Ultrasound Physics Chapter 4: Understanding Pulsed Waves and Duty Factor
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is pulsed sound?
. a collection of cycles that travel together,
.a pulse must have a beginning and an end.
what are the 2 components of pulsed ultrasound?
.Transmit, talking, or on time
.Receive, listening, or off time
What is Pulse Duration (PD)?
.the actual time from the start of a pulse to the end of that pulse
. a single transmit, talking, "on" time
Pulse Duration (PD) is reported in units of
time
ex. microseconds (us)
The typical value of pulse duration in diagnostic ultrasound is...
0.3 to 2.0 us (microseconds, or millionths of a second)
What is pulse duration determined by?
Sound source only
Can a sonographer alter pulse duration?
No, it is not adjustable
What is pulse duration (us) equal to?
the number of cycles in each pulse, multiplied by the period (us) of each cycle
How is pulse duration related to the number of cycles in each period?
its directly proportional
How is pulse duration related to period?
directly proportional
How is pulse duration related to frequency?
inversely proportional
What equation is used for pulse duration, frequency and # of cycles?
pulse duration (us) = #cycles/ frequency (MHz)
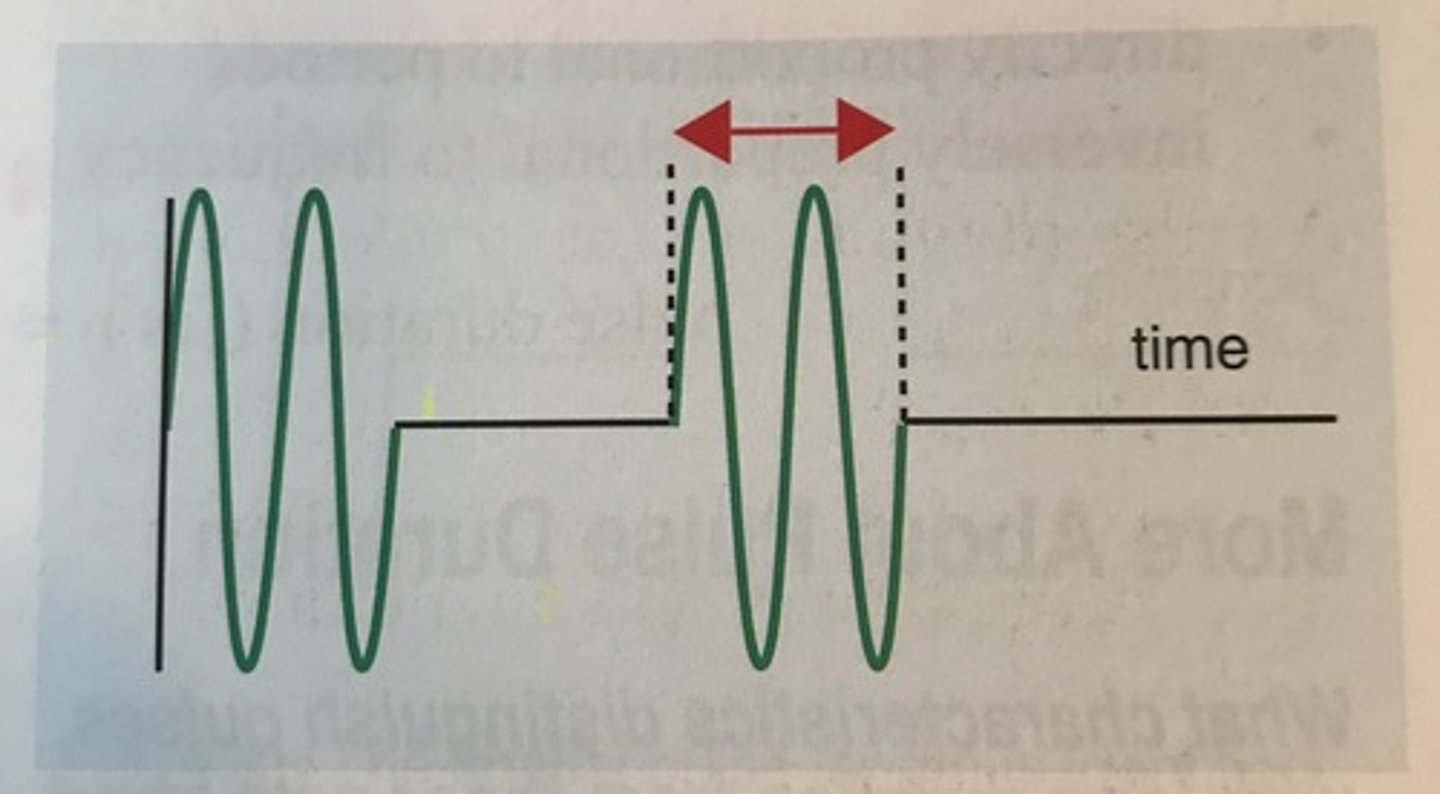
The following 2 characteristics describes:
. many cycles in the pulse, or
. individual cycles with long periods
pulses of long duration
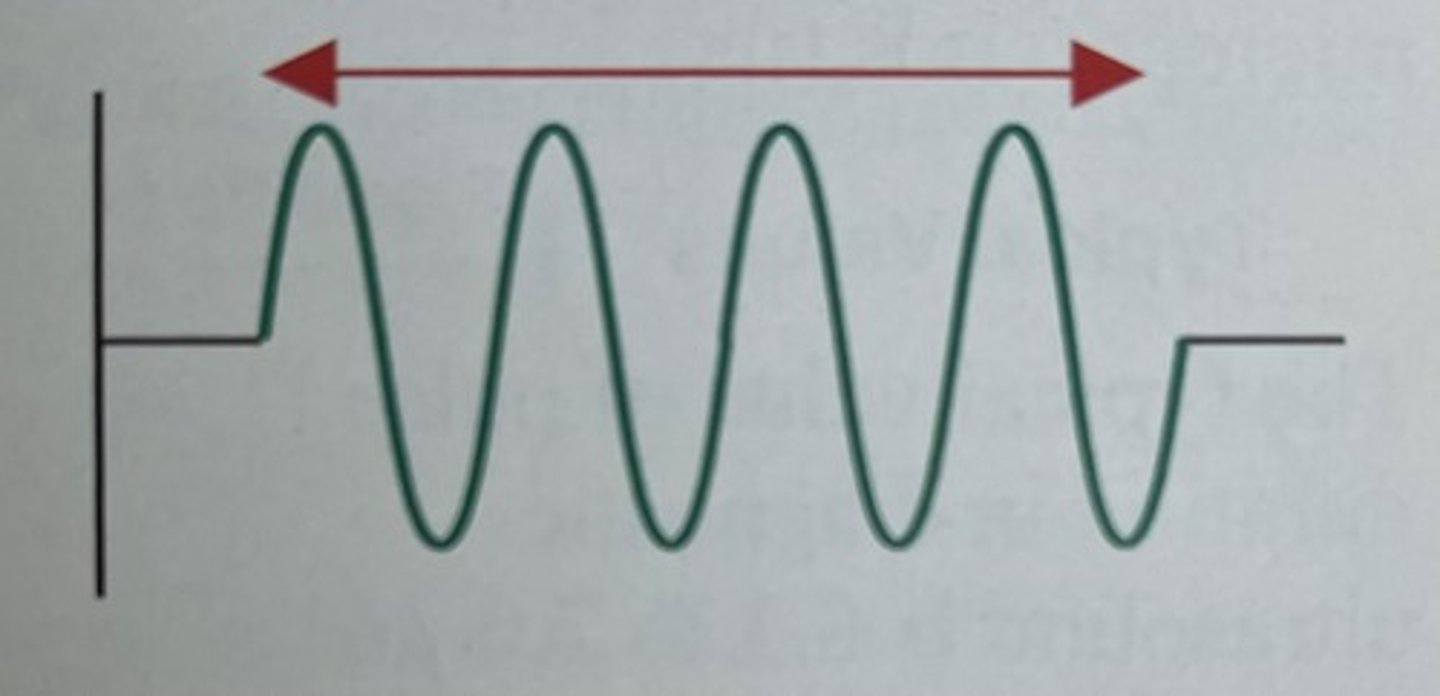
The following 2 characteristics describes:
. few cycles in the pulse, or
. individual cycles with short periods
pulses of short duration
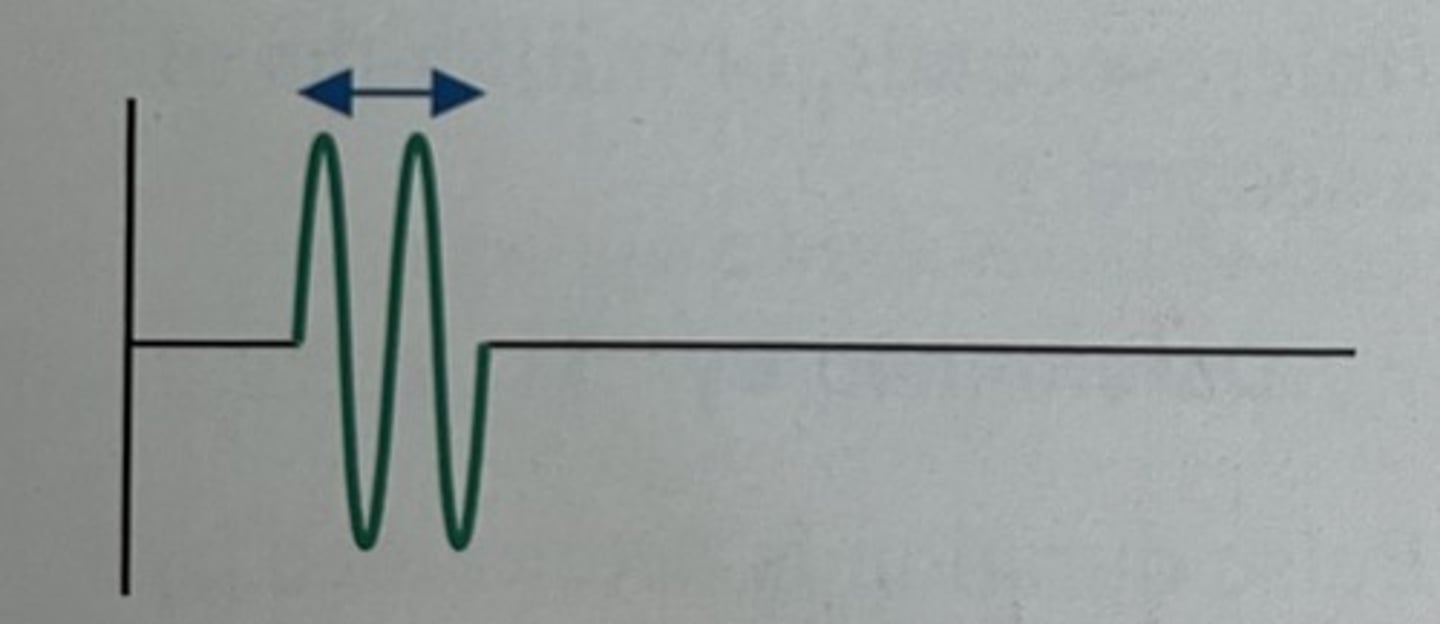
What types of pulses are more desirable in diagnostic imaging?
short duration pulses, they create images of greater accuracy
What is Spatial Pulse Length (SPL)?
the distance that a pulse occupies in space from the start to the end of a pulse
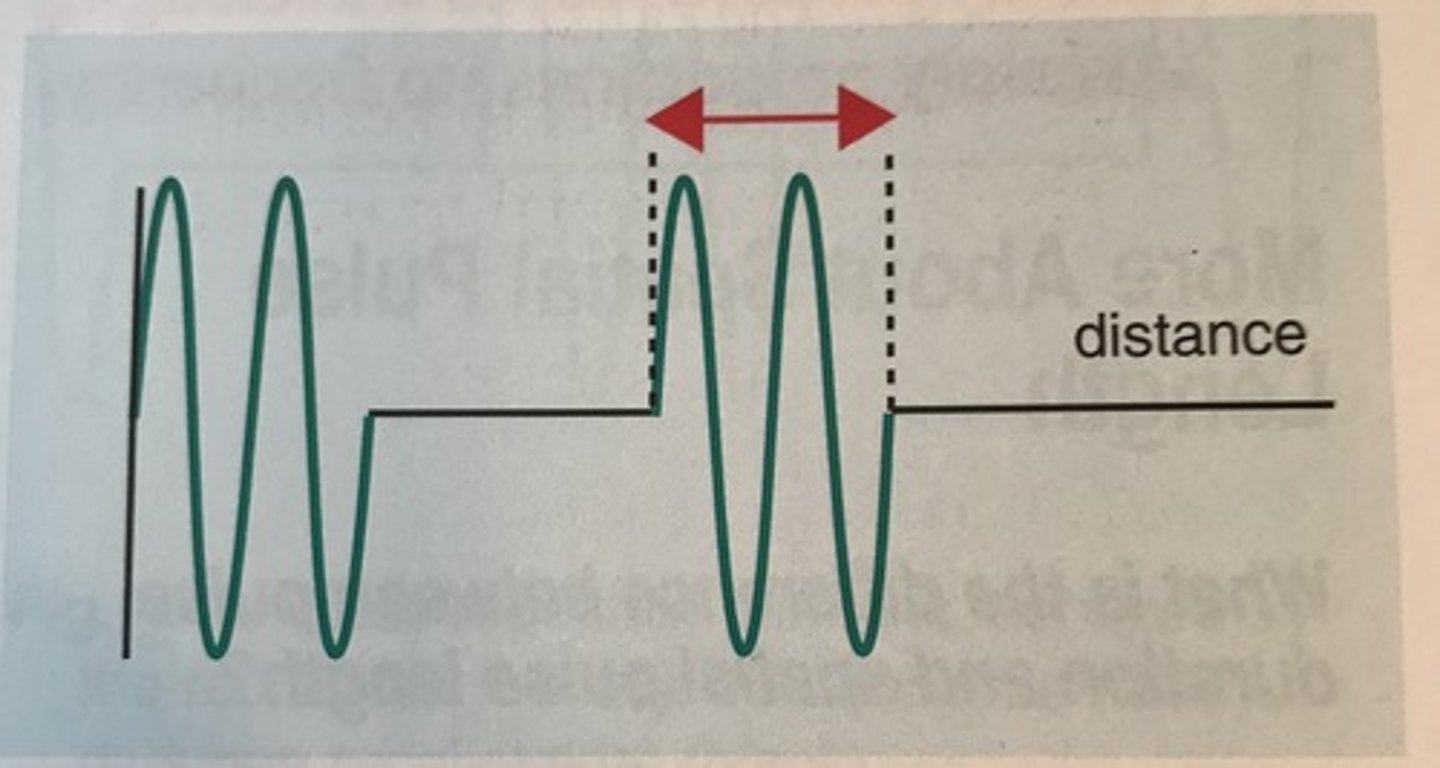
What units does Spatial Pulse Length (SPL) have?
Units of distance
ex. mm
Spatial pulse length in soft to ranges from...
0.1 to 1.0 mm
Just like wavelength, pulse length is determined by....
both the source and the medium
Can a sonographer alter pulse length?
No
What equation is used for spl, cycles and wavelength?
Spatial pulse length (mm) = # cycles x wavelength
SPL is ___________ the number of cycles in the pulse
directly proportional to
What is the relationship between SPL and wavelength?
they are directly propotional
SPL is ____________ proportional to frequency
inversely
The following describes:
. many cycles in the pulse
. cycles with longer wavelengths
Pulses with long pulse length
The following describes:
. fewer cycles in the pulse
. cycles with shorter wavelengths
Pulses with short pulse length
Which type of pulse length is more desirable in diagnostic imaging?
Pulses of short pulse length, more accurate images
The following describes:
. the time from the start of one pulse to the start of the next pulse
. includes one pulse duration("on" time) plus one listening time?
Pulse Repetition Period (PRP)
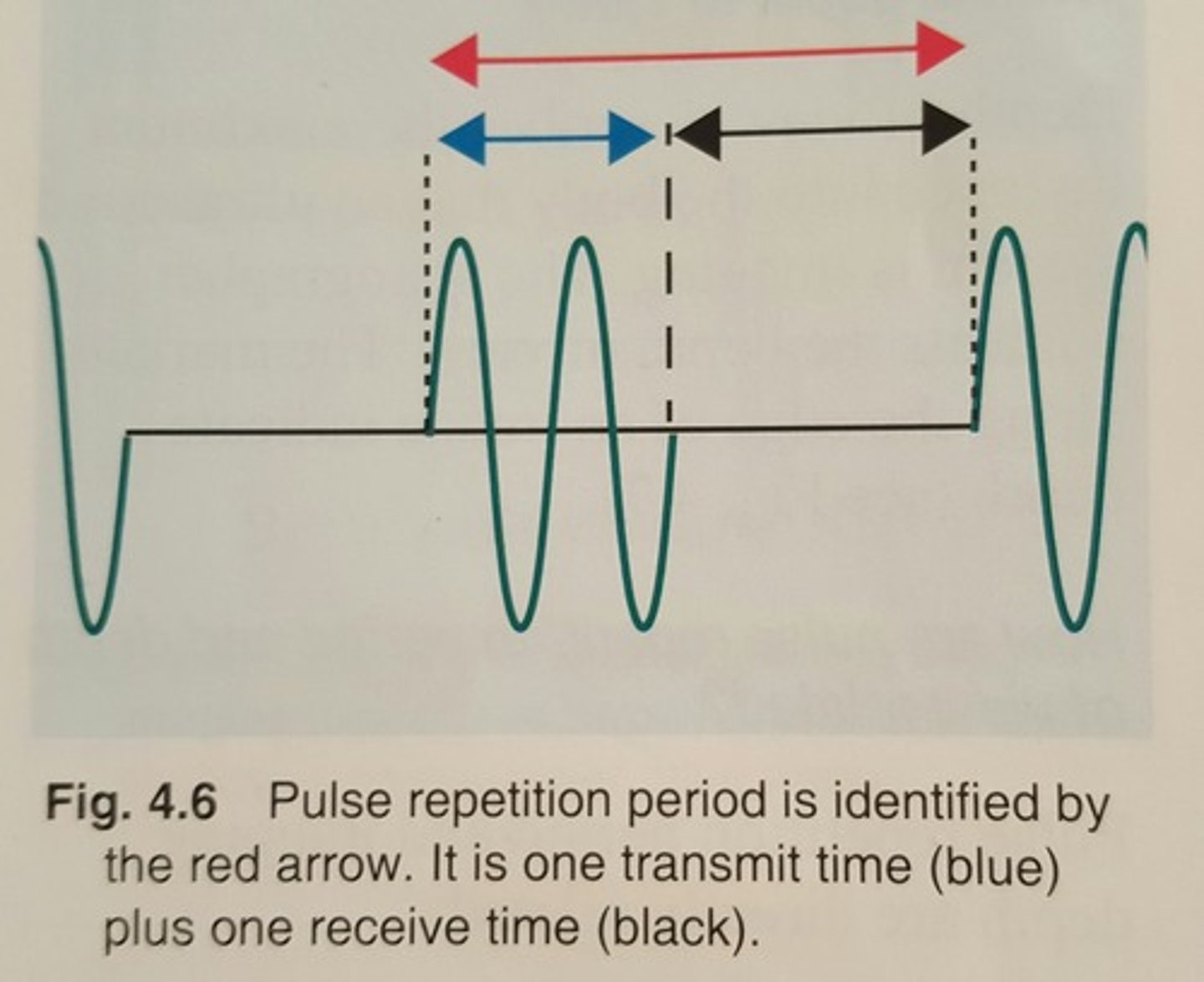
Pulse repetition is reported in units of....
time
ex. ms
The typical value of pulse repetition period is
100 microseconds (us) to 1 millisecond (ms)
PRP is generally about how many times longer than pulse duration?
100 to 1,000 times
Pulse repetition period is determined by....
. the sound source only, not the medium
. the imaging depth the sonographer selects
Can the sonographer change the PRP?
yes, by changing depth
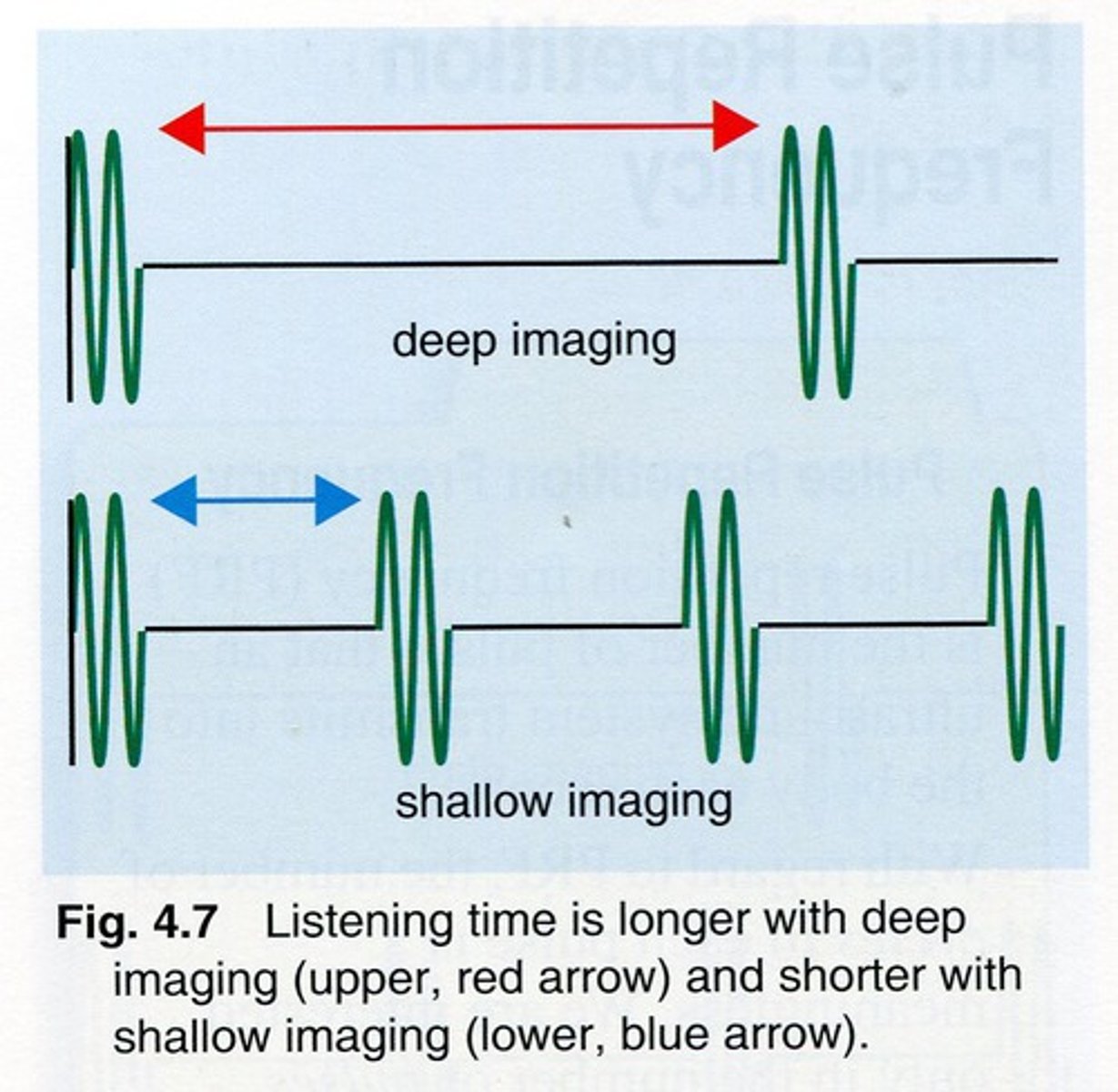
When imaging is at shallow depth the time from one pulse to the next is _________.
short
When the system is imaging more deeply, the time from one pulse to the next is _________.
longer
what is depth of view?
maximum distance into the body that an ultrasound system is imaging
How are PRP and depth of view related?
Directly - as depth of view increases pulse repetition period increases.
. Dov decreases = prp decreases
What are the 2 components of pulse repetition period?
. the transmit time or on time
. the receive time or off time
Which of the 2 components of PRP can the sonographer change?
The receive/listening time of the pulse
. deeper imaging = longer prp and listening time
. shallower imaging = shorter listening time and prp
The following describes:
. the number of pulses that an ultrasound system transmits into the body each second
. the # of cycles in each pulse is meaningless, only interested in pulses each second
Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF)
Pulse repetition frequency is reported in units of.....
Hz (hertz), or per second
What are the typical values of PRF
. 1,000 - 10,000 Hz (1-10kHz)
. or 1 to 10 thousand pulses per second
Pulse repetition frequency is determined by.....
. the sound source only
. the max imaging depth of the system
Can PRF be changed by the sonographer?
yes, with depth of view
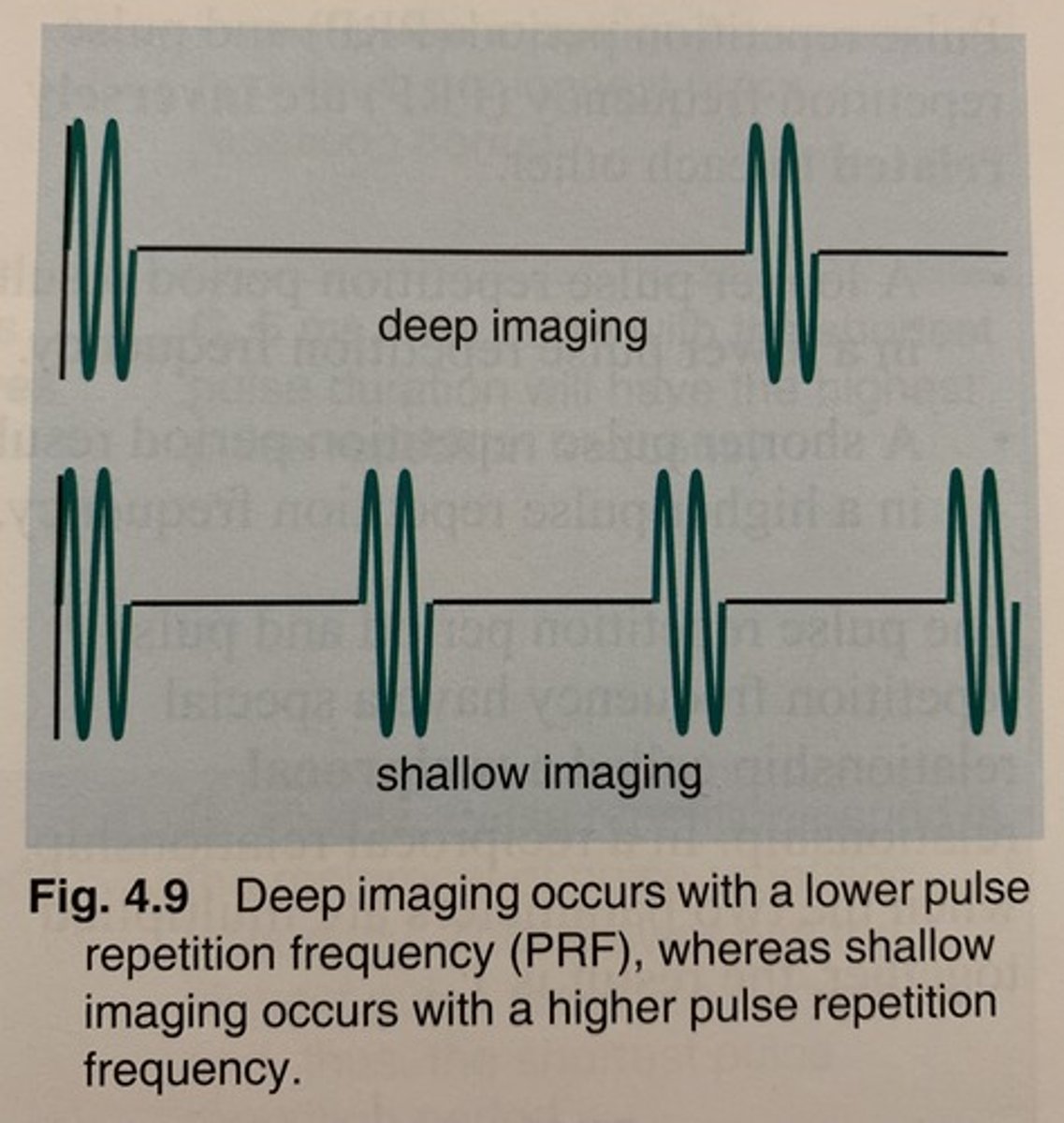
When the system is imaging shallow, the pulse repetition frequency is_______.
higher
When the system is imaging deep, the pulse repetition frequency is _______.
lower
How are PRF and depth of view related?
Inversely related (as depth of view increases, PRF decreases)
How are PRP and PRF related?
inversely related
. A longer PRP results in a lower PRF
. A shorter PRP results in a higher PRF
What type of relationship do PRP and PRF have?
.reciprocal relationship (when multiplied they = 1)
complementary units
> seconds (PRP) and hertz (PRF)
> milliseconds (PRP) and kilohertz (PRF)
What is Duty Factor (DF)?
the percent of time the machine is doing work, PD/PRP
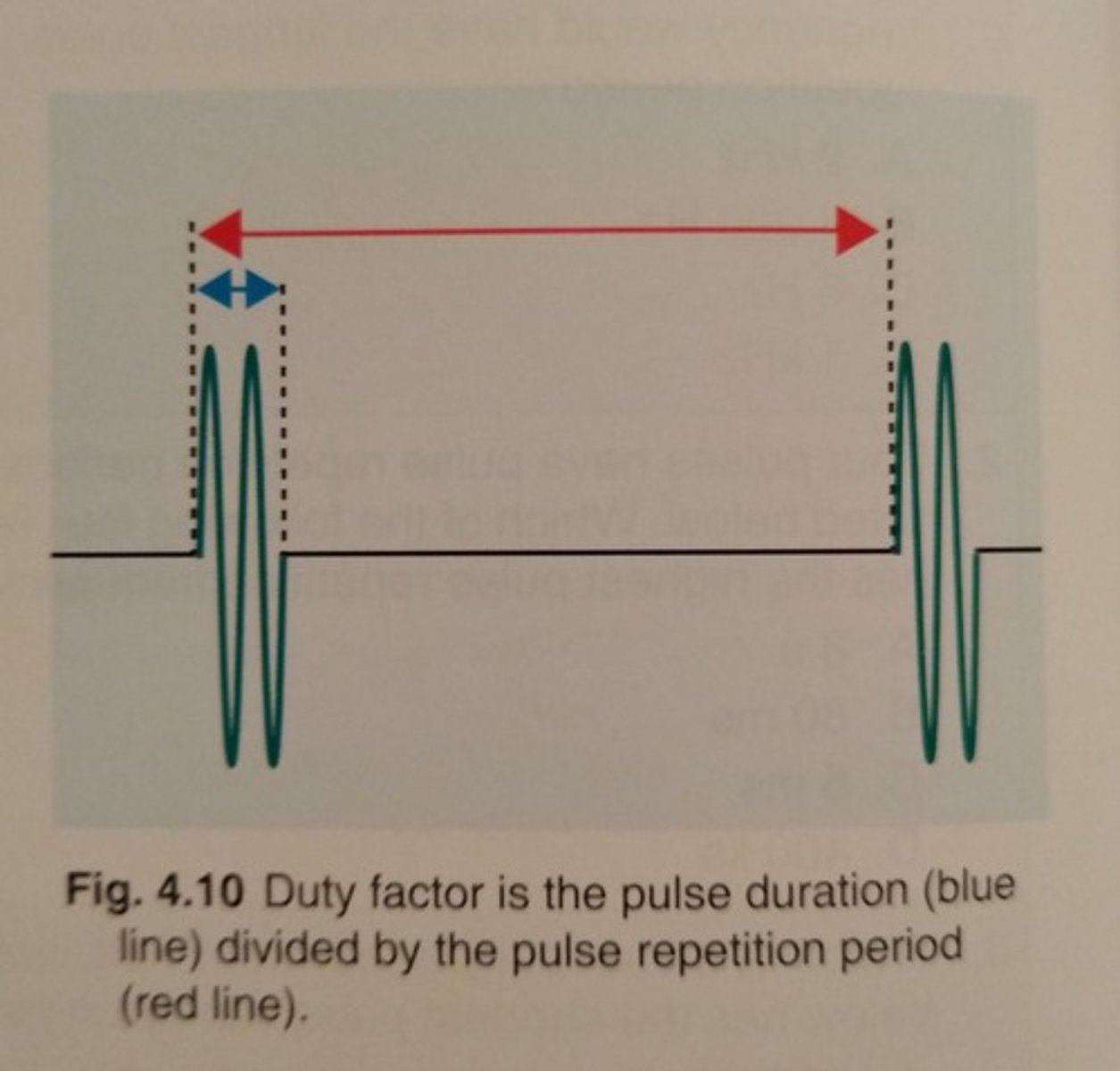
What are the units duty factor is reported in?
None
.DF is a percentage, therefore dimensionless
duty factor ranges from
. 0.2% to 0.5% or 0.002 - 0.005
When creating anatomic images duty factors are in the range of _____ indicating that ultrasound systems spend a very small percentage of time _____ and a very large percentage of time (98.8%) ______.
0.2%, transmitting, receiving
What is the duty factor for a continuous wave?
. 1.0 or 100%
. because the system is always transmitting; always on
What is duty factor determined by?
Sound source only
is duty factor adjustable by sonographer?
yes, by changing the depth of view
Duty factor is _____ related to imaging depth.
inversely.
>High duty factor at shallow depths, low duty factor with deeper depths
How can DF be represented mathematically?
DF (%) = pulse duration divided by PRP > x 100
The following describes:
. 1 or 100%
. this value is only achieved w/ continuous wave
. continuous wave can't create anatomic images; therefore DF for imaging systems must always be less than 100%
The maximum value for duty factor
The following describes:
. 0%, which only exist when the transducer is silent
. with anatomic imaging a typical value for DF is 0.2%, which means the system is listening approximately 500 times longer than it is transmitting
Minimum value of DF
The following are characteristics of:
. Less listening
. Shorter PRP
. Higher PRF
. Higher DF
Shallow Imaging
The following are characteristics of:
. More listening
. Longer PRP
. Lower PRF
. lower DF
Deep Imaging