Deep Learning - Computer Vision
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
what is deep learning
a subset of machine learning that uses artificial multi-layered neural networks to learn and simulate the complex decision making power of the human brain
what part of ML is DL part of
mainly supervised learning, but has techniques that can be used in unsupervised and reinforcement learning
what is compter vision
a field in AI using DL to teach computers and systems to derive important information from images, videos, and other visual inputs, in order to make recommendations or take certain actions
what can computer vision be used for
image classification
object detection
face recognition
image synthesis
OCR - convert images to machine readable text
enhance image resolution
what is natural language processing
subfield of AI using ML and DL that enables computers to understand and communicate with human language e.g. recognise, generate, and understand text
what can natural language processing be used for
translate text
generate text
sentiment analysis
summarise text
converse with humans
what domains can deep learning be used on
self driving cars
medical imaging
robot navigation
what factors allowed deep learning to grow in popularity
data availability: better training datasets
GPU power: increased computation to train with large datasets and complex models
bigger NN models: can learn better and more complex patterns
hardware-constrained optimisation - using the biggest model that fits in the hardware we have
moore’s law: exponential growth of computing power over time (idea that the number of transistors on a single chip doubles every two years)
difference between an neural network and a perceptron
perceptron is a single layer neural network for linear binary classification while neural network is multi-layered (contains many hidden layers) and can perform more complex tasks with unsupervised learning
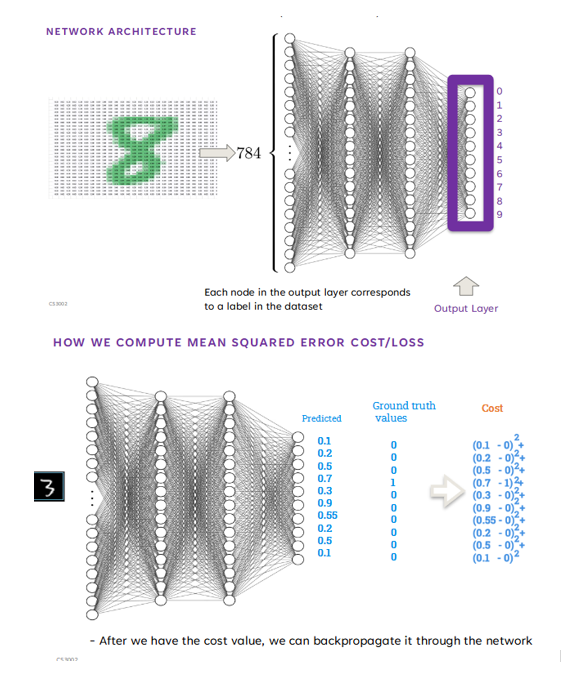
what is the network architecture of a NN
input layer
many hidden layers
output layers where each node in the output layer corresponds to a label in the dataset
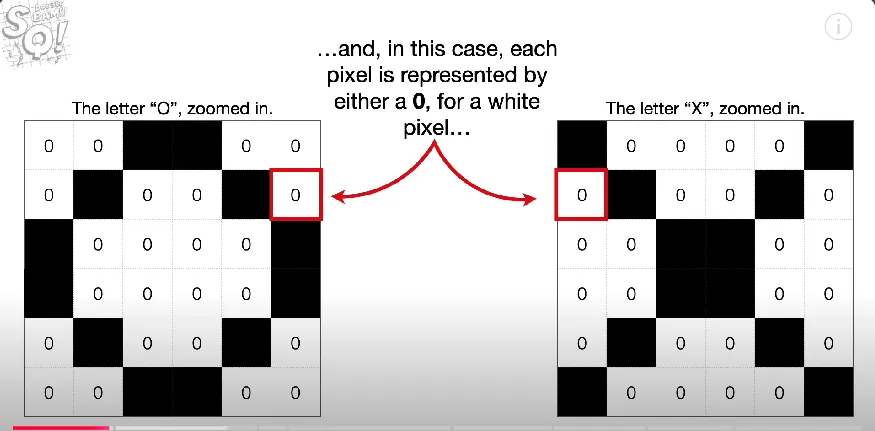
how do computers view images
each image is made up of pixels with different values depending on the colour of the pixel.
what are the steps to train a NN for image classification (basic feed forward network)
weights and bias initialised to random values
each image in the dataset is given as an input to the NN
convert/flatten each image
aka. grid of pixels as a 2D array, into a vector (1D array) of input nodes. e.g. 3×3 image has 9 input nodes, each node in the FIRST hidden layer will have 9 connections - fully connected to each input node
perform a forward pass - activation functions and neuron firing
obtain output as a vector of values (predicted value) for each image
compute the loss, e.g. using mean squared error
after a batch, perform Backpropagation to compute the gradient of the loss for each weight
update the weights by using an optimisation algorithm based on the gradients
repeat forward pass, computer loss, backward pass, weight update for each batch in training data until full epoch has completed
repeat for as many epochs as defined.
what optimisation algorithms can we use to fine-tune the weights
Gradient Descent (Batch Gradient Descent)
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
Mini-Batch Gradient Descent
Momentum
Adagrad (Adaptive Gradient Algorithm)
RMSprop (Root Mean Square Propagation)
Adam (Adaptive Moment Estimation)
Adadelta
Nadam (Nesterov-accelerated Adaptive Moment Estimation)
L-BFGS (Limited-memory Broyden-FletcherGoldfarb-Shanno)
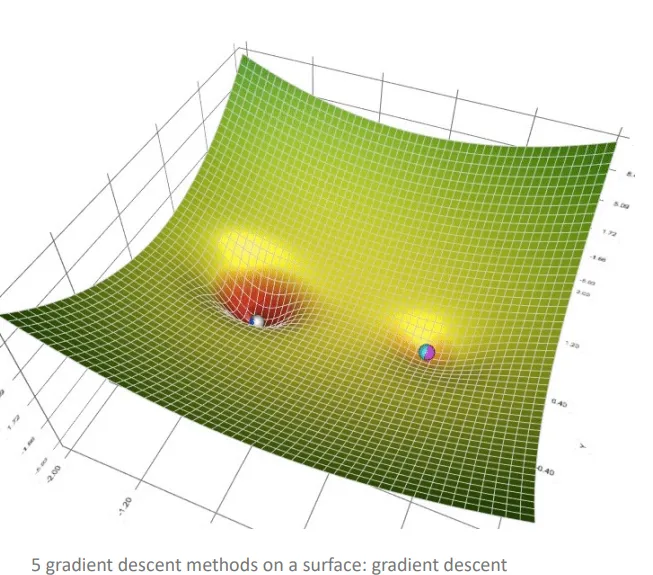
what is the point of gradient descent
lower the loss function for a machine learning problem relatively fast and reliably - not getting stuck at local minima, saddle points, or plateaus but reaching the global minima
optimise the values of all thetas (weights) such that the final combination of weights reduces the loss function to it’s global minima
what is an epoch
1 complete pass through the training data
what is a batch
a subset of the training data, as a hyperparameter defines number of samples to go through before processing instead of processing each data point individually to improve efficiency
e.g. group images and compute mean error, and backpropagate the mean error to update the weights
common batch size is 4 - 512 depending on size of images and memory
how can neural networks be differentiated
shallow networks
deep networks
what is a shallow neural network
have 1 or none hidden layers
faster to train and less prone to overfitting due to smaller size
have limited capability to extract complex features
what is a deep neural network
had many hidden layers
more complex to train and prone to overfitting due to larger size
can extract the hierarchy of features
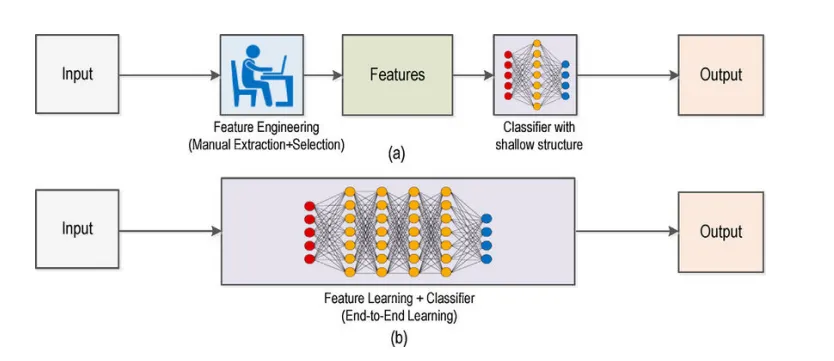
what is the difference between deep learning and machine learning
machine learning requires manual feature extraction and selection, and uses a classifier (machine learning model) with a shallow structure
neural networks have feature learning combined with the classifier
what are some different types of neural networks
recurrent neural networks RNN
deep convolutional networks DCN / CCN
long short term memory LSTM
what is a convolutional neural network
a type of neural network that uses three-dimensional data for image classification and object recognition tasks.
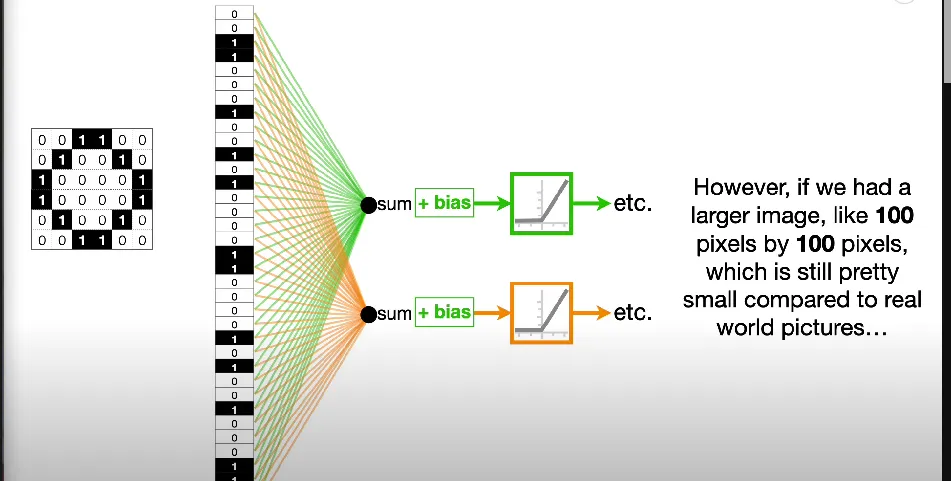
why do we need convolutional neural networks
better for large and complex images
classifying images using a basic feed-forward neural network doesn’t scale well with larger images, since as the number of hidden layers increases, the number of nodes and connections increases, with weights that need to be assigned to each connection - computationally expensive
here, need to estimate 10k weights per node in the hidden layer
not clear if the NN will perform well if the image is shifted by one pixel
doesn’t take into consideration that there may be a correlation between pixels in an image, e.g. a picture of Pongu, blue pixels likely to be near other blue pixels
what do convolutional neural networks do differently to make image classification practical
reduce number of input nodes (pooling)
tolerate small shifts in where the pixels are in the image
takes advantage of the correlation between pixels in complex images (using the filter to look at a region of pixels at a time)
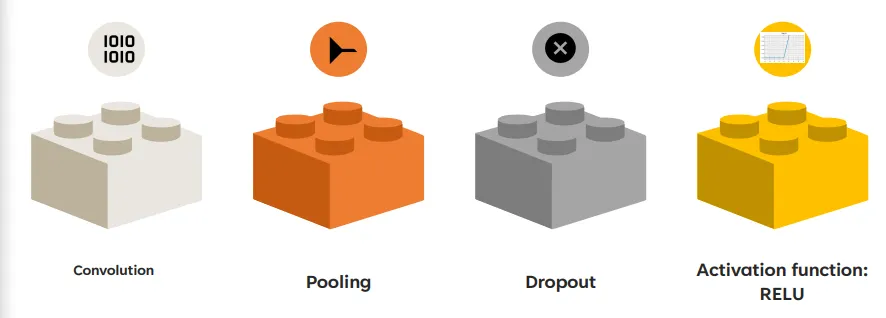
what are the layers/ operations in a CNN
convolution
pooling
dropout
activation function: RELU
what is the convolution operation
applies a filter / kernel to the input image in produce a feature map
what is a filter / kernel
a smaller square (usually 3x3 pixels), that contains a value for each pixel - the intensity of each pixel is randomised at first and then determined by backpropagation
looks at a group of pixels at a time and can detect local features like edges, textures, and patterns in an image
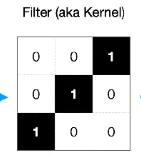
how does the convolution operation work
overlay the filter onto the input image and calculate the dot product for that section
dot product = multiply each overlapping pixel together and then sum the products (and then add bias after)
the dot product is placed on the feature map
shift the filter on the image and repeat the process until the whole feature map has been created (overlap allowed)
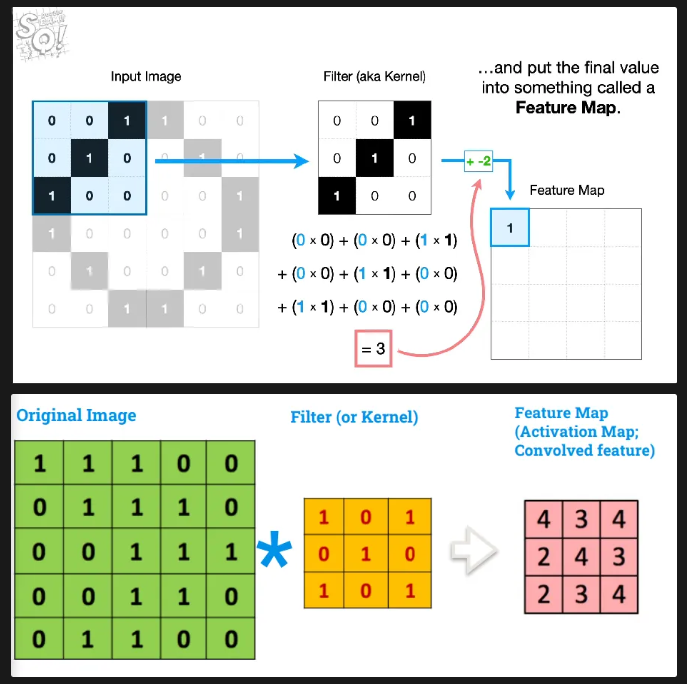
what values do we need to determine to do the convolution operator
filter size - usually 3x3 means 9 weight parameters and 1 bias parameter
step size - by how many pixels should the filter shift at each iteration, e.g. shift by 1 pixel to the right, shift by 4 pixels to the right
what do we do after the convolution operator
run the feature map through the RELU activation function before passing it through the pooling operator
done to introduce non-linearity so that the NN can learn complex patterns (e.g. learning textures and abstract features instead of just edges)

what is the pooling operator
a way of sub-sampling, aka. reducing the dimension (width and height) of the input
reduce the resolution of the feature map while still retaining the important features for classification
how does pooling work
another filter / kernel is applied to the feature map
apply a pooling operator like Max or Average to the overlap and get a value
the filter moves so that it does not overlap, and covers a new area of the feature map
the process is repeated until the whole feature map has been covered and the Pooled Layer output has been produced
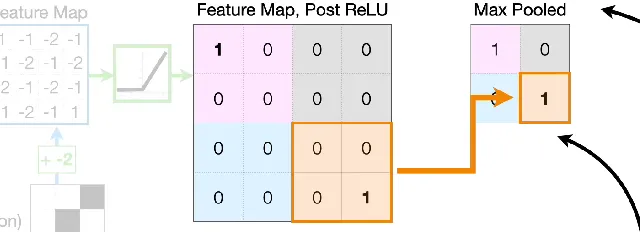
what values need to be defined for the pooling operator
pooling size - similar to kernel size
step
type of operator used, e.g. max pooling or average pooling
what is max pooling
take the highest value from the area covered by the kernel
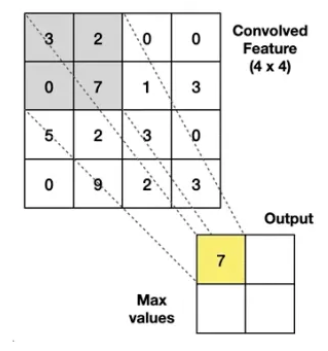
what is average pooling
calculates the average value form the area covered by the kernel
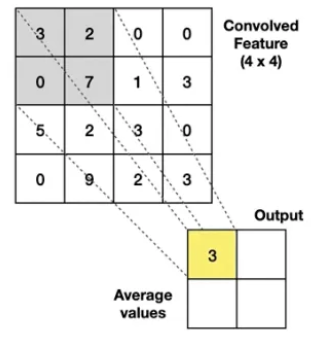
how do we convert the Pooled Layer into a neural network
turn the pooled layer into a vector / column of input nodes and use them as the input nodes for the NN
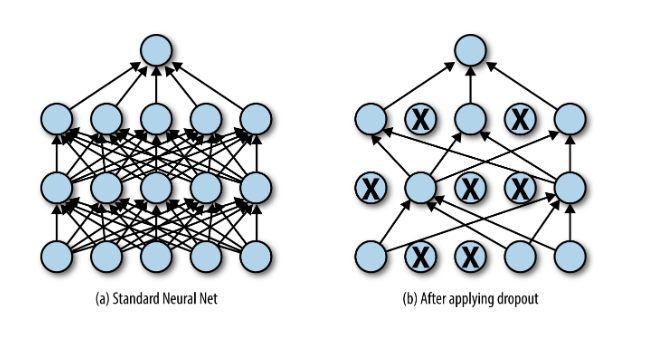
what is the dropout layer
a regularisation technique where nodes are dropped, meaning the activation for that node is considered 0
helps the network generalise better and prevents overfitting
how does dropout occur
dropout rate p
during the training stage, a percentage of nodes are randomly set to 0
during the testing stage, dropout is not enabled, but remaining nodes are scaled up by a factor of (1 - dropout rate) to compensate for the amount of dropped neurons during training, and to make the output more consistent between training and testing (even though all nodes used during testing)
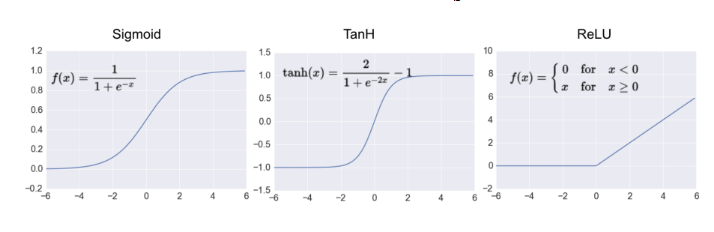
what are the different types of activation functions for convolutional neural networks
TanH
ReLU function - applied to the feature map before pooling
softmax function - applied to the output of the CNN
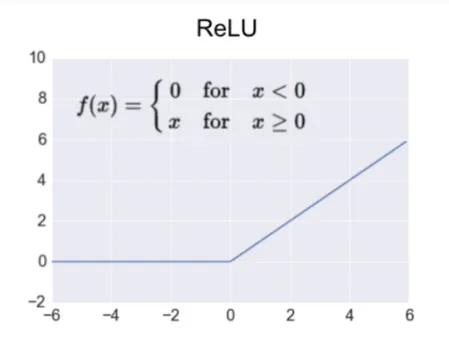
what is the RELU function
a type of activation function that we apply to our feature map before it gets pooled (essentially sets any negative values to 0)
most common function used for deep learning
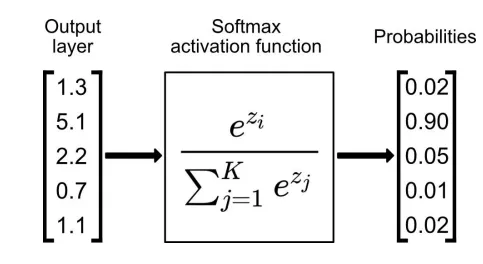
what is the SoftMax function
a nonlinear, unbounded function that maps ‘real-valued’ inputs into a vector of probabilities, where the vector sums to 1
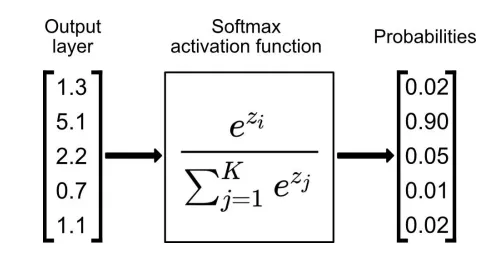
how is the softmax function used
used as the activation function of the last layer of the neural network
the input vector that has the highest probability is the decision made e.g. above, node with 0.9 has the highest activation so that is the most likely classification
that output node will fire, remaining nodes will not fire
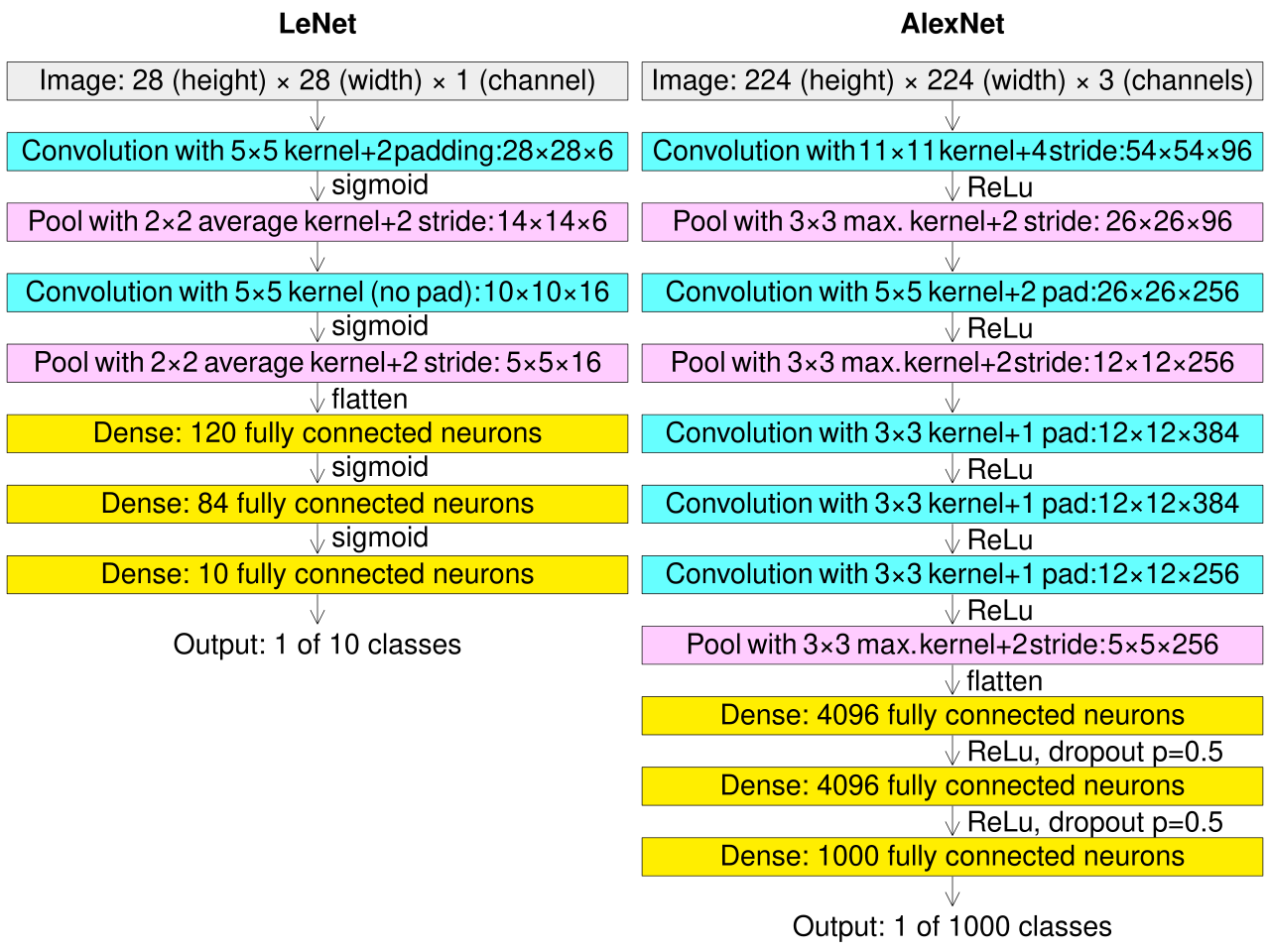
what are examples of CNN architectures (aka. implementations
LENET architecture
ALEXNET architecture
takes the principles of CNN and implements them in different ways, e.g. different number of layers and filters, unstacked vs stacked convolutional layers, different activation functions used
what is transfer learning
a ML technique where a model developed for a particular tasks is reused as the starting point for another model doing another task
what are the advantages of deep learning compared to classical ML
can outperform ML algorithms on most tasks
can learn directly from raw data without needing manual feature extraction which is good for image and speech recognition
same NN architectures can be used for different tasks with only minor modifications
DL models scale well with more data, computational inference time stays same but performance usually increases
transfer learning by fine-tuning is easy and common
what are the disadvantages of deep learning compared to classical ML
small datasets prone to overfitting so requires large labelled datasets to train prevent this
resource intensive and long time to train especially with large datasets (hours to weeks)
black box - meaning difficult to understand the reasoning behind it’s predictions
hyperparameters can significantly affect performance e.g. num layers, type of layers, learning rate, batch size
vulnerable to adversarial attacks where an unnoticed change in the input an cause the model to make incorrect predictions
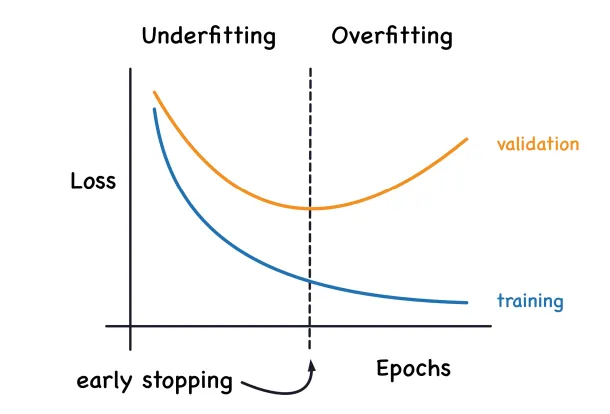
why is it important to monitor the loss of a NN
monitoring the loss helps us monitor the performance of the NN
what is a validation dataset
The sample of data used to provide an unbiased evaluation of a model fit on the training dataset while fine-tuning model hyperparameters.
how does the validation set differ from training and testing set
different from training as training actually makes the NN learn the patterns, but val just improves upon already learnt parameters
different from the test set as val is used for fine tuning and impacts the model, but the test set is only used for evaluation and does not change the model
why could a neural network model not perform well
not enough training data
not trained for long enough - underfitting
trained for too long - overfitting
testing data distribution is different from training data
what programming libraries can be used to create a NN
tensorflow
keras
pytorch