Lab 5.1 Comparative anatomy
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Structures to compare GI vs Excretory vs Circulation
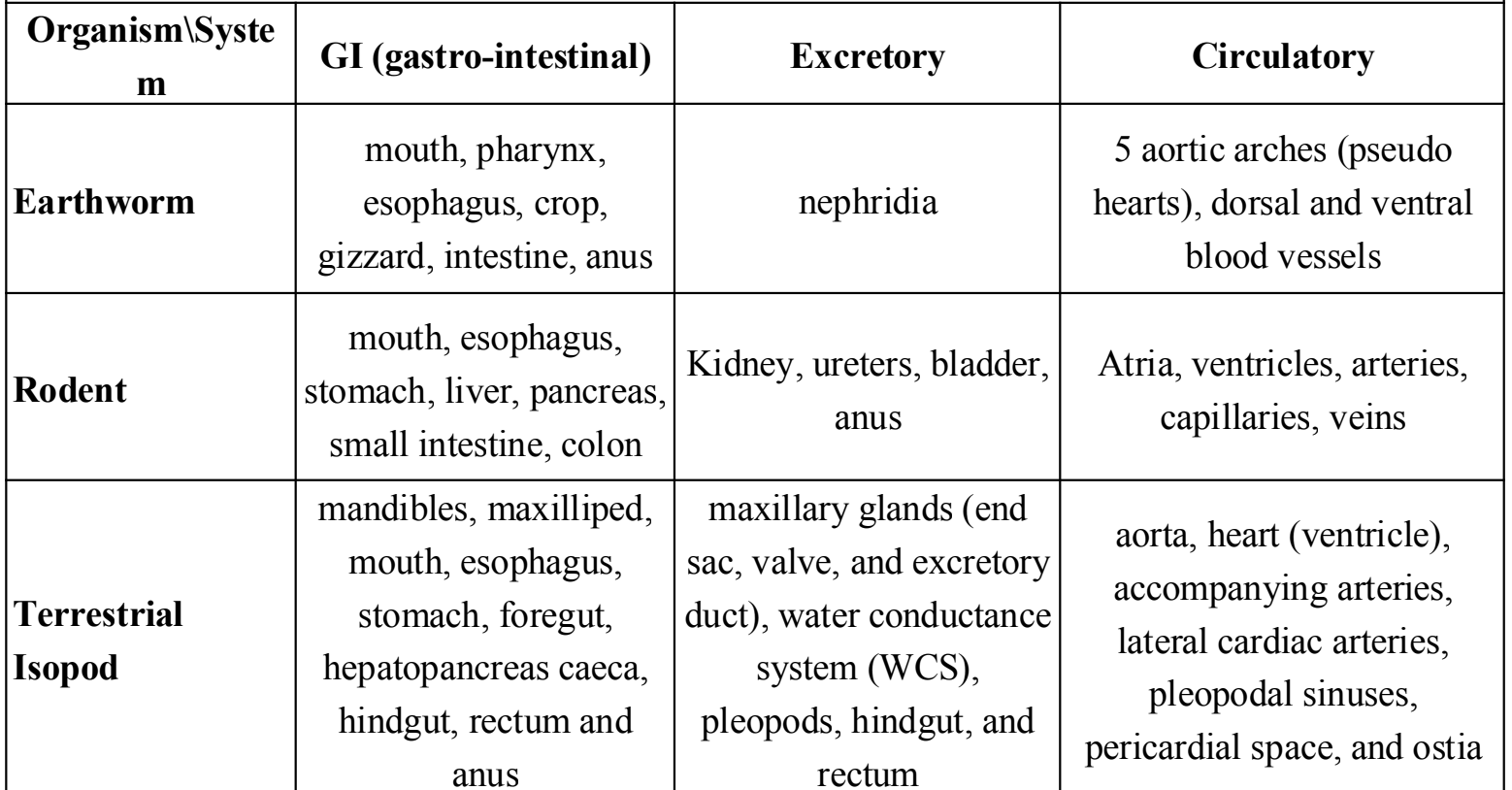
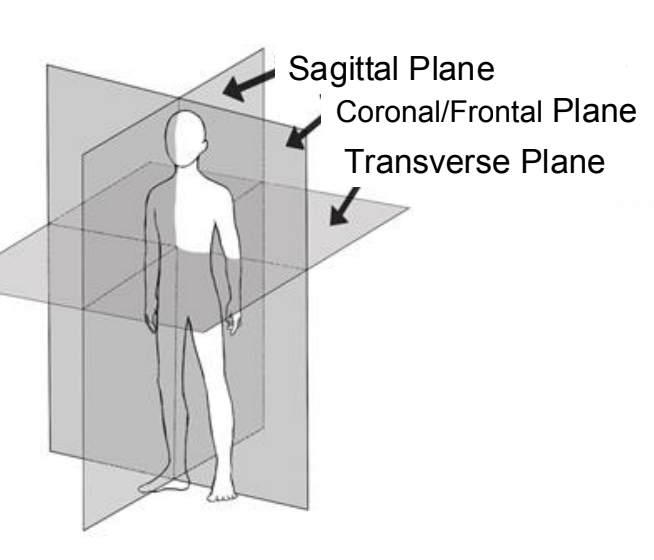
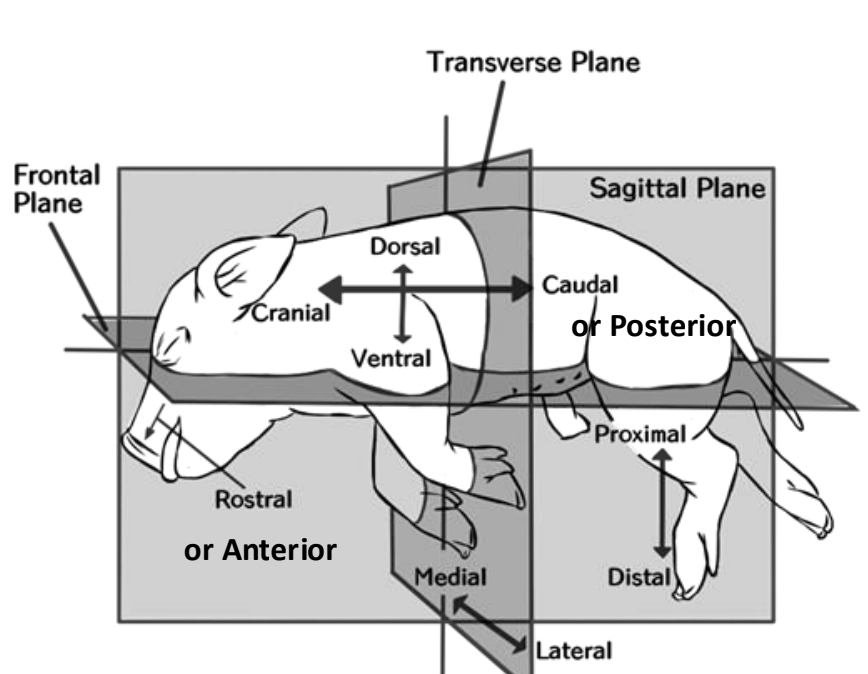
transverse plane
top and bottom
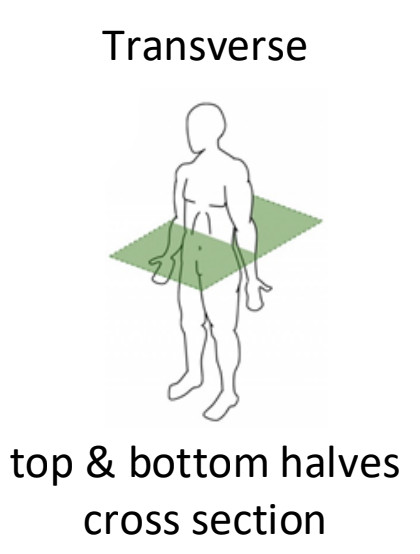
coronal/frontal plane
front and back halves
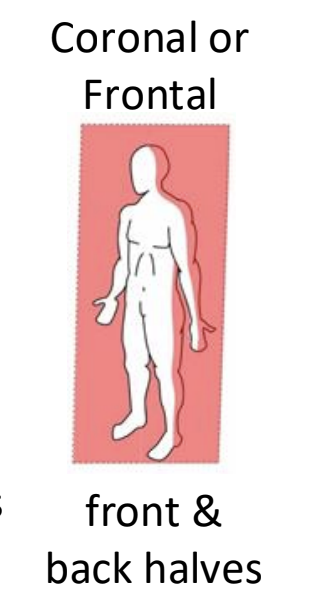
sagittal plane
right and left halves
anatomical planes (sagittal, coronal, transverse)
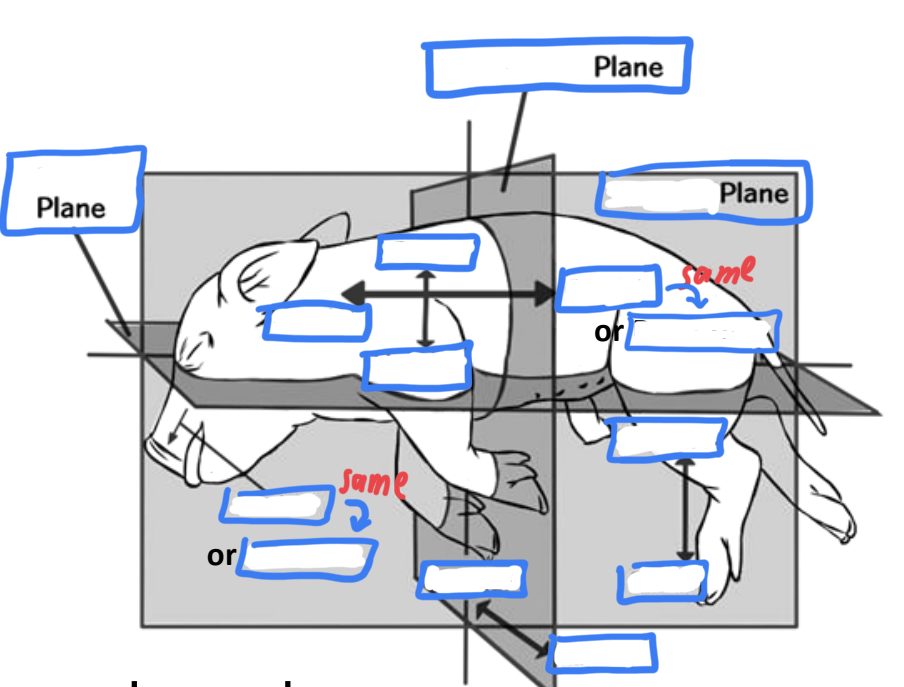
anatomical plane in pig
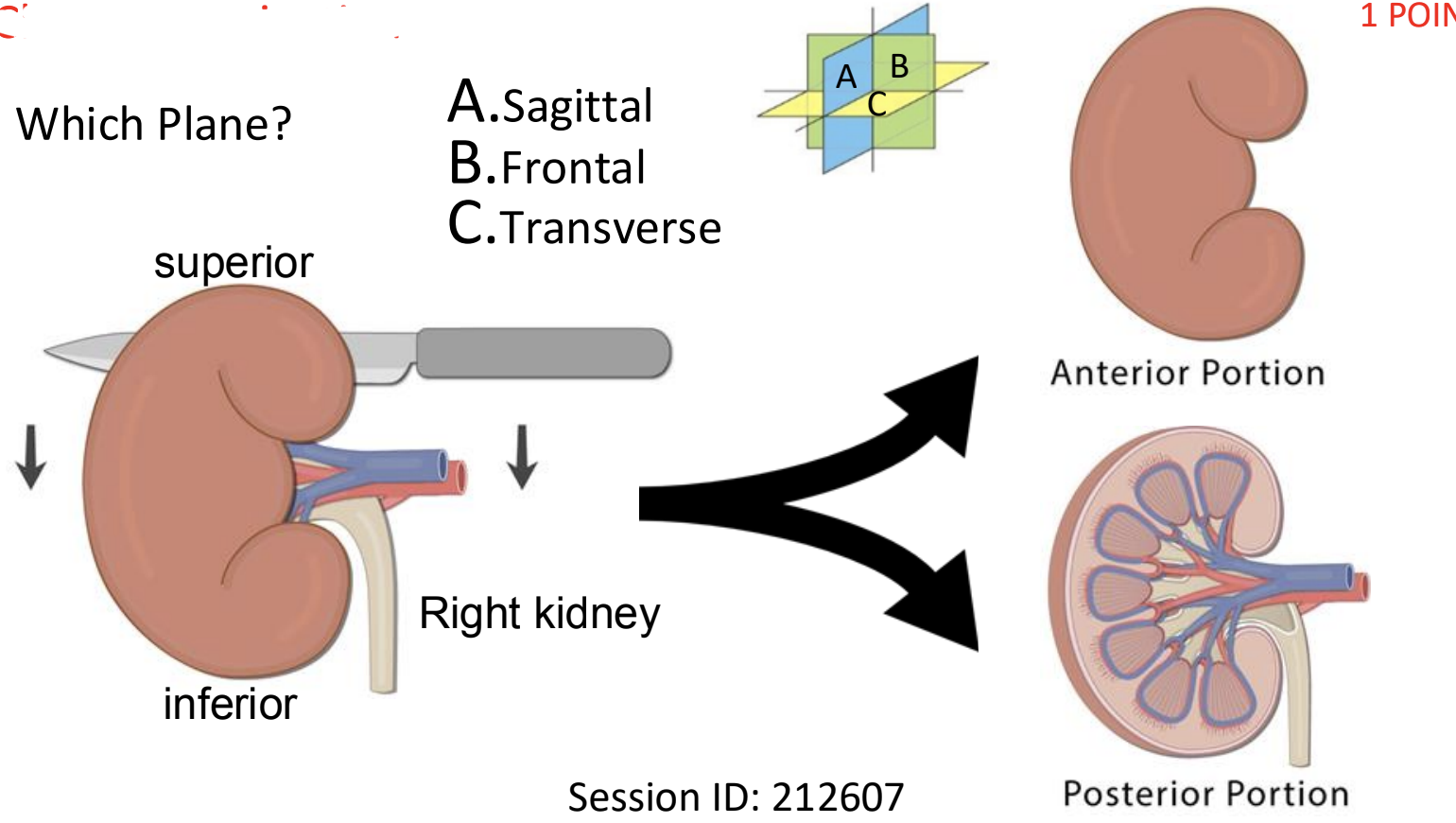
which plane?
a) sagittal ???
where are the kidneys relative ot the sternum in human
A. Superior
B. Inferior
C. Dorsal
D. Anterior
E. Both A and D
F. Both B and C
F) both B and C
Inferior and dorsal
Biological hierarchy
Respiratory system (Earthworm, rat, isopod) chart
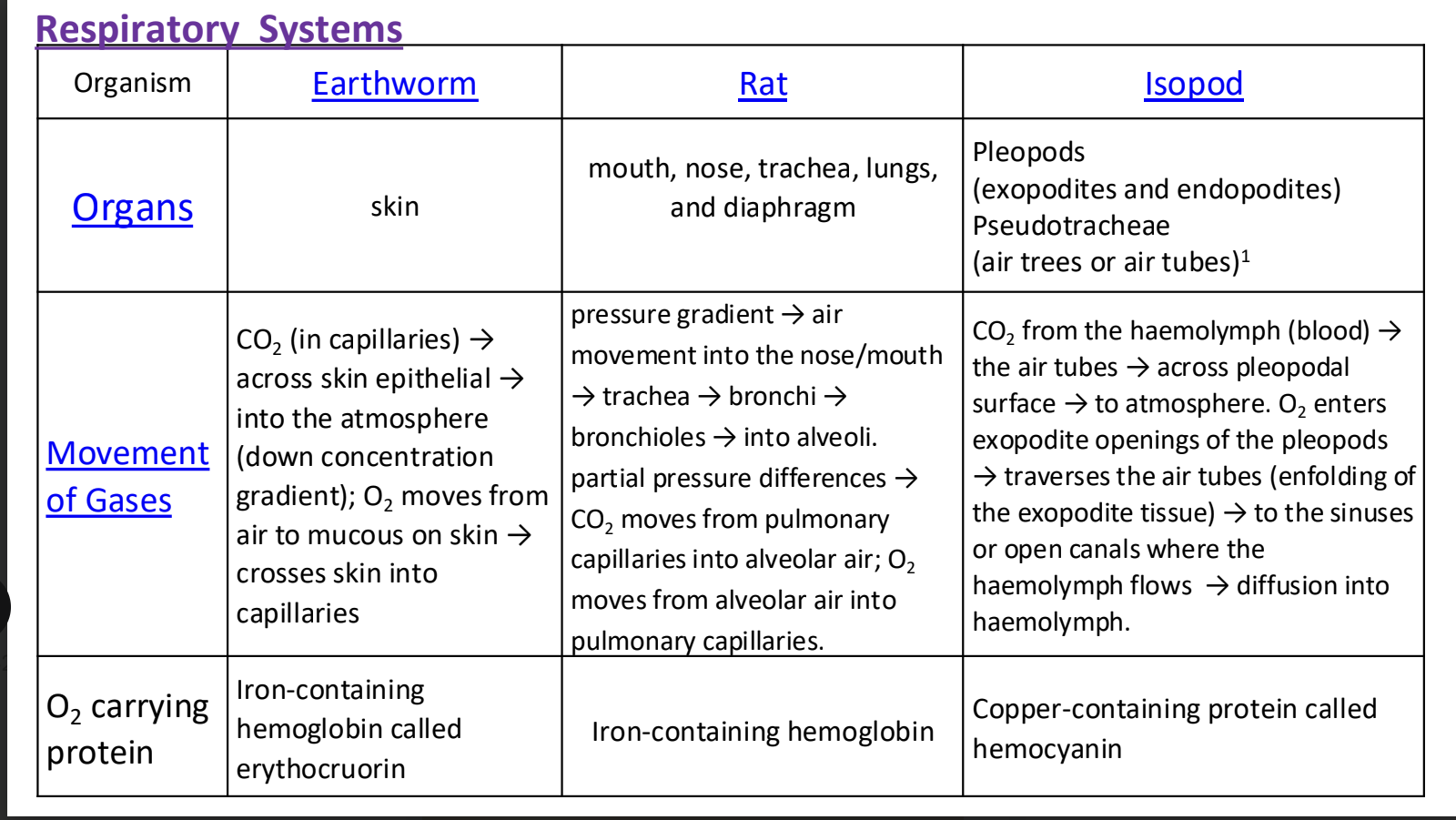
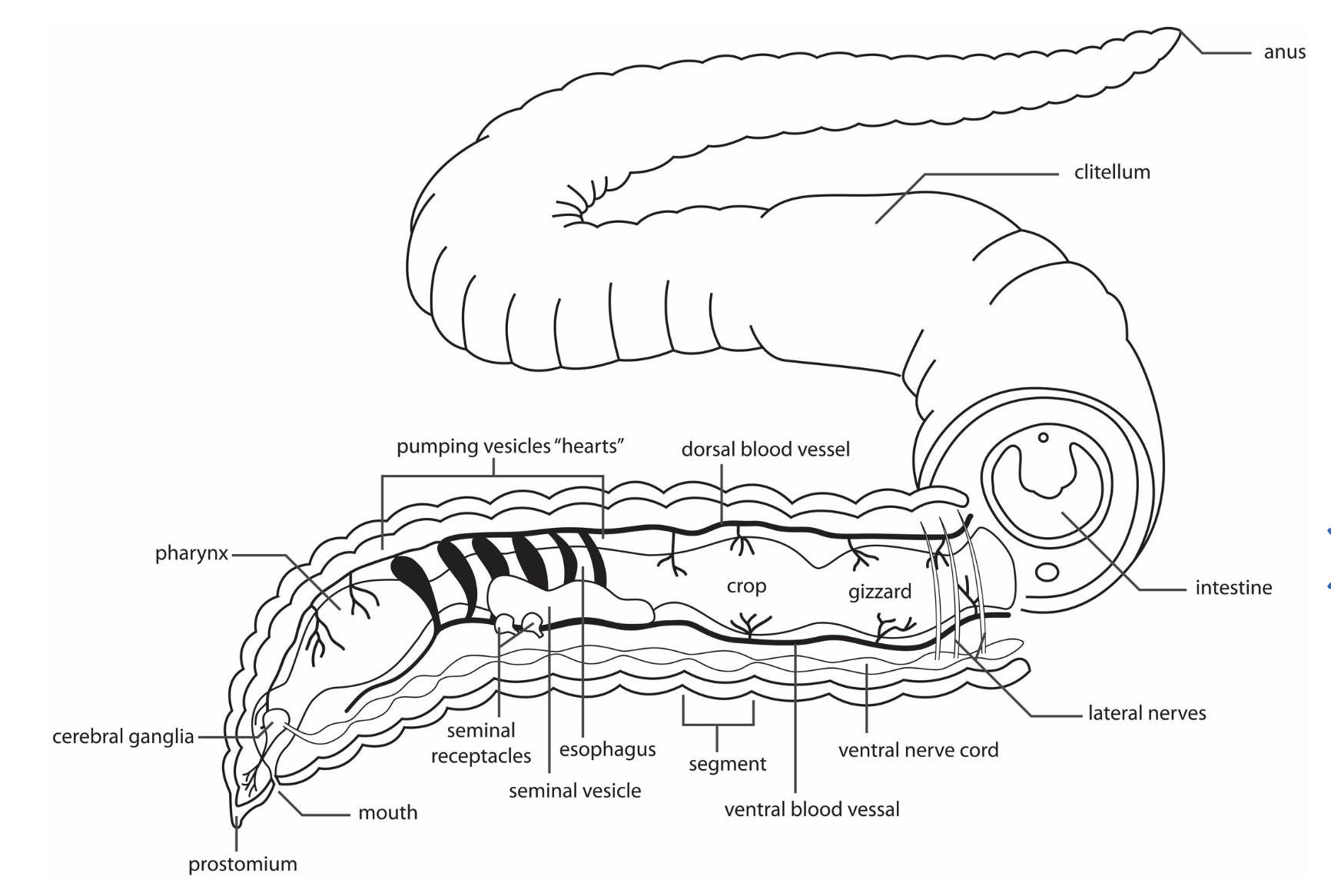
earthworm organ (respiratory system)
earthworm movement of gases (respiratory system)
CO2 in capillaries —> across skin epithelial —> into the atmosphere (down concentration gradient); O2 moves from air to mucous on skin —> crosses skin into capillaries
Earthworm O2 carrying protein (respiratory system)
iron containing hemoglobin called erythrocruorin
rat organs (respiratory system)
mouth, nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm
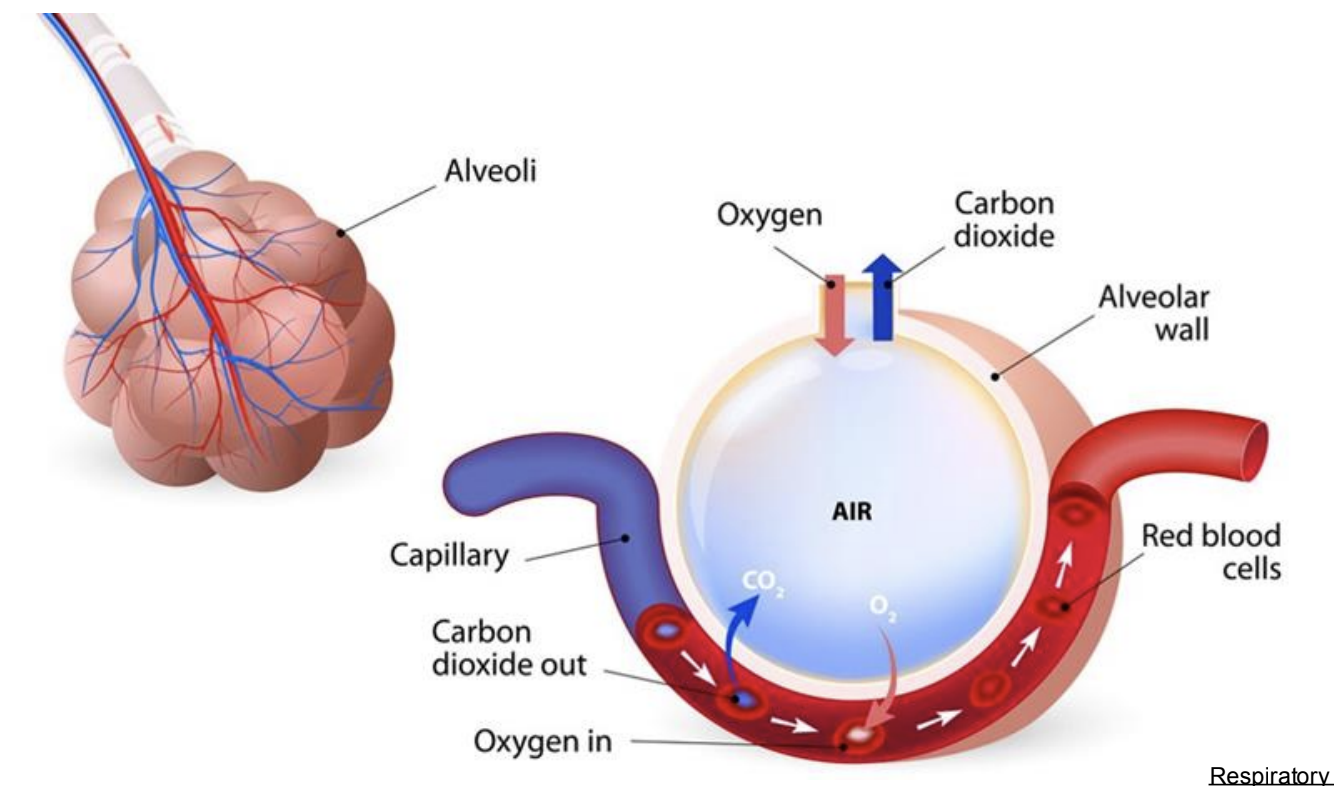
rat movement of gases (respiratory system)
pressure gradient —> air movement into the nose/mouth —> trachea —>
bronchi —> bronchioles —> into alveoli partial pressure differences —> CO2 moves from pulmonary capillaries into alveolar air; O2 moves from alveolar air into pulmonary capillaries
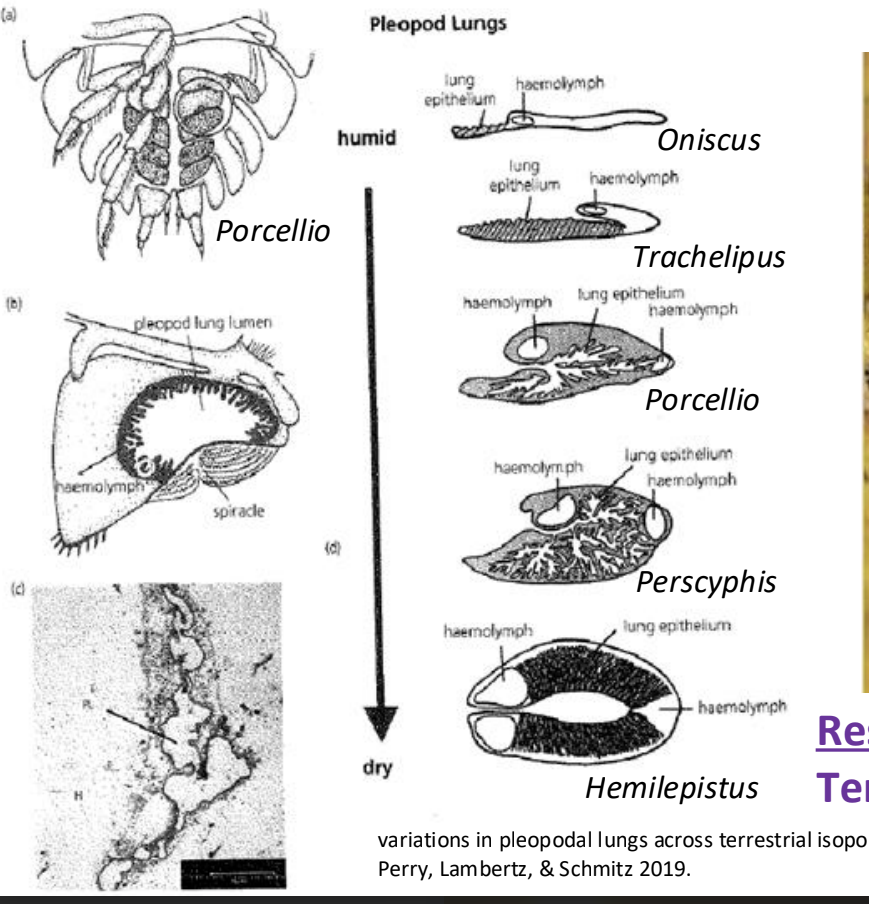
Isopod organ (respiratory system)
pleopods (exopodites and endopodites)
pseudo tracheae (air trees or air tubes)
isopod movement of gases (respiratory system)
CO2 from the haemolymph (blood) —> air tubes —> across pleopodal surface —> to atmosphere O2 enters exopodite openings of the pleopods —> transverses the air tubes (enfolding of the exopodite tissue —> to the sinuses or open canals where the haemolymph flows —> diffusion into haemolymph
Isopod O2 carrying protein (respiratory system)
copper containing protein called hemocyanin
earthworm skin
epidermal tissue surrounded by a cuticle
cuticle moistened by secretion from epidermal mucous glands
earthworm circulatory system (diagram)
A closed circulatory system, consisting of dorsal and ventral blood vessels and several aortic arches that pump blood throughout the body.

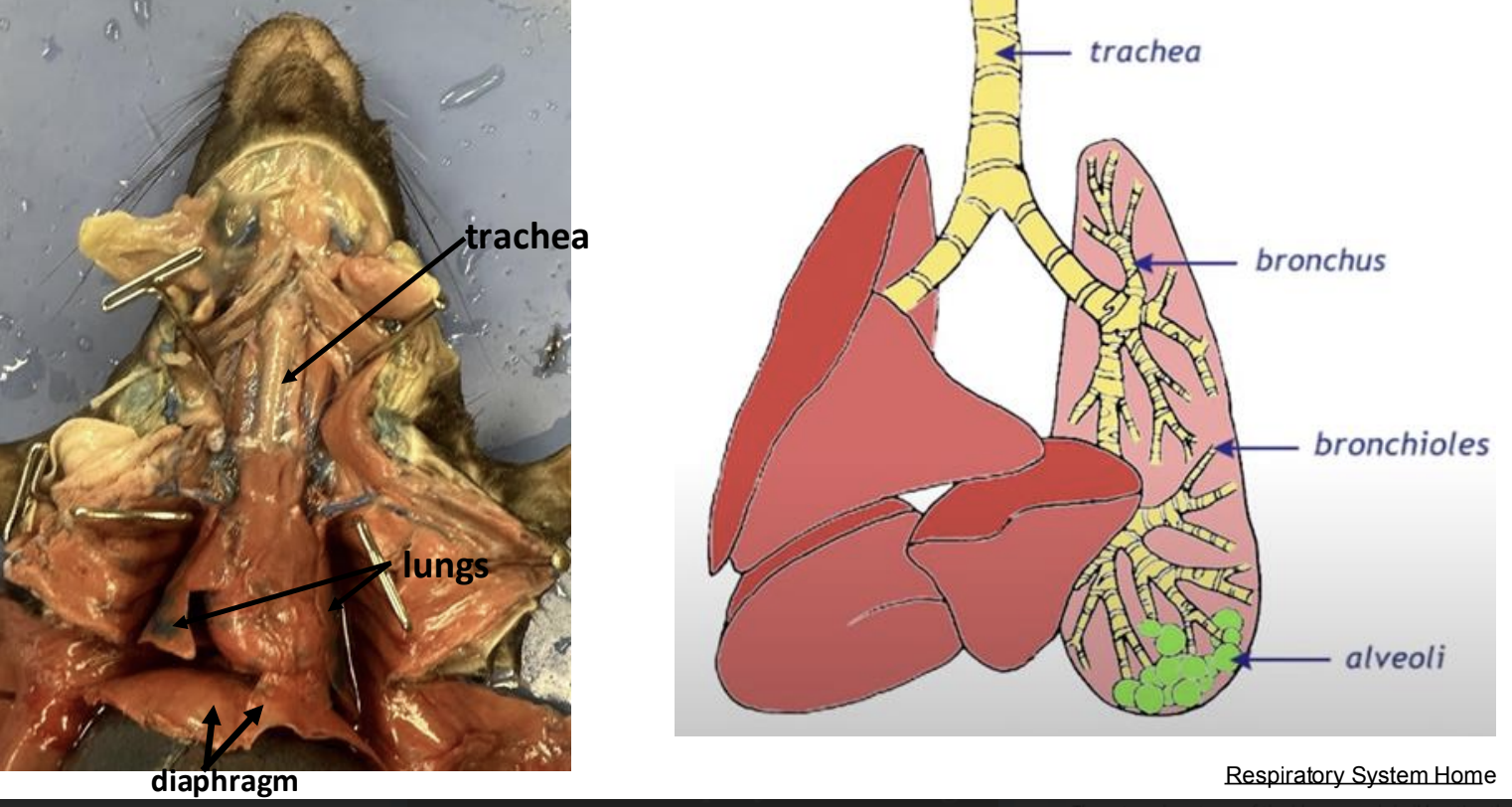
rat respiratory system (diagram)
The rat respiratory system includes the trachea, bronchi, and lung
facilitating gas exchange by delivering oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.
rat circulation (digram)
The rat circulatory system consists of a closed system featuring a four-chambered heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood throughout the body.
ispod lungs (diagram)
The ispod lungs function in gas exchange, providing oxygen to the bloodstream and removing carbon dioxide.
earthworms move in a
wavelike motion via peristalsis due to contraction and relaxation of muscles in their body wall
earthworms have
circular and longitudinal muscles that facilitate crawling, burrowing and achoring
arthropods, annelids, and chordates are universally considered
segmented
Annelids bodies are segmented called
metamerism
earthworms are
bilaterally symmetrical, triblastic organisms with organ systems in a true coelomate body plan
earthworm adaptations enable them to
live and reproduce on land, a contrast with their relatives like marine, freshwater, and parasitic annelids as well as mollusks
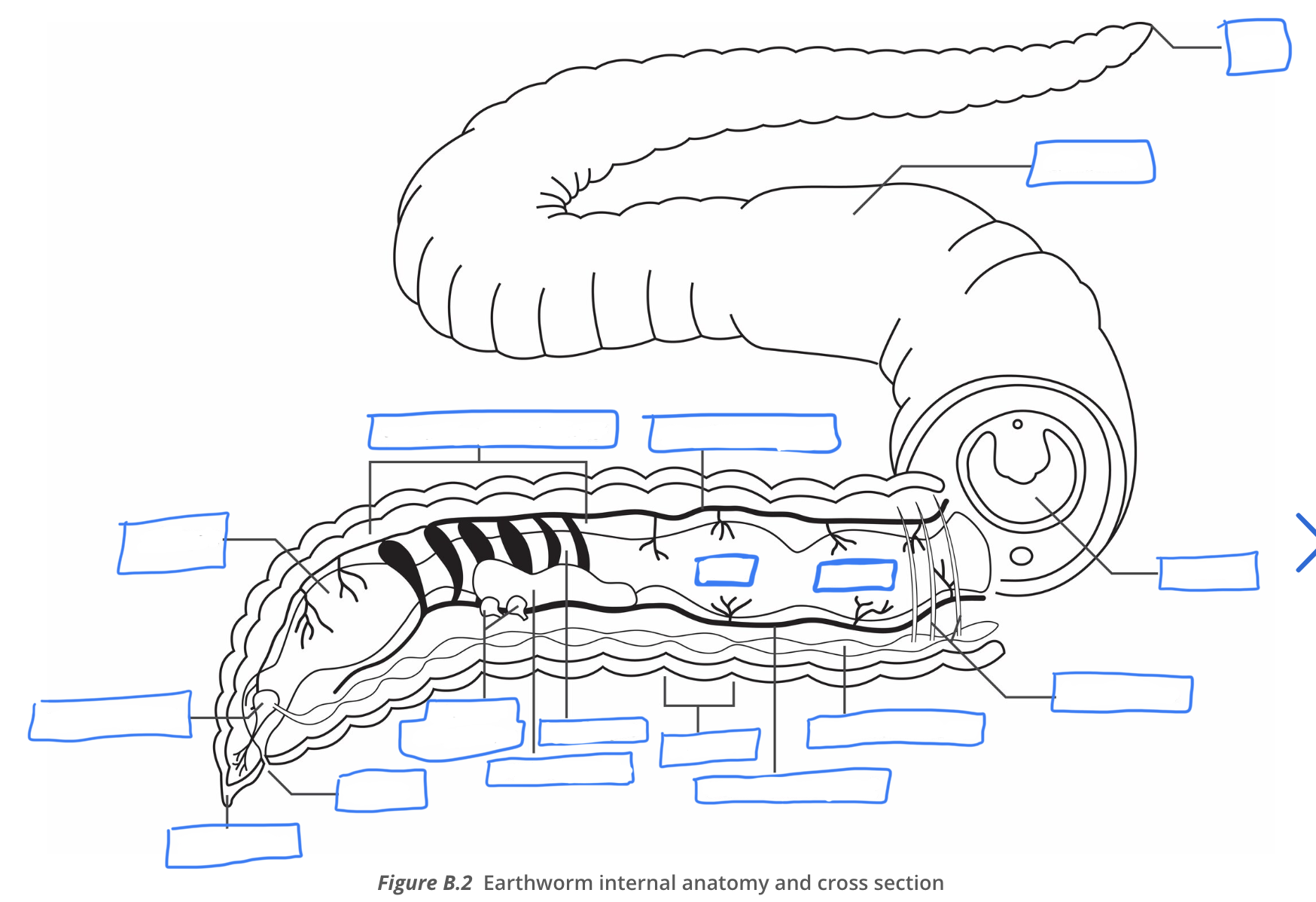
earthworm diagram
rodent - clear away the connective tissue in the throat region and you see the
thymus and thyroid glands
thymus gland
large, can be found in throat region and thoracic cavity, surrounding the heart
grainy texture which differentiates it from the connective tissue
thyroid (rat)
small, dark, symmetrical organ in midline of rat’s neck
trachea
dorsal to thyroid
ringed catilage prevents collapse of the trachea during inspiration
larynx is
anterior to the trachea
esophagus is
dorsal to the trachea
jugular veins
large vessels near the surface of the neck
jugular veins, carotid arteries, and vagi are all
bilateral structures
tissues throughout the body
metabolize glucose and oxygen (O2) and produce carbon dioxide (CO2) as waste
large, multicellular organisms require a
cardiovascular system which delivers O2 and glucose to the tissues via arteries and removes CO2 via veins
highly metabolic tissues (muscles and nervous tissue) are highly vascularized
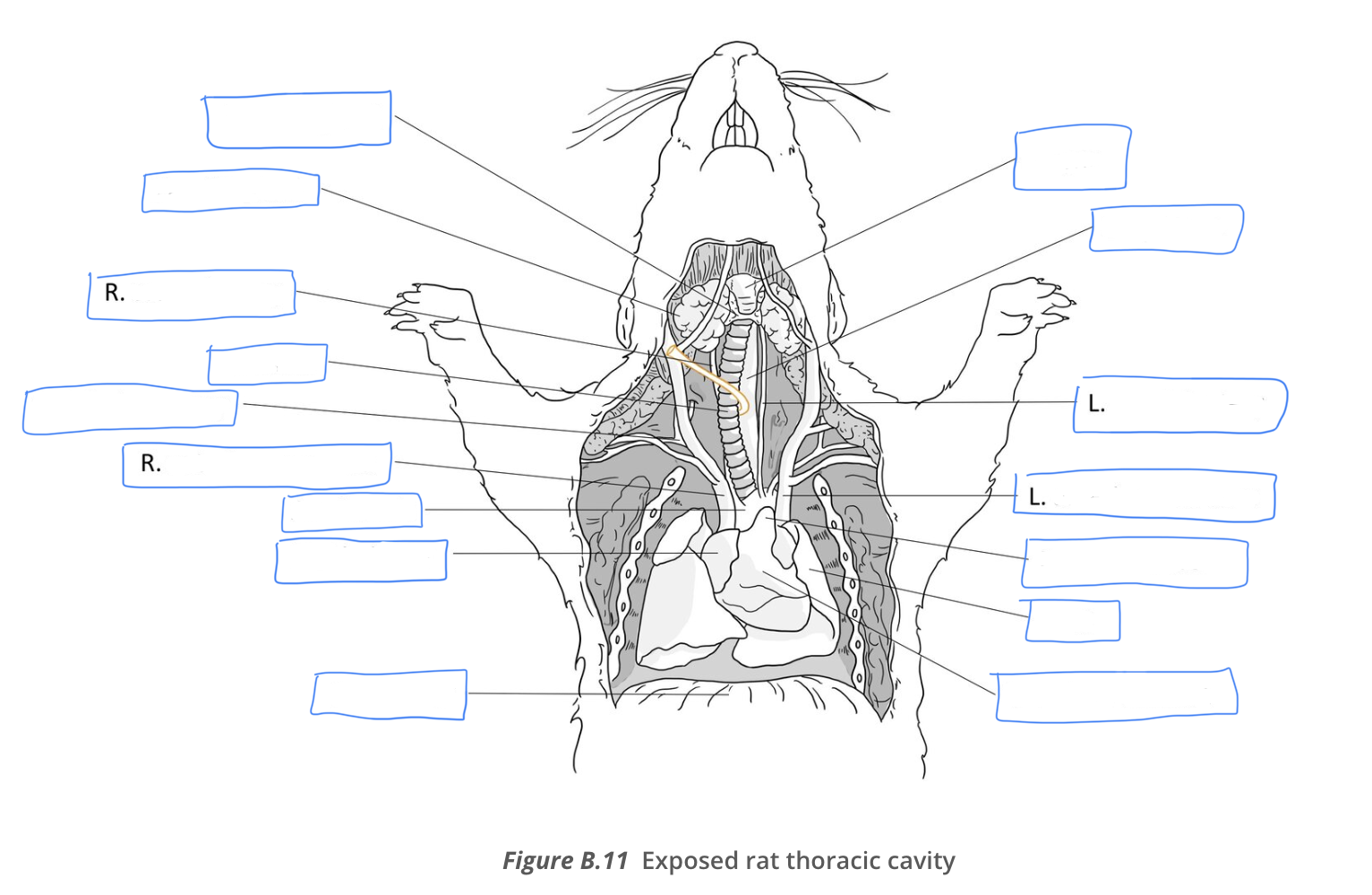
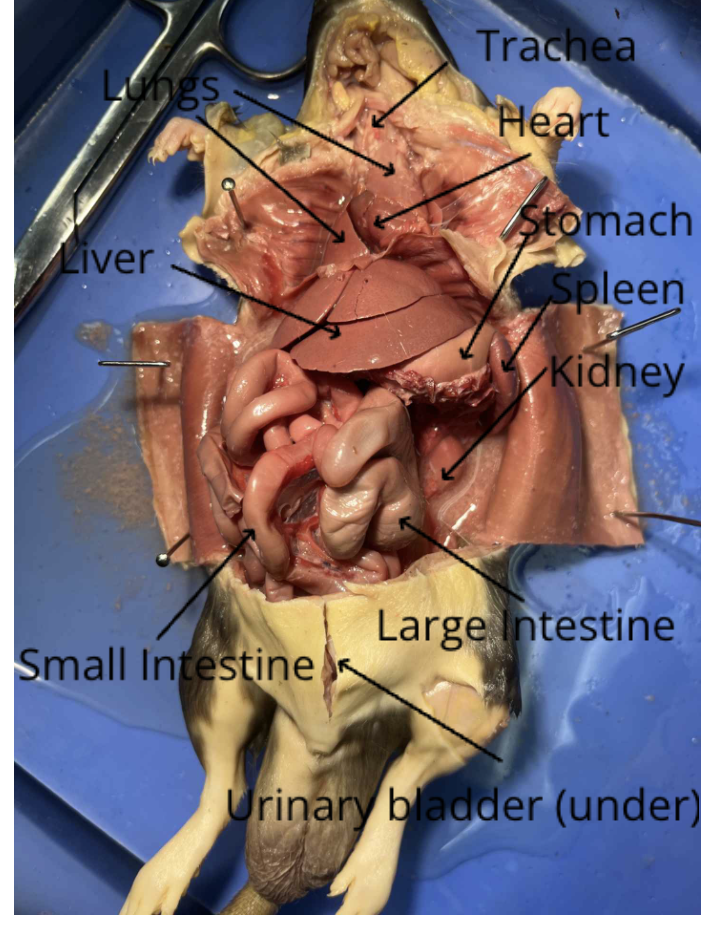
Rat thoracic cavity diagram
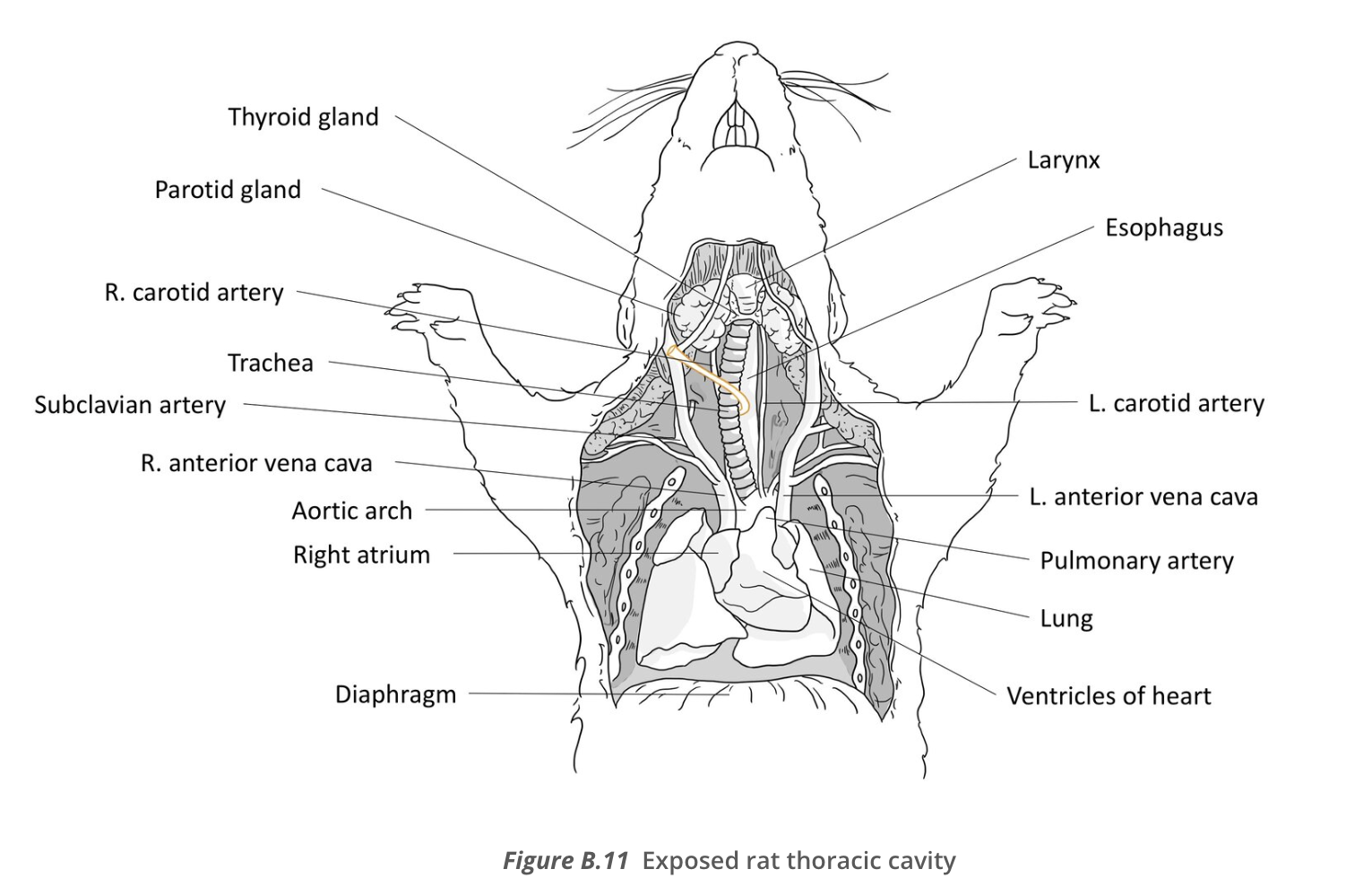
after ingestion the GI tract must
digest macromolecules, absorb nutrients, and egest (eliminate unused food)
GI tract is a
long assembly line of processes that normally involve the secretion of special enzymes by glands such as the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, etc.
GI tract begins in the ___ and ends at the ____
mouth and anus
all materials absorbed from food and liquid must
pass through the wall of the tract to enter the body
food in the mammalian tract is digested
mechanically and chemically
chewing by teeth in mouth is purely
mechanical and breaks the food into smaller particles, which increase the surface area on which digestive enzymes can act
as the bolus passes through the
pharynx, the epiglottis folds over the trachea so that the bolus can pass into the esophagus
food moves caudally within the
esophagus into the stomach
esophagus passes through the diaphragm and is found in both the
in both the thoracic and abdominal cavities
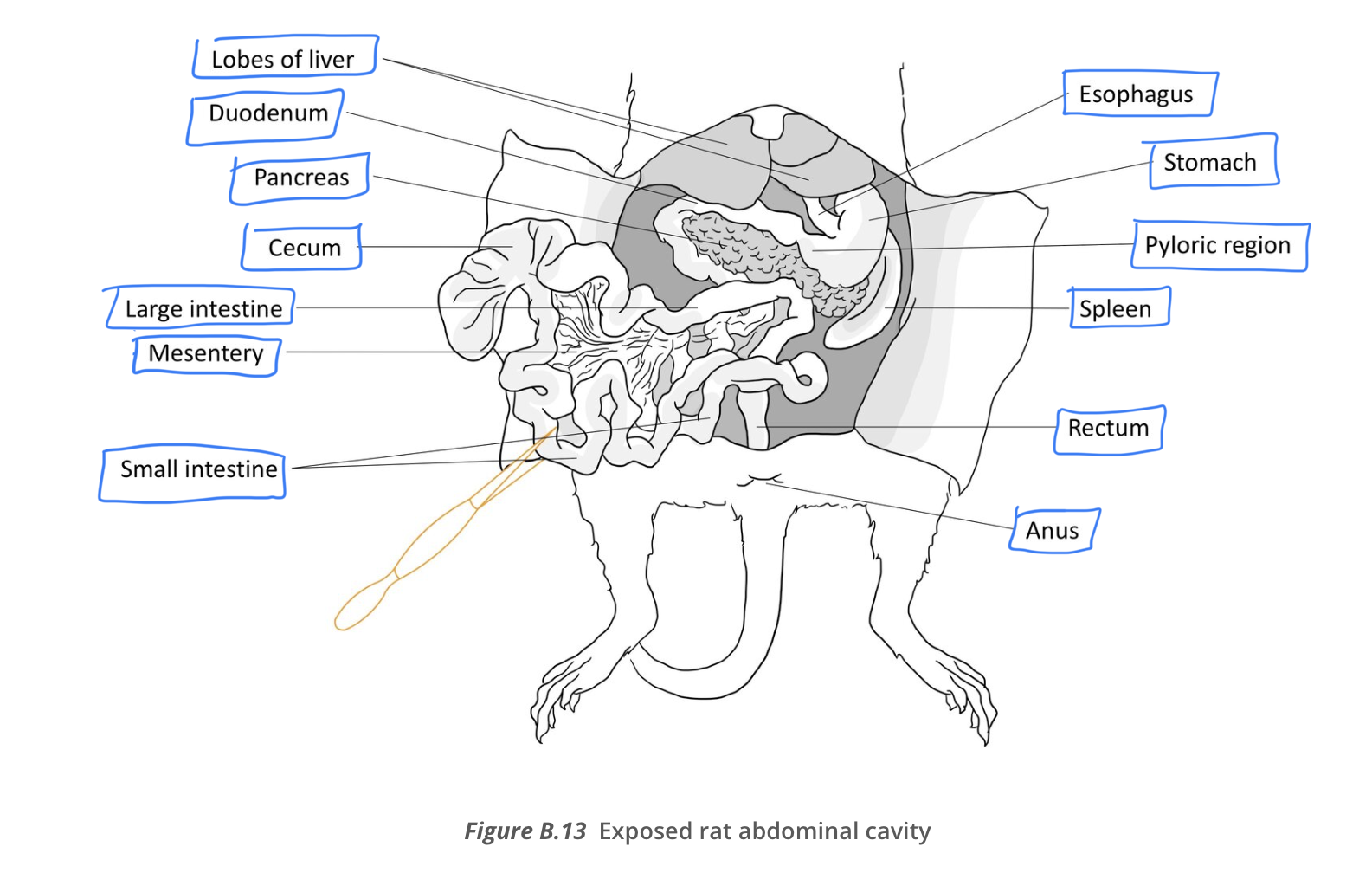
liver in rat must be
lifted in order to see the stomach
spleen
dark purple organ in the region on the left side of the stomach (when stomach is lifted up)
the stomach has a
muscular wall and contraction of this wall mixes the food and enzymes
Epithelial cells in the stomach
secrete HCl which lowers the pH (acid) of the stomach contents
HCl stimulates
release of pepsinogen, a zymogen (inactive proenzyme) that is converted to the active enzyme, pepsin
pepsin is a
protease that digests protein
stomache empties into the first section of the
small intestine called the duodenum
pancreas is in the
bend of the duodenum caudal to the stomach
small intestine
where majority of the nutrient and water absorption takes place
lining has a long of folds
folds increase
surface area for greater food absorption
intestine are surrounded by
mesentery
mesentery is a
two layered membrane of mesothelium and connective tissue that supports the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nervous tissue of the intestines
diagram of rat abdominal cavity
kidney are the
primary organ and they filter the blood to form urine
ovaries in female are
small kidney shaped organs withing the abdominal cavity just caudal to the kidney
horn of the uterus are
equivalent to fallopian tubes in humans
join centrally at the uterus
down the uterus is the
vagina (must cut the ventral pubic bone) where it joins the urethra and exits the body
in males the scrotal sacs are on the
exteriori
in order to find the testes
locate the two ductus deferens: tubes which join dorsally to the caudal end of the bladder which can be traced to the abdominal wall
dissection strategy outline
research organism
work slow
examine external structure
document
dissect superficially
gently separate tissues and identify structures
determine function of structures
make connections between systems
blunt edged tools
used before the pointed tools as they are more forgiving and less likely to cut tissue
use scissoes
more control over cut
scalpel only when needed, for clean straight incision in skin
most organs are easier to see when
immersed in water
inflate organs
immerse in solution to make organs float to improve identification of small, cardiovascular structure
forceps
grasp parts for cutting or pill things out of the way such as with initial incisions of the skin
dissecting needle
used to tear connective tissue to separate organs one from another
blunt probe
allows you to move or hold organs and tissues out of the way without worrying about ripping or tearing them
allows you to probe organs in the regions of an animal without destroying organs, it allows you to explore inside of hollow organs
scissors
allows you to cut through organs or cut out organs for removal to gain access to another organ
cut through skin and make specific incisions
cutter
allows you to cut through bone or thick muscle (not to be used on earthworm)
dissected earthworm (diagram)

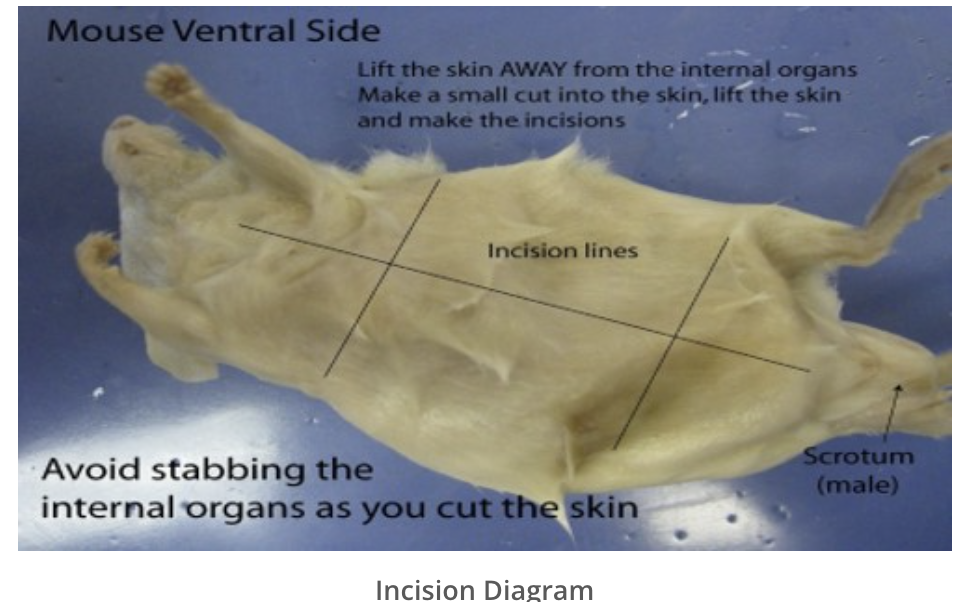
rat incession lines
rat dissection labeled
Which spatial planes would you use to dissect a mouse if you want to produce 1) a dorsal and ventral half of the mouse? 2) a right and left half of the mouse?
A) 1) frontal ; 2) transverse
B) 1) sagittal; 2) frontal
C) 1) transverse; 2) sagittal
D) 1) sagittal; 2) transverse
E) 1) frontal; 2) sagittal
E) 1) frontal; 2) sagittal
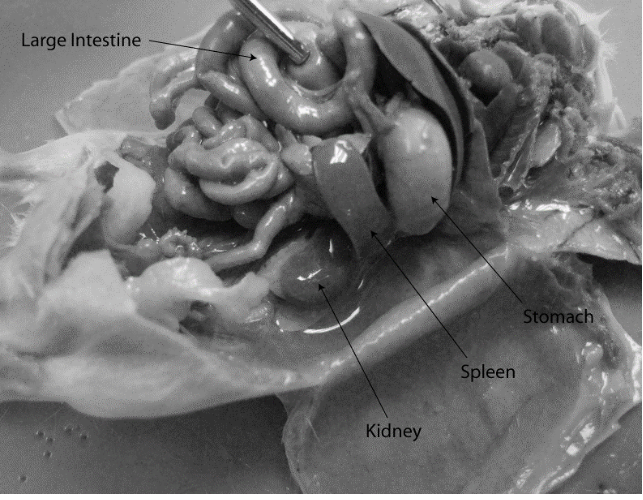
The kidney is _______ to most of the small and large intestine in the rat (see image).
A) dorsal
B) ventral
C) cranial
D) anterior
E) rostral
B) rostral
which of the following is correct
A) Earthworms, rats, and mice are mammals and belong to the Phylum Chordata.
B) Circulatory systems usually function to transport materials throughout the animal body.
C) Earthworms are not hermaphroditic.
D) Although isopods are technically vertebrates, rodents are considered a higher form of vertebrate.
E) Excretory systems are usually involved in gas exchange for O2 and CO2.
B) Circulatory systems usually function to transport materials throughout the animal body.