IB Biology: Topic 2: Genetics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
ABO Bloods types
- Multiple Alleles
- Based of different sugars present on the surface of the cell
- Universal Blood Donor = O
- Universal Blood Receiver = AB
- IB i and IA i = shows dominance of one type of sugar present
ABO Bloods types: A
- A = IA IA, IA i
- One sugar present
ABO Bloods types: B
- B = IB IB, IB i
- Different sugar than A present
ABO Bloods types: AB
- AB = IA IB
- Codominance
- Both sugars present
Chi-squared

Discrete Variation
Separate categories with no intermediates; trait is influenced by one gene
Continuous Variation
The range of types possible with no distinct categories; can be influenced by environment
Genes
- A sequence of DNA
- Heritable factors that can be passed on
- Influences specific traits
- Occupies a specific position on a chromosome
- DNA= genetic blueprint
- Codes for a specific trait
- Traits may be influenced by multiple genes
- Loci/locus: the location of a gene on a chromosome
Alleles
- Alternative forms of a gene
- Codes for different variations of a trait; eye colour, hair colour
Gene Mutations
- A change in the nucleotide sequence of a section of DNA
- New alleles are formed by mutations
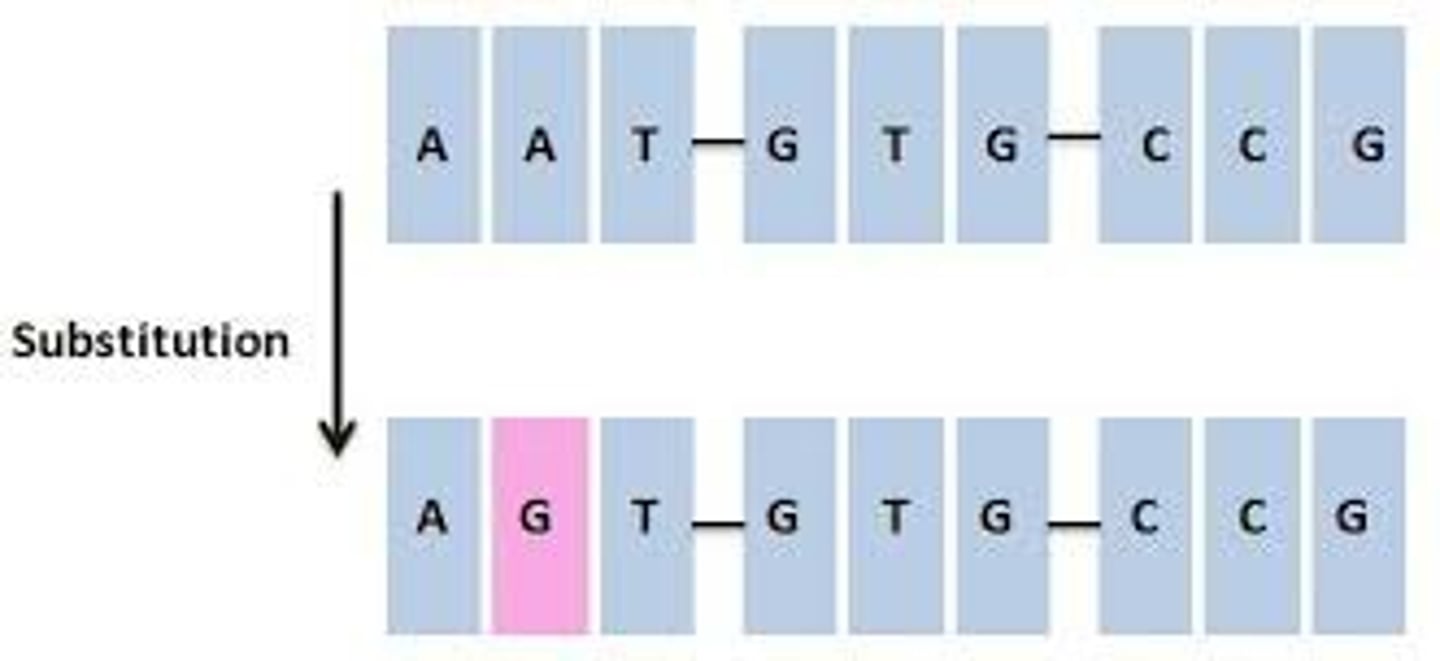
Gene Mutations: Substitution
- One base in the sequence is replaced by a different base
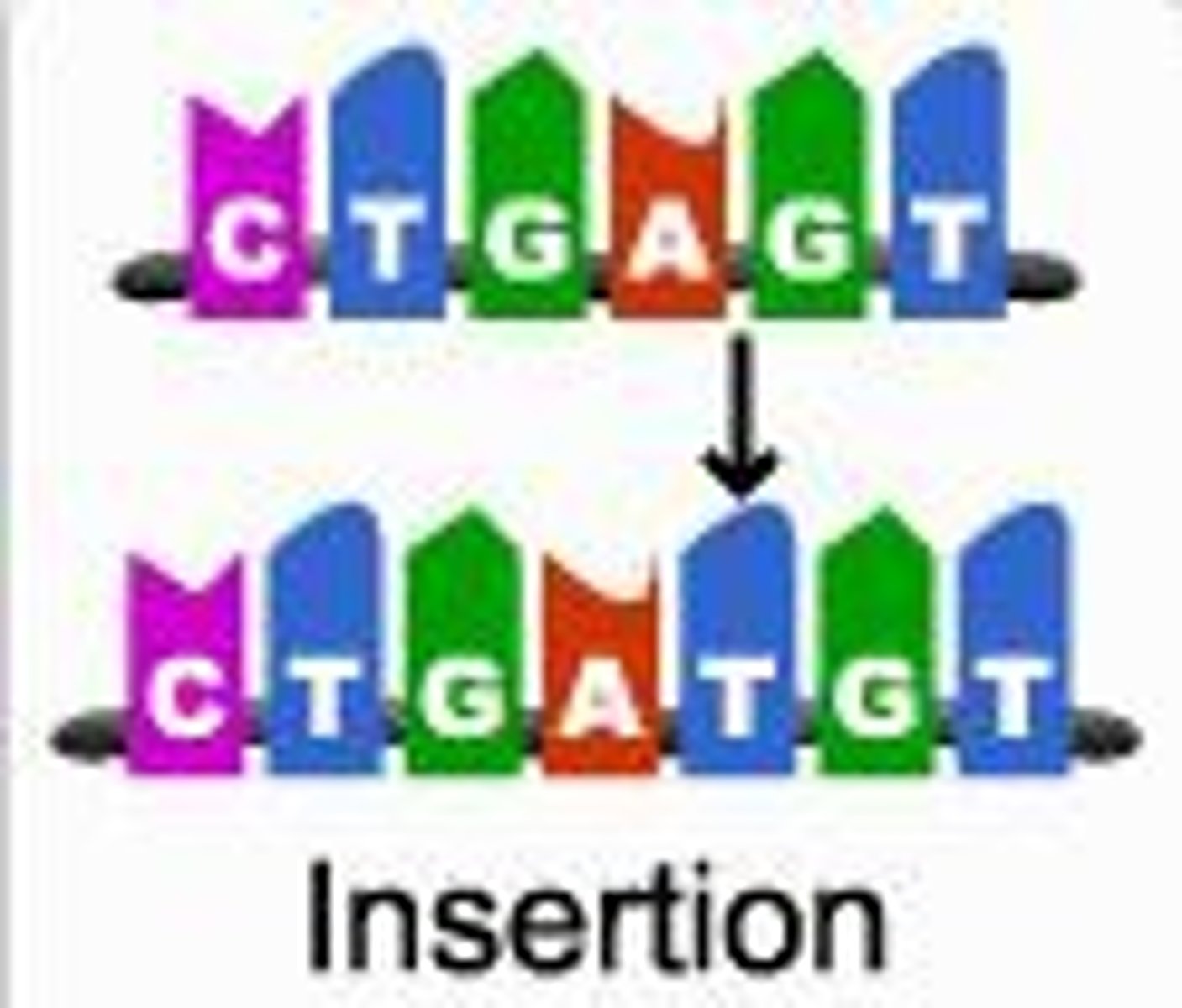
Gene Mutations: Insertion
- A nucleotide is inserted into the base sequence
Gene Mutations: Deletion
- A nucleotide is removed from the base sequence

Codons
- Three base words in creating proteins
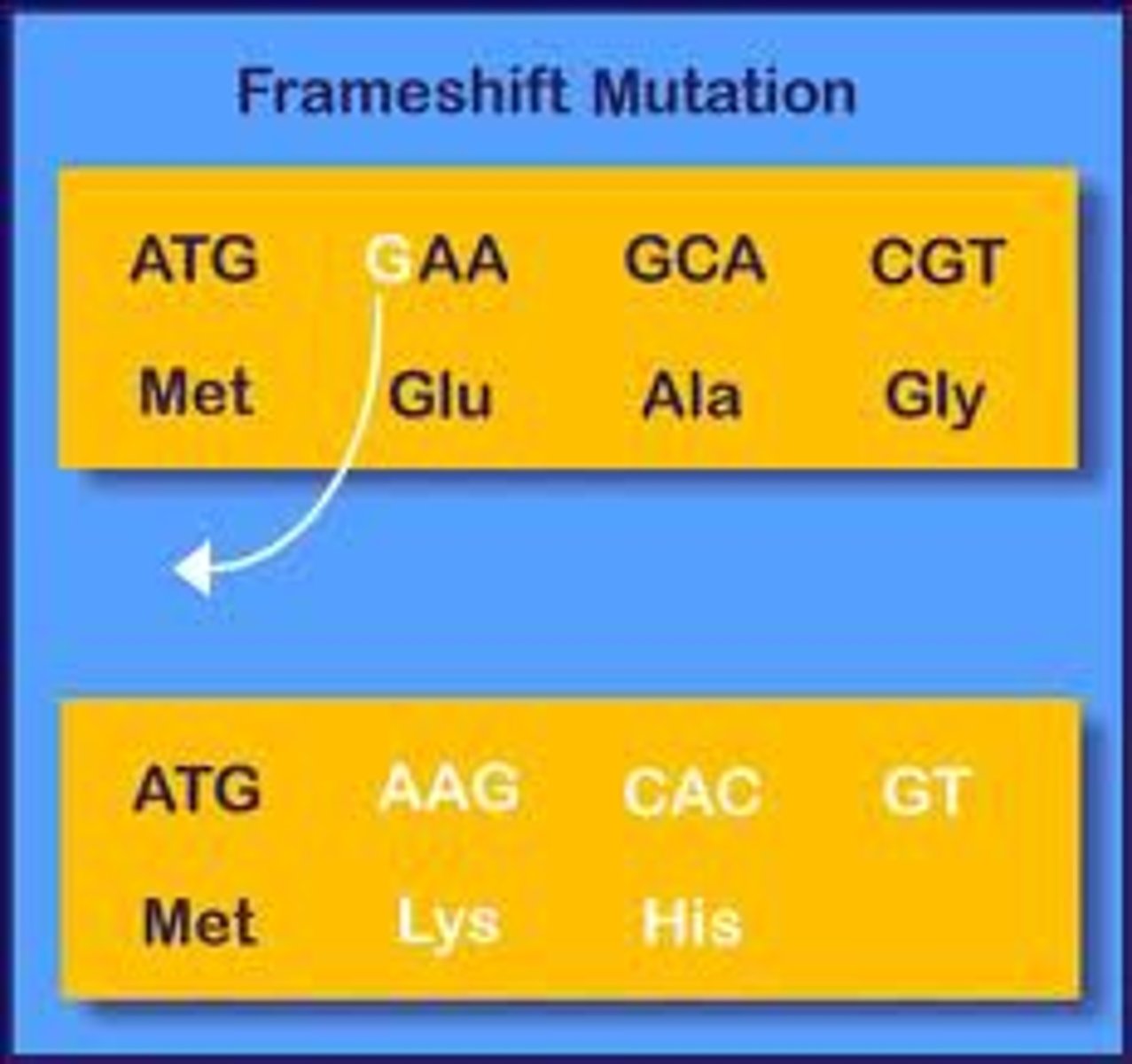
Gene Mutations: Frameshift
- A change occurs in every codon after the mutation
- Occurs in Insertion and Deletion
Consequences of Base Substitutions
Missense Mutations
- Beneficial mutation
- Changes the gene sequence to create new variations of a trait
Nonsense Mutations
- Detrimental mutation
- Shortens the gene sequence to avaid the normal shape
Silent Mutation
- Neutral mutation
- No effect
Sickle Cell Anemia
- A base substitution mutation
- Change in base sequence of mRNA transcribed from it
- Change in the base sequence of poly peptides in hemoglobin
- Single base was changed in the gene sequence
- Insoluble hemoglobin cannot process oxygen effectively
- More susceptible to illnesses
- May cause blood clotting in arteries
- Cells are destroyed more rapidly
- Low red blood count
- Heterozygous state provides protection against malaria
Genomes
- The entire set of DNA instruction found in a cell
Linked Genes
- Genes located close together on the same chromosome
Linked Genes: Autosomal Gene Linkage
- Genes that don't assort independently
- Fall close together on the same chromosome
- Stays together since they are too close to cross over
Linked Genes: Sex-Linked Genes
- Genes controlling characteristics located on the same chromosome
- SRY: Y chromosome = sex determinations
- X= Albinism, colour blindness, hemophilia
- Inheritance pattern where ratios are different
Hemophilia
- Inability to make factor VIII clotting blood protein
- Alleles = recessive on the X-chromosome
- Males only have one copy (XY)
- Inherited from the mother
- If the mother has a copy of that alleles= male offspring= hemophilia
- Females can only be hemophiliac if the father is hemophilic
- They will also inherit the allele from the mother
- Life expectancy: 10 years
- Treatment: infusing Factor VIII purified from blood donors
Codominance
- When both alleles have an effect
- Both alleles are expressed in the phenotype
Incomplete Dominance
- Both alleles have an influence but niether is dominant = blended inheritance
Blended Inheritance
- The result of no immediate phenotype
Phenotype
- Gene mutations
- Spontaneous
- Caused by copying error during DNA replication
- Induced by exposure to external elements; Radiation/chemical
Mutagen
- Carcinogens: formation of cancer
Monogenic Traits
- Characteristics controlled by a single gene loci (location)
- Exhibits discrete variation with individuals expressing one of a number of distinct phenotypes
Polygenic Traits
- Characteristics controlled by more than two gene loci (location)
- Exhibits continuous variation with an individuals phenotype exiting somewhere along the continuous spectrum of potential phenotypes
Unlinked Genes
- Genes resided on separate chromosomes
- Independent assortment
- Chromosomes independent from each other
- Segregate independently = no effect on each other
- Occurs because chromosomes pair up and line us in metaphase 1 without concern of which chromosome is facing which pole
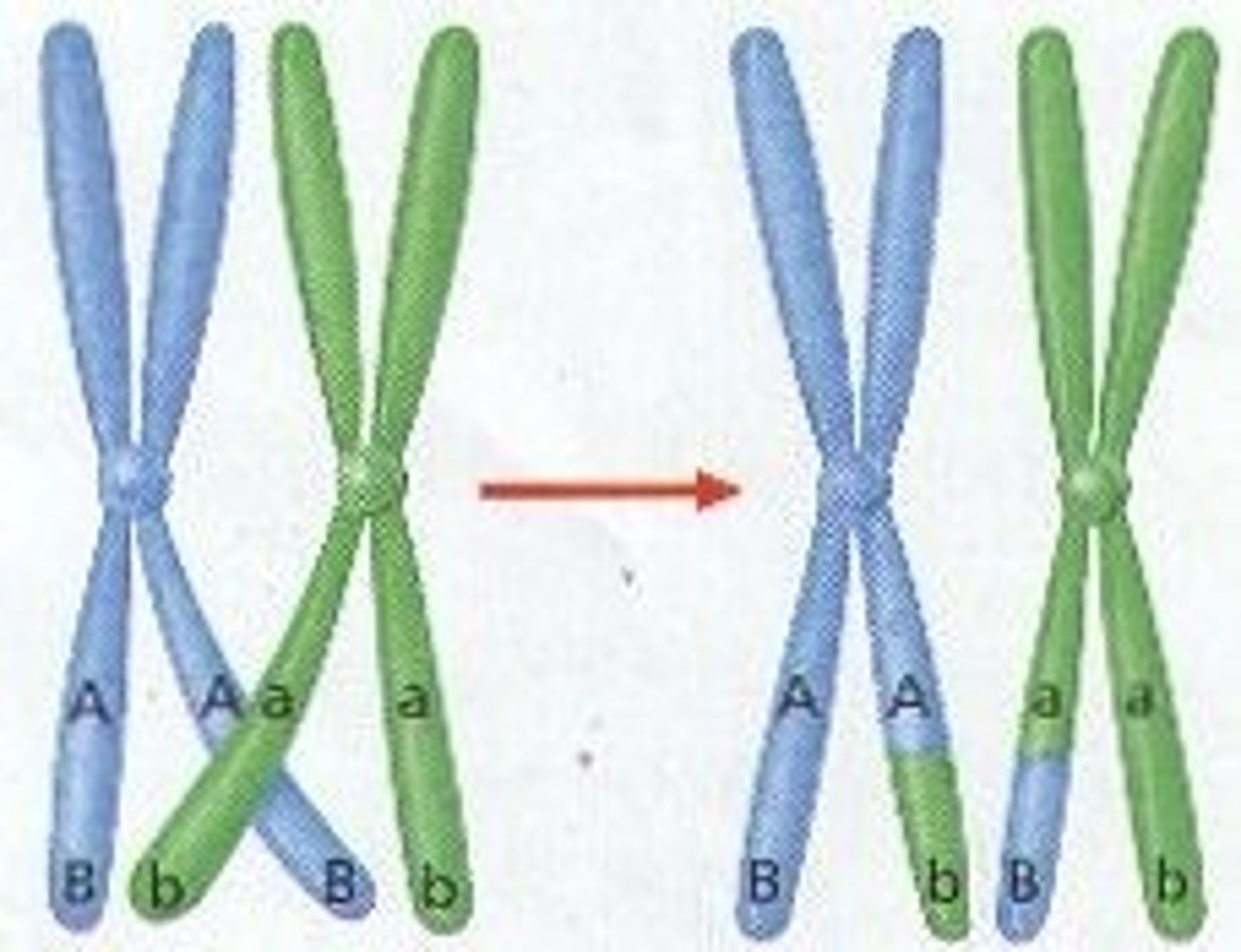
Crossing over
Punnet Square hemophilia
