Cell Respiration Task Cards
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
List two reasons why food is important to living organisms
1. food is full of energy to build ATP
2. used to build macromolecules
Name the principal molecule that stores and releases energy as needed to the cells of a living organism
ATP
ATP and ADP are initials for what words?
ATP - Adenosine Triphosphate
ADP - Adenosine Diphosphate
Describe two basic differences between ADP and ATP
1. energy poor and energy rich
2. 2 phosphates, 3 phosphates
List the three basic components of an ATP molecule
1. Nitrogenous Base
2. Ribose Sugar
3. Phosphate Groups
What is the role of ATP in living cells?
energy
How does ADP become ATP?
stick a phosphate group onto ADP
What happens when a phosphate molecule is removed from ATP?
it gives off energy (electrons)
List three cellular processes that require the energy from ATP
1. muscle contractions
2. pumping against the gradient
3. cell division
4. ribosomes
5. protein transport
Fill in the blanks: Energy flows into an ecosystem in the form of ___a___ and leaves as ___b___.
a. sunlight
b. heat
Describe the relationship that exists between photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
they depend on each other (products & reactants)
Write the definition of cellular respiration
taking in glucose and releasing its energy slowly to make ATP
Which living organisms carry out cellular respiration?
all living organisms
Write a chemical equation that gives the reactants and products of cellular respiration.
6O2 + C6H12O6 = 6CO2 + 6H2O
In order to carry out cellular respiration, eukaryotic organisms require what cell organelle?
mitochondria
Do prokaryotic organisms carry out cellular respiration? If so, how?
yes; on the cell membrane
Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic respiration
aerobic - requires oxygen
anaerobic - requires no oxygen
List the three main stages of cellular respiration (include aerobic or anaerobic)
1. glycolysis - anaerobic
2. krebs cycle - aerobic
3. ETC - aerobic
What stage of cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell?
glycolysis
What stages of cellular respiration occur in the mitochondria?
krebs cycle and ETC
Describe the process of glycolysis in one sentence.
splitting of glucose
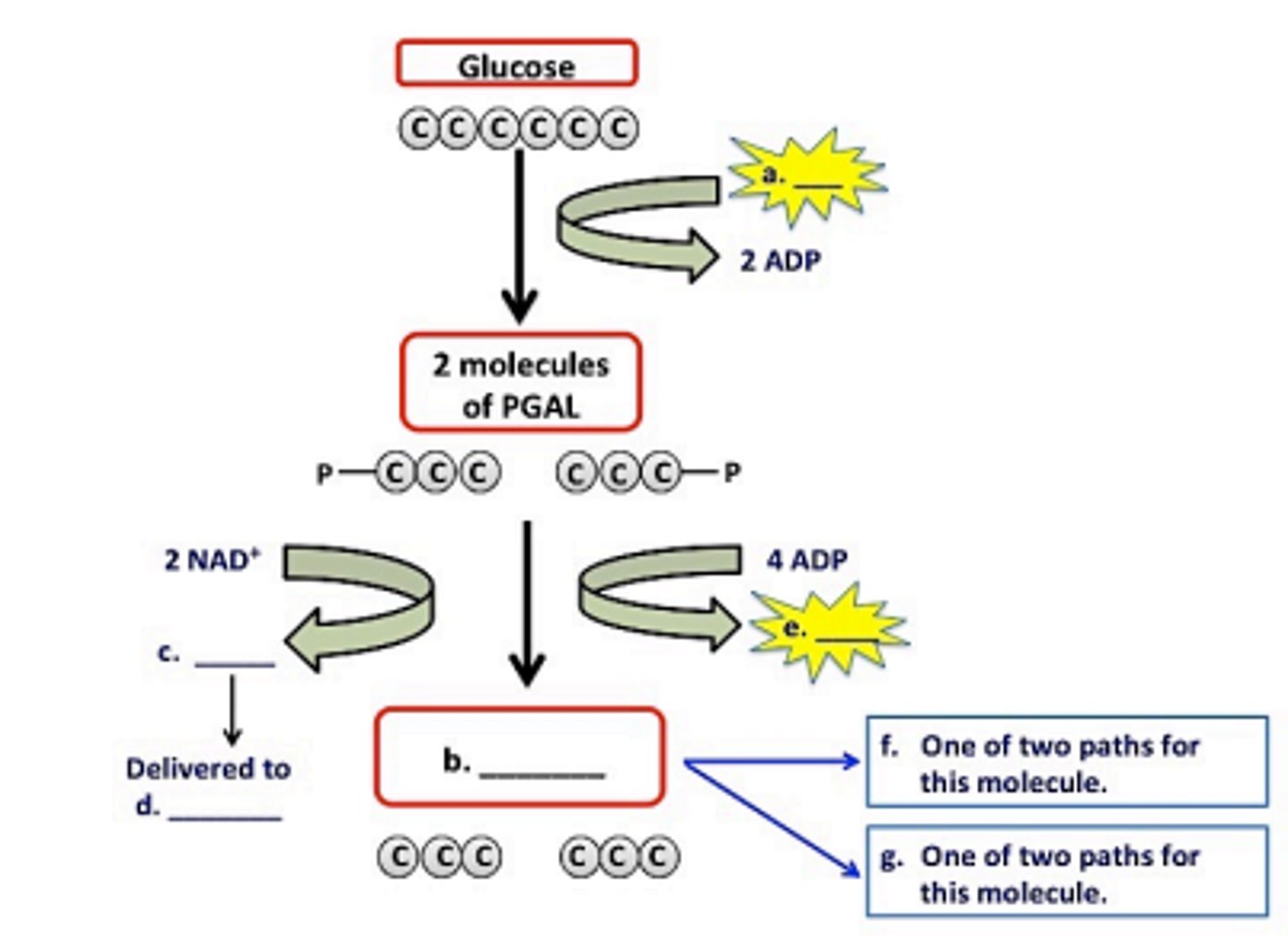
Even though respiration is an energy-releasing process, a small amount of energy must be invested to get the reactions going. During glycolysis, the energy of ___a___ ATP is consumed, but by the end of the process, ___b___ ATP are produced.
a. 2
b. 4
What is NAD+ and what is its role in cellular respiration?
electron carrier; carries energy to ETC
What molecule is formed when NAD+ accepts a pair of high-energy electrons?
NADH (high energy molecule)
How many molecules of NADH are produced during glycolysis?
2
As molecules of NADH are produced, they will be delivered to what stage of respiration?
ETC
List three end products of glycolysis
1. NADH
2. ATP
3. Pyruvic Acid
What are two possible paths for the pyruvic acid molecules produced in glycolysis?
1. aerobic respiration (mitochondria)
2. anaerobic/fermentation (cytoplasm)
What are the two advantages of glycolysis?
1. ATP (makes lots of)
2. requires no oxygen
What is a disadvantage of glycolysis?
1. runs out of NAD+
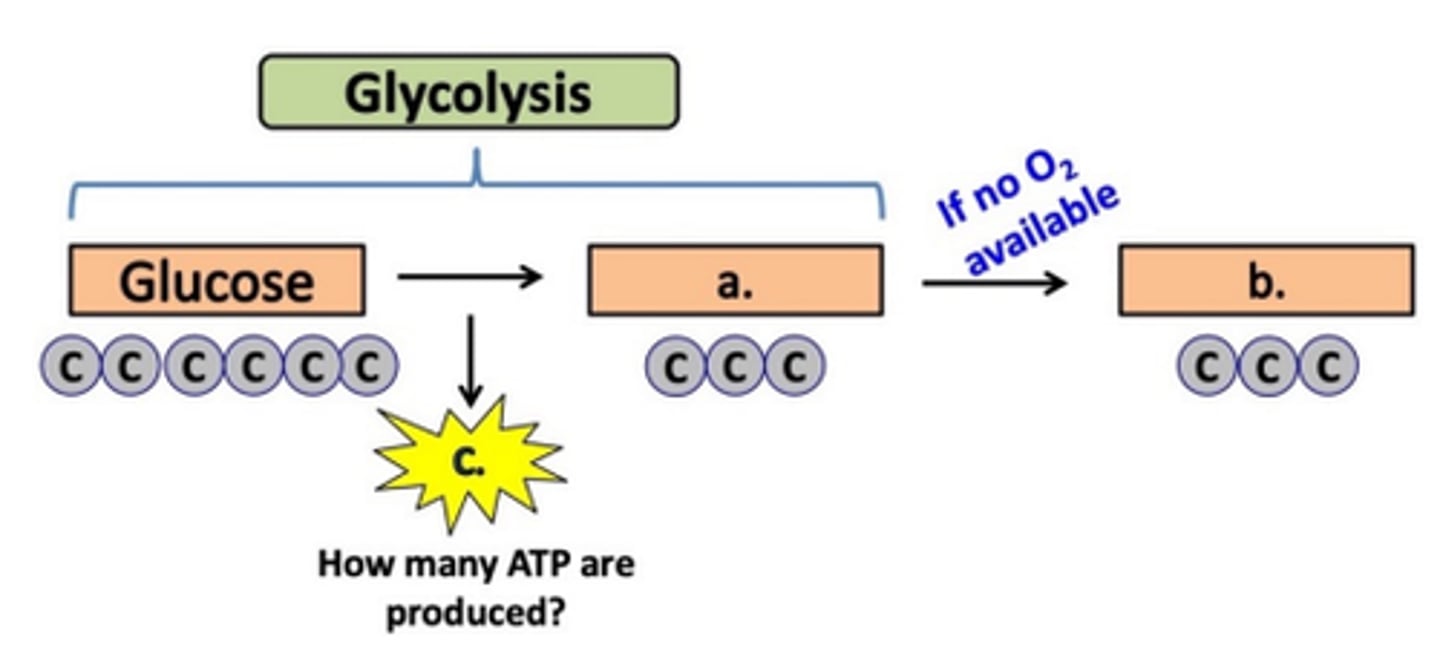
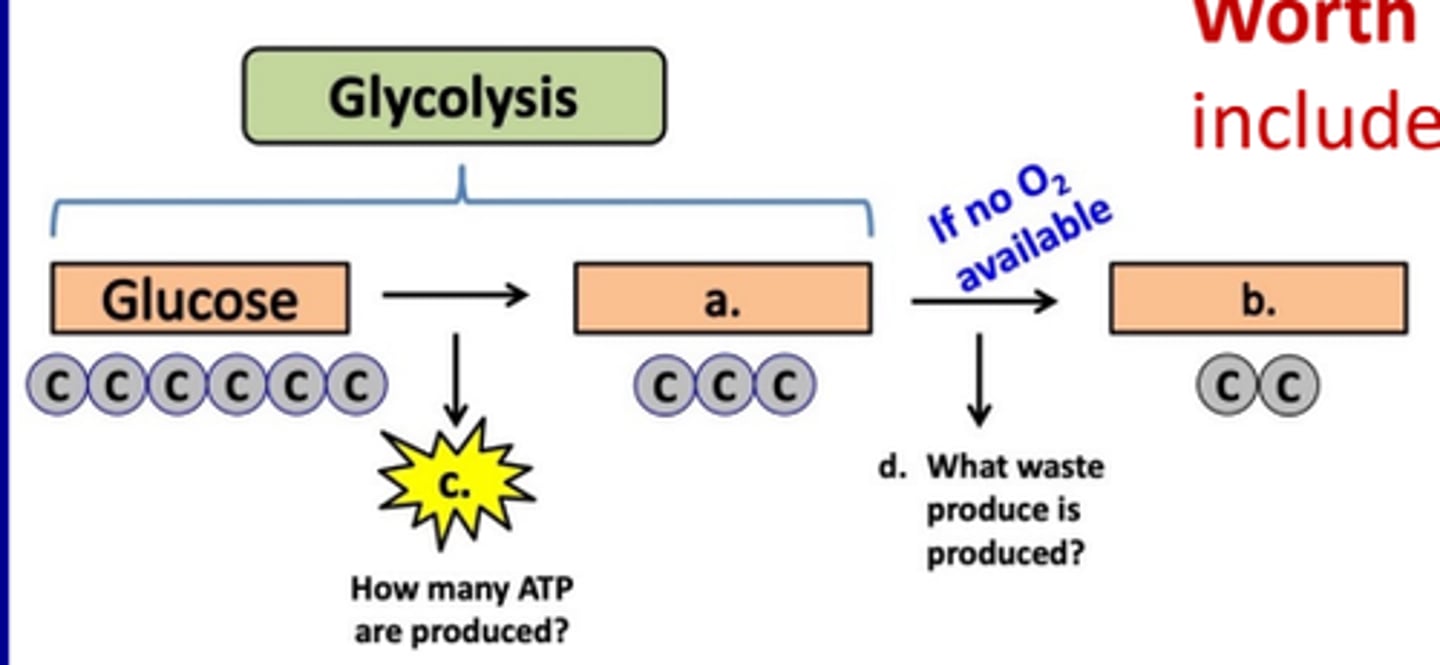
Summary of glycolysis. Fill in the missing parts (a-g) in the diagram below.
a. 2 ATP
b. 2 pyruvic acid
c. 2 NADH
d. ETC
e. 4 ATP
f. aerobic respiration
g. anaerobic respiration
What happens to the pyruvic acid that is produced during glycolysis if NO oxygen is avaliable to the cell? Fill in the missing parts (a-c) in the diagram below.
a. fermentation
b. cytoplasm
c. 0
What happens to the pyruvic acid that is produced during glycolysis if oxygen is available to the cell? Fill in the missing parts (a-c) in the diagram below.
a. aerobic respiration
b. mitochondria
c. 34
Label the structures of a mitochondrion
a. DNA
b. ribosomes
c. matrix
d. outer membrane
e. inner membrane
f. cristae
g. inter-membrane space
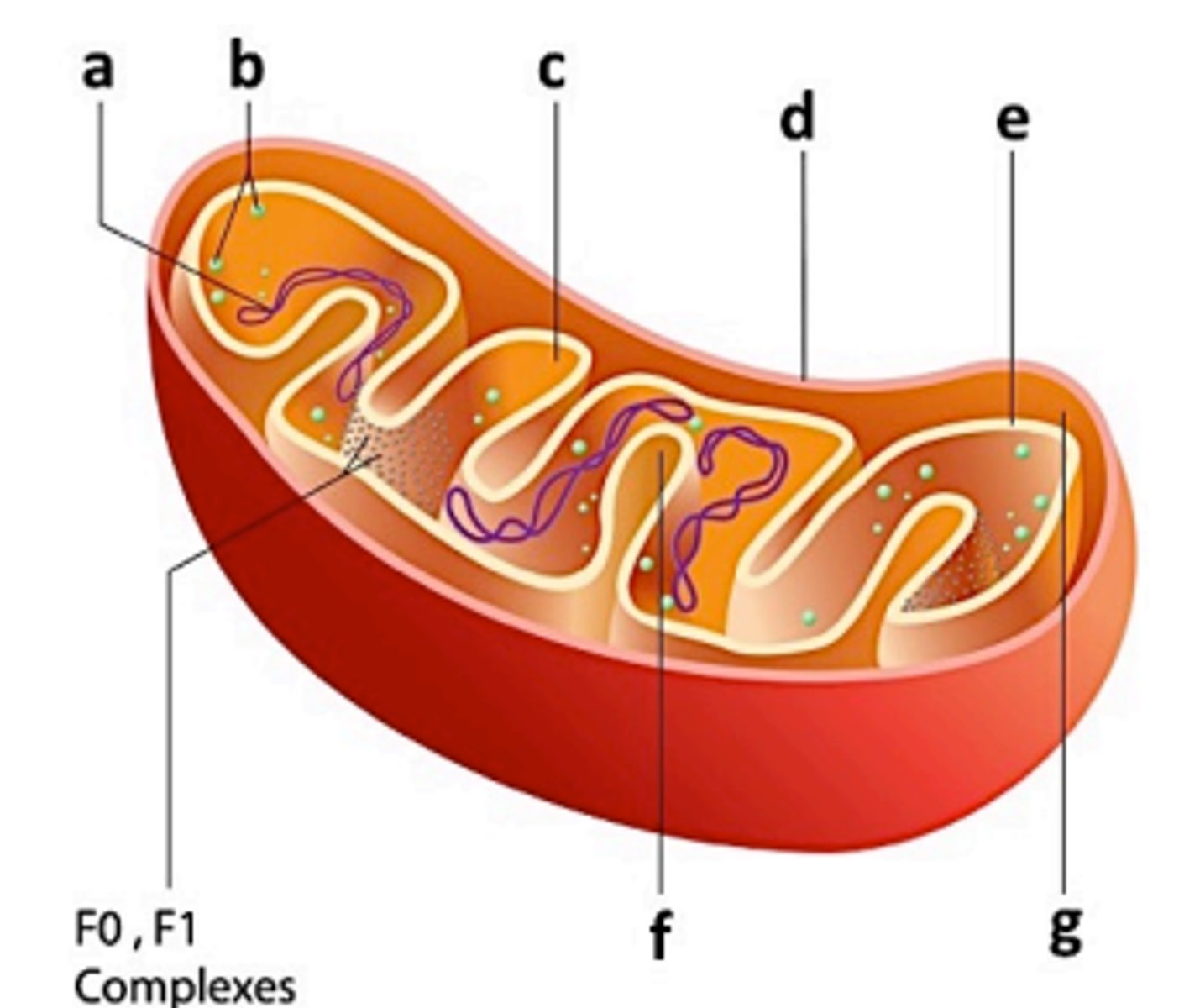
What name is given to the space inside the mitochondria that contains enzymes, DNA, and ribosomes?
matrix
The inner membrane of the mitochondria has many loops and folds. What name is given to these loops and folds, and what is their purpose?
cristae; increases surface area (more ATP can be made)
What two stages of aerobic respiration occur inside the mitochondria? Where in the mitochondria does each take place?
1. krebs cycle
2. ETC
The Krebs cycle begins when _______ produced by glycolysis enters the mitochondrion.
pyruvic acid
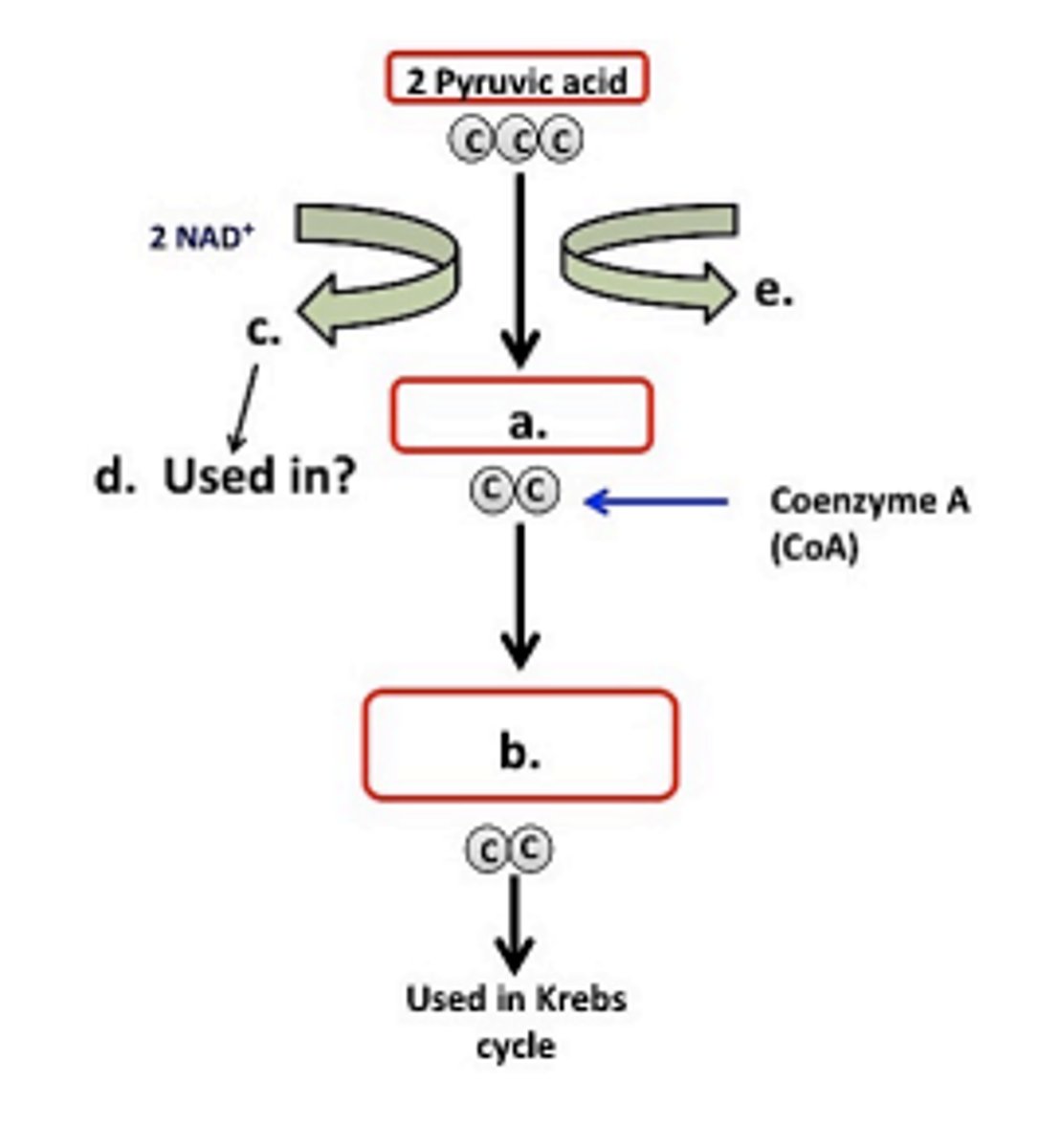
The Krebs cycle begins with a series of reactions that are sometimes referred to as the bridge reactions. In this set of reactions, pyruvic acid is converted into what compound?
2 acetyl CoA
For each pyruvic acid converted into acetyl-CoA:
a. How many molecules NADH are formed? What happens to them?
b. How many molecules of carbon dioxide are formed? What happens to them?
a. 2; goes to ETC
b. 2; exhaled out
Summary of the bridge reaction. Fill in the missing parts (a-e) in the diagram below.
a. acetate
b. 2 acetyl CoA
c. 2 NADH
d. ETC
e. 2 CO2
List four products that are continually produced in the Krebs cycle.
1. ATP
2. FADH2
3. NADH
4. CO2
What are NAD+ and FAD, and what is their role in the Krebs cycle?
electron carriers; turned into high-energy molecules
What is the total amount of each of the following produced during the Krebs cycle per molecule of pyruvic acid?
a. CO2
b. ATP
c. NADH
d. FADH2
a. 2 CO2
b. 1 ATP
c. 3 NADH
d. 1 FADH2
What is the total amount of each of the following produced during the Krebs cycle per molecule of glucose?
a. CO2
b. ATP
c. NADH
d. FADH2
a. 4 CO2
b. 2 ATP
c. 6 NADH
d. 2 FADH2
What happens to the carbon dioxide that is produced during the Krebs cycle?
exhaled out
What happens to the ATP that is produced during the Krebs cycle?
can be used for all cell activities
What happens to the NADH and FADH2 molecules that are produced during the Krebs cycle?
going to power ETC (pumps)
The high-energy electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along the ETC. As they are passed from one protein to the next, they release energy. What is this energy used for?
to pump the protons against the gradient (matrix to IMS)
What happens to the hydrogen electrons at the end of the ETC?
picked up by an O2; 2 electrons and 2 protons ----> maintaining the gradient
Explain how the ETC produces ATP.
pump electrons, diffuse through ATP Synthase, ADP + Phosphate Group ----> ATP
Recap of Electron Transport: Fill in the blanks in the paragraph below to summarize the events of the electron transport chain.
This system couples the movement of high-energy ___a___ with the production of ___b___. As the high-energy electrons move down the electron transport chain, they release ___c___. This energy is used to move ___d___ across the membrane. These ions then rush back across the membrane through proteins called ___e___ to generate enormous amounts of ___f___.
a. electrons
b. ATP
c. energy
d. protons
e. ATP Synthase
f. ATP
The Totals: How many ATP are produced in each of the following stages?
a. Glycolysis
b. Krebs Cycle
c. ETC
a. 2 (net 2)
b. 2
c. 34
The Totals: How many NADH are produced in each of the following stages?
a. Glycolysis
b. the bridge reaction
c. Krebs Cycle
a. 2
b. 2
c. 6
The Totals: How many FADH2 are produced in each of the following stages?
a. Glycolysis
b. the bridge reaction
c. Krebs Cycle
a. 0
b. 0
c. 2
The Totals: NADH and FADH2 carry high-energy electrons to the electrons transport chain.
a. How many ATP are produced for each NADH entering the ETC?
b. How many ATP are produced for each FADH2 entering the ETC?
a. 3
b. 2
In summary, for each molecule of glucose entering respiration, approximately how many ATP can be produced?
38
For each molecule of glucose in cellular respiration, how many molecules of carbon dioxide are produced? In which stage(s) are they produced?
6; Krebs cycle and bridge reactions
Is all of the energy contained in a molecule of glucose converted to ATP?
no
What is fermentation?
anaerobic respiration
During fermentation, approximately how many ATP can be produced per molecule of glucose?
2
Name two types of fermentation
1. alcoholic fermentation
2. lactic acid fermentation
Which organisms carry out alcoholic fermentation?
yeast
During alcoholic fermentation, pyruvic acid is converted into what compound?
CO2
Summary of alcoholic fermentation. Fill in the missing parts (a-d) in the diagram below.
a. pyruvic acid
b. alcohol
c. 2 ATP
d. CO2
How are yeasts (and their method of cellular respiration) used in our everyday lives?
bread dough (baking), beer & wine
Explain how yeasts (and alcoholic fermentation) can cause bread dough to rise.
releases CO2
Where does lactic acid fermentation occur?
muscle cells
Under what conditions might lactic acid fermentation occur?
- no oxygen
- extreme exertion
What effect does lactic acid have on muscle tissues?
breaks it down (causes soreness and aches)
Lactic acid fermentation is used to produce a wide variety of food items. List food items produced by this process.
- meats
- sour tasting foods
- buttermilk
Summary of lactic acid fermentation. Fill in the missing parts (a-c) in the diagram below.
a. pyruvic acid
b. lactic acid
c. 2 ATP