CDEP MDD 5 ILLUMINATION & LIGHTING (Credits: Christabelle Abad)
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Natural light
Daylight; Achieved by using windows, skylights or light shelves; Main source of light during daytime.
artificial light
Light from electrical sources, and is man-made, can be turned on and off at a flick of a switch.
General light
also known as background lighting or ambient lighting, and a direct replacement of natural light.
Local lighting
Lighting designed to provide a relatively high level of illumination over a small area with a surrounding area of lower intensity from spill light.
task lighting
designed to illuminate work areas where strong, bright light simplifies detail work
accent lighting
Lighting used primarily to draw attention to particular points of interest. purely for aesthetics; build visual accent
highlight
to emphasize an object by illuminating with a strong light
backlight
illumination from behind
sidelight
Light coming or produced from the side.
soft light
light which has a soft edge and produces subtle shadows and tones
hard light
A type of illumination used that creates sharp, distinct, and very dark shadows
information lighting
Also known as orientation or utility lighting. Provides visual information for our safety and comfort. Information lighting often based in areas of total blackness.
indirect lighting
90% to 100% of the light output is directed towards the ceiling and upper walls of the room
semi-indirect lighting
60%-90% light is directed to the ceiling; 40%-10% downwards
direct-indirect lighting
light source that cast equal amounts up and down
semi-direct
light source that focuses of 60% to 90% of it's light downward and the rest toward the ceiling
direct lighting
lighting that shines directly toward an object
general lighting
light is distributed on all sides
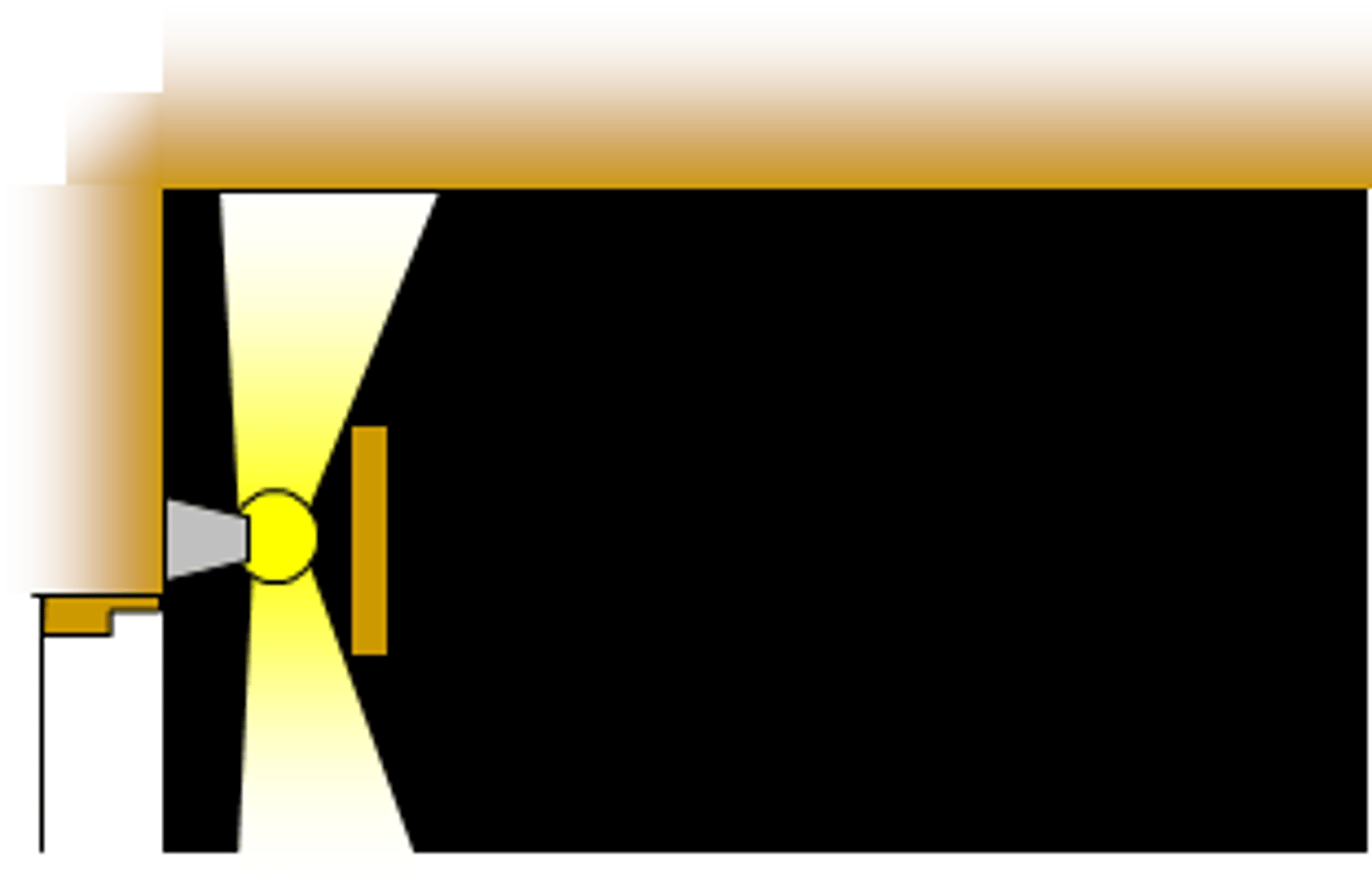
cornice lighting
A system where light sources are shielded by a panel parallel to the wall and attached to the ceiling to distribute light downwards over the wall.
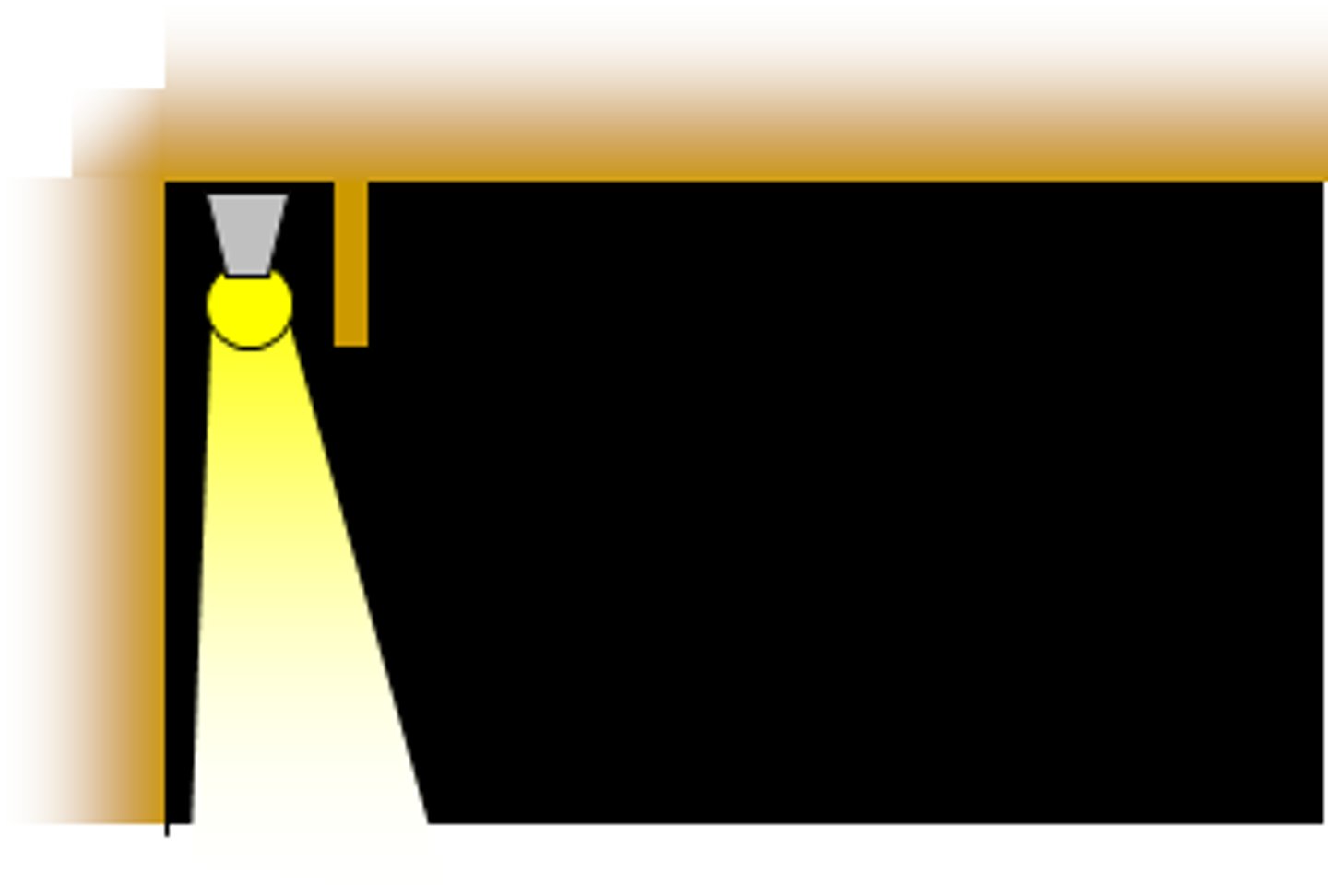
Cove lighting
A system where light sources are shielded by a ledge to distribute light upwards over the ceiling and upper wall. It is a form of indirect lighting.
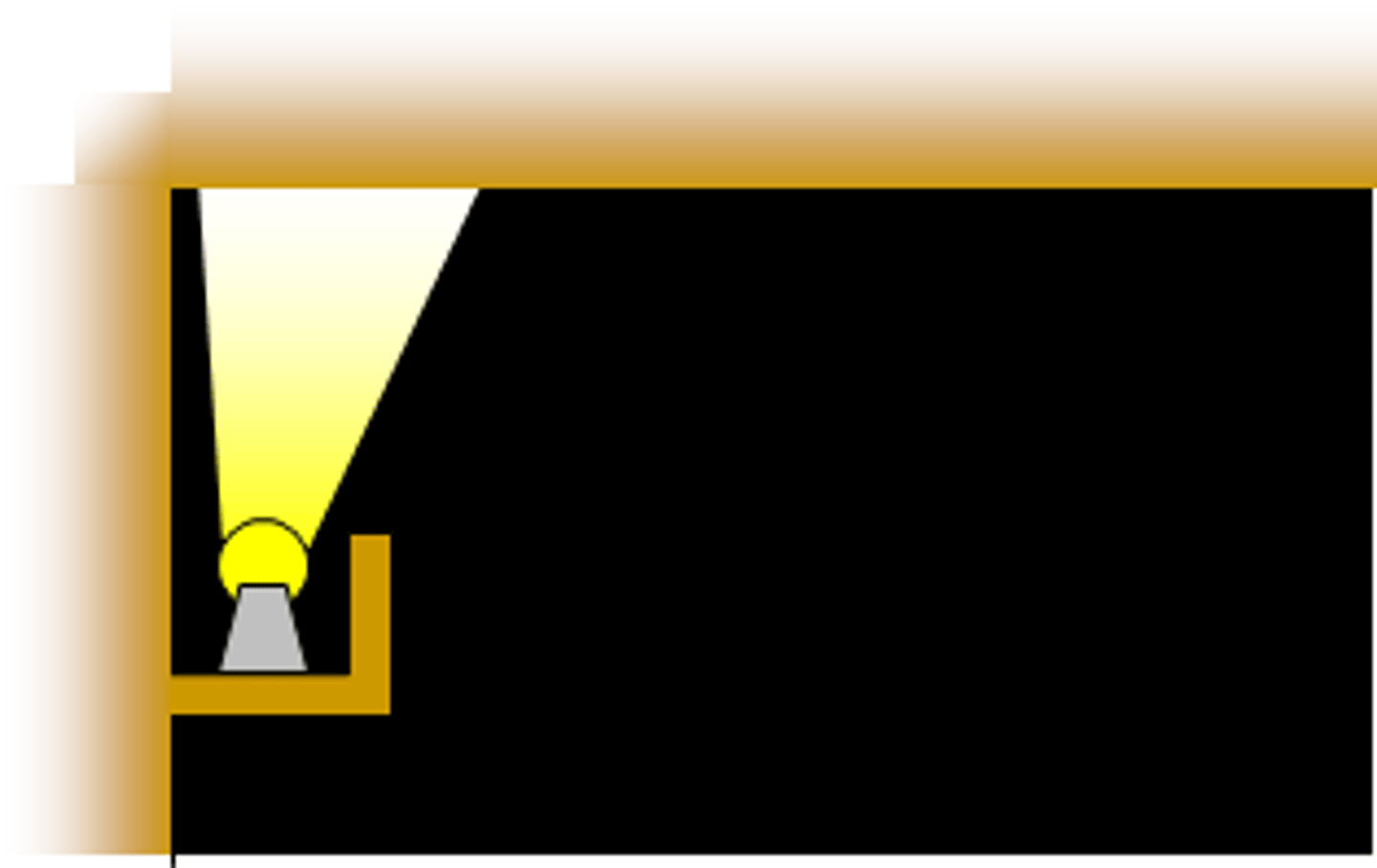
valance lighting
a system where light sources are shielded by a panel parallel to the wall usually across the top of a window. this provides light both upwards and downwards over the wall
lamp
is defined as any of various devices for producing light, either by electricity or gas; the source of light in a fixture, colloquially called a "light bulb"
incandescent lam
A lamp in which a filament inside the lamp's bulb is heated by electrical current to produce light.
filament
threadlike conductor of an electric lam that is heated to incandescence by the passage of an electric current
bulb
The glass housing of a lamp.
lamp base
a part of a bulb that connects to the lamp holder
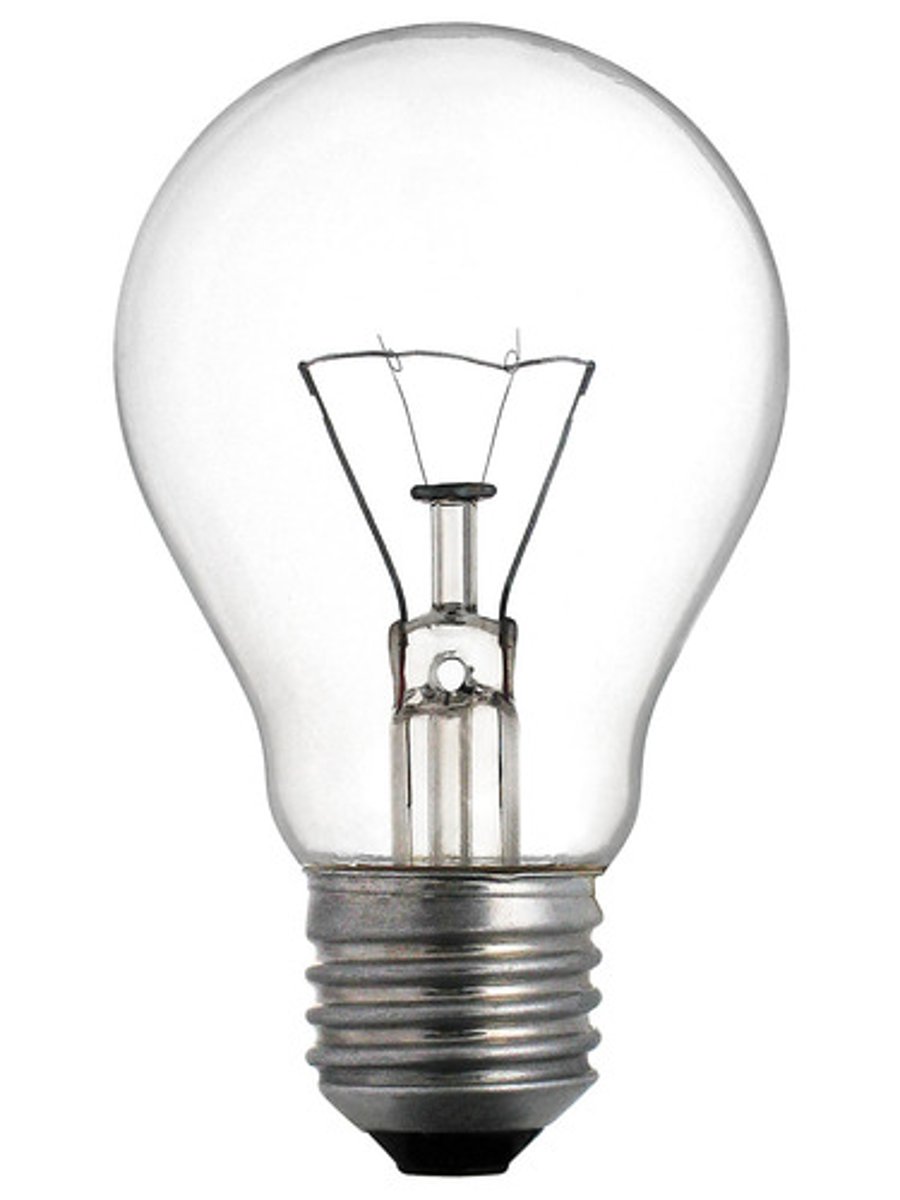
A bulb
is the standard rounded shape for the bulbs of general-service incandescent lamps

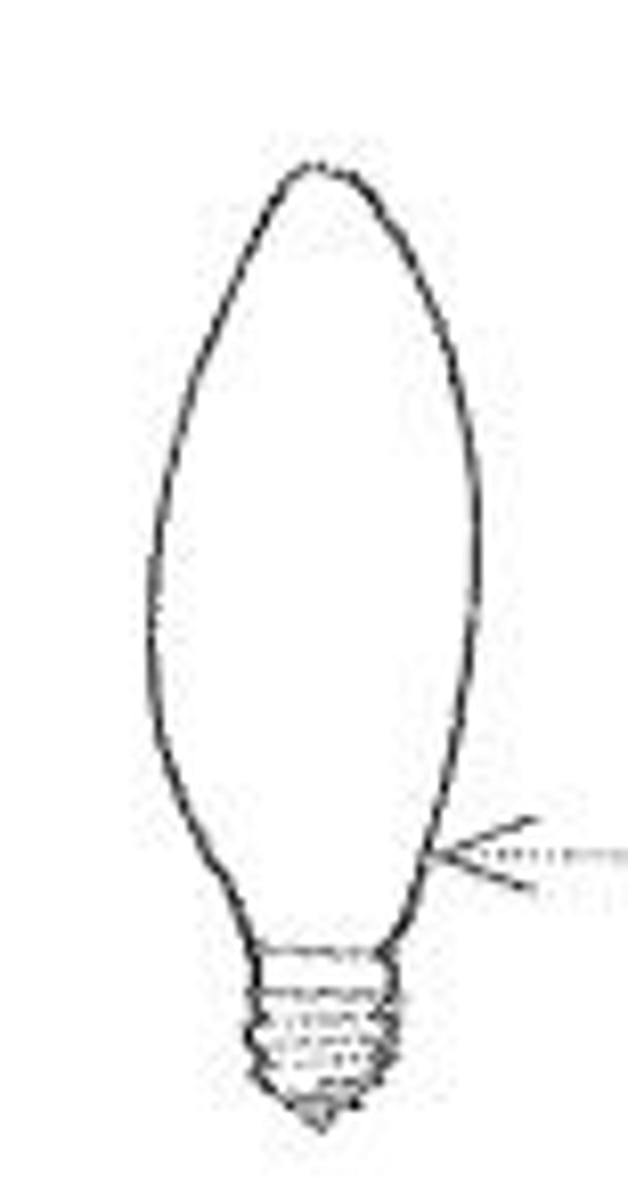
B bulb
Flame - shaped bulb for low - wattage, decorative incandescent lamps.
C bulb
Cone - shaped bulb for low - wattage, decorative incandescent lamps.
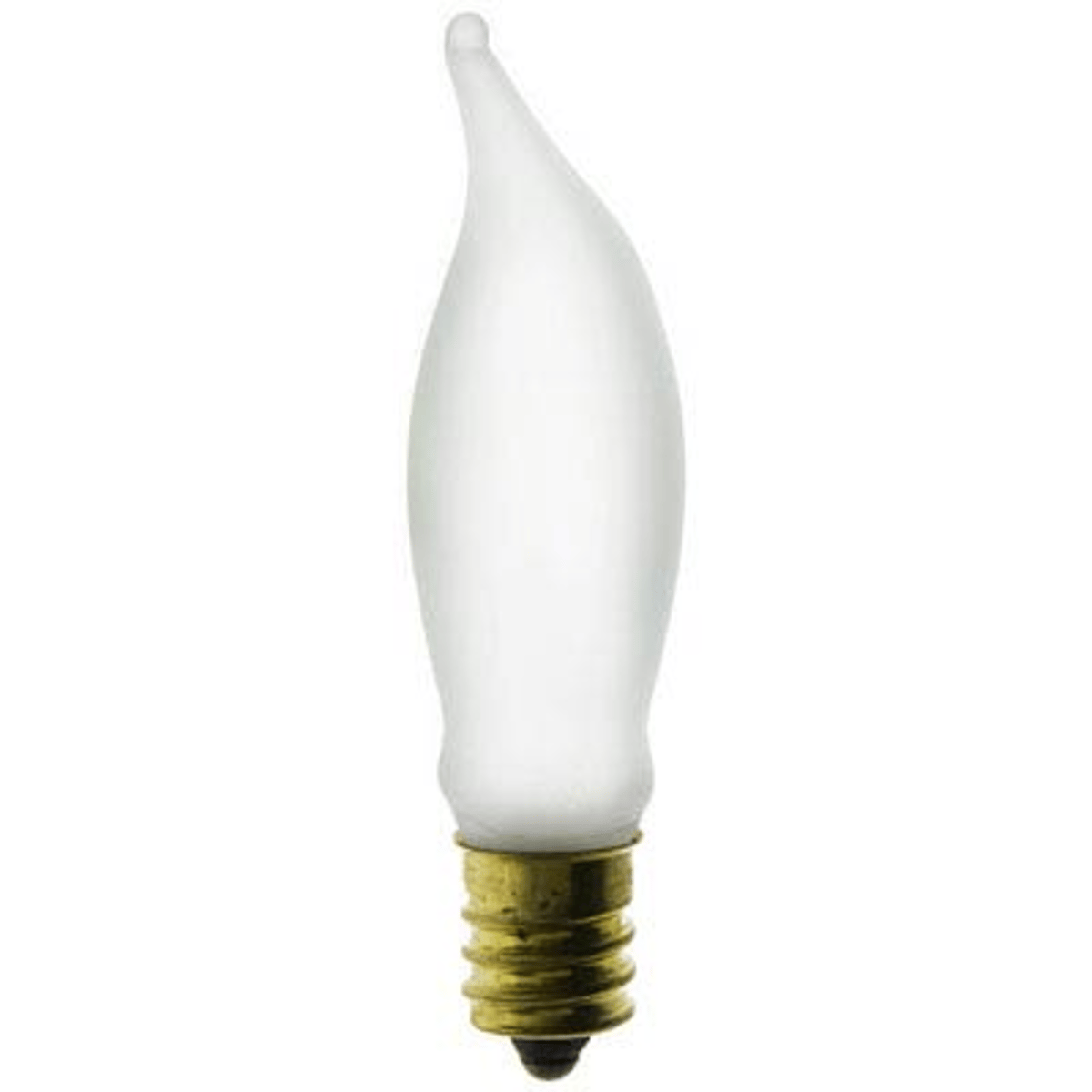
CA Bulb
Candle - shaped bulb for low - wattage, decorative incandescent lamps.

R bulb
A reflector bulb of blown glass for incandescent and high-intensity-discharge lamps, having an internal reflective coating and either a clear or frosted glass front to provide the desired beam spread.
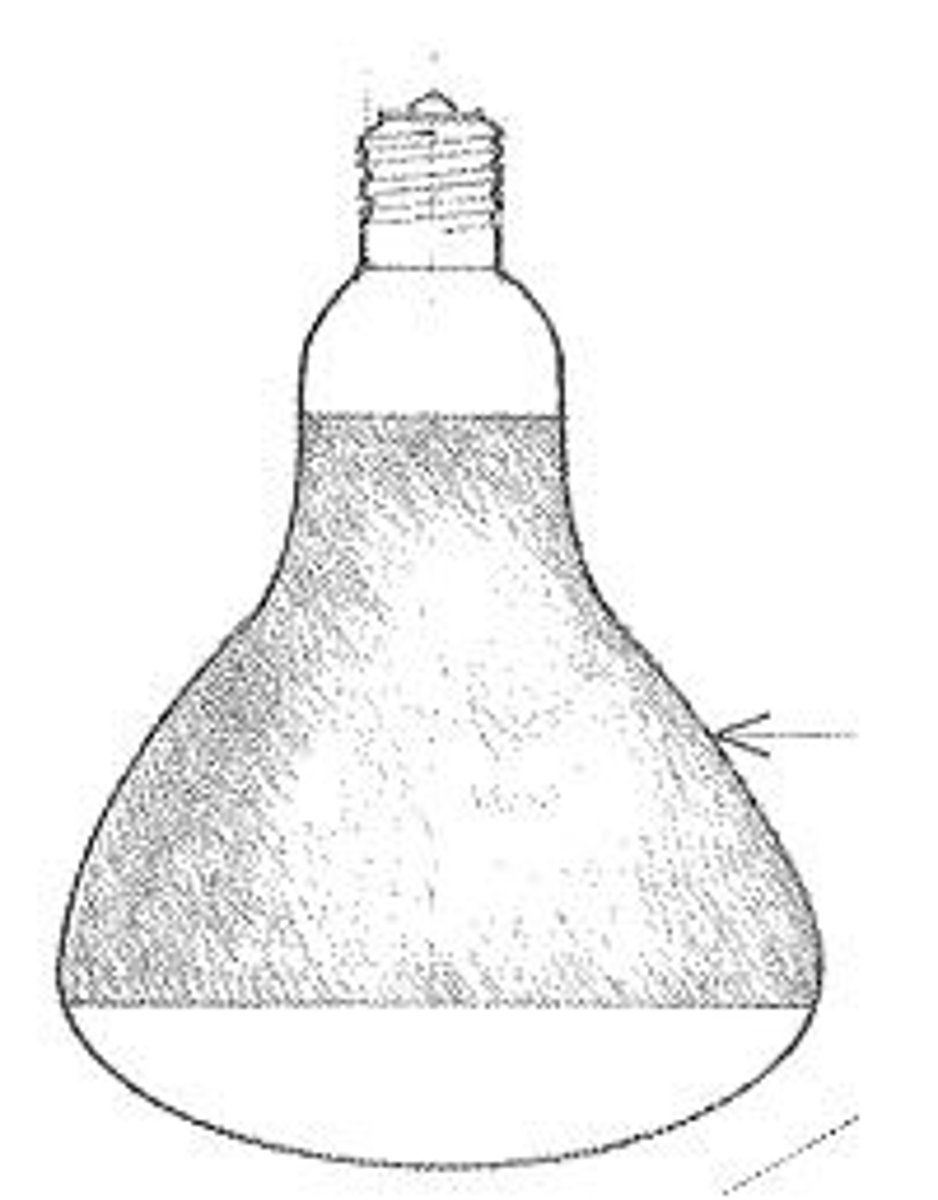
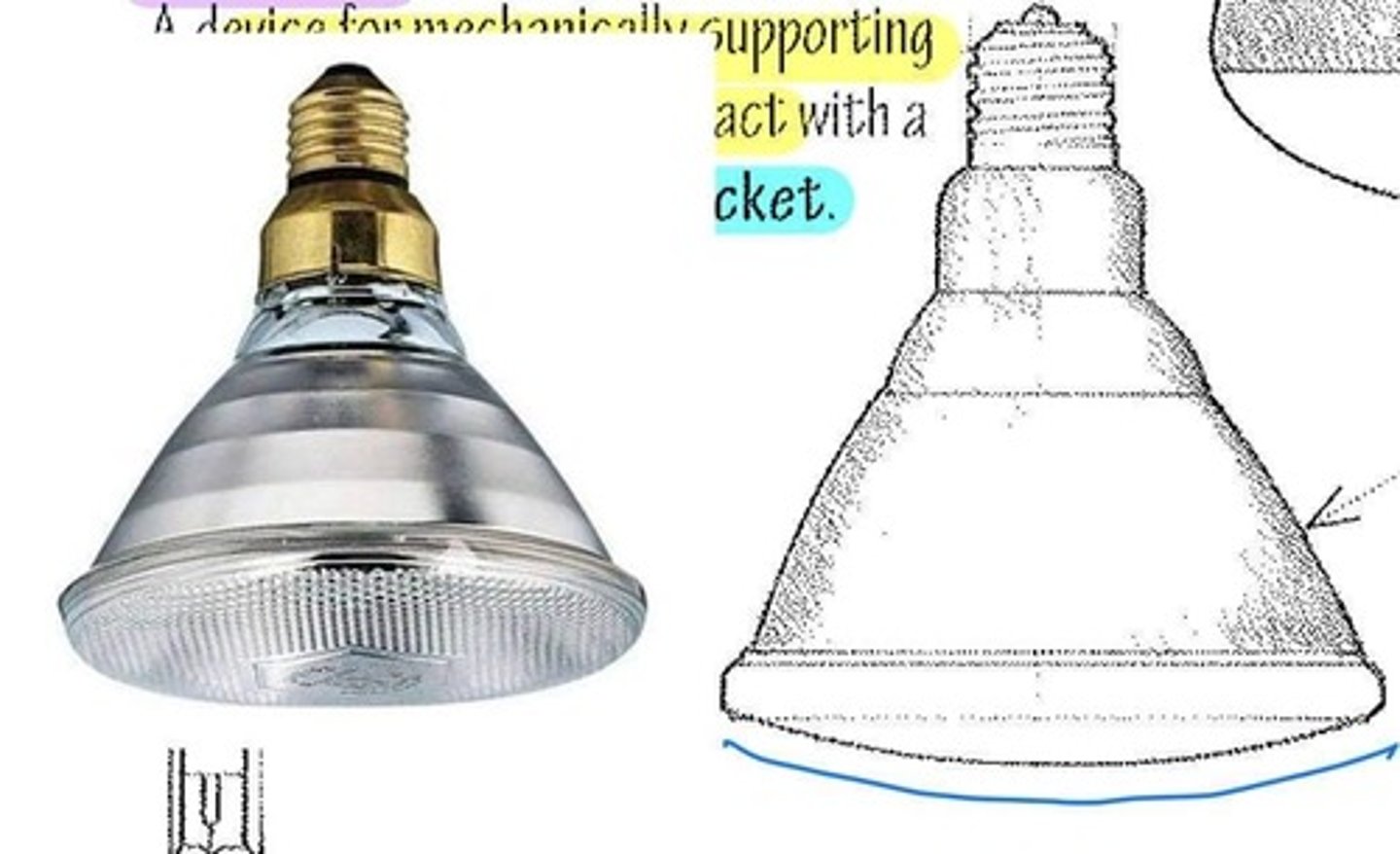
PAR Bulb
A parabolic aluminized reflector bulb cast glass for incandescent and high intensity discharge lamps, having a precisely formed internal reflector and a lensed front to provide the desired beam spread.
ER bulb
An ellipsoidal reflector bulb for incandescent lamps, having a precisely formed internal reflector that collects light and redirects it into a dispersed pattern at some distance in front of the light source.
A/SB bulb
An A - Bulb having a hemispherical reflective silver bowl opposite the lamp base to decrease glare.
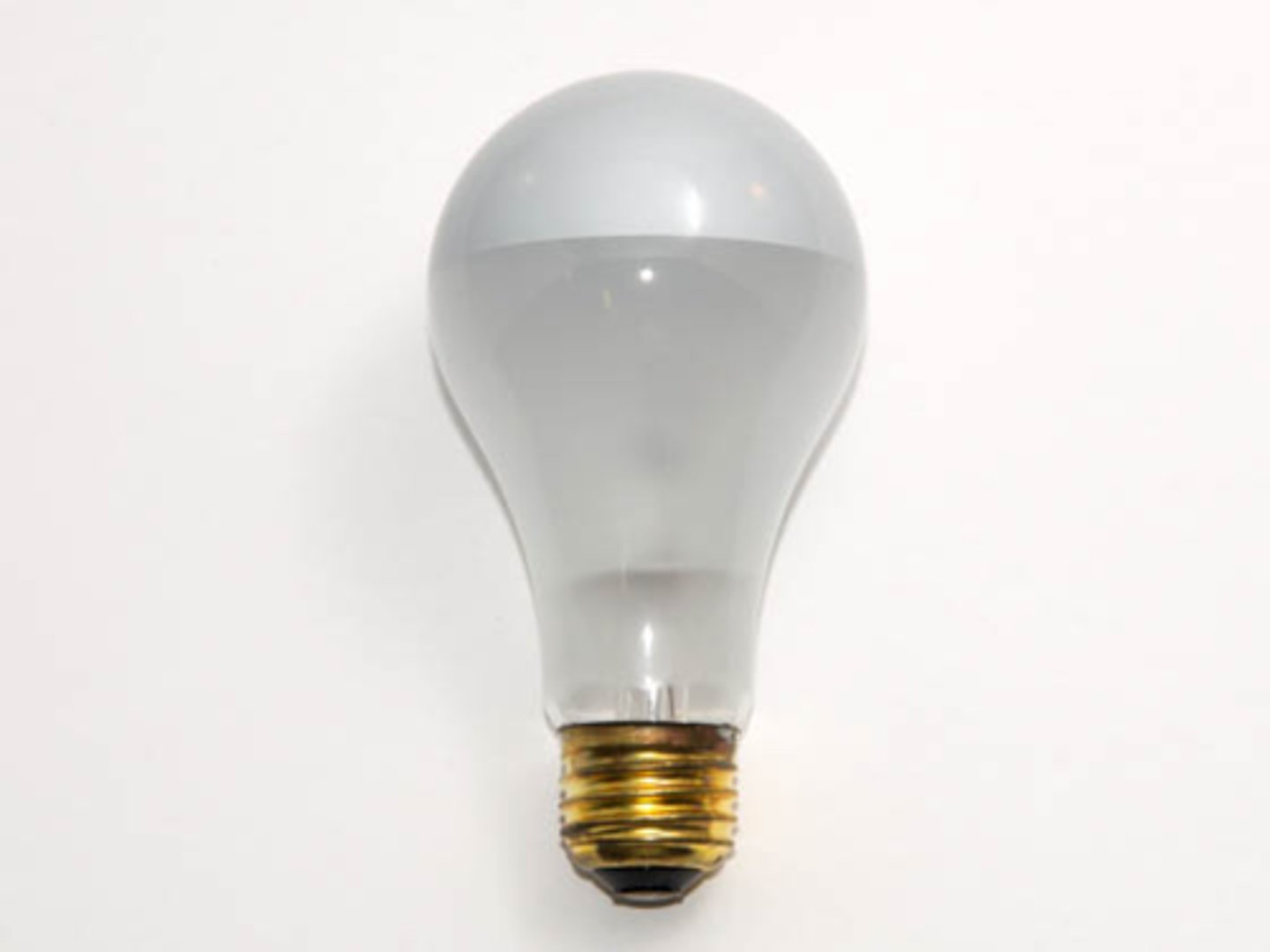

pS bulb
Pear-shaped bulb for large incandescent lamps
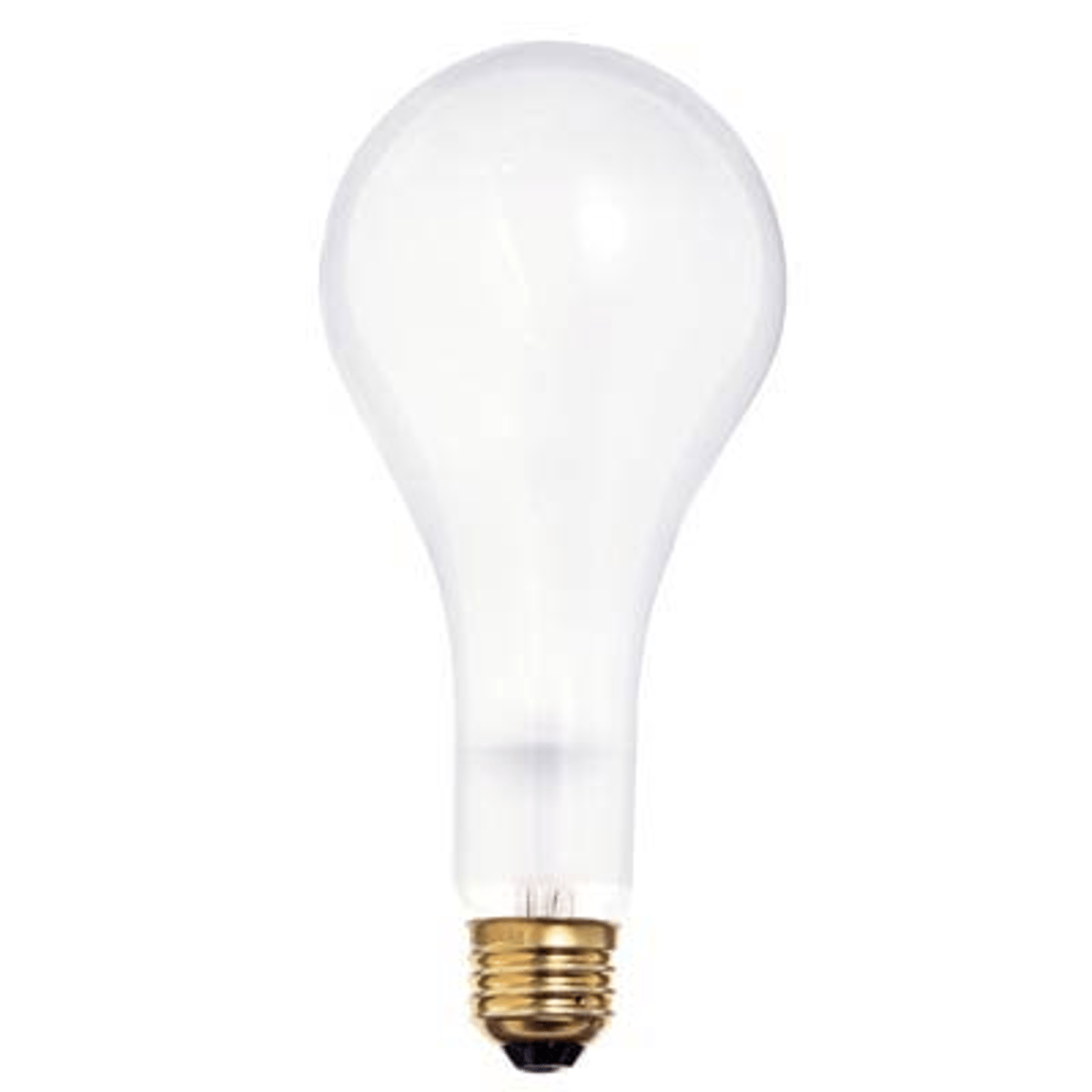

G bulb
A globe - shaped bulb for incandescent lamps, having a low brightness for exposed use.
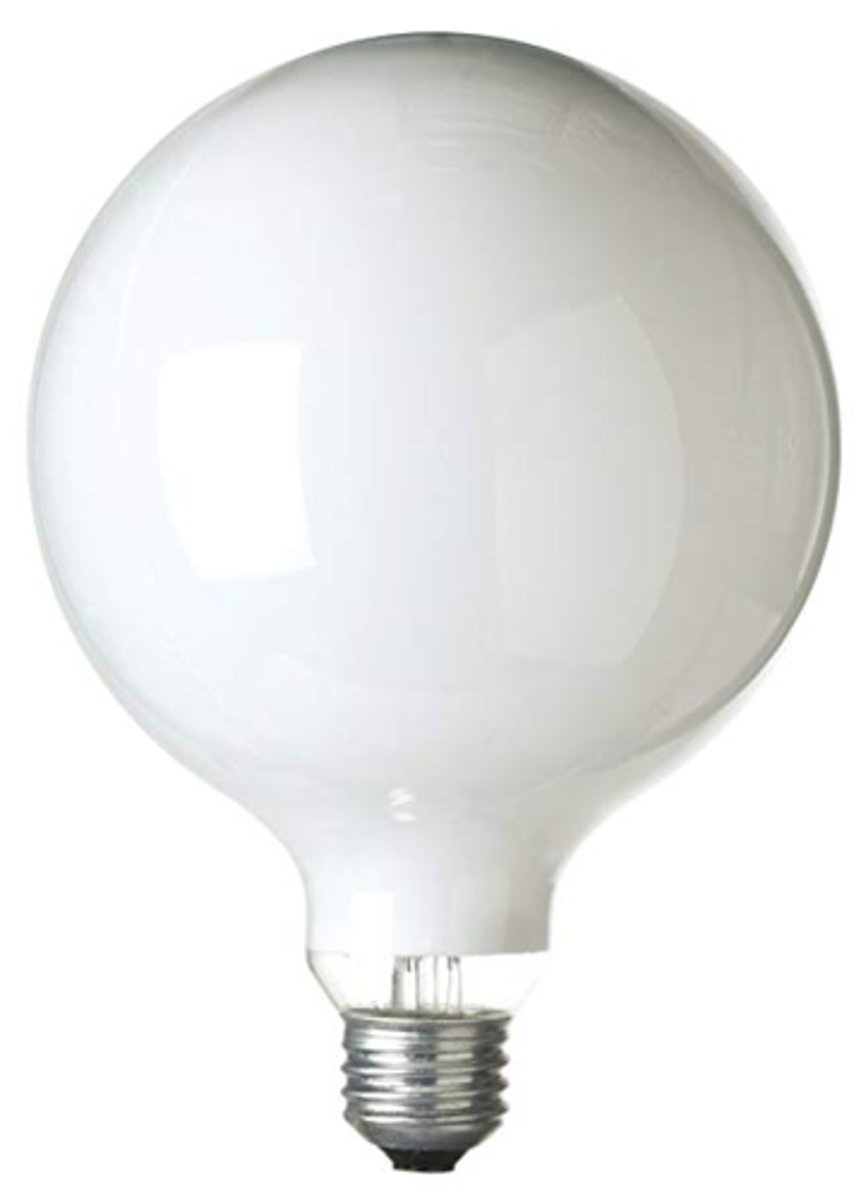

S bulb
A straight - sided bulb for low - wattage decorative incandescent lamps.
Tungsten - Ha
Also called "quartz" or "quartz- iodine lamps"
These use a halogen gas cycle to prevent rapid depreciation of the lamp filament and darkening of the transparent envelop.
floodlights
A broad-beamed, high-intensity bulb. They are often used to illuminate outdoor playing fields.

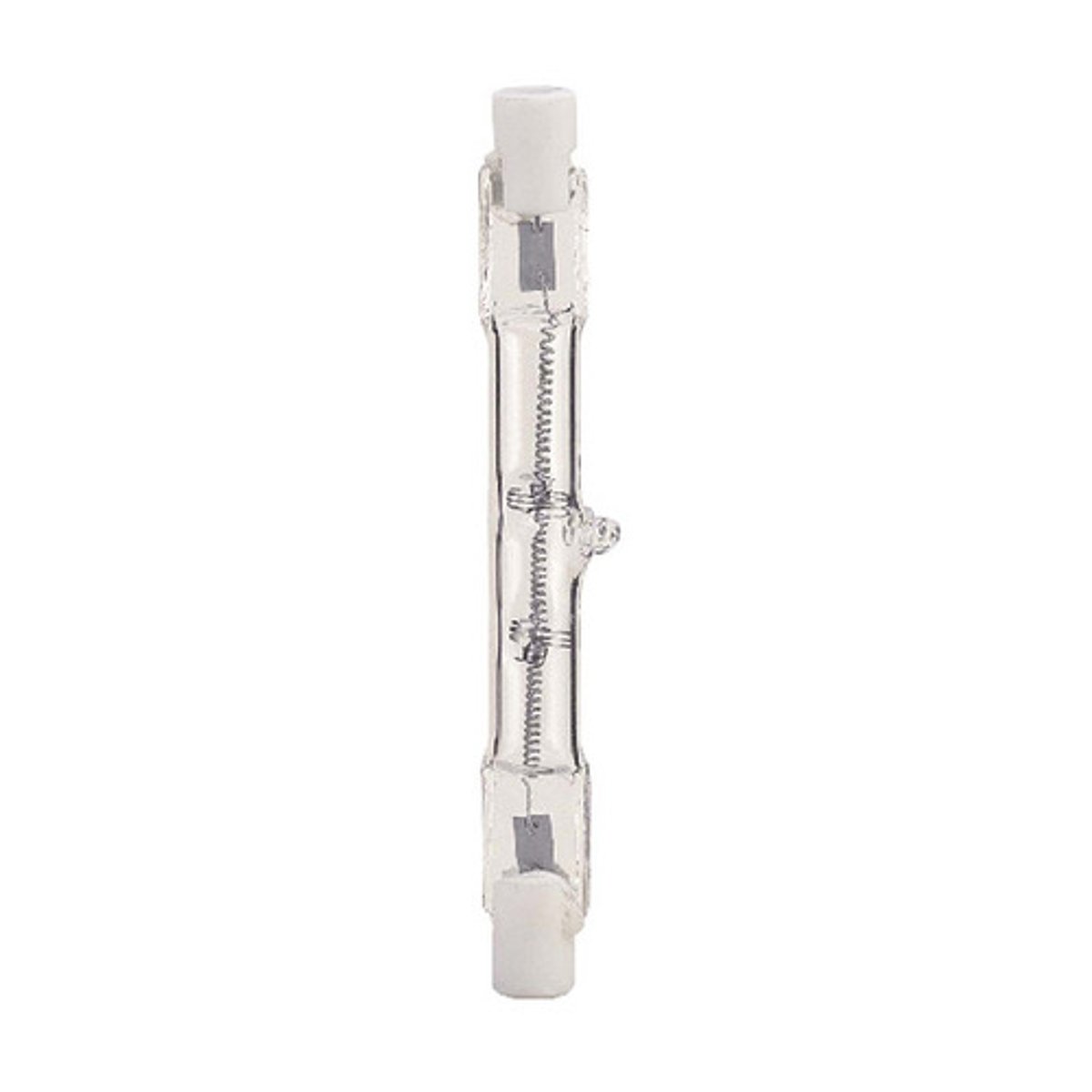
J type bulb
This is double-ended and commonly used as security lighting.

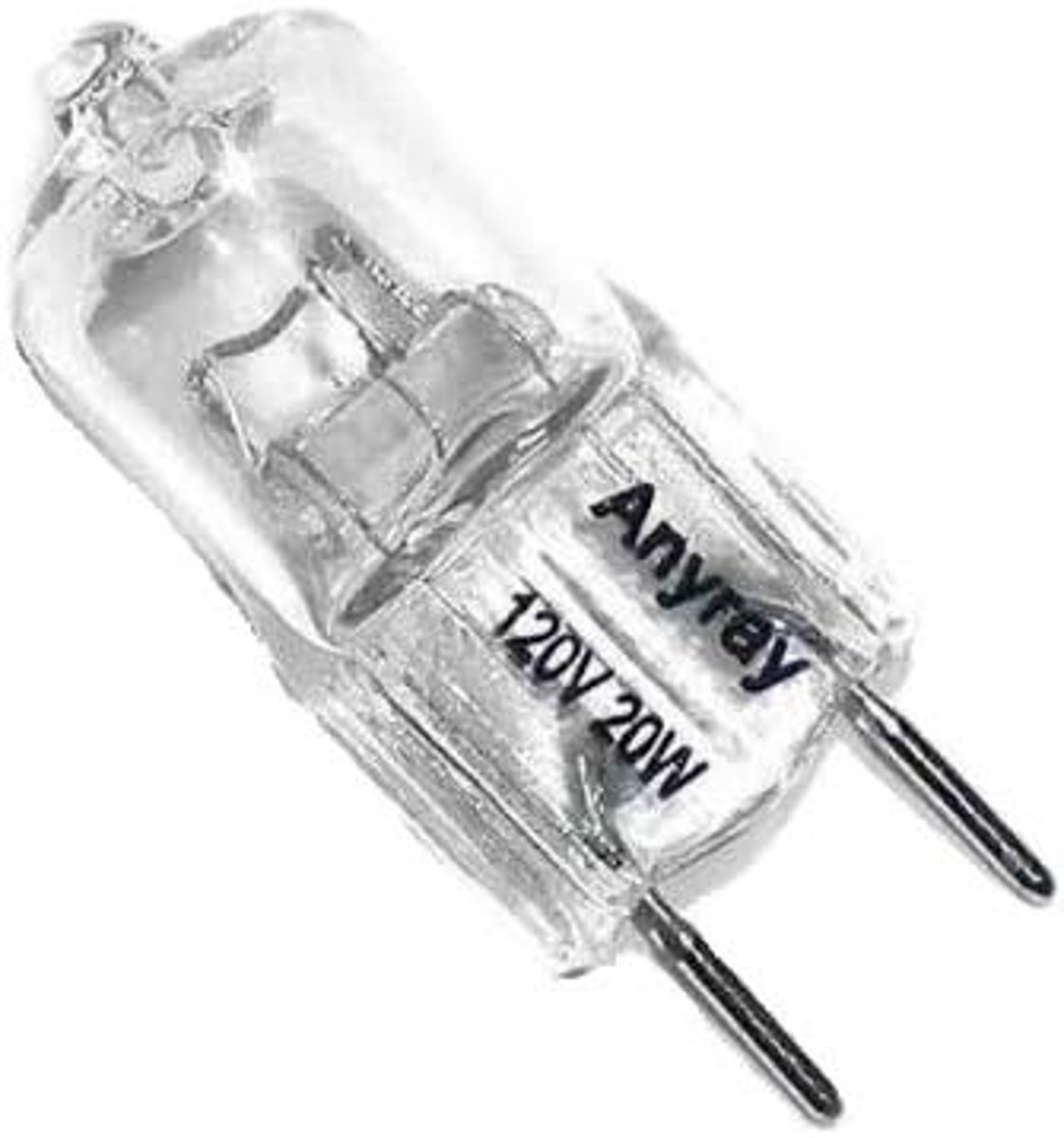
JC Type
This is a low voltage bulb, commonly found under counters in desk lamps, or as accent lighting. They come in capsule shape, with 2 pins at the base.

JCD Type
they are commonly used in under-counter lighting, desk lamps, accent lighting, or pendant lighting. Similar to JC type since they have pins at the end, but different since they use a higher voltage

JDD type
These are generally used in the foodservice industry and come in the standard base size. They have a halogen filament that is enclosed in glass, and then surrounded again by an overall glass jacket

JDR type
These are small reflector floodlights that are commonly used in range hoods or as track lighting. They come in clear or frosted glass finishes and can be purchased with or without a glass cover

MR bulb
a multifaceted reflector bulb for tungsten-halogen lamps; polished reflector arranged in discrete segments to provide desired beam spread

fluorescent
produces light by passing an electric current through a long tube filled with a low-pressure mixture of mercury vapor and argon; requires a ballast

fluorescence
the emission of radiation, especially of visible light, by a substance when exposed to external radiation
Phosphor
a solid material that emits light by fluorescence
Standard fluorescent
Otherwise known as T-bulb. This is in tubular form, and is the standard shape of a fluorescent bulb. It comes in 4 tpyes, T12, T8, T5, and T4
slim-line (fluorescent
Does not require a starter, have single-pin bases, come in diameter 3/4", 1", and 1- 1/2", and come in lengths from 42" (4ft) to 96" (8ft)
circline (fl
Dougnut shaped for circular luminaaries
u-bent (fluorescent)
U-shaped and used for square or rectangular luminaries
Pre-heat
requires a starter that pre-heats the cathodes so that less voltage is required to strike an arc.
Instant start
A type of fluorescent lamp; can operate without starters; ballast provides a high enough voltage to strike the arc without preheating them; also called "Slimline Lamps"
Rapid-start
Ballast that applies voltage and heats the cathodes simultaneously; continuously heats electrodes with special circuits
choke coil
All fluorescent light sources require a control device or an auxiliary, called a _____________, located in the metal base.
automatic switch or starter
self contained in a small tubular jacket which is inserted in the fixture body and is a replaceable part
Compact Fluorescent Lamp (CFL)
A small fluorescent lamp, used as a more efficient alternative to incandescent lighting; also called a PL, twin-tube, or biax lamp. (EPA)
spiral
most popular type of compact fluorescent bulb. it can be used anywhere that a traditional incandescent light bulb works.
incandescent shaped
It is basically an A-shaped compact fluorescent bulb. Essentially, it's a spiral bulb with a dome of clear glass that mimics and incandescent bulb
post
these are basically spiral CFLs on the inside, with a durable cover on top that is sealed to withstand wind, rain, and snow. They are designed for long life in outdoor conditions, and is a wise choice for outdoor light fixtures
Reflector
these are used in place of incandescent floodlights because they provide directional light. They can also be used in recessed or track lighting
Neon vapor lamps
a cold cathode lamp emitting a glow when a high voltage is applied across two electrodes in a neon filled glass-tube. It discharges a lamp even not heated. Bendable
High-intensity discharge lamps
Light is produced when a high - pressure electric arc is passed through a gas vapor.
Typically used when high levels of light over large areas are required, and when energy efficiency and/or light intensity are desired.
Mercury Vapor
A lamp in which ultraviolet and yellowish-green to blue visible light is produced by an electric discharge through mercury vapor. The color spectrum may be corrected by the addition of a phosphor coating, and ultraviolet blocking is required to prevent injury.
Metal Halide
a modification of the mercury vapor with an arc of improved color. In addition to mercury, the arc tube contains metallic vapors such as indium iodide, thallium iodide, or sodium iodide. It possesses therefore increased light output, improved color rendition without the use of phosphors, and small source size.
High Pressure Sodium Lamp
a discharge lamp that excites mercury and sodium vapor to create visible light
solid state lighting
a type of illumination that operates with semiconductors and includes LEDs and OLEDs
OLED
A type of monitor that uses a thin LED layer or film between two grids of electrodes and does not use backlighting.
Luminaires
Also called a lighting fixture;
A complete lighting unit consisting of a lamp or lamps together with the housing designed to distribute the light position and protect the lamps, and connect the lamps to the power supply.
lens
a piece of glass or other transparent substance with curved sides for concentrating or dispersing light rays, used singly (as in a magnifying glass) or with other lenses (as in a telescope).
diffuser
any of a variety of translucent materials for filtering glare of a light source and distributing the light over an extended area. Its purpose is to create a lit environment with minimal shadows. and to spread illumination far and wide.
Louver
a grid-shaped unit of a luminaire designed to shield light from view
Suspended ceiling
The most common type of lighting fixture offering the greatest variety of designs. Light distribution can be any method depending on the shade you choose and the length of cord to which the bulb hangs
Chandelier
a decorative hanging light with branches for several light bulbs or candles.
drop light
A lighting fixture suapended from a ceiling or wall by a flexible cord, by which it can be raised or lowered
pendant l
like a droplight, but is fixed and is suspended by a cord, wire, or chains
wall lights
A wall-mounted light fixture that diffuses light into the room, usually through a translucent housing
sconce
a decorative wall bracket for holding candles or lights
wall washers
Used to bathe a wall in an even stream of light usually ceiling mounted, recessed in the ceiling or mounted on a light track
ceiling lights
Ceiling-mounted lighting that is not recessed. It provides general lighting.
downlights
provides directional light in a downward stream. It is normally recessed or semi-recessed in the ceiling, and when fully recessed is one of the most visually inconspicuous and attractive luminaires
troffer lights
It is a rectangular light fixture that fits into a modular dropped ceiling grid
prismatic troffer
Troffer Lens that distribute light over a spectrum and distribute concentrated light source over a larger surface area
parabolic lo
A gird of baffles which redirect light downward and provide very low luminaire brightness.
upligh
LED lights that shine upward from the ground.
Spotlights
Ceiling-,wall-, or floor-mounted, or attached to a track, this is a flexible adjustable luminaire that directs light a controlled beam.
floor lamps
Light fixtures that are freestanding. Lighting distribution depends on the shade used.
table lamps
A variety of decorative lights which gives a soft glow. Can be used as bedside reading lights as well as for stylistic effects in the living room.
Desk lamps
Essential to provide task lighting, it gives a concentrated directional light to a specific area
Strip lighting
is a rigid flexible tape with exposed low-voltage light sources. It is generally a fluorescent fixture but some type can be tungsten or neon.
High-bay Lights
These are used to illuminate spaces with high ceilings, usually ceilings that are above 20 feet in height.
Visual Oddities
Designed for visual impact rather than the way they distribute light. Provide aesthetic stimulation and amusement.
Illumination
intensity of light per unit area. refers to man-made lighting
electric illuminat
Essential to provide task lighting giving a concentrated directional light to a specific area.
Brightness
The lightness or darkness of reflected light, determined in large part by the light's intensity.
contrast
this is the difference in brightness between an object and its background
glare
refers to an excessive luminance ration in the field of vision, and is a strong, steady, dazzling light or reflection
Direct glare
results when a light source in the field of vision causes discomfort and interference with the visual task
indirect glare
Refers to excessive brightness; either blinding, disabling, or discomforting, in your field of view from reflective surfaces