enzymes
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Enzymes
Globular proteins, with a specific tertiary structure, which catalyse metabolic reactions in living organisms. Biological catalysts which speed up chemical reactions and are not used in the reaction.
Catalyst
A molecule that speeds up a chemical reaction without being used up itself.
Substrate
A substance that is used up in an enzyme controlled reaction, leading to the formation of a product.
Enzyme-Substrate Complex
Intermediate structure formed when a substrate molecule binds to an enzyme's active site.
Enzyme-Product complex
Intermediate structure in which product molecules are bound to an enzyme's active site.
Primary Structure
The sequence of amino acids found in a protein molecule joined by peptide bonds.
Tertiary Structure
The 3D shape of a protein molecule held together by hydrogen bonds, disulphide bridges, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions.
Active site
An area on an enzyme molecule which the substrate binds as it is the complementary shape.
Allosteric site
Another part on a enzyme where a substrate could bind, away from the active site.
Carbohydrase
Enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds.
Lipase
Enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of ester bonds.
Protease
Enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of peptide bonds.
Activation Energy
The level of energy required to enable a reaction to take place.
Lock and Key
The theory in which the enzyme active site is complementary to the substrate molecule.
Induced Fit
The theory in which the enzyme active site changes shape to fit the substrate more closely as it binds to it.
Denature
When an irreversible change has been made to the tertiary structure of a protein molecule, leading to loss of function.
Optimum
Condition that gives the fastest rate of reaction in enzyme controlled reactions.
Metabolism
The chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life e.g respiration and photosynthesis.
How does the role of enzymes affect metabolism at a cellular level?
Allows products in a metabolic pathway to be formed quicker.
Intracellular enzymes
- Remain within cell walls
- Reduce the energy used inside the cell for the reaction.
- E.g DNA Polymerase in DNA
Extracellular enzymes
- Work outside the cell
- This makes it easier for the cell to bring it into the cell for further processing.
- E.g Trypsin in digestion
What is the role of catalase in catalysing intracellular reactions?
This ensures hydrogen peroxide is broken down to harmless water and oxygen.
What is the role of amylase and trypsin in catalysing extracellular reactions?
- Amylase breaks down starches (carbohydrates) into sugars.
- Trypsin breaks down proteins into amino acids.
Specificity
The active site of an enzyme is a specific shape, depending on the reaction that it catalyses, meaning that other molecules won't fit into the active site.
Lock and key hypothesis
The theory of enzyme action in which the enzyme active site is complementary to the substrate molecule, like a lock and key.
Induced fit hypothesis
The theory of enzyme action in which the enzyme molecule changes shape to fit the substrate molecule more closely as it binds to it.
Enzyme substrate complex
The intermediary formed when a substrate molecule binds to an enzyme molecule.
Enzyme product complex
The intermediate structure in which product molecules are bound to an enzyme molecule lowering.
Lowering the activation energy
Enzymes reduce the activation enthalpy so the reaction can proceed at a much lower temperature
What are the effects of pH on enzyme activity?
- Low pH means lots of H+ ions, high pH means little H+ ions
- Either extreme of H+ ion concentration can interfere with the hydrogen and ionic bonds holding the tertiary structure together.
- The pH affects the charge of the amino acids at the active site, so the properties of the active site change and the substrate can no longer bind.
- reaction slows and stops, enzyme is denatured
What are the effects of temperature on enzyme activity?
increasing temp, increases KE of particles
particles collide faster/ more frequently
more enzyme-substrate complexes form
higher temps cause the bonds in tertiary structure to break
active site changes shape, enzyme denatures
active site is no longer complementary to substrate
What is Q10?
The temperature coefficient (Q10) of a reaction is a measure of how much the rate of reaction increases with a 10 degree increase in temperature. However, this no longer applies when the enzymes have denatured.
What are the effects of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity?
- As enzyme concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases as there are more active sites available
- This carries on until the substrate concentration becomes a limiting factor and the rate stops increasing.
What are the effects of substrate concentration on enzyme activity?
- As the substrate concentration rises, the rate of reaction rises because there are more substrate molecules to react.
- At higher concentrations, all of the active sites become filled, so the rate of reaction remains the same.
Give an example on how you could measure the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction.
Measure how fast oxygen is given off when catalase is used to catalyse the break down of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
Coenzymes
Small, organic, non-protein molecules that temporarily bind to an enzyme before or same time substrate binds and is needed to allow the enzyme to function
Cofactors
Ions that increase the rate of enzyme-controlled reactions.
Prosthetic group
A (co-factor) non-protein group combined with a protein.
Why are co-enzymes needed in some enzyme controlled reactions?
They carry chemical groups between enzymes so they link together enzyme-controlled reactions that need to take place in sequence.
Why are cofactors needed in some enzyme controlled reactions?
They help enzymes and substrates to bind together which helps to speed up the rate of enzyme controlled reactions.
Why are prosthetic group needed in some enzyme controlled reactions?
They are cofactors that bind tightly to proteins or enzymes and help to catalyse some enzyme controlled reactions.
Zn2+
A prosthetic group for carbonic anhydrase.
Cl-
Cofactor for amylase.
Vitaimins
A source of co-enzymes.
what is an inhibitor?
any substance or molecule that slows down the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction by affecting the enzyme molecule in any way
What is the effect of a competitive inhibitor on the rate of enzyme controlled reactions?
- similar shape to substrate ∴ complementary shape to active site
- binds to active site instead of substrate
- can be irreversible or reversible
- slows down the ROR as there is competition between inhibitor and substrate for active site
- effects can be overcome by adding more substrate
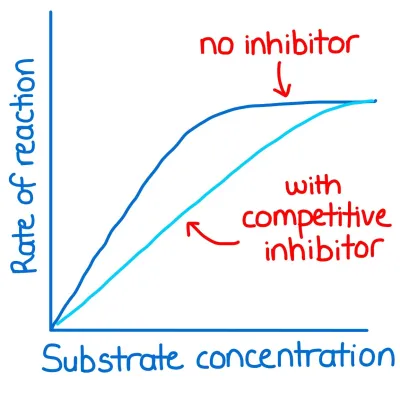
What is the effect of a non competitive inhibitor on the rate of enzyme controlled reactions?
- different shape to active site
- Attach to the enzyme in a region away from the active site (allosteric site).
- This distorts the tertiary structure of the enzyme molecule,
- changes active site
- Substrate can no longer fits into the active site so the enzyme-substrate complexes cannot form and the reaction rate decreases.
- Most bind permanently to the enzyme molecule.
- Irreversible reaction
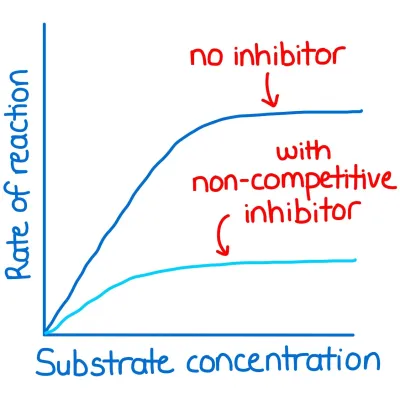
Reversible inhibitors
When the bonds are weak H or ionic bonds and the inhibitor can be removed.
Irreversible inhibitors
When the bonds are strong and covalent and the inhibitor cant be removed easily.
Medicinal drugs
Examples include antiviral drugs and antibiotics.
How do antiviral drugs work?
They inhibit the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which catalyses the replication of viral DNA. This stops the virus from replicating.
How do antibiotics work?
They inhibit the enzyme transpeptidase, which catalyses the formation of proteins in bacterial cell walls. This weakens the cell wall which therefore bursts and the bacterium is killed.
State 3 enzyme that catalyses respiration reactions.
Cytochrome c oxidase, dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Metabolic poisons
These interfere with the reactions which occur in cells and cause damage, illnes or death (often enzyme inhibitors)
State three metabolic poisons
- Cyanide
- Malonate
- Arsenic
Cyanide
An irreversible inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase so that cells cant respire, die.
Malonate
An irreversible inhibitor of dehydrogenase so that cells cant respire, die.
Arsenic
An irreversible inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase so that cells cant respire, die.
Metabolic pathway
- A series of connected metabolic reactions (the productvof the first reaction takes part in the second reaction)
- Each reaction is catalysed by a different enzyme.
Product inhibiton
Where enzymes are inhibited by the product of the reaction they catalyse.
End product inhibiton
When the final product in a metabolic pathway inhibitis an enzyme that acts earlier on in the path way.
What is the importance of end product inhibition?
Controls the amount of end product that gets made. Eg. 1. Phosphofructokinase is involved in breaking down glucose to make ATP.
- ATP inhibits the action of phosphofructokinase.
- Therefore, a high level of ATP stops more ATP from being made.
How does enzyme inhibition help to protect cells?
- Enzymes can be synthesised as inactive precursors in a metabolic pathway.
- This prevents damage to cells.
- Part of the precursor molecule inhibits its action as an enzyme.
- Once this part is removed (by a chemical reaction) the enzyme becomes active.
inactive precursor
- enzymes that require biochemical changes for it to become active
what activates an inactive precursor
- adding a cofactor
- change inn conditions
- action of another enzyme