Prokaryotes (Bacteria and Archaea)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are deeply branching bacteria? *
closest living relatives of the earliest living things on Earth
Live in habitats similar to early Earth (Anaerobic to Microaerophilic, + Thermophilic)
Examples = Aquifex and Deinococcus bacterium
Autotrophic + not pathogenic
What are Gram-Negative ProteoBacteria?
Largest + most diverse group of bacteria
Arose from common photosynthetic ancestor
Phylogenetic relationship is based on rRNA studies
Classes of gram-negative proteobacteria include:
- Alphaproteobacteria
- Betaproteobacteria
- Gammaproteobacteria
- Deltaproteobacteria
- Epsilonproteobacteria
What are Alphaproteobacteria?
Class of gram-negative bacteria that can grow in low nutrient conditions
Some have protrusions known as prosthecae*
Stalks or buds
Important! Includes bacteria capable of nitrogen fixation.
Important for plants and animals (us)
What are Non-proteobacteria gram-negative bacteria? *
These are phototrophic bacteria
Have photosynthetic lamellae
5 bacteria types based on pigments + source of electrons
Blue-green (Cyanobacteria)
Green sulfur
Green non sulfur
Purple sulfur
Purple non sulfur
Other Gram-Negative Bacteria *
Phylum - Chlamydiae
Genus: Chlamydia*
Do NOT contain peptidoglycan in their cell walls
Human-to-human transfer
Obligate intracellular parasites
Causes -
Chlamydia trachomatis
Pneumonia
STI’s
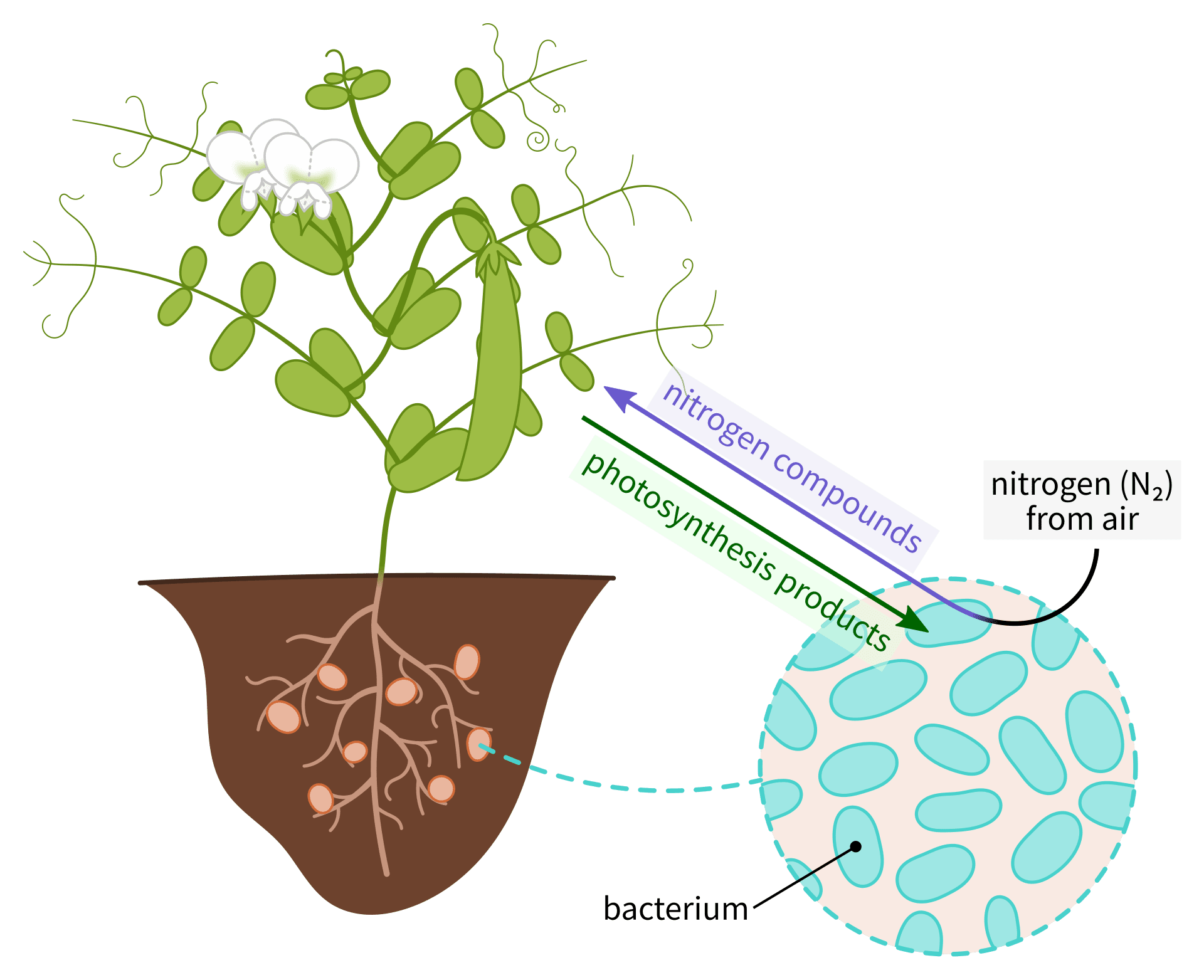
Azospirillium
Soil microorganisms associated w/ roots
Tropical grasses + sugar cane
Symbiotic relationship w/ plants! Mutualism
Fixes nitrogen from the atmosphere usable for plants
Plant provides nutrients for the microorganism
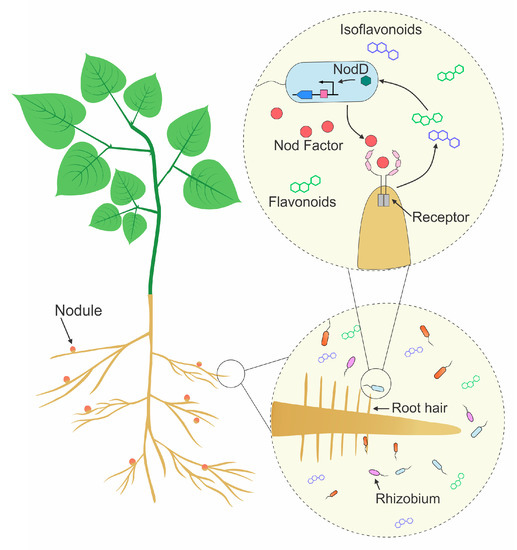
Rhizobium *
Agriculturally important - Infect the roots of legumes, rhizobia
Causes formation of nodules on roots
Mutualism + fixes nitrogen
Grows inside cortical cells, creating the nodules
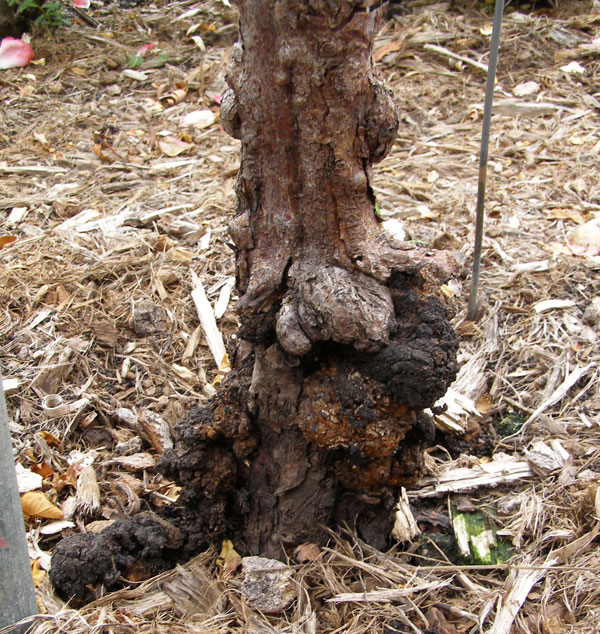
Agrobacterium *
Plant pathogen
Uses horizontal gene transfer causing tumors/gall
Contain plasmids that randomly integrate into the plant’s genome
Agrobacterium tumefaciens - causes Crown gall disease

Nitrobacter and Nitrosomes
Free-living, nitrifying bacteria + in soil
Chemoautotrophs
Crucial to the nitrogen cycle
NO(3) can be used by plants and is better than NH(3)
Motile in soil, easily absorbed, synergistically promotes the uptake of other cations

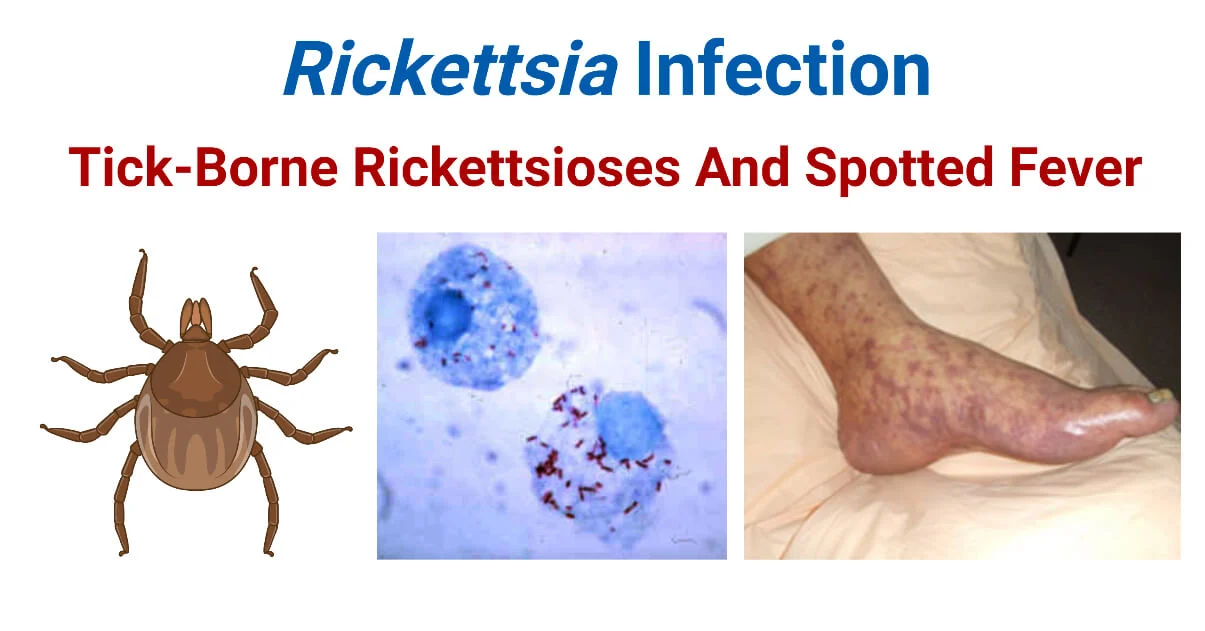
Rickettsia *
Coccobacilli
Obligate intracellular parasite
Only reproduce in mammalian cells
Transmit to humans by insect bites
Enters by phagocytosis, multiplies quickly in host cell
R. rickettsii - causes Rocky mountain spotted fever (ticks = vector)
can lead to amputation, hearing loss, mental disability, 20-30% fatality w/ no antibiotics
Caulobacter *
Found in low nutrient environments - lakes
Have stalks that anchors it to surfaces
Helps catch nutrients in continuous flowing water
Divide by budding
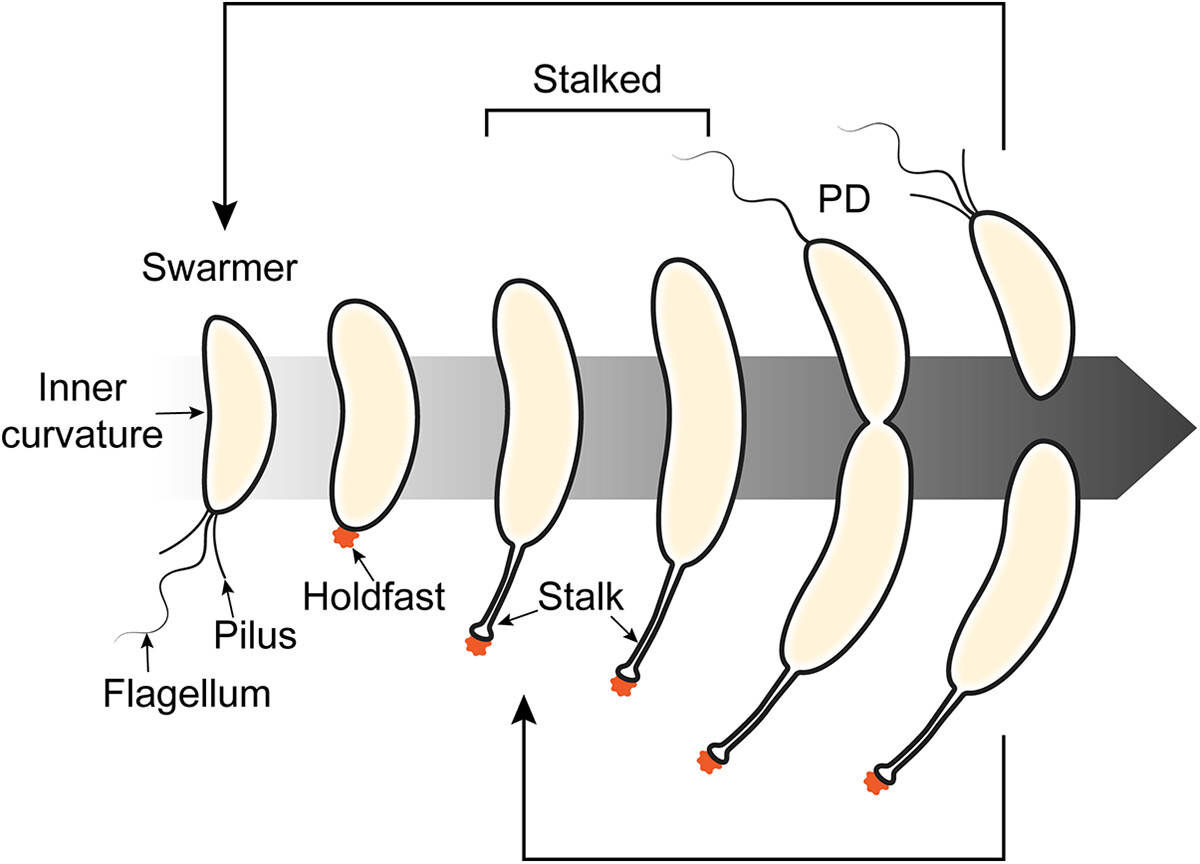
Pseudomonas *
Aerobic, rod-shaped, and moves w/ polar flagella
Very large genomes
Forms fluorescent pigments
Common in soil - decomposition of uncommon chemicals like pesticides
Opportunistic pathogen - causes disease in a weakened host, UTI, and wounds
Produce a variety of enzymes, allowing them to grow on small traces of unusual carbons
grows on soaps + antiseptics
Resistant to antibiotics
Porins in the cell wall won’t allow antibiotics in
Efflux pumps eject antibiotics away
Legionella *
Intracellular pathogens
require a mammalian host to reproduce
Legionella - Found naturally in streams (can infect water supplies)
Can survive + reproduce in aquatic amoebas = hard to eradicate
Causes legionnaires disease (pneumonia)
NOT transferable person-to-person
Enterobacteriaceae (Enterics) *
Large family of gram-negative bacteria
Facultative anaerobes, rods, if mobile it is peritrichously (all over) flagellated
Called Enterics - found in intestinal tracts
Active fermenters of glucose + other carbohydrates
Fimbrae helps adhere to surfaces, pili - exchange genetic info
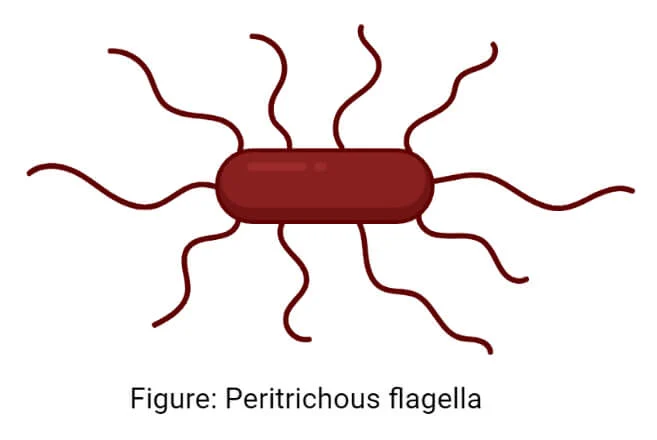
Examples of Enterics (7)
Escherichia -
Most numerous inhabitant of our gut
Important to science and biotechnology
Indicator of fecal contamination in water
Not usually pathogenic, E.coli 0157 = serious food poisoning
Salmonella -
All members of the genus are potentially pathogenic
Causes Salmonellosis
Shigella -
Shigellosis: Life-threatening, bloody diarrhea w/ fever and cramps. Toxins produced.
Klebsiella -
Found in soil + water
Many islets can fix nitrogen
Occasionally causes serious pneumonia
Yersinia -
Yersinia pestis: Bubonic plague
Ground squirrels in southwest
Fleas on animals → humans
Proteus -
Swarm on agar plates
Causes UTI in patients w/long-term catheterization
Serratia -
Produces red pigment at 25 degrees Celsius
Found in catheters & irrigation solutions (Urinary + respiratory tract infections)
Bdellovibrio (genus) *
Attaches and penetrates the membrane of other gram-negative bacteria and reproduces in the periplasm
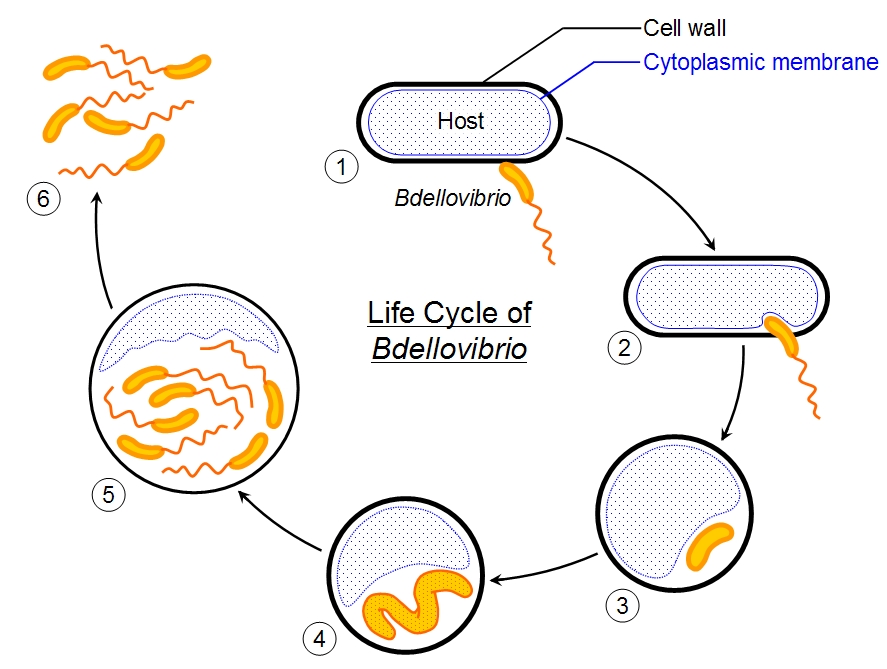
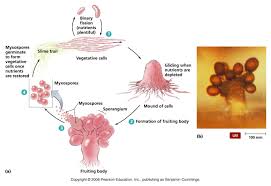
Myxobacteria (group) *
Vegetative cells glide and leave a slime trail
Digest bacteria they encounter
Form a mound in low-nutrient environments and then becomes a fruiting body that produces spores
Cyanobacteria (group) *
Blue-green pigment
Does photosynthesis
Most can fix Nitrogen from the atmosphere
occurs in specialized cells called heterocysts
Unicellular to colonial to filamentous
Their filamentous form exhibits cellular differentiation
Gram-Positive Bacteria (Low G + C) *
DNA has lower % of Guanine and Cytosine, < 50%
Phylum - Firmicutes
Important for endospore formers
Includes:
Clostridia* (21-54%)
Mycoplasma (23-40%)
Bacilli
Listeria
Lactobacillus
Cocci
Streptococcus*(33-44%)
Enterococcus
Staphylococcus*
Gram-Positive Bacteria (High G + C) *
DNA contains high G + C content, > 60%
Phylum - Actinobacteria
High pleomorphic morphology
Alters shape + size in response to environmental conditions
Includes:
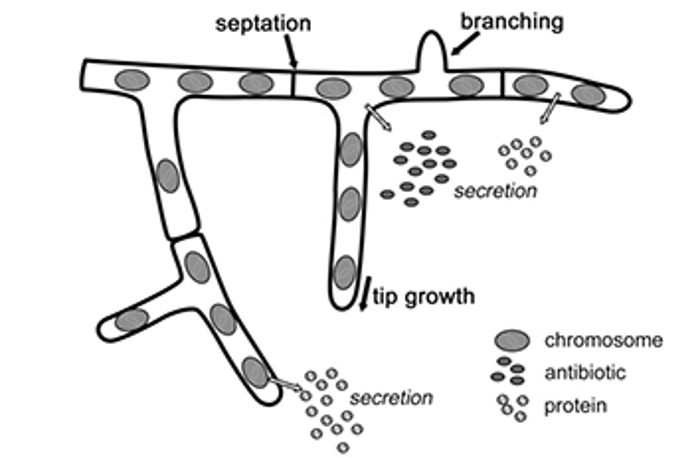
Streptomyces* - branching filament growth (star-like colonies)
Mycobacterium* - TB and leprosy
Streptomyces
Filamentous growth
Aerobic, found in soil
Have spores at the end of aerial filaments
Produce most of our common antibiotics
Antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic
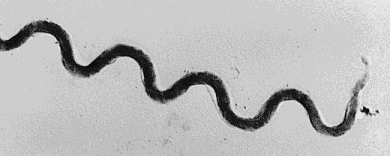
Spirochetes
Coiled morphology
Axial filaments: Corkscrew-like motility
Found in the human oral cavity
Associated diseases:
Treponema - Syphilis
Borrelia - Lyme disease
Mycobacterium
Aerobic, non-spore-forming rods
Distinctive cell wall
Acid fast
Drug resistance
Pathogenicity
Causes:
M. tuberculosis
M. leprae
Skin sores, nerve damage, muscle weakness
Streptococcus
Spherical, usually in chains
Produce extracellular substances, contributing to pathogenesis
Enzymes that:
Destroy phagocytic cells
Digest connective tissue
Digest fibrin in blood clots
Responsible for the most illnesses/diseases than any group
Beta-hemolytic: Produce hemolysin that lyses blood cells forming clear zones on blood agar plates
S. pyogenes, “Group A Strep)
Scarlet fever
Sore throat
Rheumatic fever
S. agglactiae “Group B Strep)
Postpartum infections + neonatal sepsis
Alpha-hemolytic:
Appears greenish hue on blood agar due to partial destruction of blood cells
S. pneumoniae -
Pneumococcal pneumonia
S. mutans -
Dental decay
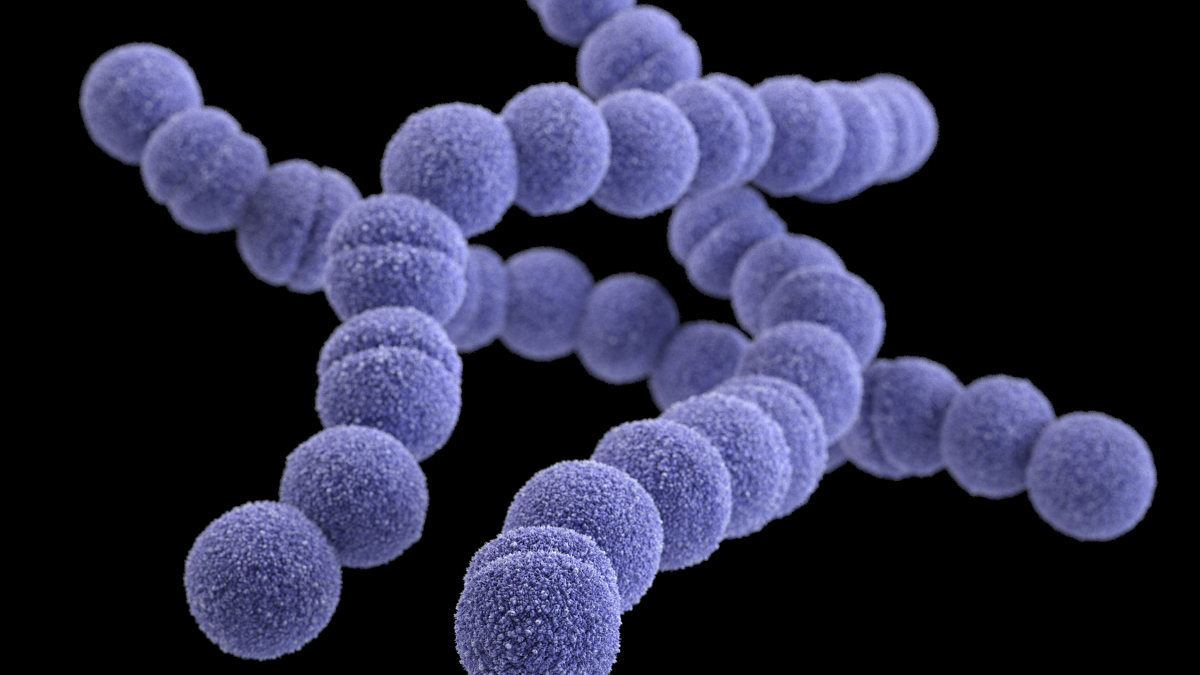
Staphylococcus
Cocci, “grape clusters”
Grows in nasal passages + skin, normal microbiota
S. aureus -
MRSA
Infection of wounds of surgical procedures
Production of toxins contributing to pathogenicity
Toxic shock syndrome
Becomes drug-resistant quickly
Archea
Common features:
Lack of true peptidoglycan
Cell membranes have branched hydrocarbon chains
Start codon - methionine
Reproduction: Binary fission or budding
Cocci, bacilli, or spiral
NOT disease causing
What are Extremophiles?
Organisms that thrive in extreme environmental conditions
What are Methanogens?
Anaerobic
Convert CO2, H2, and organic acids into Methane (CH4)
Convert organic wastes in ponds, lakes, and the ocean
Thermophiles
DNA, RNA, cytoplasmic membranes, and proteins don’t function below 45 degrees Celsius
Found in hot springs, deep sea vents, etc.
Halophiles
Thrive in high salt concentrations. Require > 9% NaCl to maintain cell wall integrity
Found in -
Salted fish and hyper saline lakes
Acidophiles
Grow in low pH
volcanic fields, sulfuric acid pools
Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
Azospirillium
Nitrobacter
Nitrosomes
Rhizobium
Klebsiella (enteric)
Cyanobacteria
Clostridium (Clostridia)
Obligate anaerobes
Rod-shaped w/ endospores
Plays an important role in pathogenicity + food spoilage
Diseases associated w/ clostridia
C. tetani
C. perfringens
C. botulinum
C. difficile
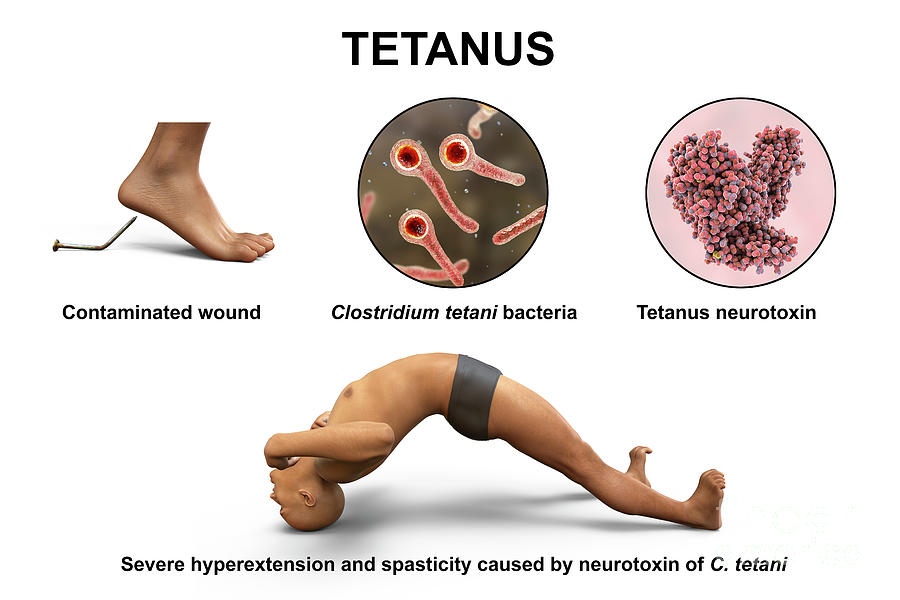
C. Tetani
Tetanus
Infection characterized by muscle spasms
Contaminated objects
C. perfringens
Normal in decaying vegetation and microbiota of animals, insects, and marine sediments
Foodborne disease
Gas gangrene - open wounds
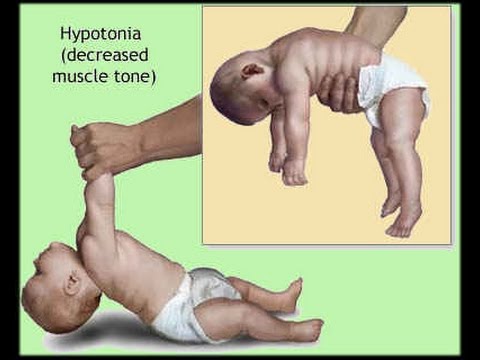
C. botulinum
Botulism - muscle weakness
Floppy baby syndrome
C. botulinum spores in honey
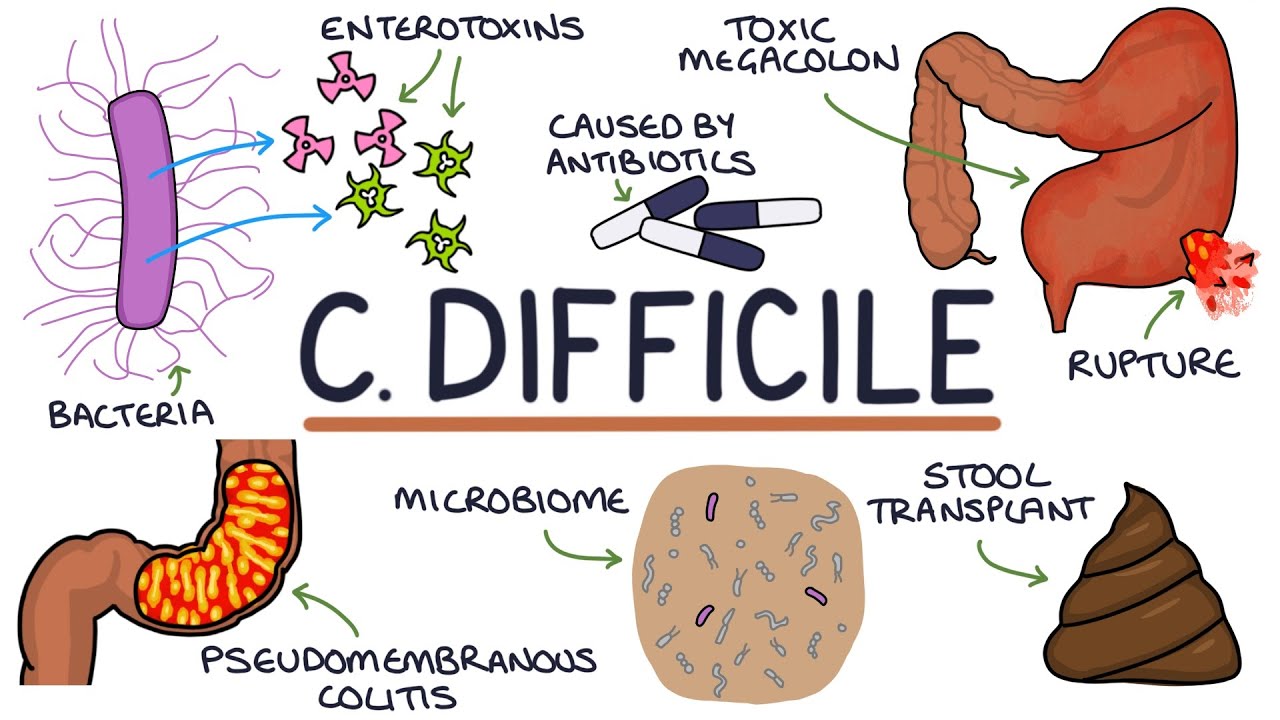
C. difficile
Diarrhea (C. diff)
Wash hands w/ water