(4.6-4.10) Thermal Energy Transfer + Radiation
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are 3 ways energy can be transferred by heat?
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
How long will objects continue to lose heat?
Until they reach thermal equilibrium with their surroundings.
What is conduction?
When a substance is heated,
atoms vibrate more and collide,
transferring energy from atom to atom.
Why are metals such good conductors?
They have delocalised electrons
that can also collide with atoms,
speeding up the transfer of energy.
Why are liquids and gases poor conductors?
The atoms are very far apart so collisions are rarer.
What makes material with trapped air pockets such good insulators?
Air is a gas and a poor conductor
so materials with pockets of air will be bad at conducting.
What is the main way that thermal energy is transferred through liquids and gases?
Convection, which cannot occur in solids
Describe the process of convection.
When a fluid is heated, molecules push each other apart, making it expand.
This makes the fluid less dense than the surroundings.
The hot fluid rises and cooler fluid moves in to take its place.
Hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again.
The resulting motion is called a convection current.
Where can convection be seen in everyday phenomena?
Hot drinks cooling
The ocean
Rooms- the air near a heater
What is thermal radiation?
The transfer of energy through EM waves that can occur through a vacuum
as it doesn’t need particles.
Describe the absorbing and emitting power of: Black
Good Absorber
Good Emitter
Describe the absorbing and emitting power of: Dull
Reasonable Absorber
Reasonable Emitter
Describe the absorbing and emitting power of: White
Poor Absorber
Poor Emitter
Describe the absorbing and emitting power of: Shiny
Very Poor Absorber (reflects it)
Very Poor Emitter
How does temperature affect the radiation?
The hotter the object, the more radiation occurs.
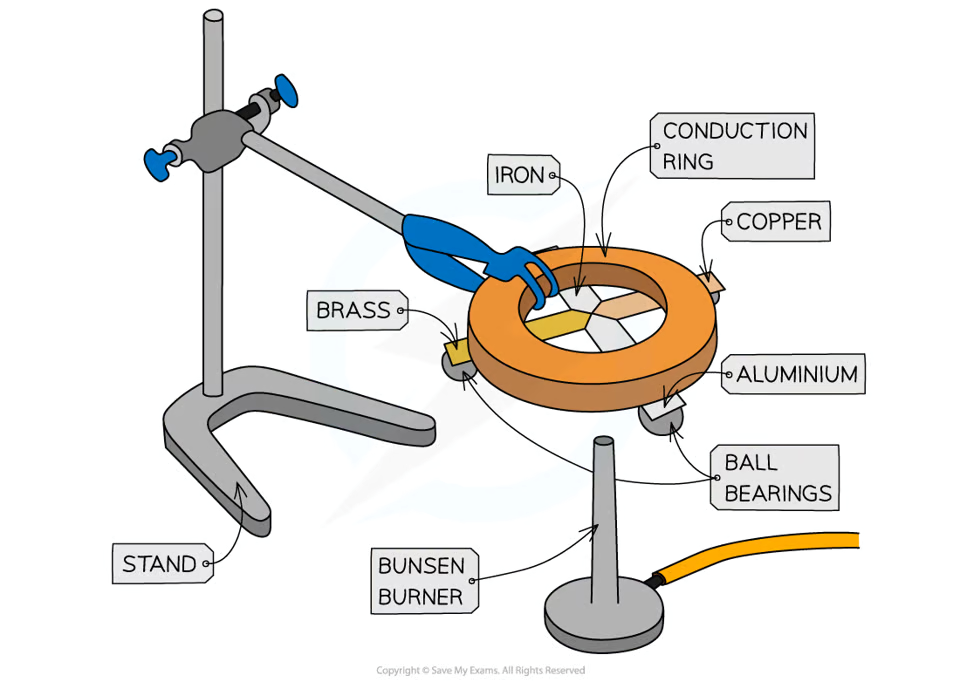
Detail the experiment for conduction:
Investigate the rate of conduction in 4 different metals.
Attach ball bearing to the ends of each metal strip, equal distance from centre, with wax.
Turn the strips upside down and heat the center, where the strips meet, using a Bunsen burner.
When heat is conducted to the ball bearing, the wax will melt and the ball bearing will drop.
Measure the time taken for each strip to drop and record in a table.
Repeat 3 times and calculate an average time for each metal.
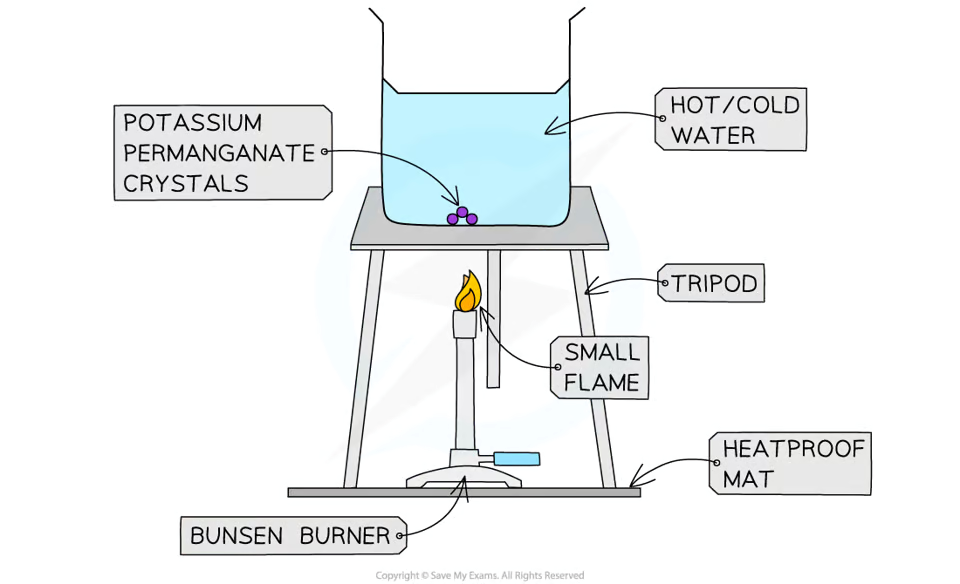
Detail the experiment for convection:
To investigate the rate of convection of potassium permanganate crystals in two different temperatures of water.
Fill the beaker with cold water and put it on top of a tripod and a heatproof mat.
With forceps, drop the crystal into the center of the beaker carefully.
Heat the beaker with a Bunsen burner and record observations.
Repeat the experiment with hot water and record observations.
What should the convection experiment show?
Conduction transfers heat through the beaker.
Water becomes less dense and rises, drawing the dissolved crystal with it.
Water cools at the top and falls, we can see this through the crystal.
Convection current is faster in hot water:
higher temp→ higher kinetic energy
Detail the experiment for radiation:
To investigate how the amount of IR absorbed or emitted by a surface depends on the nature of that surface.
Set up 4 identical flasks painted black, grey, white and silver.
Fill the flasks with hot water- at the same starting temperature.
Measure the temperature at regular temperatures for 10 minutes.
or use a Leslie cube and an IR detector
What should the radiation experiment tell us?
Convection and conduction acts the same in all beakers so any difference in transferred energy must be because of radiation.
Plot a graph of temperature against time and plot all the flasks on it.
Best to worst should be black-grey-white-silver
How can conduction be reduced to conserve energy?
Use materials with low thermal conductivity- insulators.
How can convection be reduced to conserve energy?
Fluid must be prevented from moving so fluid cannot form a current.
How do insulators work?
contain trapped air which is a poor conductor → trapped air means no convection transfer → reduces rate of energy transfer.