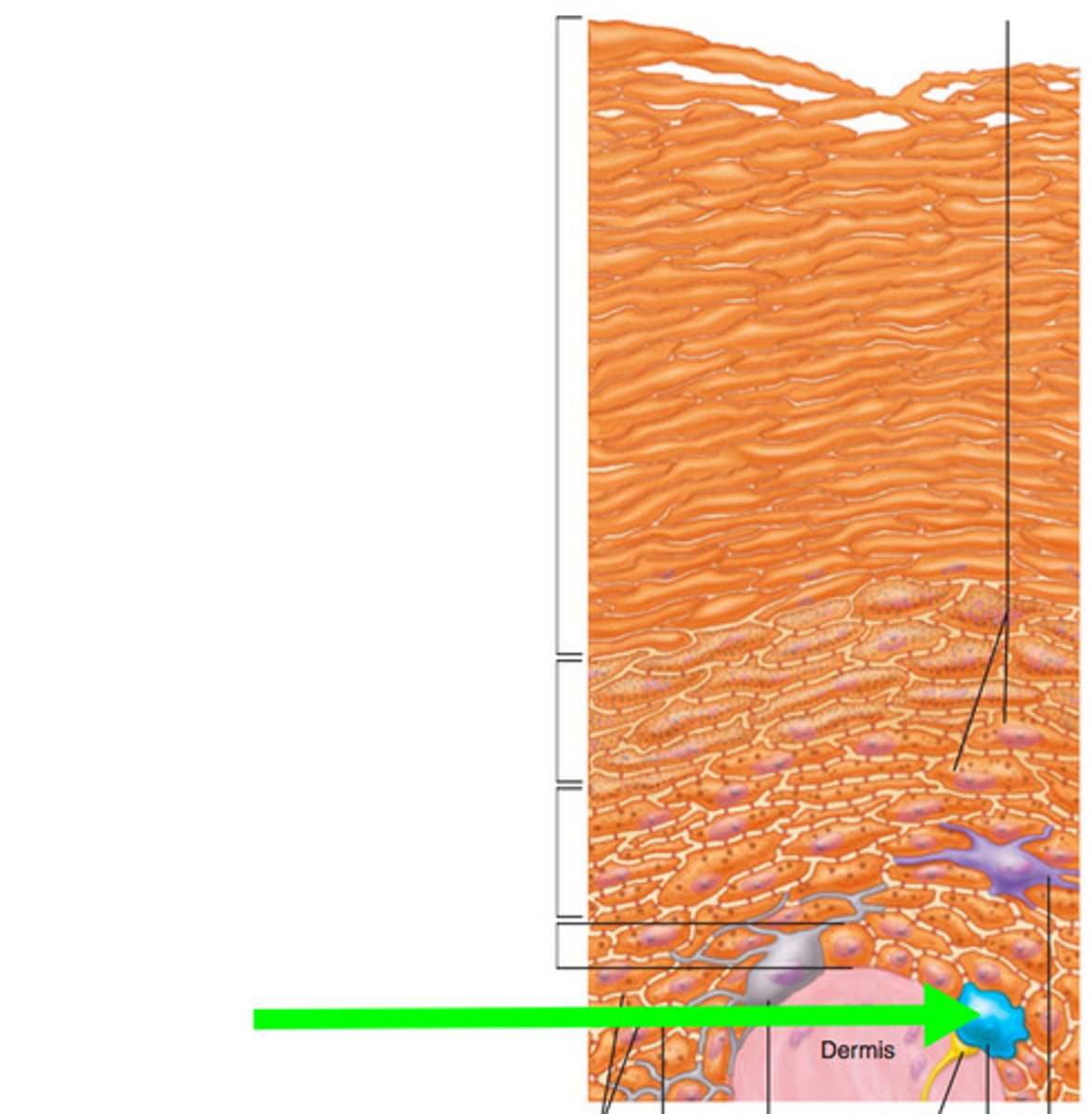
Melanocytes
Identify cell
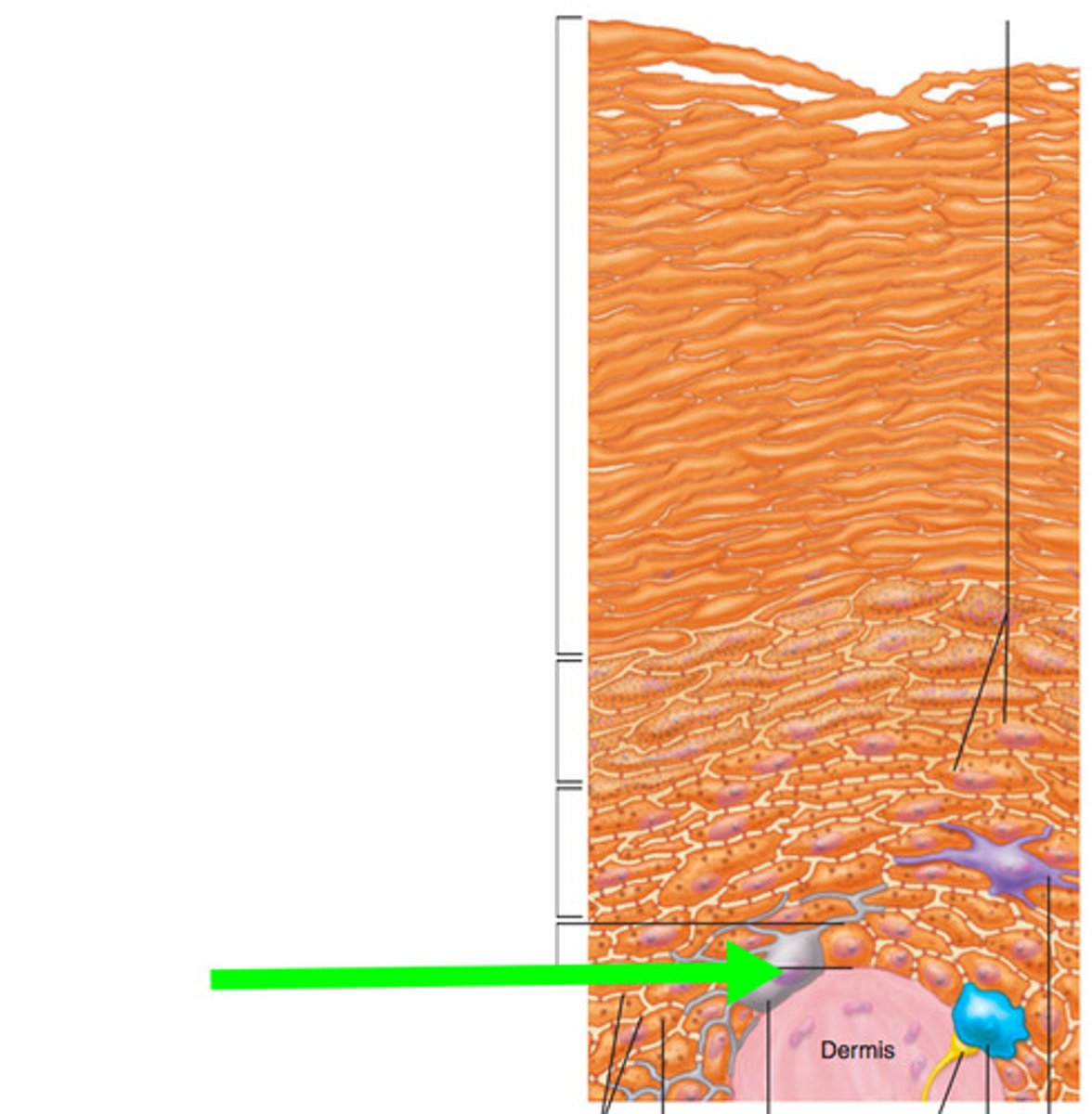
Keratinocytes
Identify cell
has 20-30 layers of flattened, dead, keratin filled cells, Continuously shed and replaced
What is the basic function of Stratum corneum?
3-5 layers of clear flattened dead cells with keratin. Only found in thick skin.
Basic function of stratum lucidum
3-5 layers of flattened cells with keratohyaline granules. Where the nucleus is broken down, cell death is initiated.
basic function of stratum granulosum
8-10 layers of closely packed cells. spot desmosomes as cell junction. Contains langerhans cells
Basic function of stratum spinosum
a single layer of cuboidal/columnar cells, stem cells (Keratinocytes), Melanocytes, and Merkel cells located here. Stem cells (keratinocytes) mitosis pushes the other layers to the top.
Basic function of stratum basale
2-4 weeks
How long does it take for each cell to form and to move from the stratum basale to the surface?
Papillary and reticular regions
What two regions make up the Dermis?
Areolar connective tissue
what tissue makes the papillary region?
Dense irregular connective tissue
What tissue makes up the reticular region?
Dermal papillae
name this structure
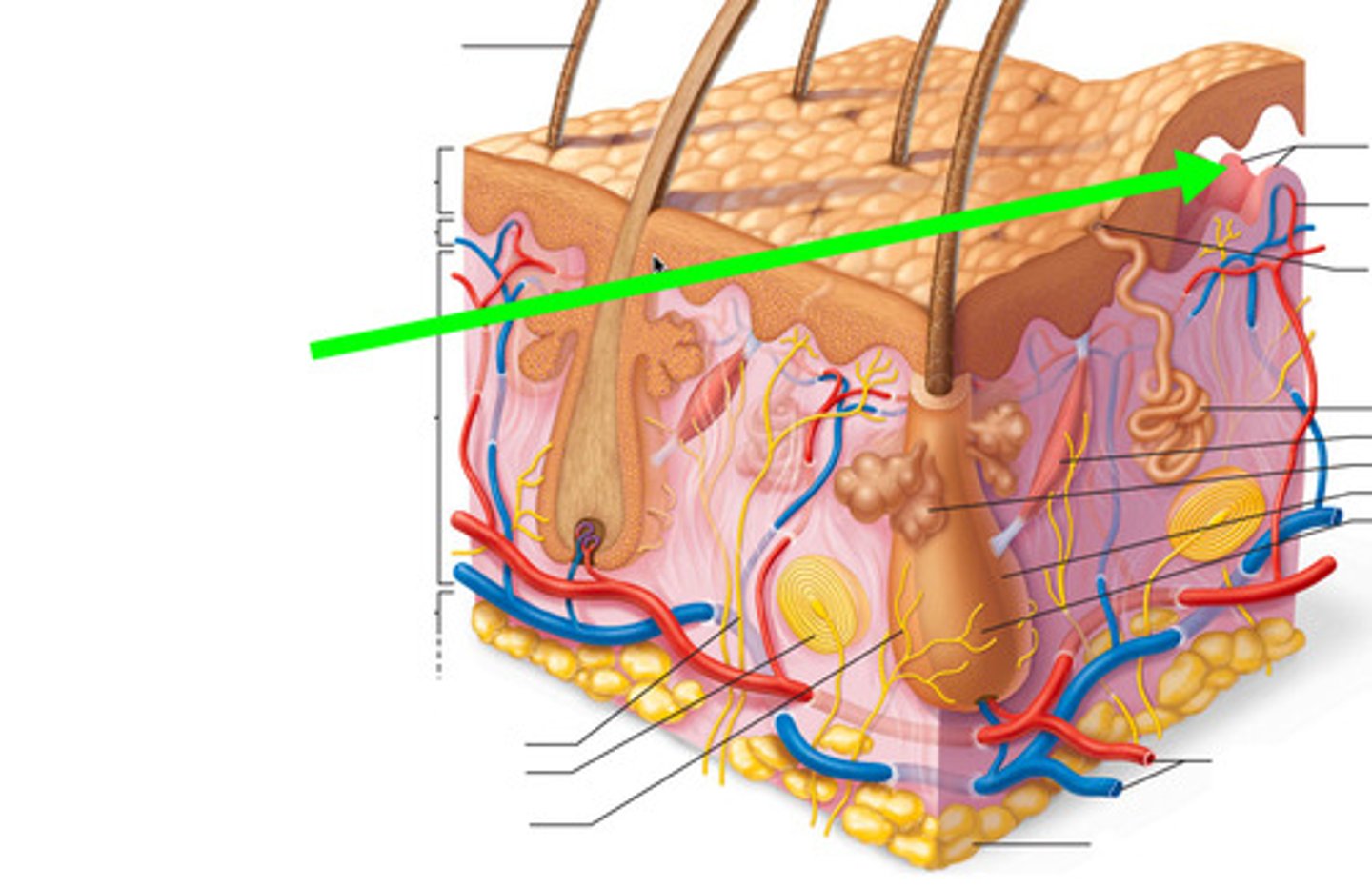
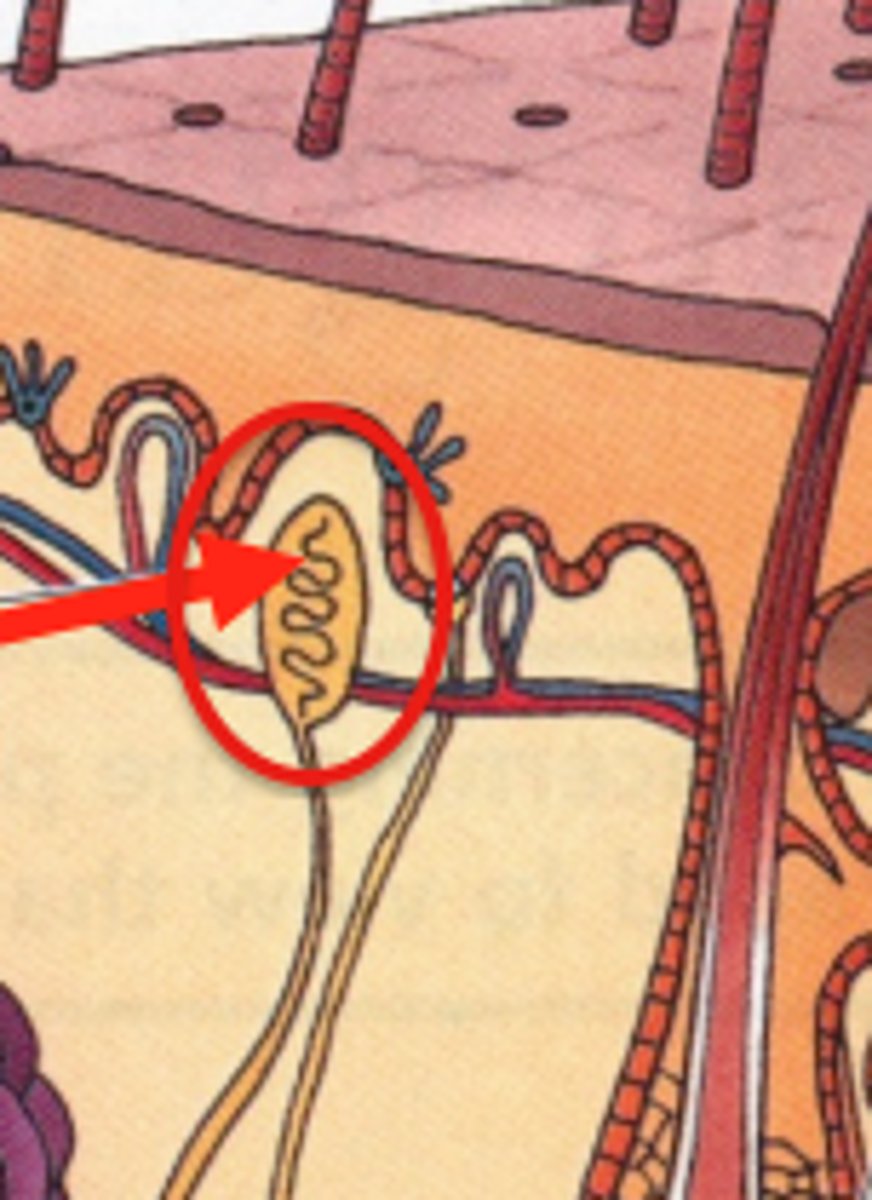
Meissner's corpuscles
name this structure
Melanin
What produces yellow to black pigment
Carotene
what produces yellow/orange pigment in the dermis?
Hemogloblin
What produces a red to pink tint?
Erythema
A red skin color is caused by what?
Pallor
A pale skin color is caused by what?
Cyanosis
A bluish tint of the skin is caused by what?
Jaundice
A yellow/orange skin color is caused by what?
Addison's disease
A metallic bronzy skin color is caused by what?
bruises (contusions)
Black and blue marks on the skin is caused by what?
From the stratum basale; least malignant - 99% full cure
what are the characteristics of Basal cell carcinoma?
From the stratum spinosum; prognoses is good if removed early
What are the characteristics of squamous cell carcinoma?
Melanocyte cancer; highly metastatic; and resistant to chemotherapy
What are the characteristics of melanoma?
A- asymmetric
B- boarder irregularity
C- color: several present
D- Diameter; greater than 6mm
Used to identify type/severity of skin pathologies
What does the ABCD Rule stand/used for?
only the epidermis is damaged; symptoms include localized redness, swelling, and pain; No Blisters; heals in 2-3 days; Partial thickness
Characteristics of 1st degree burns
Epidermis and upper regions of dermis are damaged; symptoms mimic 1st degree burns but blisters appear; heals in 3-4 weeks with good care; partial thickness
Characteristics of 2nd degree burns
Entire thickness of the skin is damaged; burned areas appear grey-white, cherry red, or black; there is no initial edema (swelling) or pain (since nerve endings were destroyed); much fluid loss and infection - skin grafting is commonly needed; full thickness
Characteristics of 3rd degree burns?
Over 25% of the body has 2nd degree burns
Over 10% of the body has 3rd degree burns
There are 3rd degree burns on the face, hands, or feet.
Burns are considered critical if:?
Medulla
Identify
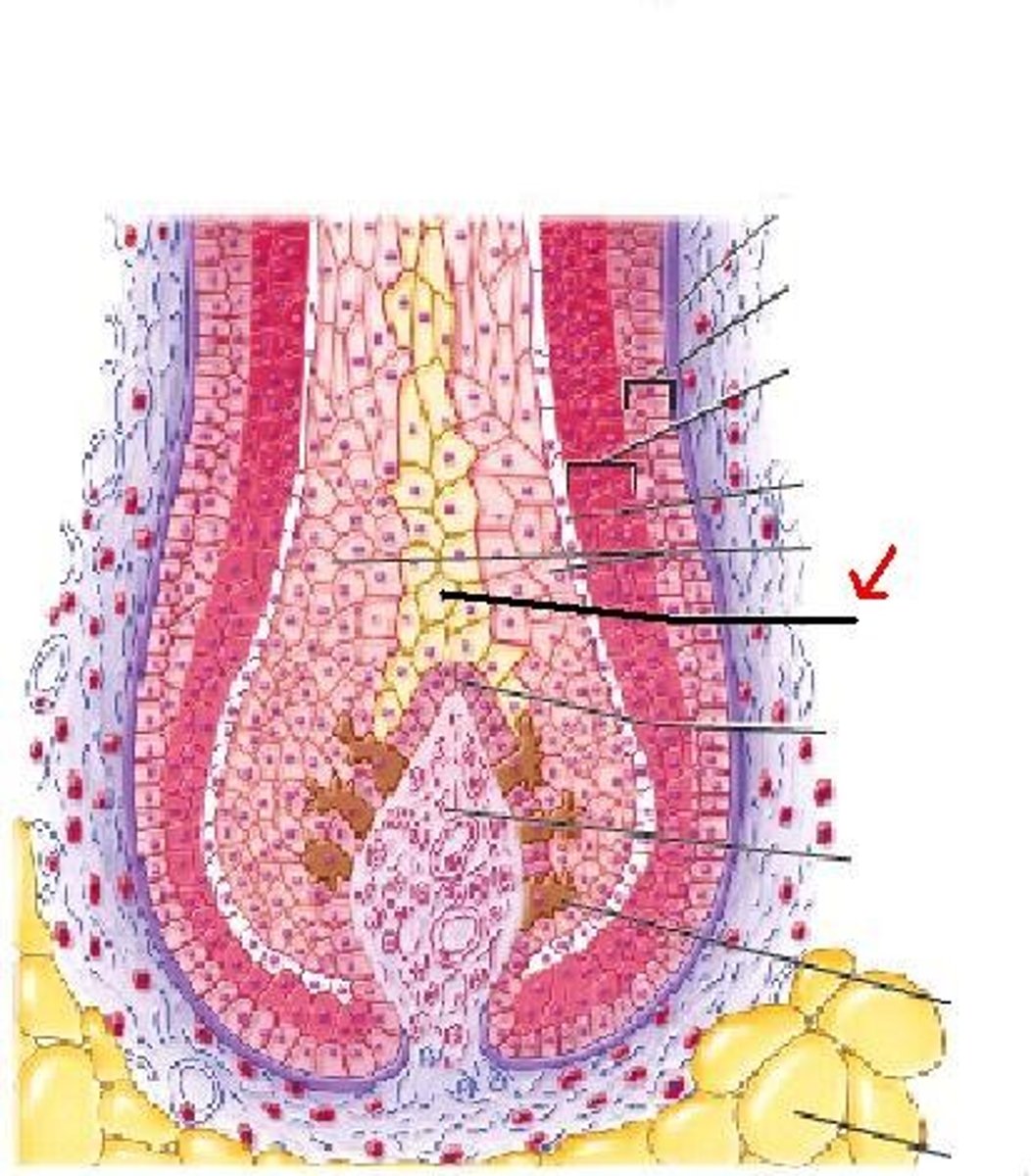
Cortex
identify
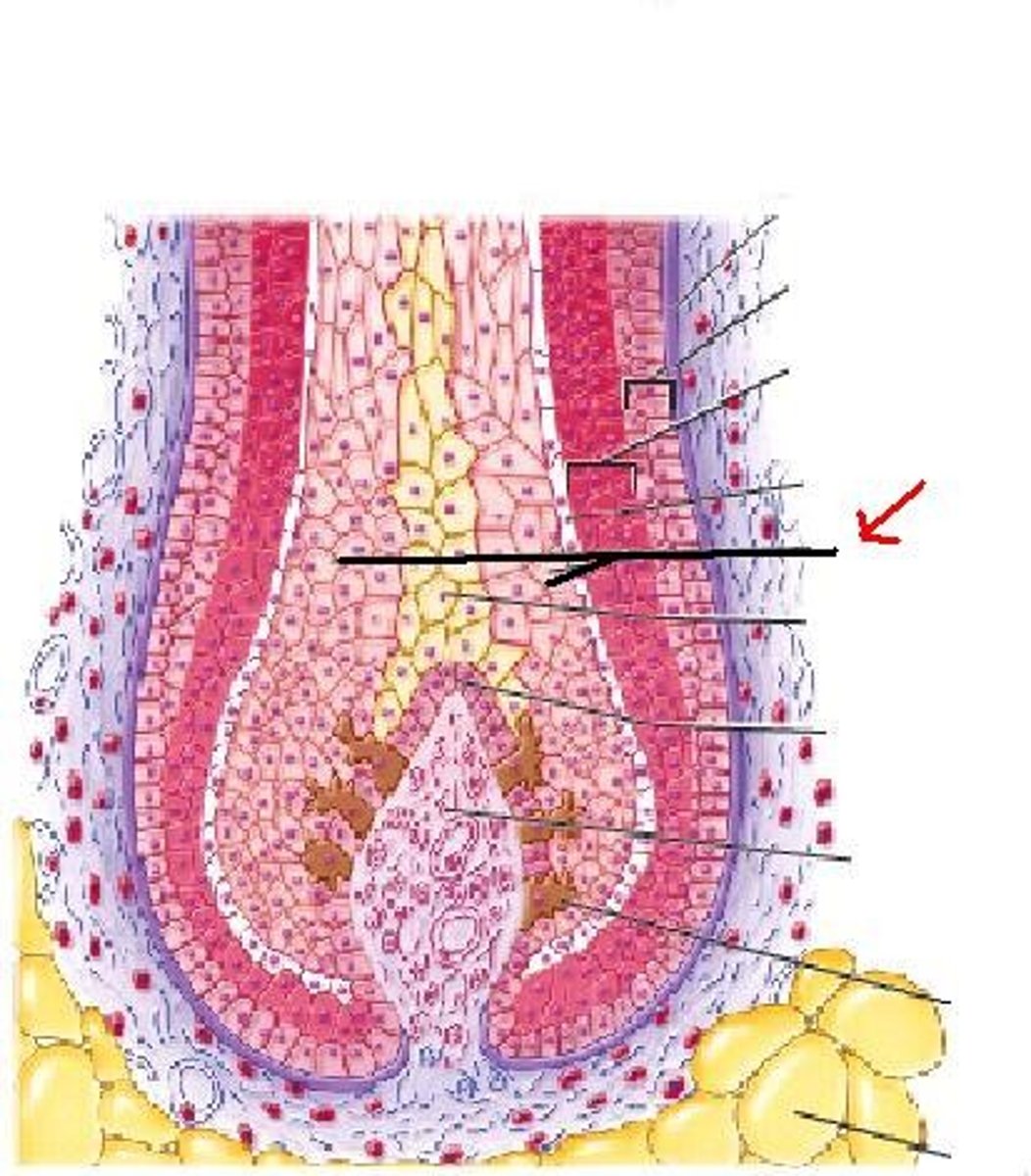
Cuticle
identify
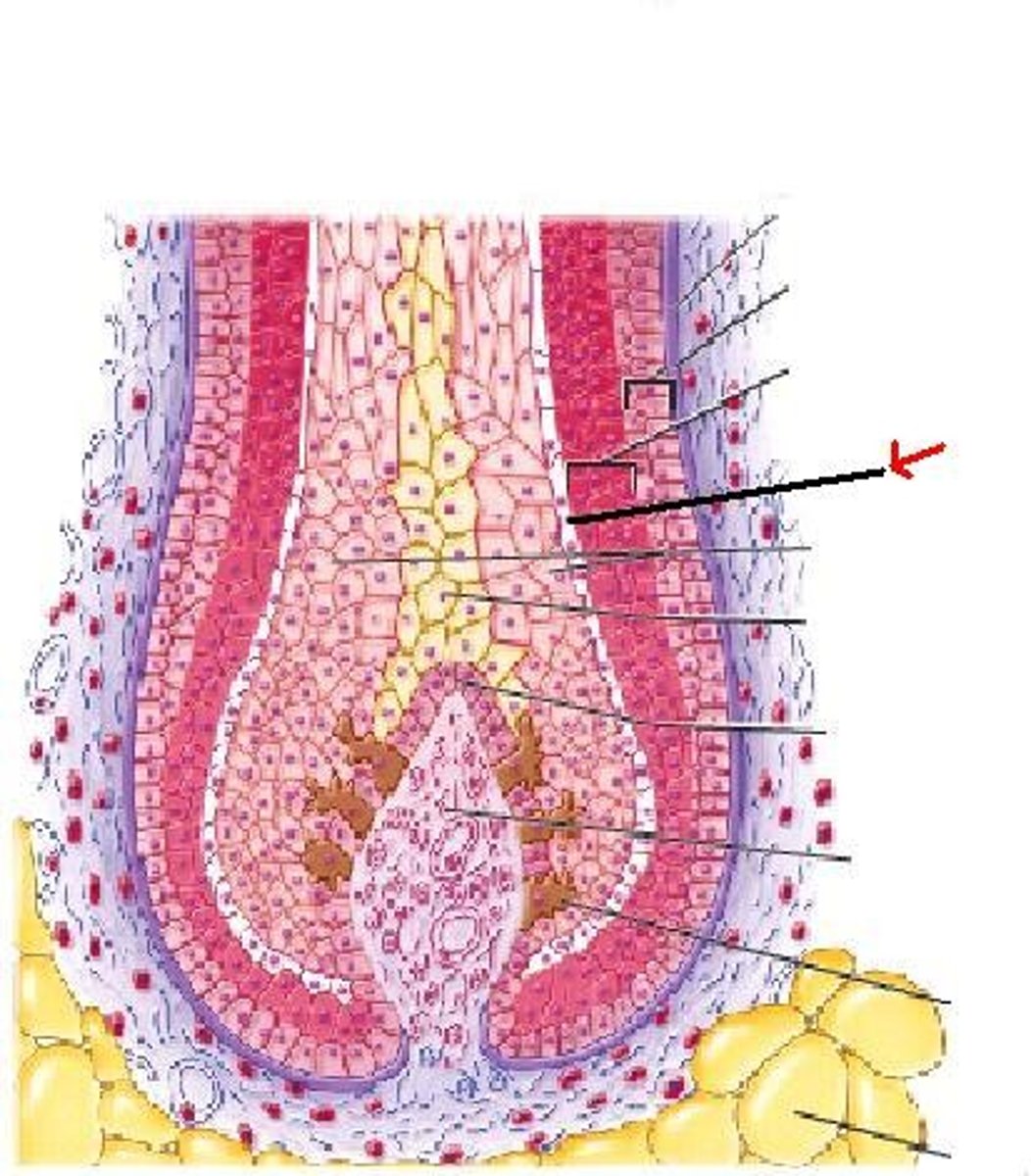
Sebum
What do sebaceous glands secrete?
arrector pili muscle
identify
Smooth muscle
what type of muscle tissue is the arrector pili muscle made of?
holocrine gland
What kind of gland is the sebaceous gland?
excess hair production in females or pre-pubertal males; male pattern hair in females
what is Hirsutism?
excess testosterone production (from tumor or hormonal imbalance)
what causes hirsutism?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT); genetic predisposition
What causes male pattern baldness?
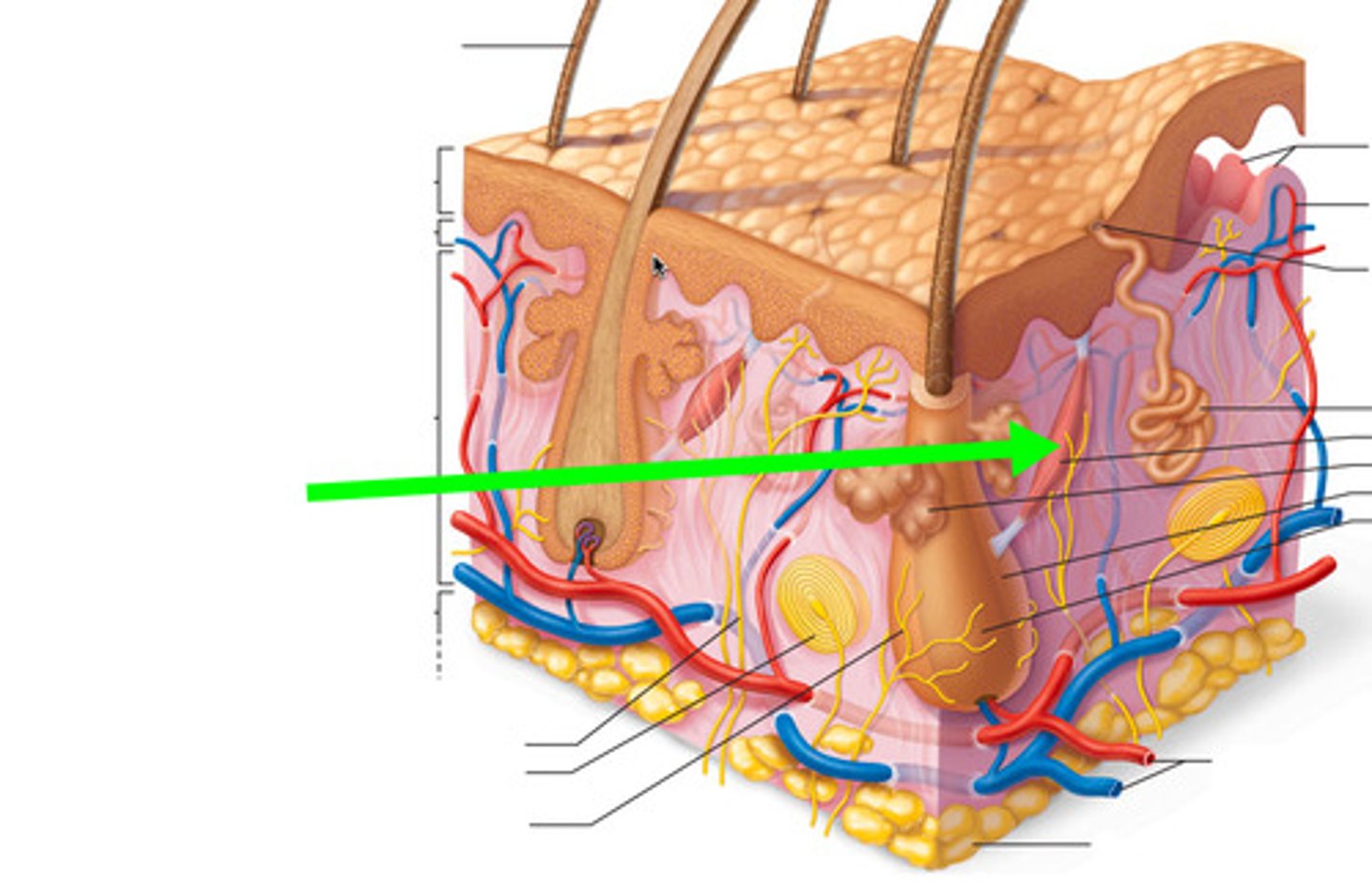
sweat glands
What are sudoriferous glands?
Eccrine and apocrine sweat glands
What are the two types of sudoriferous glands?
Eccrine glands are most abundant in the palms, soles, and forehead
Of the two types of sudoriferous glands, which one is most abundant and where?
Apocrine glands are least abundant located in the axillary and anogenital (groin) regions; also in the areolae of the breast
Which of the two sudoriferous glands are least abundant and where are they located?
Merocrine process
Through what process do apocrine glands secrete?
Ceruminous (ear wax) glands and mammary glands
What are the two types of modified sudoriferous (sweat) glands?
Produce bitter waxy secretions (cerumen) to protect against ectoparasites (bugs); located in the external auditory meatus (ear canal) or into local sebaceous glands
What is the function/location of ceruminous glands?
highly specialized in milk production; located in the mammary
What is the function/locations of mammary glands?
Estrogen, prolactin, and oxytocin
what regulates mammary glands?
An error of the cystic Fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR Gene); CFTR "stuck" in the rough endoplasmic reticulum
What causes cystic fibrosis?
it reduces chloride reabsorption, ,changing the characteristics of most glandular secretions. Primarily affecting the respiratory and digestive systems with thick clogging secretions.
What does cystic fibrosis affect?
With a chloride sweat test; CF babies have an elevated sweat chloride levels
how is cystic fibrosis detected in infants?
37 years
what is the average lifespan of someone with CF?
Tightly packed cells with keratin
What are nails?
Under the root of the nail
Where is the nail matrix located?
Nail growth
What happens at the nail matrix?
Support, protection, mineral homeostasis, movement, and the site of blood cell production.
what are the functions of bone?
Bone is a reservoir of Calcium
What is bone a reservoir of?
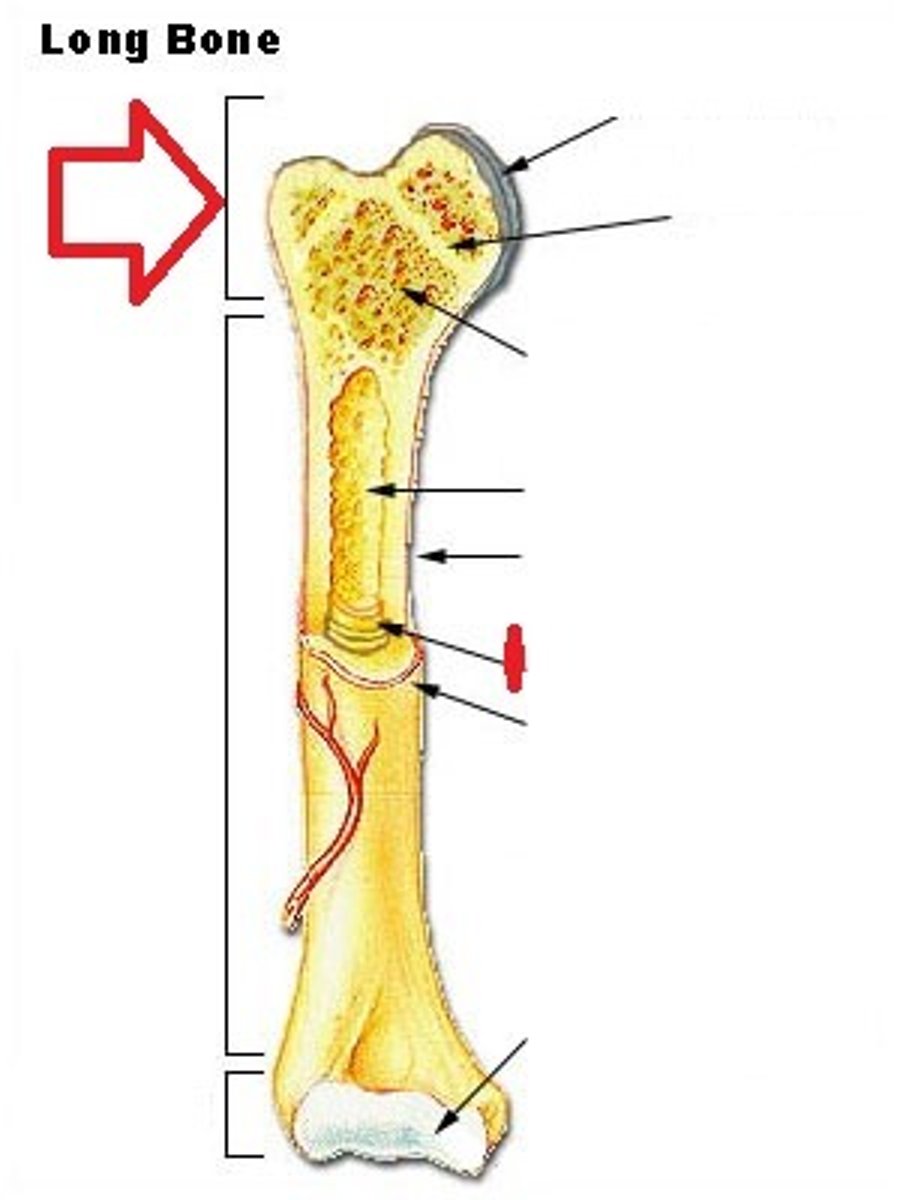
The shaft of a long bone
What is the Diaphysis?
The ends of the a long bone
What is the Epiphysis?
Diaphysis
Identify
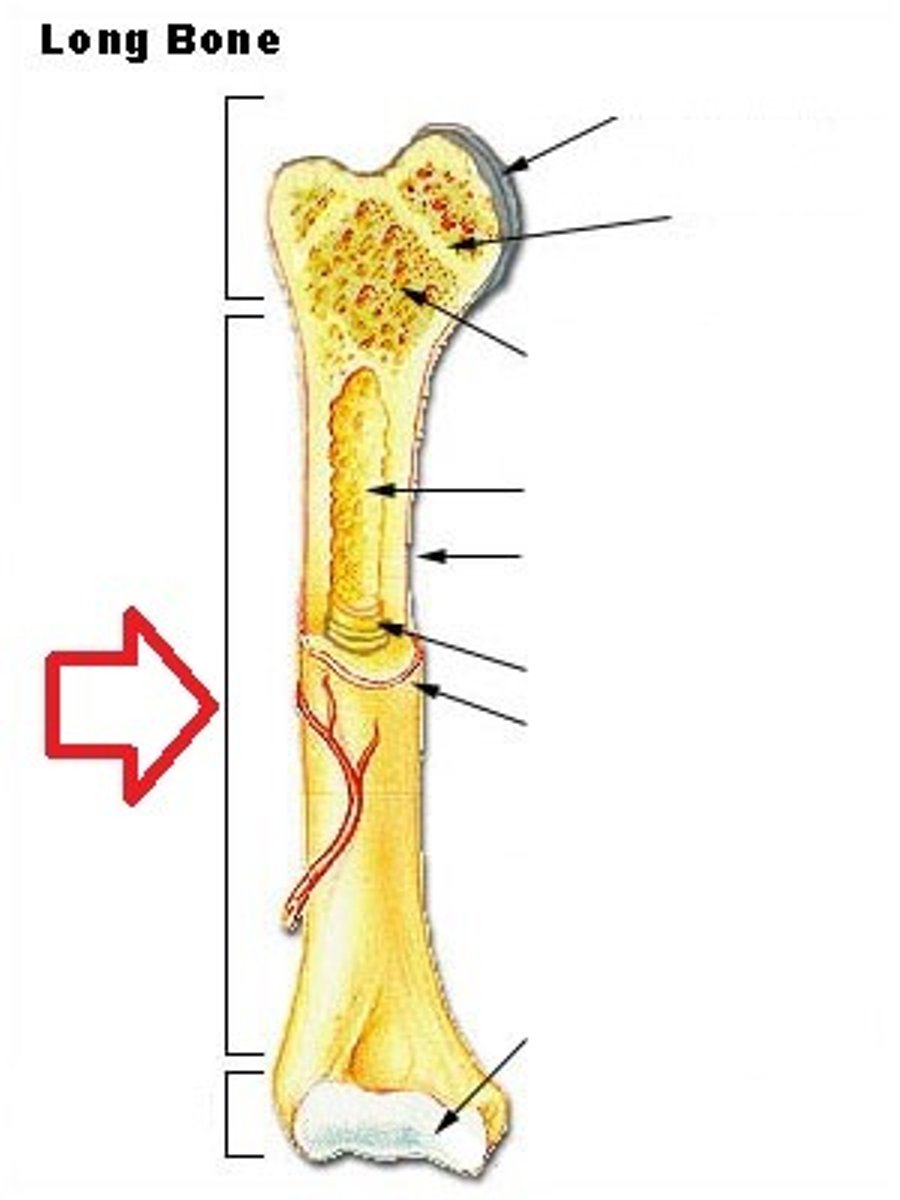
Proximal Epiphysis
Identify
Distal epiphysis
Identify
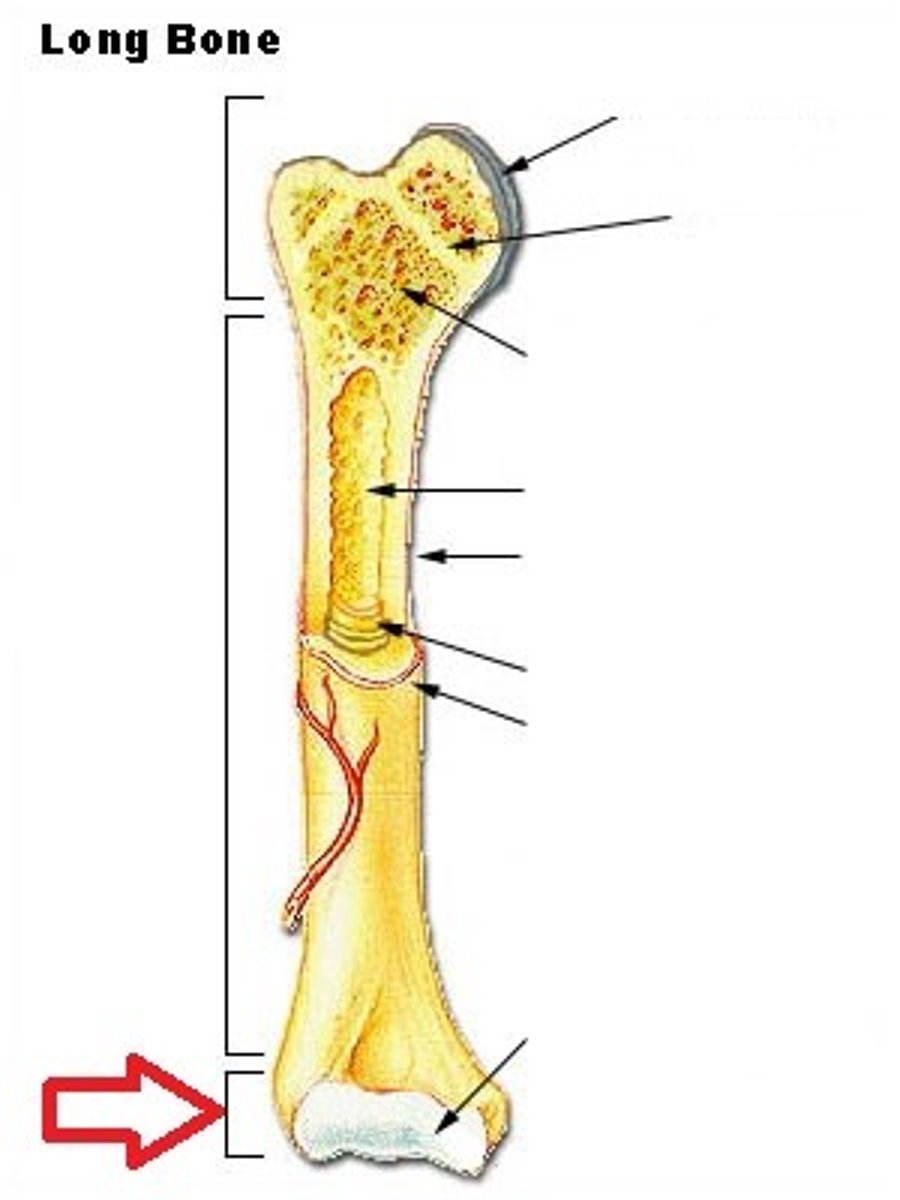
Medullary cavity or marrow cavity
What does the Diaphysis contain?
Red (hemopoietic) bone marrow
What kind of bone marrow do infants have?
Red bone marrow is gradually replaced by yellow (fatty) bone marrow
What does red (hemopoietic) bone marrow get replaced with as time passes?
A growth plate in the epiphysis
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Hyaline cartilage
What is the epiphyseal plate mate of?
Articular cartilage
What is covering the epiphysis?
Hyaline cartilage
What is articular cartilage made of?
Periosteum
identify letter E
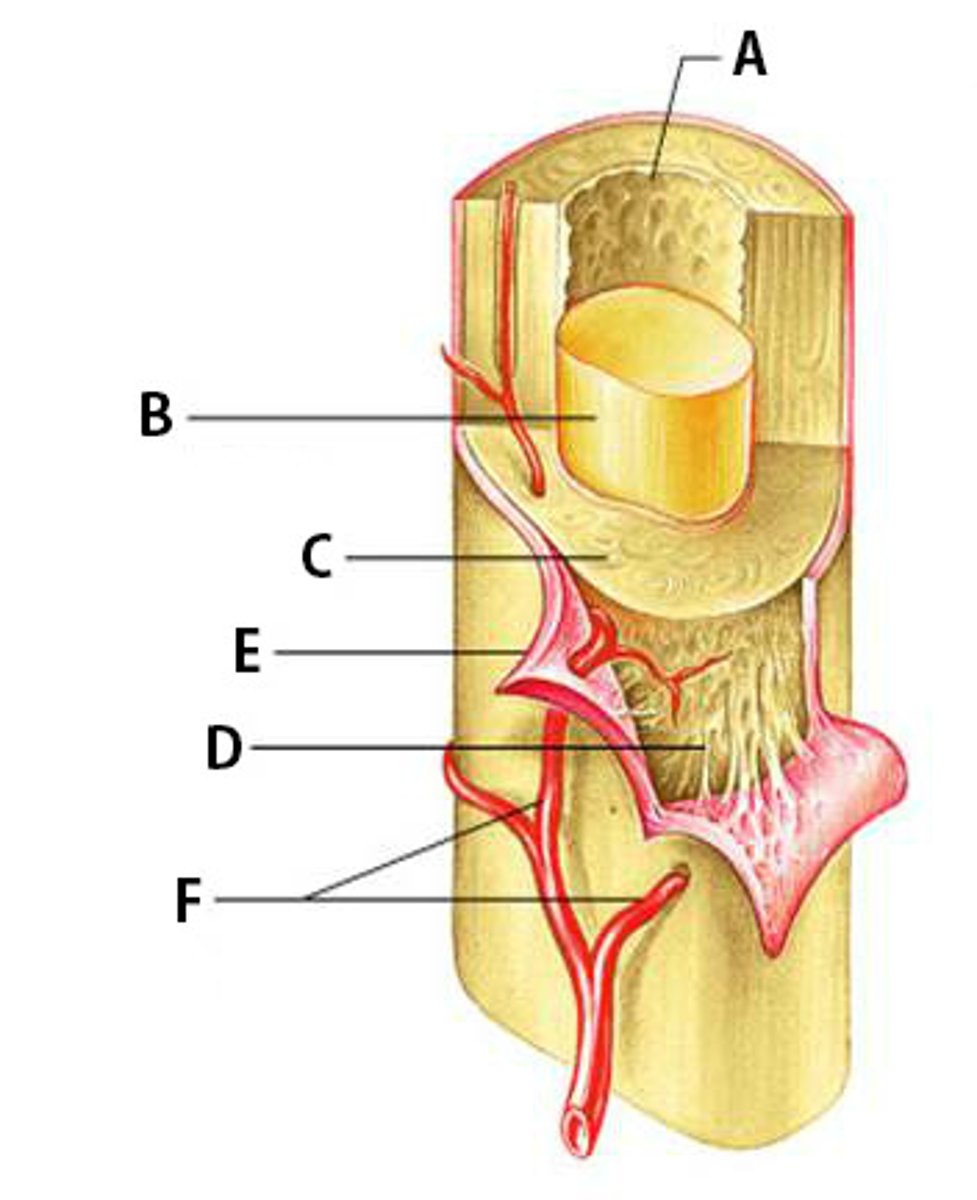
Fibrous layer (outer layer) and Osteogenic layer (inner layer)
What are the two layers that make up the periosteum?
Osteoblasts and osteoclasts
What two cells are in the osteogenic layer (Inner layer) of the periosteum?
Bone forming (building bone)
What do osteoblasts do?
Bone resorption (teardown bone)
What do osteoclasts do?
Dense irregular connective tissue
What tissue makes up the fibrous layer (outer layer) of the periosteum?
Nerves and blood vessels
What does the periosteum have a large supply of?
Sharpey's fibers
What anchors the periosteum to the bone?
Finasteride
What is used to help treat male pattern baldness?
By secreting collagen and other organic components for bone synthesis
How do Osteoblasts form bone?
Mature bone cell
What is an osteocyte?
In the lacunae which are connected to one another by canaliculi
Where are osteocytes located?