Biology - Carbohydrates and lipids
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Properties of carbon
Has four outer shell electrons so it can form four bonds
Can therefore be a component of large stable molecules
present in all four major categories of biological molecules
life one earth is described as “carbon based”
four major categories of biological molecules
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
nucleic acids
what can carbon do
bond to other carbon atoms or other atoms
form molecules with long branched chains
form long straight unbranched molecules
form molecules containing cyclic single rings
form molecules containing multiple rings
produce tetrahedral structures
the monomers and polymers of main groups
carbohydrates - monosaccharides
lipids - fatty acids, glycerol, phosphate group
proteins - amino acids
nucleic acids - nucleotides
formation of macromolecules
formed during condensation reactions, when molecules combine together forming covalent bonds and water is removed
polysaccharides formation
condensation reaction between 2 oH groups of 2 carbohydrates forms the covalent glycosidic bond. water is removed.
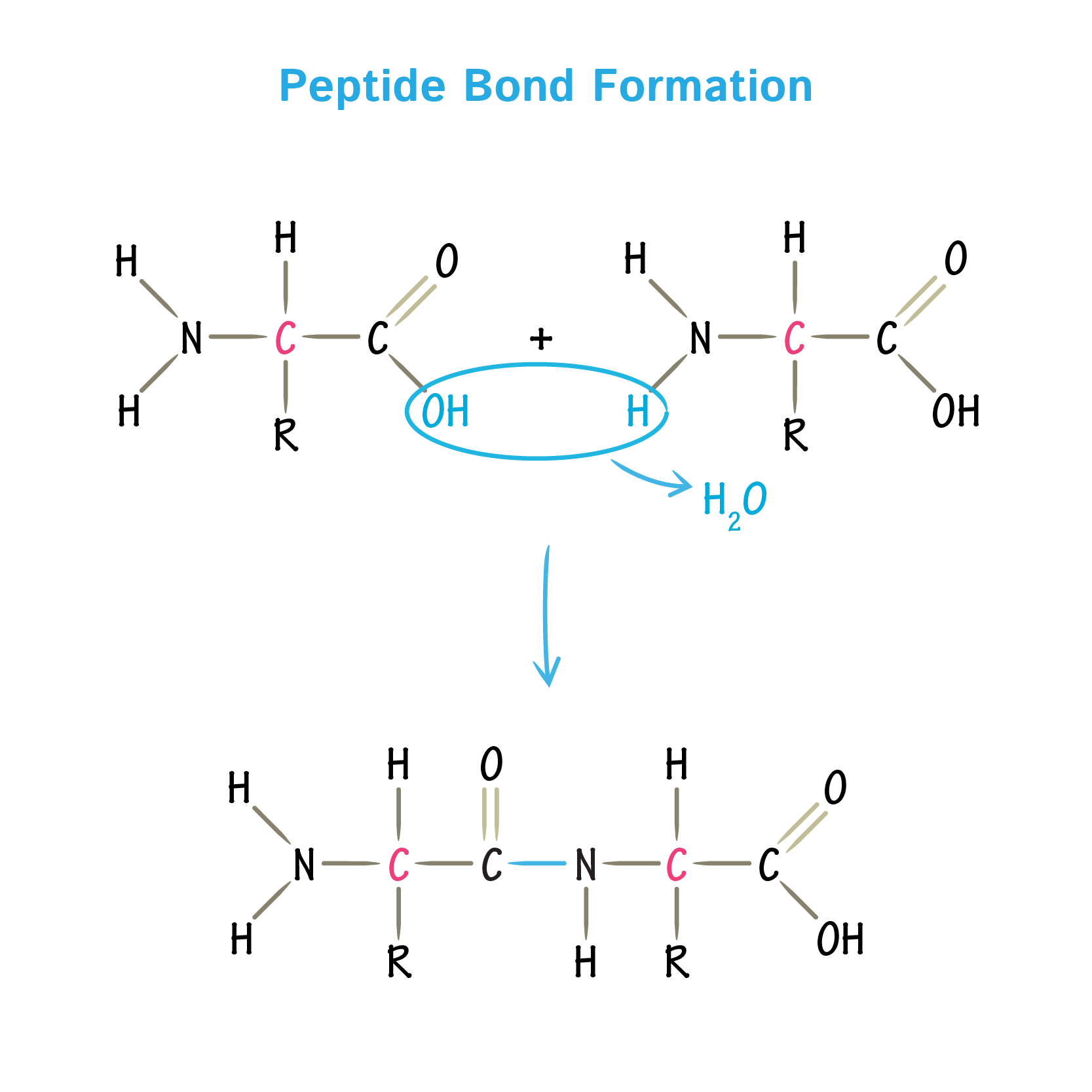
polypeptides formation
condensation reaction between 2 amino acids to form a covalent peptide bond.
nucleic acid formation
joined by condensation reactions between phosphate group of one nucleotide and pentose sugar of another. forms a phosphodiester bond.
digestion of polymers
Hydrolysis reaction. Covalent bonds are broken when water is added.
general formula of monosaccharide
CnH2nOn
types of monosaccharides
triose, pentose (ribose), hexose (glucose
glucose
two types: alpha glucose (1st OH group below the ring), beta glucose (1st OH group above the ring) are isomers of eachother
properties of glucose
stable structure (strong covalent bonds), soluble in water (polar nature), easily transportable, source of chemical energy
function of carbohydrates
energy storage (starch and glycogen) because they are compact and insoluble
structural (cellulose) because it is strong and durable, insoluble and slightly elastic and chemically inert (not easily hydrolysed)
Starch
storage polysaccharide of plants
made of alpha glucose monomers
constructed from amylose and amyloplectein
amylose: unbranched helix shaped chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds. Helix shape makes it compact and resistant to digestion
amyloplectein: 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds creating branched molecule. branched means it can be easily hydrolysed due to the increased number of terminal glucose molecules
glycogen
storage polysaccharide in animals and fungi
1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
more branched than amyloplectein
can get broken down quickly which supplies the higher metabolic needs of animal cells
for example, in liver and muscle cells
cellulose
structural carbohydrates found in cell wall of plants
molecules are unbranched
polymer of beta glucose so in order to form glycosidic bonds with itself it must invert itself
alternating pattern allows hydrogen bonding to occur between strands which increases strength
several molecules of cellulose = microfibils
role of glycoproteins
formed from combination of carbohydrates and polypeptides (classified as protein)
act as receptor molecule in: cell recognition/ identification, receptors for cell signalling, endocytosis, and cell adhesion
can act as antigens which identify as self or non-self where the non- self would trigger an immune response
Lipids forms
fats, oils, waxes, steroids
lipids characteristics
contain hydrocarbon molecules with many non-polar covalent bonds so lipids are insoluble in water
triglycerides
3 fatty acids bonded to one glycerol molecule, formed by esterification (-OH) of glycerol and (-COOH) of fatty acids (condensation reaction so three water molecules are released)
phospholipids
2 fatty acids bonded to one glycerol molecule, third fatty acid replaced by phosphate ion.
phosphate is polar so phospholipids are amphipathic
properties of triglycerides
energy dense due to high number of ch bonds (more energy dense than carbohydrates)
insoluble
a lot of water is produced when respired called metabolic water and can be used as water source in for example a camels hump and birds egg
ideal for long term storage
storage of lipids
stored in adipose tissue in animals, subcutaneous fats are below the akin and visceral fats around major organs. fat is stored in adipose cells which are specialised to contain large globules of fat and shrink when fat is respired
used as thermal insulator in for example, seals and walruses.
saturated fatty acids
all single bonds, straight molecules, so lipid molecules containing them can pack tightly together and increase melting point. usually solid at room temp which makes them useful as storage molecules in animals
unsaturated fatty acids
not all single bonds, some double bonds so there is not the max amount of hydrogen atoms, causes tail to kink and bond meaning they can not pack as tightly, so usually liquid at room temp
use of phospholipids
form basic structure of cell membranes, when placed in water the hydrophilic phosphate head orients itself towards the water and the hydrophobic tail away, forming a phospholipid monolayer. when mixed with water phospholipid bilayers are formed.
transport through phospholipid
amphipathic, small non polar molecules are soluble in the bilayer and can cross, larger non polar molecules can also cross bilayer. (eg steroid hormones)
steroid hormones
contain cholesterol (a type of lipid) hydrocarbon region of cholesterol is non-polar, allowing it to cross bilayer
eg. oestradiol and testosterone can cross lipid bilayer