Dog Cat Medicine EXAM 1
1/725
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
726 Terms
what do the canine core vaccines protect against?
rabies
distemper
adenovirus
parvovirus
what do the feline core vaccines protect against?
rabies
panleukopenia
herpesvirus
calicivirus
feline leukemia virus (cats < 1 yr)
what do the canine noncore vaccines protect against?
parainfluenza
bordetella
leptospirosis
borrelia burgdorferi
influenza
what do the feline noncore vaccines protect against?
feline leukemia virus
chlamydophila felis
bordetella
distemper, adenovirus and parvovirus are given in a __________ vaccine
combination
what are canine core vaccine protocols for dogs below 16 weeks old?
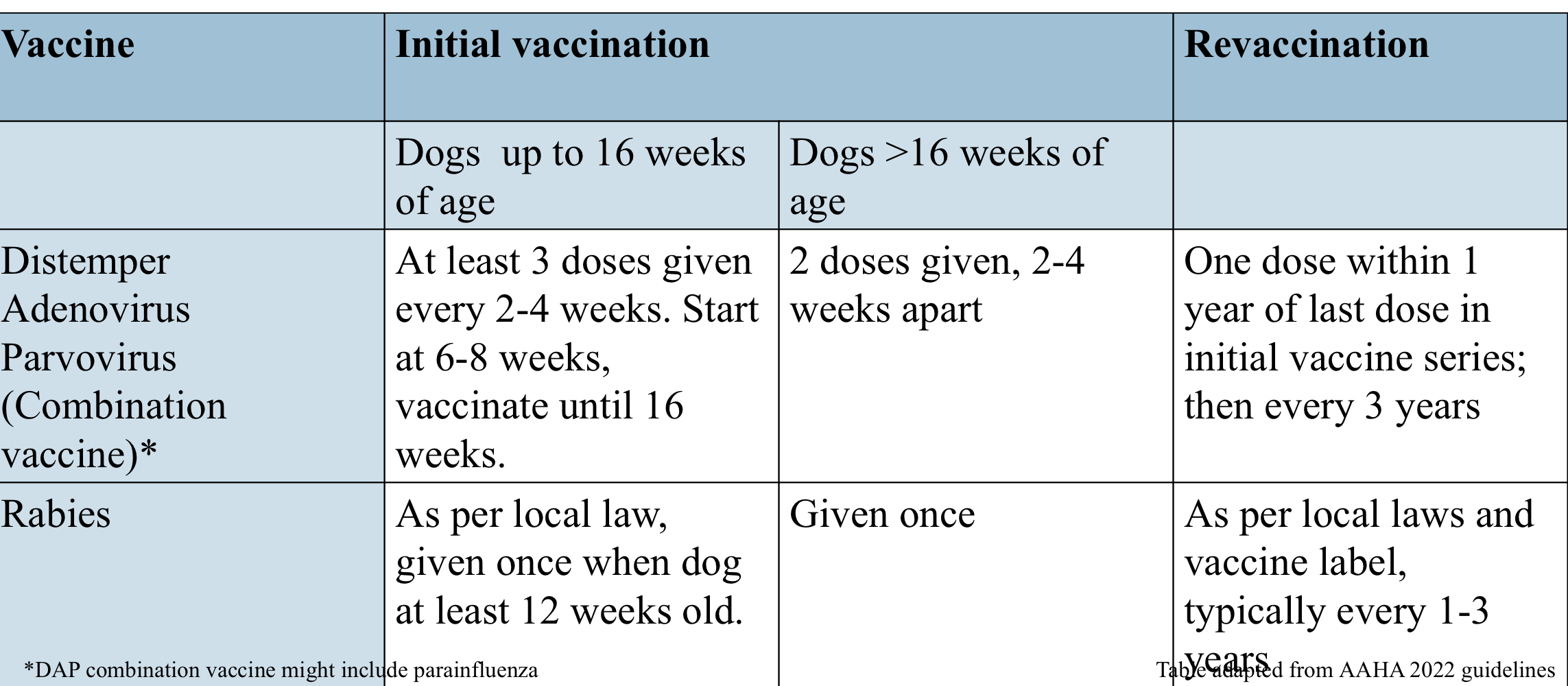
what are canine core vaccine protocols for dogs above 16 weeks old?
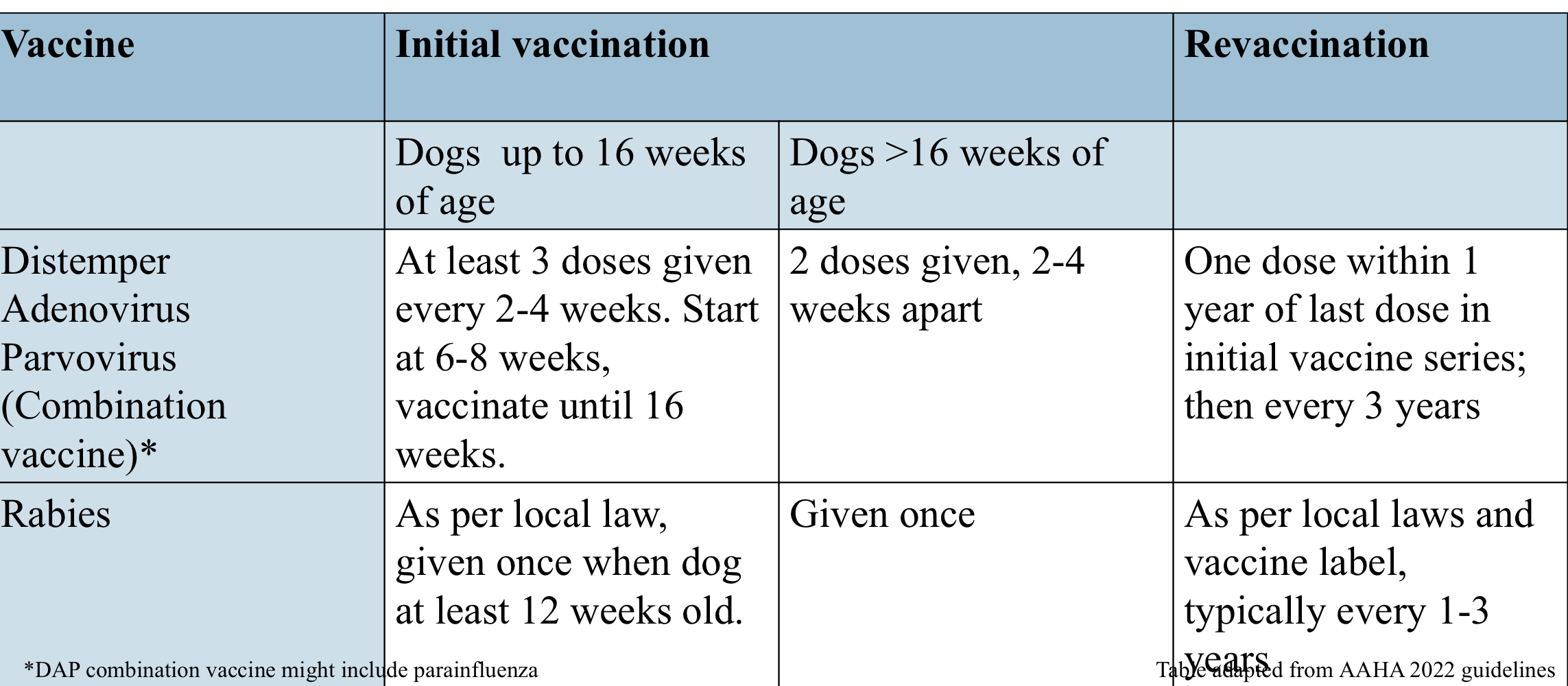
leptospirosis vaccine might not ________ for serovars not listed on the vaccine
cross-protect
leptospirosis vaccine protocol:
vaccinate dogs > 12 weeks of age with a series of 2-3 vaccines, 3-4 weeks apart. Repeat annually if risk persists
intransal bordetella vaccine also includes…
CAV-2, parainfluenza virus
bordetella vaccine protocol:
can be given at >8 weeks of age. recommended at least 1 week prior to exposure
canine influenza vaccine targets which strains?
H3N8 ± H3N2
canine infuenza vaccine protocol:
2 doses given 2-4 weeks apart, revaccinate annually if risk persists
borrelia vaccine protocol:
2 doses given 2-4 weeks apart, revaccinate annually if risk persists
what are feline core vaccine protocols for cats up to 16 weeks old?
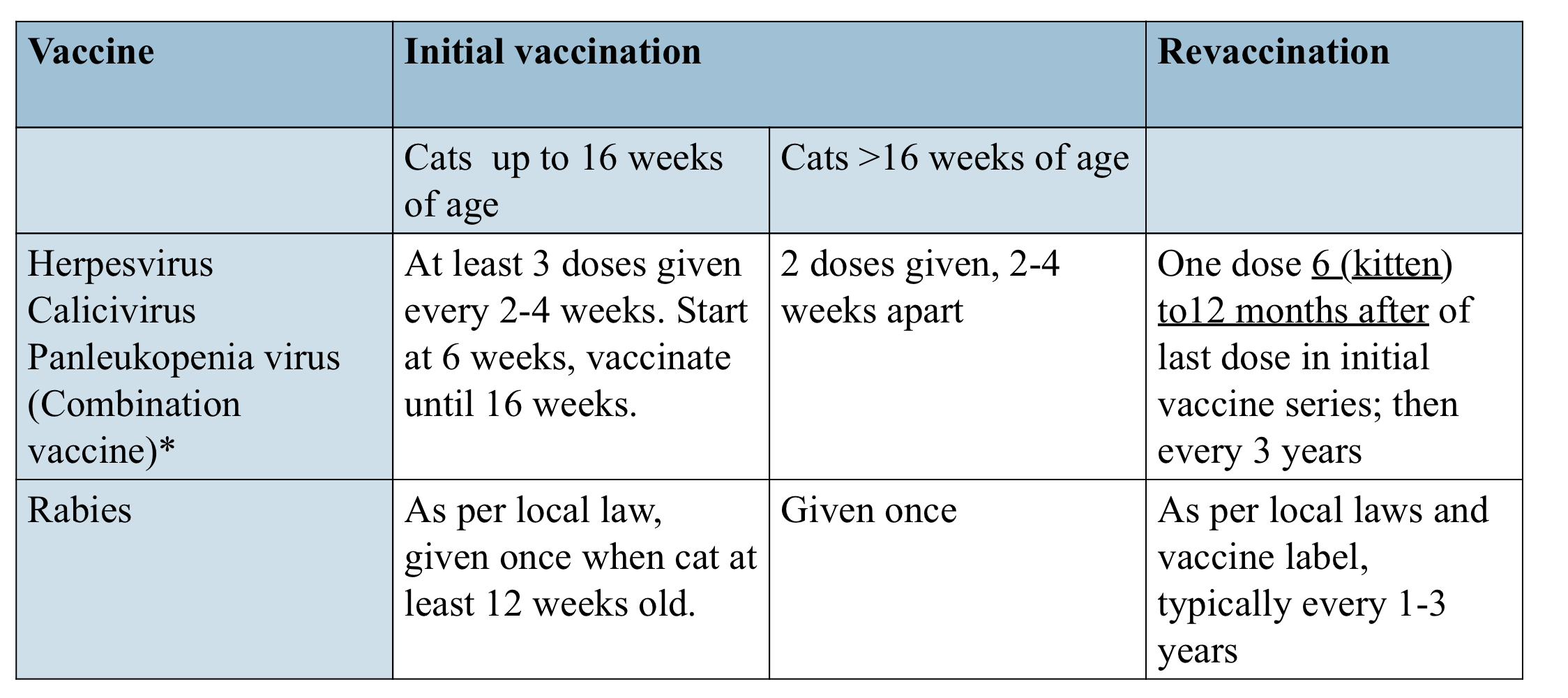
what are feline core vaccine protocols for cats above 16 weeks old?
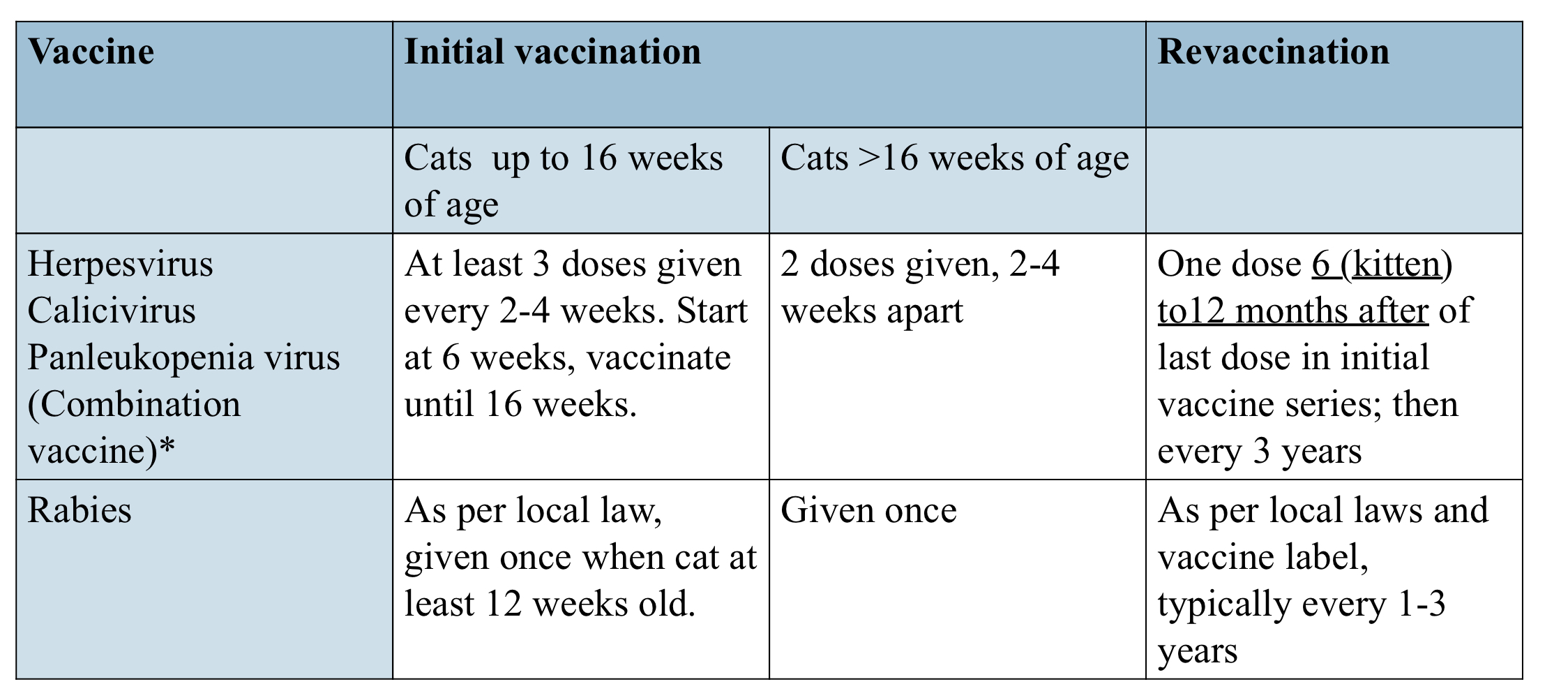
FeLV is considered core in cats ______ years of age because of increased susceptibility
<1 year
what is FeLV vaccine protocol:
2 doses, 3-4 weeks apart after 6 weeks of age. Revaccinate 12 months after last dose in series and continue to vaccinate annually if risk persists
FHV-1 and FCV vaccines do not offer…
complete protection
can rabies serology be accepted in lieu of vaccination?
no
when can you not vaccinate?
systemic, not stabilized disease is present
receiving immunosuppressive treatments
another vaccine given very recently
FeLV +
components of hemostasis:
blood vessel
adequate platelet mass and function
adequate plasma coagulation factor levels and function
what cause hemorrhage?
trauma or inflammation
reduced platelet number or function
reduced number or function of coagulation factors
primary hemostatic defect
lack of platelet plug
signs of primary hemostatic defect:
petechia/ecchymoses
gingival bleeding
epistaxis
hematuria
hematemesis/melena/hematochezia
hematoma after venipuncture
signs of secondary hemostatic defect:
hemothorax
hemoabdomen
hemarthrosis
epistaxis
hematemesis/melena/hematochezia
large eccymoses
von Willebrand disease
quantitative or qualitative deficiency in von Willebrand factor
von Willebrand factor
glycoprotein that helps platelets adhere to sites of vessel injury
larger von willebrand factors are more/less effective
more
von Willebrand disease signs:
prolonged bleeding
excessive bruising after trauma
bleeding from gums, nose
type 1 VWD
most common
quantitative VWF reduction but remaining functions the same
type 2 VWD
decrease in large VWF
moderate to severe bleeding, spontaneous hemorrhage
type 3 VWD
complete absence of VWF
severe bleeding, spontaneous hemorrhage
diagnosing VWD
BMBT
VWF antigen test
DNA test
interpreting VWF antigen results
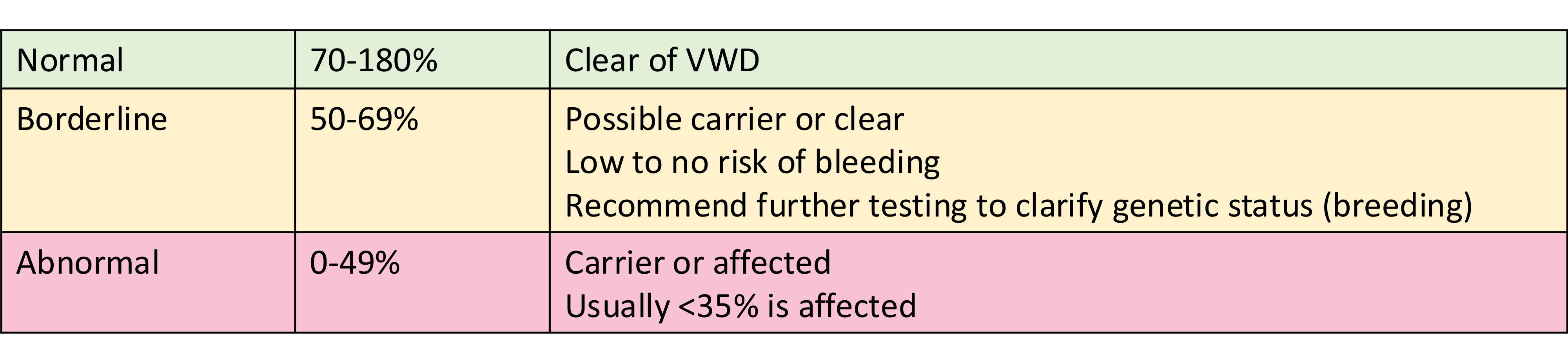
managing type 1 VWD with no previous bleeding:
DDAVP (desmopressin)
given 30 min prior to surgery
helps for 2-4 hrs in affected dogs
DDAVP (desmopressin)
stimulates VWF release
managing type 1 VWD with mild previous bleeding:
give DDAVP
± plasma with VWF prior to procedure
managing type 1 VWD with moderate-severe previous bleeding:
consider risk vs benefit of procedure
consider referral to hospital with 24 hr monitoring following procedure, transfusion support, specialty care
how to treat VWD bleeding event:
first aid (compress, cold pack)
one dose DDAVP
plasma
potentially RBC
secondary hemostatic disorders:
hereditary
hemophilia A, B
other factor deficiencies
acquired
liver dysfunction
toxicity
DIC
others
anticoagulant rodenticides cause bleeding via…
vitamin K antagonism→lack of production of factors II, VII, IX, X
signs of anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity:
dyspnea, coughing
exercise intolerance
hematomas
hematemesis
melena
hematuria
pale MMs
signs secondary to bleeding in other location
anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity diagnosis:
prolongation of PT, PTT, ACT
anemia and thrombocytopenia
effusions
anticoagulant rodenticide toxicity treatment:
vitamin K1 2.5-5 mg/kg
transfusion
supportive care
thoracocentesis if effusion
charcoal and emesis if acute ingestion
hemophilia A
factor VIII deficiency
hemophilia B
factor IX deficiency
delayed post op bleeding happens in around 30% of _________
greyhounds
diagnosing DIC:
thrombocytopenia
increasing PT/PTT
evidence of fibrin clot lysis
CBC-schistocytes/RBC fragments
treating DIC:
treatment of underlying disorder
supportive care
treatment of coagulation abnormality depending on phase of DIC
thromboembolic disease
inappropriate clot formation secondary to other diseases
mechanisms of thromboembolic disease:
increased prothrombotic factors
endothelial dysfunction
decreased endogenous anticoagulant factors
most common thromboembolic diseases:
arterial thromboembolism in cats with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
pulmonary thromboembolism
thromboembolic disease signs:
lack of arterial perfusion
lack of venous drainage
dyspnea with PTE
acute patient physiological lab evaluation (APPLE) triage system requires…
blood results
what are parts of veterinary triage?
telephone triage
waiting room triage
primary survey
secondary survey
steps of telephone triage:
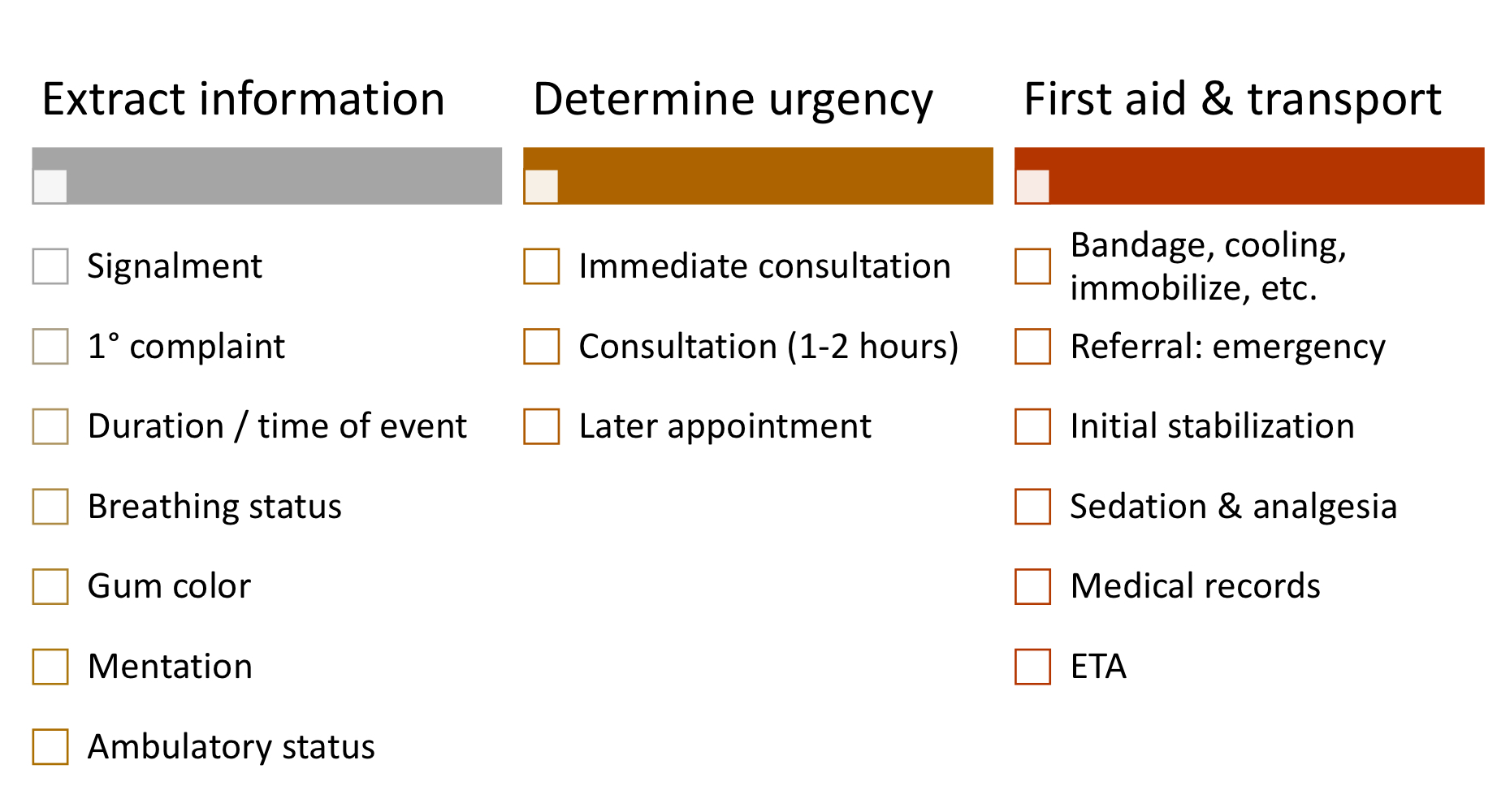
what conditions require immediate consultation?
respiratory distress
choking, gagging, coughing
cyanosis, white MM
collapse, loss of consciousness
status epilepticus
heat stress/heatstroke
distended abdomen, unproductive retching
massive bleeding
inability to urinate/no urine production
acute poisoning
electric shock/burns
what conditions require consultation ASAP (1-2 hrs)?
cluster seizures
paresis/paraplegia
esophageal/linear foreign body
trauma, bite wounds, fractures
stranguria
severe vomiting/diarrhea
hematemesis/hematochezia
opthalmological abnormalities
acute deterioration
lethargy, recumbancy
pain
what is examined on waiting room triage?
level of consciousness
respiratory pattern, rate, effort, noise
HR, MM, CRT, pulse quality
temp
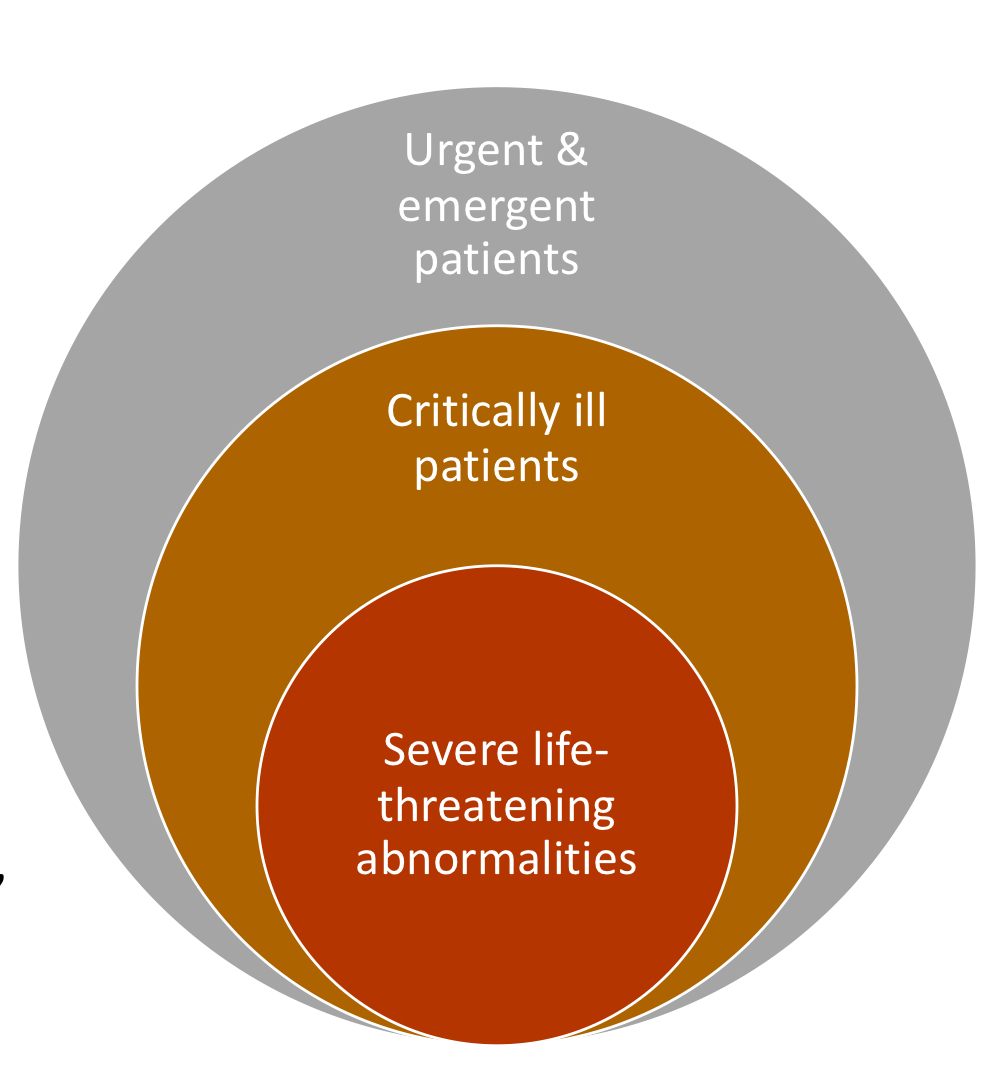
what are considered life threatening abnormalities?
white, cyanotic, grey muddy, severely hyperemic MM
bradycardia: cat <120 bpm, dog <40-60 bpm
tachycardia: cat >240 bpm, dog >180 bpm
irregular heart rhythm
perforated or open body cavities
distended abdomen
hyperthermia >41 degrees C
hypothermia <36.7 degrees C
stranguria with firm bladder
dystocia
acute poisoning
burns, chemical injury
with verbal consent, what can be done in waiting room triage?
IV
initial diagnostics and stabilization
emergency procedures
resuscitation status
what drugs can be used to treat hypoglycemia?
dextrose
what drugs can be used to treat hypocalcemia?
calcium gluconate
what drugs can be used to treat hyperkalemia?
dextrose
insulin
calcium gluconate
what drugs can be used to treat seizures?
midazolam
diazepam
what drugs can be used to treat malignant ventricular arrhythmias?
lidocaine
what drugs can be used to treat anaphylaxis?
epinephrine
what drugs can be used to for cardiopulmonary resuscitation?
lidocaine
epinephrine
vasopressin
atropine
flumazenil
naloxone
atipamezole
primary survey steps:
CPR if needed
assessment of major body systems
brief history
what body systems are assessed in the primary survey?
respiratory
cardiovascular
CNS
other: urogenital, abdomen, etc
what are parts of respiratory system evaluation?
visual exam
auscultation
pulse ox
increased inspiratory effort =
upper airway obstruction
increased expiratory effort =
lower airway obstruction
rapid shallow breathing =
pleural space disease, reduced lung compliance
brown MM =
methemoglobinemia
dull/quiet lungs =
pleural space disease, lung consolidation
how to stabilize respiratory distress?
minimize stress
sedate
oxygen supplementation
what are parts of cardiovascular system evaluation?
perfusion
auscultation and pulse
shock index
ECG rhythm
how to stabilize cardiovascular distress:
vascular access
IV fluid resuscitation
vasopressors, antiarrhythmics, pericardiocentesis
4 criteria to treat ventricular tachycardia:
symptomatic
>160-180 bpm
polymorphic/ multiform VPCs
R on T phenomenon
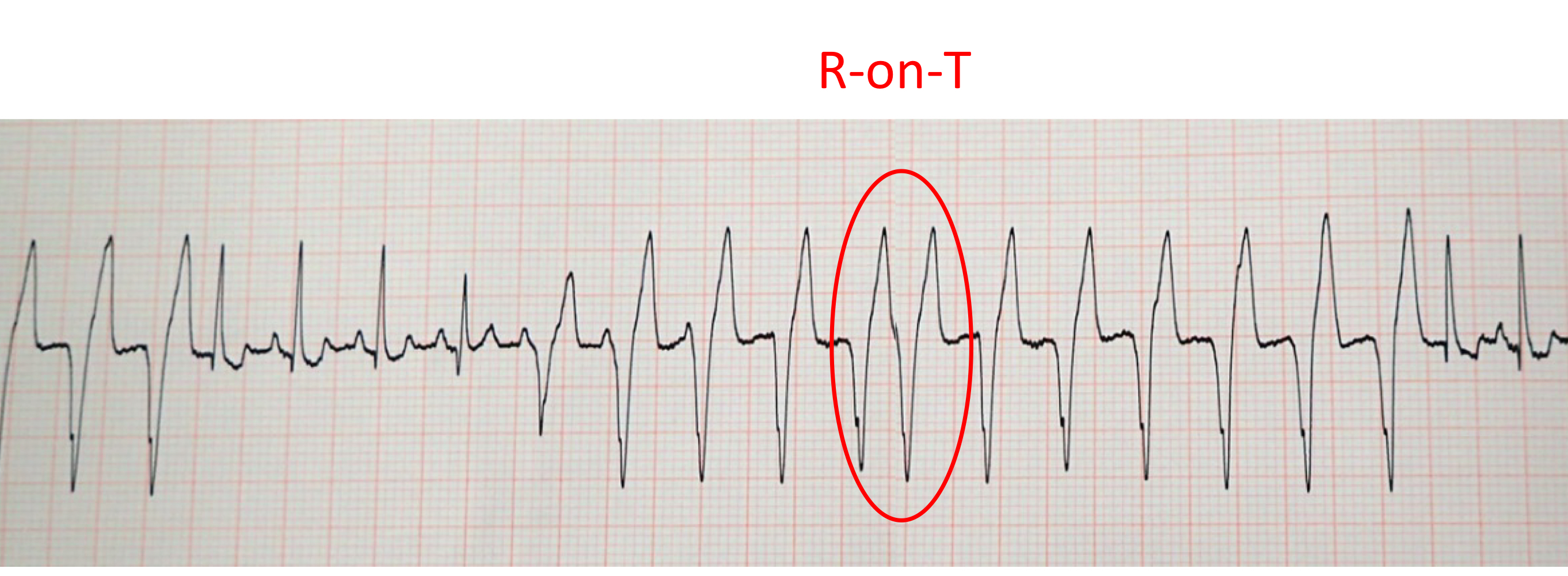
how to treat ventricular tachycardia:
lidocaine bolus of 2 mg/kg
followed by lidocaine CRI
what are parts of CNS evaluation?
mentation/level of consciousness
pupils
cushings reflex
posture
gait and spinal integrity
cushings reflex
CNS response to increased ICP→hypertension, reflex bradycardia
how to stabilize seizures:
diazepam .5 mg/kg
phenobarbital, levetiracetam
propofol, isoflurane
how to stabilize increased ICP:
hypertonic saline
mannitol
how to stabilize hypoglycemia:
oral corn syrup
50% dextrose bolus: .5-1 mL/kg
2.5-5% dextrose CRI
how to stabilize hypocalcemia:
10% calcium gluconate: .5 mL/kg IV
how to stabilize hyperkalemia:
10% calcium gluconate: .5-1 mL/kg IV over 2-5 min
insulin .25-.5 u/kg IV + 50% dextrose 2-4 mL/u insulin
diagnosing sepsis in triage:
glucose >1.1 mmol/L
blood lactate >2 mmol/L
diagnosing uroabdomen in triage:
serum K+ dog >1.4:1
serum K+ cat >1.9:1
diagnosing bile peritonitis in triage:
serum bilirubin >2:1
what is completed in secondary survey:
full PE
thorough history
problem list
diagnostic plans
full discussion (findings, prognosis, financial implications, written consent)
TBW is ___% BW
60
how much of BW is ICF?
40%
how much of BW is ECF?
20%
ECF consists of…
interstitial fluid
plasma
how much of BW is interstitial fluid?
15%
how much of BW is plasma?
5%
what questions are indications for fluid therapy?
resuscitation: is the patient in shock?
rehydration: is patient dehydrated?
maintenance: is patient eating or drinking?
ongoing losses: how to predict?