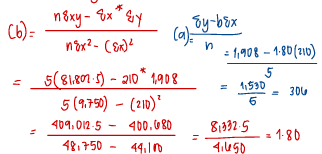ACYMANS1: Cost and Cost Concepts
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
That kind of accounting concerned with providing information to management in making decisions about the operations of the business
a. Responsibility accounting
b. Cost accounting
c. Financial accounting
d. Management accounting
d. Management accounting
Management accounting
a. Is governed by generally accepted accounting principles
b. Is geared primarily to the past rather than the future
c. Places more emphasis on precision of data compared with financial accounting which does not
d. Draws from disciplines beyond accounting
d. Draws from disciplines beyond accounting
Which of the following characteristics does not relate to management accounting?
a. Accounting reports may include non-monetary information
b. Reports are often based on estimates and are seldom useful for anything other than the purpose for which they are prepared
c. It is subject to restrictions imposed by GAAP
d. It provides data for internal users within the business organization
c. It is subject to restrictions imposed by GAAP
The primary purpose of management advisory services is
a. To conduct special studies, preparation of recommendation, development plans and programs, and provision of advise and assistance in their implementation
b. To provide service or to fulfill some social need
c. To improve the client’s use of its capabilities and resources to achieve the objectives of the organization
d. To earn the best rate of return on resources entrusted to its care with safety of investment being taken into account and consistent with the firm’s social and legal responsibilities
c. To improve the client’s use of its capabilities and resources to achieve the objectives of the organization
The chief management accountant called “controller” traditionally performs these functions, except
a. The establishment and implementation of the financial planning process
b. Financial and management reporting and interpretation
c. Protection of company’s resources and economic conditions
d. Preparation of proposals for product promotions
d. Preparation of proposals for product promotions
The amount of variable cost per unit and total fixed cost within a relevant range behave this way in relation to production level
a. Production increases, unit variable cost increases, total fixed cost increases
b. Production decreases, unit variable cost decreases, total fixed cost decreases
c. Production increases, unit variable cost remains constant, total fixed cost remains the same
d. Production increases, unit variable cost decreases, total fixed cost remains the same
c. Production increases, unit variable cost remains constant, total fixed cost remains the same
Which of the following statements is false?
a. At zero production level, fixed costs are positive
b. At zero production level, variable costs are usually zero
c. At zero production level, total costs equal total fixed costs
d. At zero production level, fixed costs is also zero
d. At zero production level, fixed costs is also zero
Costs that increase as the volume of activity decreases within the relevant range are
a. Average costs per unit
b. Total fixed costs
c. Average variable costs per unit
d. Total variable costs
a. Average costs per unit
Total fixed costs - CONSTANT
Average variable costs per unit - CONSTANT
Direct materials are a
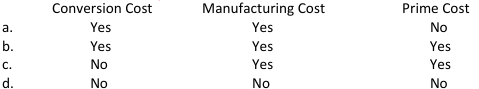
Conversion Cost - Manufacturing Cost - Prime Cost
c. NO - YES - YES

The cost of rent for a manufacturing plant is generally considered to be a
Period Cost - Product Cost
a. NO - YES
An opportunity cost is
a. The difference in total costs which results from selecting one choice instead of another
b. A cost that may be shifted to the future with little or no effect on current operations
c. A cost that may be saved by not adopting an alternative
d. The profit foregone by selecting one choice instead of another
d. The profit foregone by selecting one choice instead of another
Sunk costs
a. Are relevant to long-term decisions but not to short-term decisions
b. Are relevant to decision making
c. Are subtitles for opportunity costs
d. In themselves are not relevant to decision making
d. In themselves are not relevant to decision making
These are among the methods of segregating fixed cost and variable costs, except
a. Regression analysis
b. Scattergraph method
c. Breakeven method
d. High-low method
c. Breakeven method
Weaknesses of the high-low method include all of the following, except
a. Only two observations are used to develop the cost function
b. The high and low activity levels may not be representative
c. The method does not detect if the cost behavior is nonlinear
d. The mathematical calculations are relatively complex
d. The mathematical calculations are relatively complex
Regression analysis
a. Estimates the independent cost variable
b. Uses probability assumptions to determine total project costs
c. Estimates the dependent cost variable
d. Ignores the coefficient of determination
c. Estimates the dependent cost variable
In the formula y = a + bx, y represents
a. Fixed cost
b. Total cost
c. Variable cost
d. Mixed cost
b. Total cost
In regression analysis, the coefficient of determination is a measure of
a. The amount of variation in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables
b. The amount of variation in the dependent variable unexplained by the independent variables
c. The slope of the regression line
d. The predicted value of the independent variable
a. The amount of variation in the dependent variable explained by the independent variables
Correlation is a term frequently used in conjunction with regression analysis and is measured by the value of the coefficient of correlation, “r”. The best explanation of the value “r” is that it
a. Interprets variances in terms of the independent variable
b. Ranges in size from negative infinity to positive infinity
c. Is a measure of the relative relationship between two variables
d. Is positive only for downward-sloping regression lines
c. Is a measure of the relative relationship between two variables
The objective of a scatter diagram is
a. To determine, by visual fit, the relationship of two variables in a graph
b. Divide a universe of data into homogenous groups
c. Show the vital trend and separate trivial items
d. None of the choices
a. To determine, by visual fit, the relationship of two variables in a graph
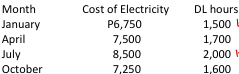
Company X wants to develop a cost estimating equation for its monthly cost of electricity. It has the following data:
Using the high-low method, what is the best equation?
a. Y = P750 + P3.50X
b. Y = P1,500 + P5.00X
c. Y = P750 + P5.00X
d. Y = P1,500 + P3.50X
d. Y = P1,500 + P3.50X
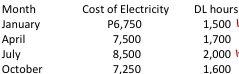
Company X wants to develop a cost estimating equation for its monthly cost of electricity. It has the following data:
How much is the total cost for the month of November if 1,000 DL hours are incurred?
a. P5,000
b. P6,000
c. P3,500
d. P1,500
a. P5,000
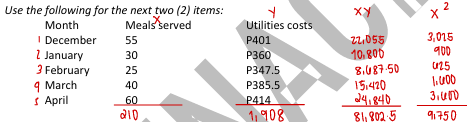
Using the method of least squares, the variable rate for utilities costs per meal served is
a. P1.90
b. P1.80
c. P2.00
d. P3.00
b. P1.80
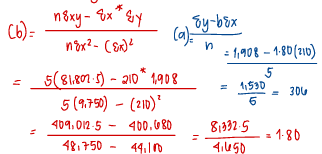
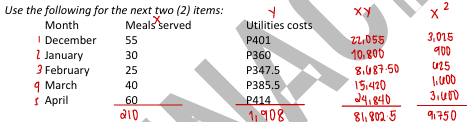
Using the method of least squares, the fixed cost is
a. P300
b. P331
c. P306
d. P303
c. P306