Alkylating and Metallating Agents (Parang)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Name a key nucleophilic group found on DNA bases
N^7 of guanine
Explain why toxic ADRs occur w/ alkylating agents
They can alkylate proteins
Describe the bond formed from DNA cross-linking agents
irreversible alkylation
Describe how an alkylated guanine can result in miscoding
it prefers enol tautomer rather than keto tautomer → will interact with thymine instead of cytosine
At physiological pH, nitrogen mustards & aziridine-mediated alkylators are ionized or unionized?
Unionized
If nitrogen mustards & aziridine-mediated alkylators are unionized at physiologic pH, how do they eventually become charged?
The unionized amine allows formation of highly electrophilic aziridinium ion —> very reactive against DNA
Name the drug class that forms an aziridinium ion to target DNA
nitrogen mustards
What structural difference determines the types of characteristics a nitrogen mustard has?
if the third group (R) attached to the amino nitrogen is alipathic or aromatic
alipathic vs aromatic nitrogen mustards: which reacts faster?
alipathic
Name the only allopathic nitrogen mustards available on the US market using IV administration
Mechlorethamine
What agent is used to inactivate mechlorethamine ?
2% Sodium thiosulfate (creates inactive and water-soluble thiosulfate ester that can be washed away)
Name the most commonly used alkylating agent
Cyclophosphamide
explain why cyclophosphamide has lower toxicity compared to other alkylating agents
It is a non-toxic prodrug that is not activated until the liver, which reduces GI toxicity and nonspecific toxicity
What does cyclophosphamide produce ? And what is the resulting toxicity?
Acrolein which is associated with bladder toxicity (hemorrhagic cystitis)
Name the agent that can be used to reduce acrolein accumulation in the bladder
Mesna
Explain why aromatic nitogen mustards have a slower reaction rate and the resulting fx
the aromatic nitrogen substituent stabilizes the lone pair through resonance → allows drug to be taken via oral administration & attenuates the ADRs
Alipathic vs aromatic nitrogen mustard: which has fewer ADRs? why?
aromatic d/t increased stability from resonance
Alipathic vs aromatic nitrogen mustard: which can be admin oral?
aromatic nitrogen mustards
Which aromatic mustard is less reactive and has less toxicity
Chlroambucil
Which aromatic mustard mimics phenylalanine?
Melphalan
Which aromatic mustard contains a uracil ring (mimics nucleic acid base) ?
Uracil mustard
Which aromatic mustard is transported into cells via transport protein?
Melphalan
name the nitrogen mustard that is a tertiary aziridine and the resulting fx of this structural difference
thiotepa ; makes it less reactive
Explain the cause of ADRs from nitrosoureas
Produces isocyanate which acts as a carbamoylating agent that reacts with lysine residues, leading to alterations in protein function
Name a nitrosourea example that can be admin orally
lomustine
MOA of DNA methylators
O6 methylation of guanine nucleotides, which pair preferentially with thymine → triggers cell death
Which class of alkyating agent works by producing another alkyating agent?
nitrosoureas
nitrosoureas cause ____ crosslinking
interstrand
which DNA methylator is a prodrug?
dacarbazine
name the two drugs that are DNA methylators
procarbazine and dacarbazine
Which drug class works via production of a methyl radical that is highly reactive?
DNA methylators
dacarbazine is decomposed to form what?
methyldiazonium ion
Name the most toxic anticancer drug that is also a prodrug?
mitomycin C
name the drug that is classified as an alkyl sulfonate
busulfan
Which organoplatinium drug is a prodrug?
cisplatin
What has to happen to organoplatnium complexes prior to interacting with DNA? Why does this happen?
the electron donating ligand (Cl) has to be displaced via nucleophilic attack by water - this happens because water is a better leaving group than Cl, which will optimize the reaction
in which cells is cisplatin activated in?
cells with low chloride ion concentration
concerns with cisplatin
highly nephrotoxic
Which agent is used to mitigate the nephrotoxicity caused by cisplatin?
amifostine
Name a cytoprotective agent that is a prodrug and what toxicity it mitigates
amifostine - mitigates the nephrotoxicity linked to cisplatin
Name the advantage of carboplatin over cisplatin
has no renal toxicity
explain why carboplatin is less potent than cisplatin
forms the same cytotoxic hydrated intermediate but at a much slower rate
Which cisplatin analogue loses a oxalate in vivo to form DACH platinium analogs
oxaliplatin
Which cisplatin analog is derrived from picoline ring (2-methylpyridine) associated w/ platinium atom ?
picoplatin
Which cisplatin analogue has the least ADRs?
carboplatin
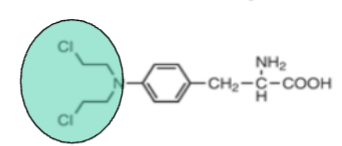
Based off the functional group (green), what is the drug class?
nitrogen mustards and aziridine-mediated alkylators
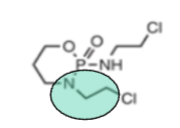
Based off the functional group (green), what is the drug class?
nitrogen mustards and aziridine-mediated alkylators
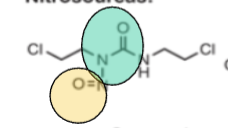
Based off the functional group (green + yellow ), what is the drug class?
nitrosoureas
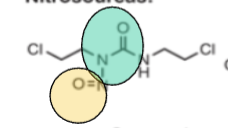
Name the FG in green
urea
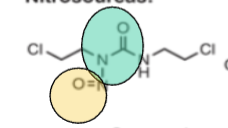
Name the FG in yellow
urea
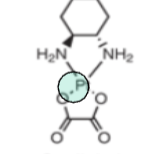
Based off the functional group (green), what is the drug class?
organoplatinium complexes
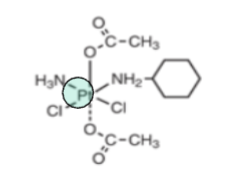
Based off the functional group (green), what is the drug class?
organoplatinium complexes
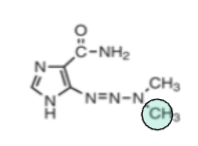
Based off the functional group (green), what is the drug class?
DNA methylators