CHEM20018: Reactions and Synthesis
1/240
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
241 Terms
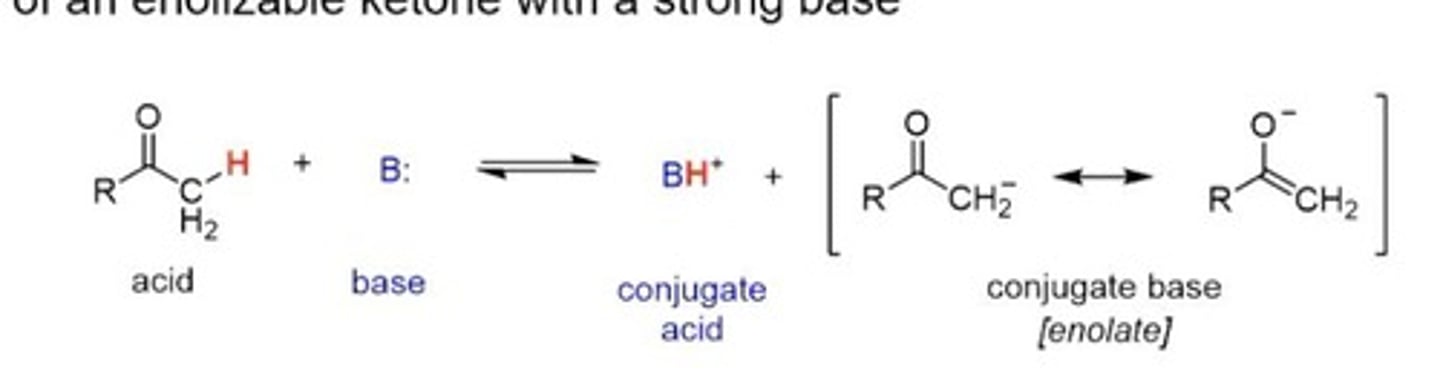
Tautomerism
Isomerism involving proton and double bond movement.
Alpha Substitution
Reactions involving substitution at alpha carbon.
Condensation Reactions
Reactions forming larger molecules by combining smaller ones.
Keto-Enol Tautomerism
Equilibrium between ketones and their enol forms.
Enol
Tautomer with alpha proton on oxygen.
Enolate
Tautomer with negatively charged oxygen.
Acid Catalysed Mechanism
Formation of tautomers using acid as catalyst.
Base Catalysed Mechanism
Formation of tautomers using base as catalyst.
Self-Catalysed Mechanism
Two ketones combine to form tautomers.
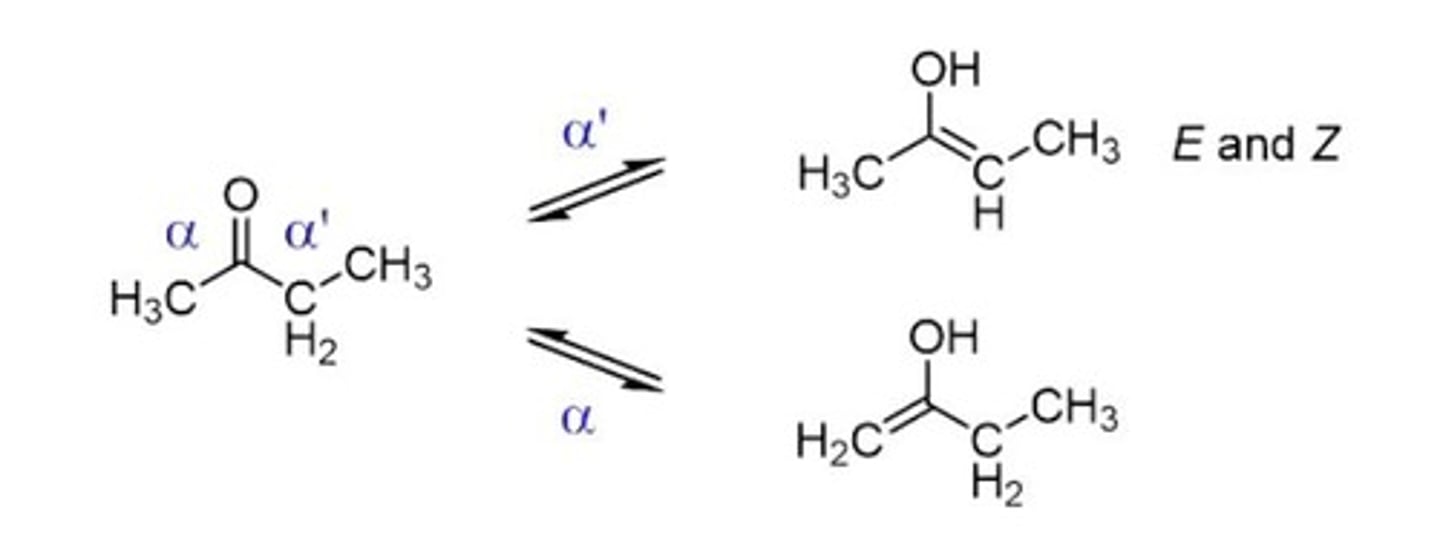
Symmetrical Ketones
Both sides have identical alpha carbons.
Asymmetrical Ketones
Different alpha carbons on either side of carbonyl.
E/Z Isomerism
Geometric isomerism due to double bond position.
Non-Enolisable Carbonyls
Carbonyls lacking alpha hydrogens cannot enolize.
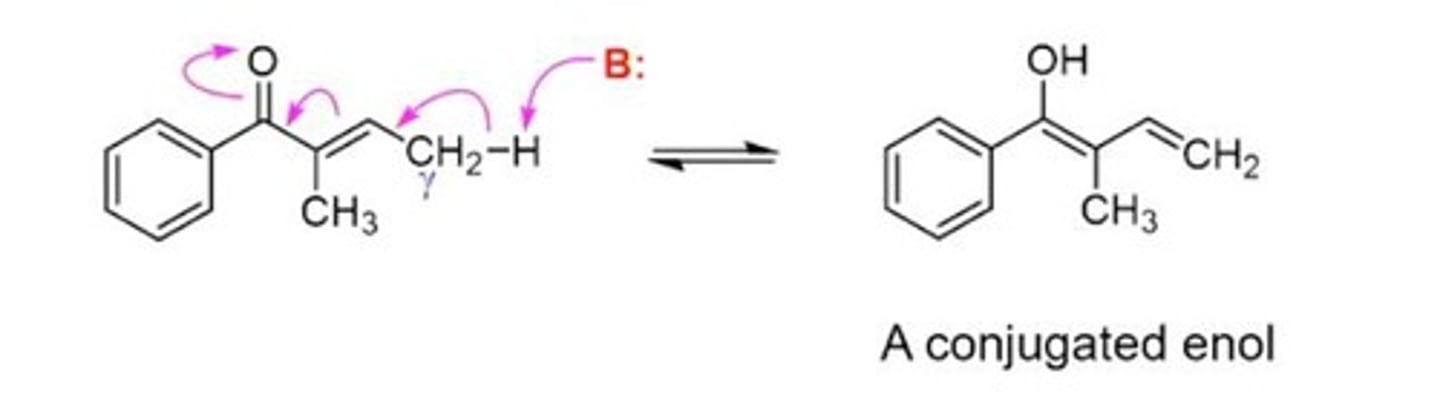
Conjugated Enols
Enols formed by enolization at gamma position.
Dicarbonyl Stabilization
1,3 disubstituted carbonyls yield more stable products.
Enol Reactivity
Enols act as nucleophiles in reactions.
Enolate Reactivity
Enolates are more reactive than enols.
Acidity of Carbonyls
Carbonyls increase acidity, lowering pKa values.
Lithium Diisopropylamide (LDA)
Strong base for forming enolates from carbonyls.
Sodium Ethoxide
Weaker base used for enolizing more acidic carbonyls.
Racemisation
Equilibrium between enol/enolate with opposite stereochemistry.
Epimers
Diastereoisomers differing by one stereocentre.
Halogens
Reactive electrophiles that can react with enols.
Monobromination
High yield reaction producing brominated compounds.
Debromination
Lower yield reaction removing bromine from compounds.
Alpha Haloketones
Halides act as leaving groups in Sn2 and E2.
Dibromination
Produces vinyl halides through double bromination.
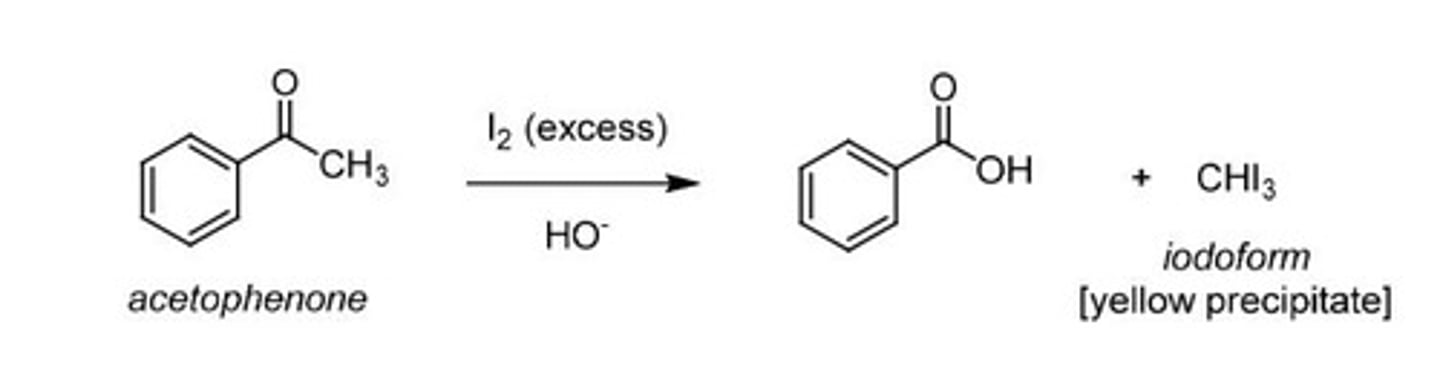
Haloform Reaction
Uses excess halogen to substitute alpha hydrogen.
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky Reaction
Alpha halogenation of carboxylic acids via enol.
Acetic Acid Reaction
Forms acid bromide via phosphorous tribromide treatment.
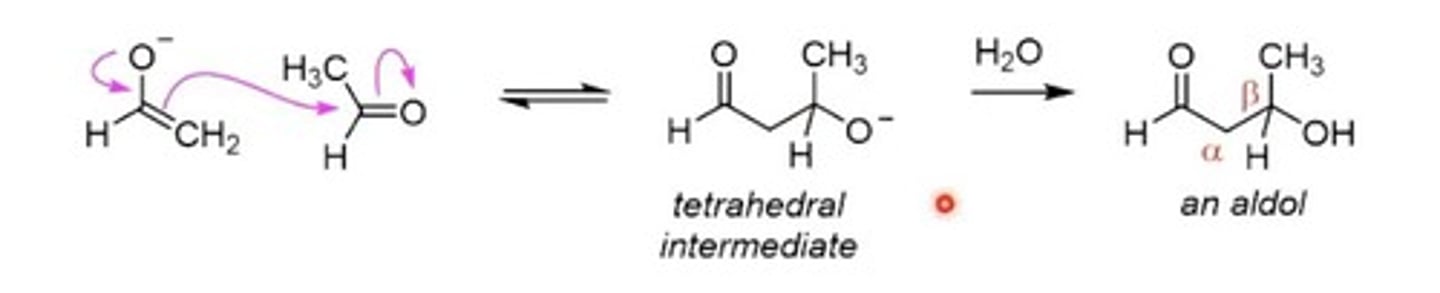
Aldol Reaction
Aldehyde or ketone forms nucleophilic enolate.
Beta Hydroxy Aldehyde
Product of aldol reaction before dehydration.
Aldol Condensation
Elimination of water from beta hydroxy aldehyde.
Dicarbonyl Reaction
Can produce carbocycles through self-reaction.
Non-enolisable Aldehydes
React to form mixed aldol products.
Aldehyde Reactivity
Less bulky, more reactive than ketones.
Ketone Stability
More stable carbocations, less reactive than aldehydes.
Malonate Chemistry
Synthesis of carboxylic acids via alkylation.
Acetoacetate Chemistry
Synthesis of methyl ketones via alkylation.
Deprotonation
Base-induced removal of hydrogen from compounds.
Saponification
Hydroxide treatment converting esters to carboxylates.
Michael Reaction
Conjugate addition of enolate to unsaturated carbonyl.
Mannich Reaction
Three-component reaction forming Mannich bases.
Mannich Base Applications
Synthesis of compounds like tropinone.
Mannich Reaction
Synthesis method for fluoxetine (Prozac).
Betti Reaction
Used in drug synthesis processes.
Carbohydrates
Hydroxy ketones or aldehydes, suffix '-ose'.
Fischer Projections
Representation showing stereochemistry of sugars.
D-glyceraldehyde
Most oxidized carbon at the top in projections.
L-Descriptor
Highest numbered stereochemical centre on the left.
D-Descriptor
Highest numbered secondary alcohol on the right.
Lobry de Bruyn-Alderda van Ekenstein Reaction
Interconversion between aldose and ketose via enediol.
Aldose
Sugar with aldehyde group at chain's end.
Ketose
Sugar with ketone group within the chain.
Simple Carbohydrate Reactions
Carbonyls reduce to alcohols; aldoses oxidize to acids.
Killani-Fischer Ascent
Cyanide addition to aldehyde forms cyanohydrin.
Cyanohydrin
Intermediate formed from aldehyde and cyanide.
Reducing Sugar
Glucose identified as a reducing sugar.
Hemiacetals
Formed from aldoses condensing, creating anomeric centre.
Anomeric Centre
New stereochemical centre from hemiacetal formation.
Furanose
5-membered ring sugar structure.
Pyranose
6-membered ring sugar structure.
Mutarotation
Optical rotation change from anomer interconversion.
Glycosides
Non-reducing sugars formed from hemiacetals.
Disaccharides
Two monosaccharide units linked by glycosidic bond.
Polysaccharides
Long chains of monosaccharides, e.g., glycogen.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Entropy change equals system plus surroundings entropy.
Spontaneous Reactions
Characterized by negative delta G value.
Lattice Enthalpy
Energy change when ionic solids form from gaseous ions.
Hess's Law
Total enthalpy change equals sum of individual steps.
Born-Haber Cycle
Calculates lattice enthalpies experimentally.
Born Forces
Lower lattice energy by 10%, includes repulsions.
Born-Lande Equation
Calculates lattice energy using ion charge and distance.
Born-Mayer equation
Describes lattice energy in ionic compounds.
Kapustinskii equation
Estimates lattice energy for unknown structures.
Lattice enthalpy
Energy change when ionic solid forms from ions.
Hydration enthalpy
Energy change when ions interact with water.
Solubility of ionic solids
Affected by lattice and hydration enthalpy.
Endothermic process
Absorbs heat, like KI dissolution.
Basic oxide
Reacts with acids, transfers protons.
Amphoteric oxide
Acts as acid or base in reactions.
Ellingham diagram
Shows temperature stability of metal oxides.
Delta G
Free energy change; negative indicates spontaneity.
Standard potential
Indicates stability of an ion in environment.
Latimer diagram
Represents complex redox reactions of molecules.
Oxidation number
Charge of an atom in a compound.
Frost diagram
Relates Gibbs free energy to oxidation states.
Disproportionation
Reaction where a species is both oxidized and reduced.
Entropy increase
More gas moles lead to higher entropy.
Proton transfer
Key feature of basic oxide dissolution.
Group 1 metals
Highly reactive with oxygen, form oxides.
Potassium superoxide
Absorbs CO2, releases O2 for purification.
Dissolution factors
Include solute breakup, intermolecular force disruption.
Hydration energy
Higher with mismatched ion sizes.
Thermodynamic graphs
Visualize relationships in chemical thermodynamics.
Disproportionation
Species above line undergoes in Frost, E on right more positive than E left in Latimer
Elemental Form
Oxidation number 0 at origin.
Standard Potential
Potential change multiplied by oxidation number change.
Stability Field of Water
pH and potential range for water stability.
Nernst Equation
Calculates potentials under non-standard conditions.