ASVAB - Electronics Information
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Volts
Measures potential difference between two points
Amperes (amps)
Measures number of electrons that move past a specific point in 1 sec
Ohms
Measures resistance, anything that could limit the flow of electrons
Current
Flows negative to positive. Electric charge rate of flow, typically carried by electrons, through a conductor.
Watt
Measures power, the rate at which electrical energy is consumed or transformed into another type of energy, such as light or heat
Conductors
Allow electrons to flow freely between different atoms. These valence shells have more empty spots than they have electrons
Semiconductors
Have half-full valence shells and are neither good conductors nor good insulators
Insulators
Valence shells are more than half full, poor conductors
Ohm’s Law
Current (amperes) = (Voltage (volts)) / Resistance (ohms) = I=\frac{V}{R}
Electrical circuit components
Voltage source
Load: source of resistance that converts electrical energy into another form of energy
Conductors: necessary to carry current from point A to point B
Series
Only one path electrical current can take. Current flow is the same in every part of the circuit.
R_{total}=R_1+R_2+\cdots+R_{n}
Parallel
Multiple components are connected side-by-side, creating multiple paths for current to flow.
\frac{1}{R_{total}}=\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}+\cdots+\frac{1}{R_{n}}
Power
P=IV
Direct Current
Current that only and always flows in one direction
Alternating Current
Current constantly changes direction in a regular pattern
Frequency
Number of times an alternating current completes two alternations of direction per second
Impedance
(Electromotive force) / (Current)
Tip: relate to Ohm’s law in reference to AC circuits. Substitute resistance in Ohm’s law with impedance and voltage with electromotive force.
Diode
A semiconducting electrical device with two terminals that ideally allows current to flow easily through in one direction but restricts the flow of current in the opposite direction
Transistor
A semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electrical signals and power
Transformer
Consists of two coils of wire. Used to step up or step down AC voltages. The primary winding receives electrical energy from a power source, while the secondary winding provides energy at a transformed (stepped up or down) voltage to a load.
\frac{V_{p}}{V_{s}}=\frac{N_{p}}{N_{s}}=\frac{I_{s}}{I_{p}}
Energy
Watt-hours
Consider these wires live at all times
Black and brown
Neutral wires
White or grey
Failsafe wires
Green
Rectifiers
Changes alternating current to direct current
Resistor (symbol)

Battery (symbol)
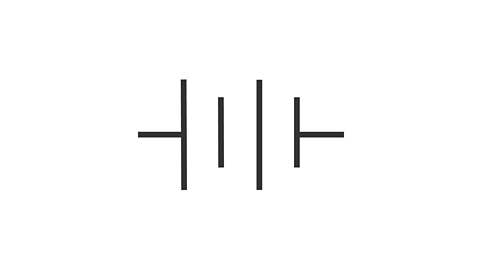
AC source (symbol)
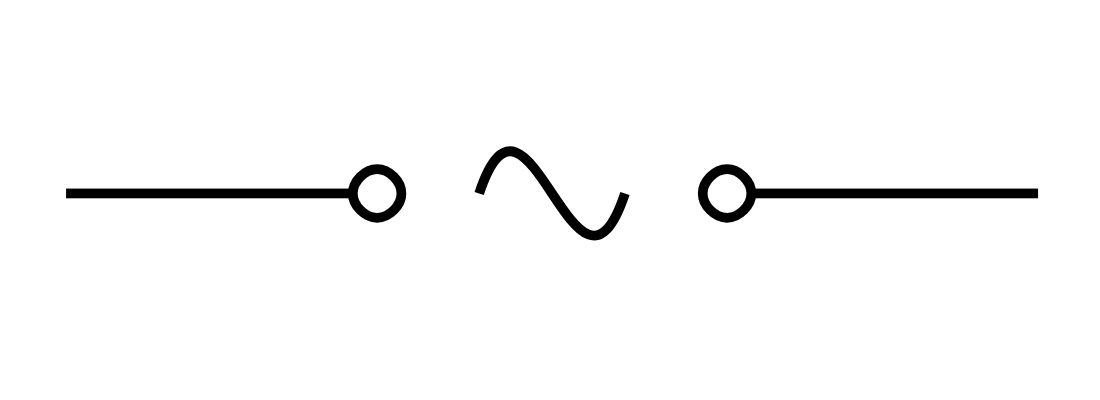
Capacitor (symbol)
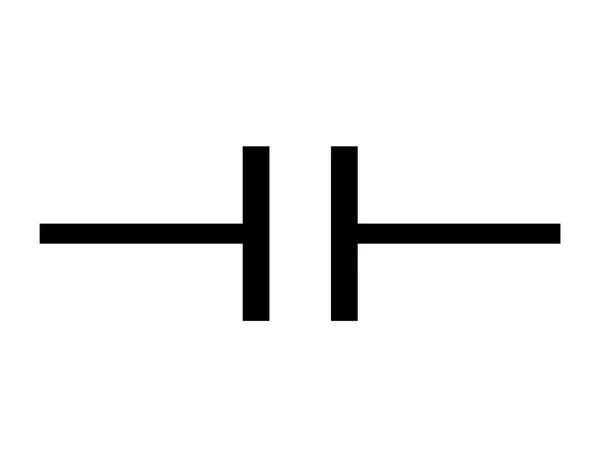
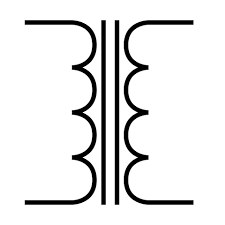
Transformer (symbol)
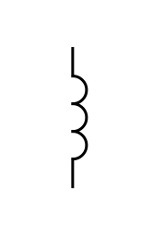
Inductor (symbol)
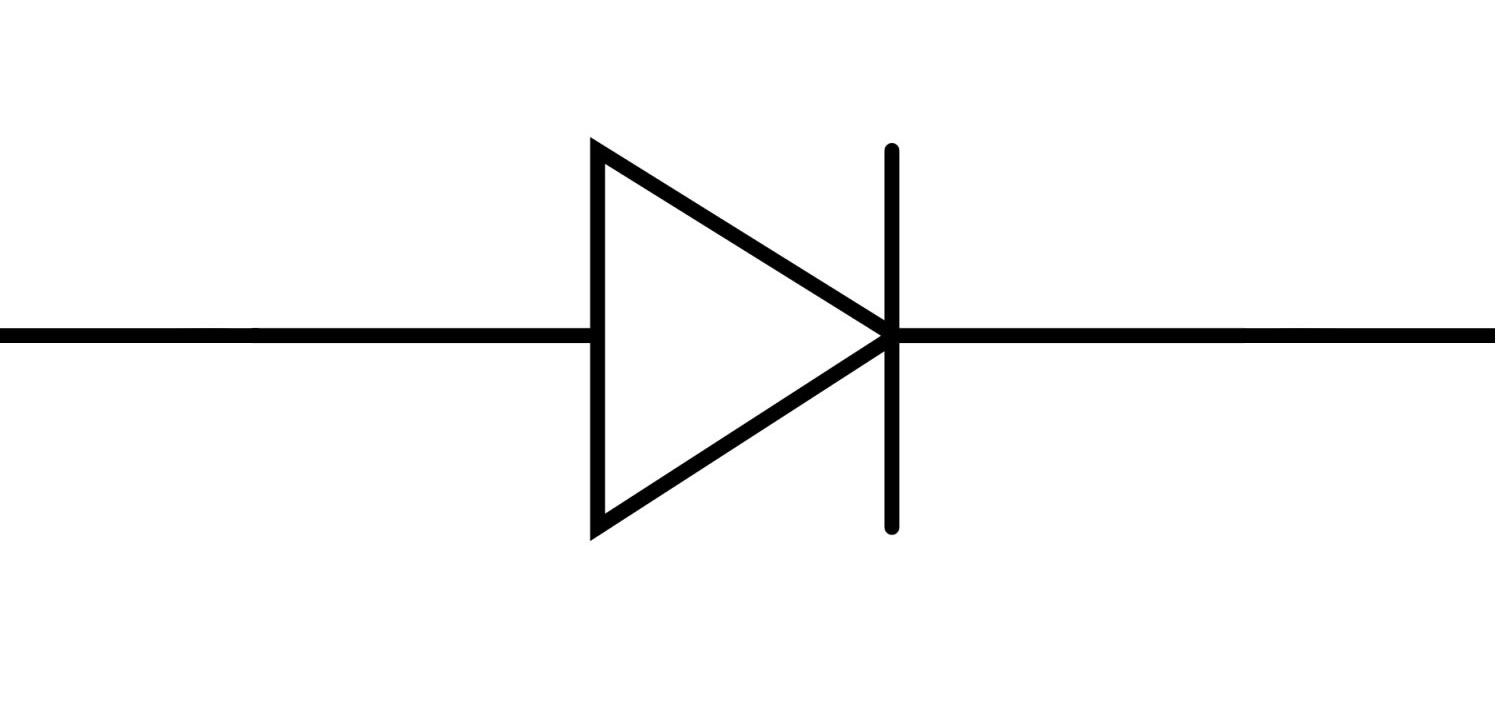
Diode (symbol)
LED (symbol)

Lamp (symbol)

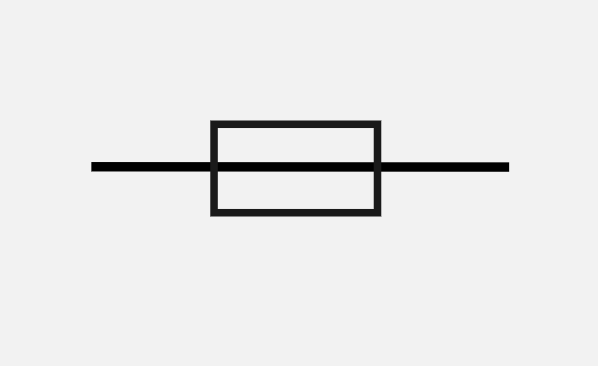
Fuse